Factorial Design
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
factorial designs
designs with more than one IV (or factor) where all levels of each IV are combined with all levels of the other IVs
main effects
the effect each variable has by itself, irrespective of the effect of the other variable
interaction effects
the effect of one IV depends on the particular level of the other IV
simple effects
the effect of one IV on the particular level of the other IV, only relevant when interaction effects are present
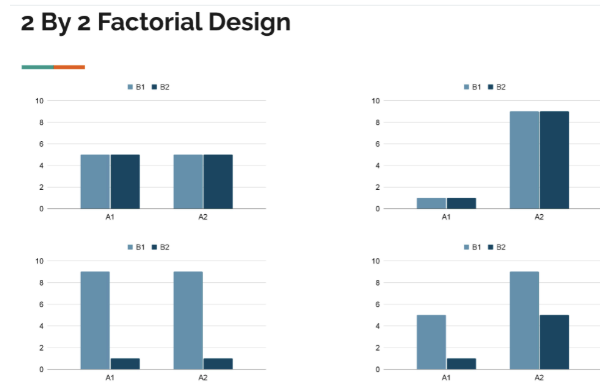
2×2 factorial design examples
Top right: main effect between A, but not B
Main effect between A - difference between A1 and A2
No main effect between B - the levels of the IV are the same
Bottom left
Main effect for B
Level for B1 is much higher than B2
No interaction effect
Bottom right
B has a main effect (can see that B1 is higher than B2)
Main effect of A (A2 is higher than A1)
experimental research vs non-experimental or quasi-experimental research
experimental research: manipulate IV
non-experimental research: non-manipulated IV
manipulated vs non-manipulated IVs
IVs in factorial designs can be manipulated or non-manipulated
If all IVs are non-manipulated → non-experimental or quasi-experimental
If any IV is manipulated → experimental
between-subject IV
each participant exposed to one level of IV
within-subject IV
each participant exposed to all levels of IV
between-subject or within-subject IVs
All IVs in factorial design are between subject → between-subject factorial design
All IVs in factorial design are within subject → within-subject factorial design
mixed factorial design
some IVs in factorial design are between-subject and some are within-subject
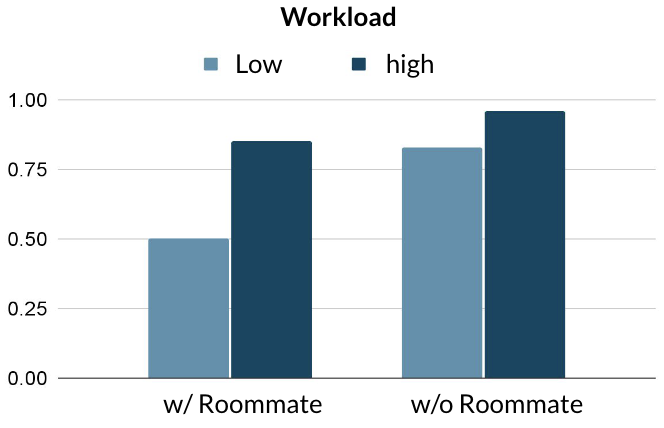
Is there a main effect(s)?
Is there an interaction effect?
Is there a simple effect?
Main Effect
- There is a main effect of workload.
Students have a higher level of stress
when the workload is high as compared
to when the workload is low.
- There is a main effect of the roommate
situation. Students have a higher level
of stress when they do not have a
roommate as compared to when they do.
- There are main effects of workload and
roommate situation.
Interaction Effect
- There is an interaction between
workload and roommate situation.
- The effect of workload on stress depends
on the roommate situation.
- The effect of roommate situation on
stress depends on the workload
Simple Effect
Only relevant when there is an
interaction.
- When students have a roommate, having
a high workload is associated with more
stress than having a low workload.
- When students do not have a roommate,
having a high workload is associated
with more stress than having a low
workload.
- The difference in stress level between
high versus low workload is larger when
students have a roommate than when
they do not.