4. Antigen Recognition and Diversity
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the two main classes of lymphocytes?
1) B lymphocytes: mediate humoral antibodies by secreting antibodies
2) T lymphocytes control cell-mediated immunity as several effector cells
helper T (TH) cells (CD4+)
cytotoxic T (TC) cells (CD8+)
regulatory T (Treg) cells
makes up 20-50% of wbc in blood, but most reside in lymphoid tissues
Helper T cells
“Commander”; one that will recognize antigen and determine whether B cells or TC cells are needed to clear the infection
Cytotoxic T cells
“Soldier”; one that kills any abnormal cells
Regulatory T cells
Controls and suppresses immune response once infection clears
B cell receptor (BCR)
Y-shaped immunoglobulin made up of 4 polypeptide chains (2 heavy + 2 light)
embedded in the plasma membrane, binds to extracellular pathogens
T cell receptor (TCR)
a heterodimer embedded in the plasma membrane to detect antigens (2 at a time) from pathogens displayed on MHC
Which region of the BCR and TCR is used to bind to antigens? To be connected to plasma membrane?
Variable; Constant
Clonal Expansion
Refers to a rapid cell division that leads to a large population of clones which are genetically-identical to the original lymphocyte
Clonal Selection
Refers to these new clones bearing highly-specific receptors for a particular antigen, inherited from the original lymphocyte
Describe the process when an antigen binds to one of the receptors.
1) Resting B/T cell
2) Encounter with antigen (clonal selection takes place), thus we select this particular cell for activation
3) Stimulated B cell gives rise to antibody-secreting plasma cells (clonal expansion); can become effector or memory cells
Somatic Recombination Process (General)
A possible set of combinations is taken and randomly put together to create a recombinant protein
BCR Diversity
Diversity comes from VH + VL domains (both have large diversity in AA’s) combined to make antigen binding site
Variable in size/shape to recognize large range of different antigenic determinants (epitopes)
Can bind to a variety of extracellular antigens from all pathogens (one antigen usually has several epitopes)
In somatic recombination of VL and VH, which one has diversity genes?
VH
V(D)J recombinase
Enzyme that identifies possible gene segments to be selected and joined together aka recombination signal sequences (RSSs)
Recombination-activating genes (RAG1 + RAG2)
Unique enzymes to B/T cells for somatic recombination,
Somatic recombination process (specific)
1) New B cells have somatic recomb in the nucleus (no receptor yet)
2) Unique gene produces unique mRNA during transcription
3) Unique mRNA holds the instructions for making unique B/T-CR
4) Protein folding/making in rough ER
5) Sent to golgi to be packaged in vesicle
6) Once received by the plasma membrane, it stays anchored as the receptor
What are the 4 Ig’s involved with mature naive B cells?
IgM and IgD: expressed by BCR
Iga and Igb: anchor BCR in membrane
Somatic hypermutation
Differentiation causes a shift in gene expression of immature plasma cells
Point mutations throughout VH and VL
creates mutant surface IgM and IgD with differing affinity for antigen
clones with high affinity mutant BCR → chosen to mature into plasma cells
secrete antibodies with high affinity
IgA
secreted across epithelium into mucosal tissues and also sweat, tears, saliva, breast milk; neutralized antigens
IgD
mediates inflammation by sensitizing basophils to release histamine and heparin
IgE
mediates inflammation by sensitizing mast cells and basophils to release histamine and heparin
IgG
several subclasses that bind and neutralize antigens, some act as opsonins, and cross the placenta
IgM (pentameric)
first antibody during initial exposure to an antigen; potent activator of complement
What are the functions of antibodies
Antibody-mediated immune responses are referred to as humoral immunity
binds to several of the same antigens at once neutralizing their pathogenic effect (i.e. blocking growth/replication)
antibodies also act as opsonins that bind to the pathogen and enhance their phagocytosis (opsonization)
Which mechanism is used to create such diversity in B cell receptors (BCRs)?
Somatic recombination + hypermutation
Which mechanism is used to create such diversity in T cell receptors (TCRs)?
Somatic recombination
What makes up the T cell receptor complex?
Core α and β heterodimer binds antigens
CD3 εδ and εγ heterodimers aid in transport and stabilization of the core TCR into membrane (makes sure α and β properly inserts into ER, then golgi, then plasma membrane)
CDζ homodimers associate with intracellular signaling molecules (crucial for T cell activation) to make changes in gene expression and proteins activity leading to clonal expansion
αβ TCR
Core: αβ heterodimer
Recognize: short peptide antigens on MHC (e.g. pathogenic on MHCII or self antigen on MCHI)
αβ T cells are involved in adaptive immunity
γδ TCR
Core: γδ heterodimer
Recognize: a variety of antigens
γδ T cells are mostly circulating in blood and doesn’t recognize something specific (more associated with innate immunity like NK’s but not really)
CD8 coreceptor
only present on TC cells
stabilizes TCR:MHC I
TCR recognizes MHC I and antigen while CD8 recognizes MHC I only
Recognizes altered self vs self vs non-self
CD4 coreceptor
present on TH (to notice pathogenic antigens) and Treg (to stop immune responses once cleared)
stabilizes TCR:MHC II
TCR recognizes MHC II and antigen while CD4 recognizes MHC II only
Recognizes self vs nonself
MHC I
found on all nucleated cells (acts like a nametag)
recognizes short peptides to bind to, can also attach to intracellular pathogens or abnormal self proteins
recognized by TC cells
MHC II
only on antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells, mast cells, macrophages and B cells)
recognizes longer peptides and extracellular pathogen peptides
recognized by TH cells
Describe the T cell activation process
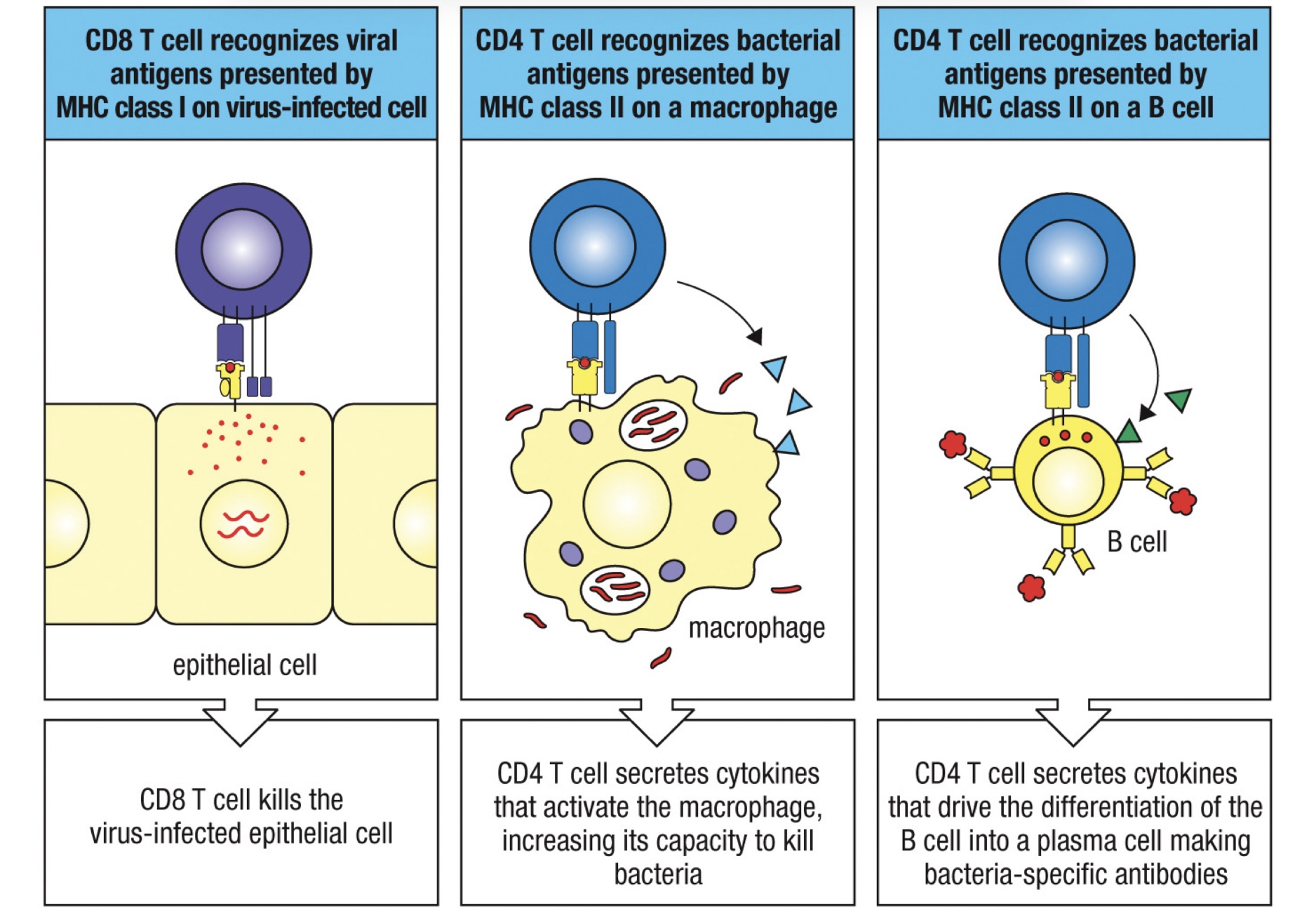
Compare the MHC I/II antigen loading pathway
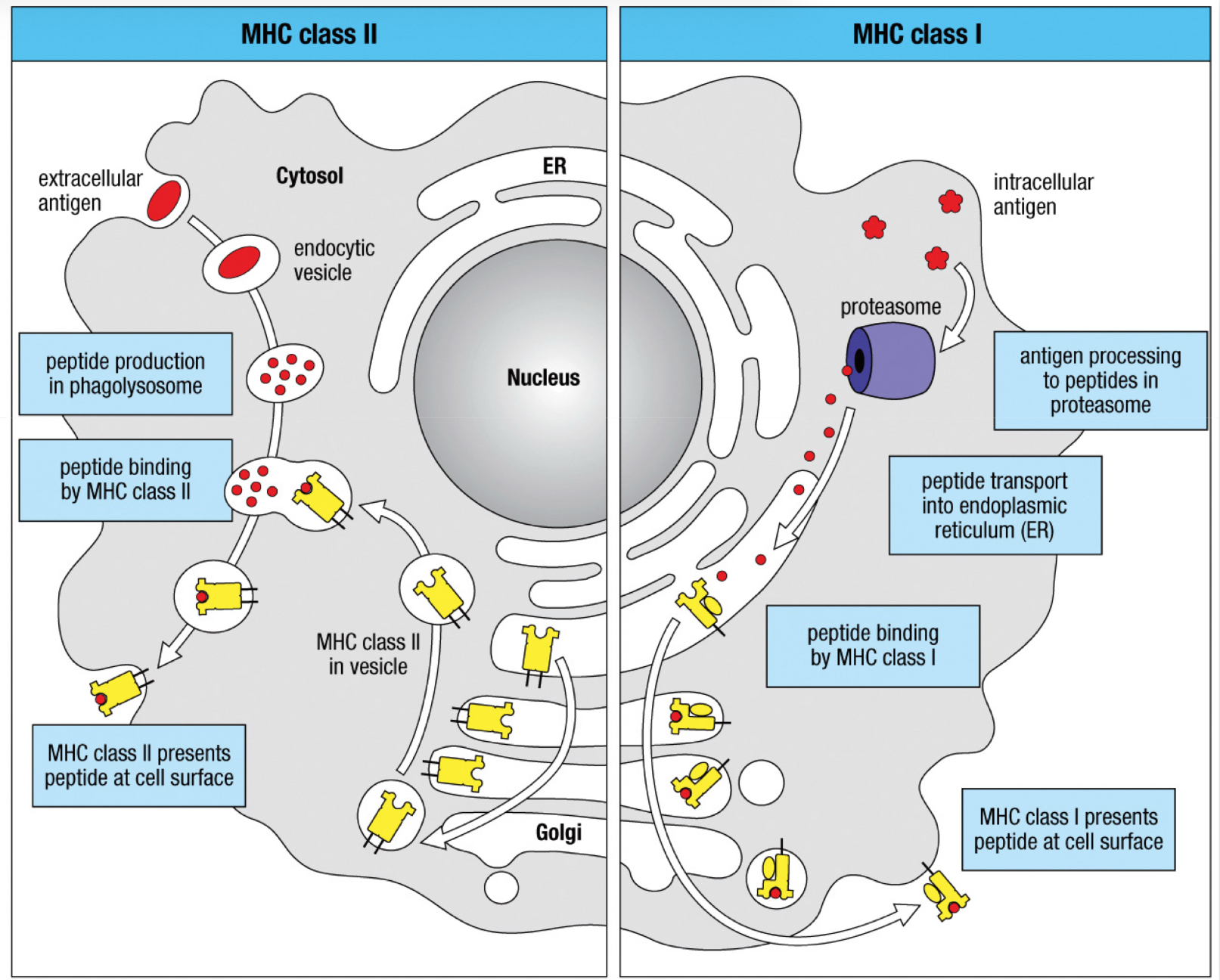
Large variation of MHC is a result of:
1) Arrangement into gene families that encode different proteins of the MHC; several genes with small differences that produce several protein isotypes
2) Genetic polymorphism of many genes (single gene can have several allotypes)
T/F? MHC II requires the low pH of the phagolysosome in order to bind peptides from extracellular pathogens.
True