geology 2.6-2.10
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Fault
a crack in Earth’s crust due to motion of one tectonic plate relative to another
What is an earthquake
the sudden shaking of the ground caused by the sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere, which creates seismic waves.
focus
The region that first breaks along a fault during an earthquake
Epicentre
The point of earths surface directly above an earthquakes focus
Seismic waves
A wave that travels though earth as a result of explosions or earthquakes

Primary wave (P- waves)
First to arrive as they gravel faster, able to travel though rock, solid, liquid, and gas
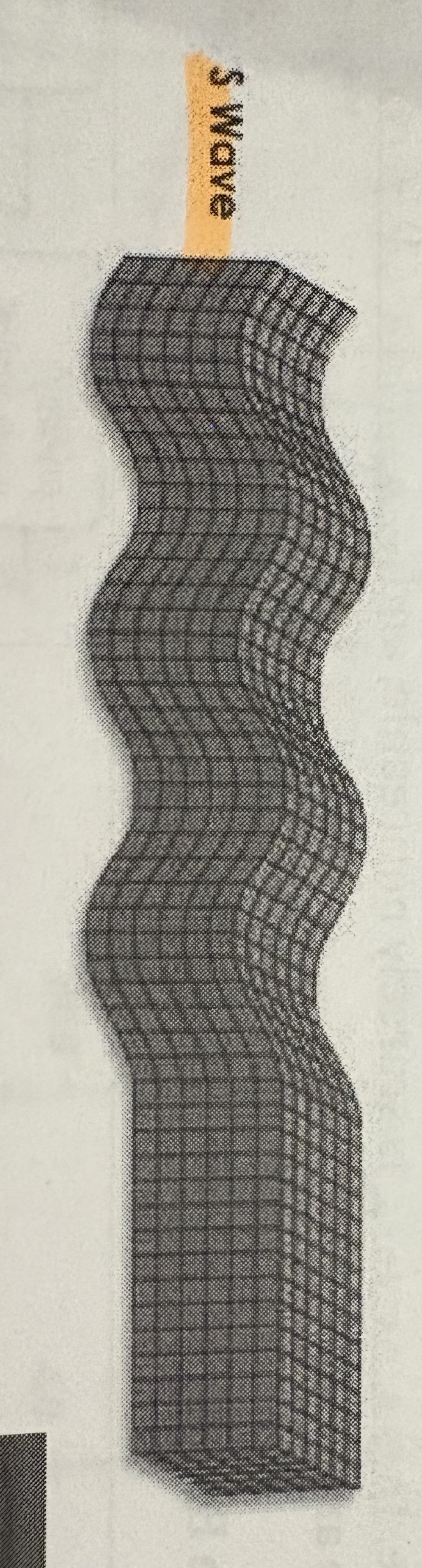
Secondary waves (S-waves)
Moves slower then P-waves and can only move though solid rock, travels up and down (left or right)
5 layers of earth
crust, mantle (lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere), outer core, inter core
Mesozoic era
Triassic period, Jurassic, period and Cretaceous period that all came to an end because a massive asteroid impact creating dust particles blocking solar energy from reaching spices that depended on it went extinct and Pangea started to break and slowly separate at this point
Cenozoic era
Plants and animals began to evolve and look more like what they do today, Holocene began to melt creating enormous glacial lakes, global conveyer a system the ocean does that circulates warm water away from tropics near oceans surface and Pangea was fully separated by now
Half life = present after a number
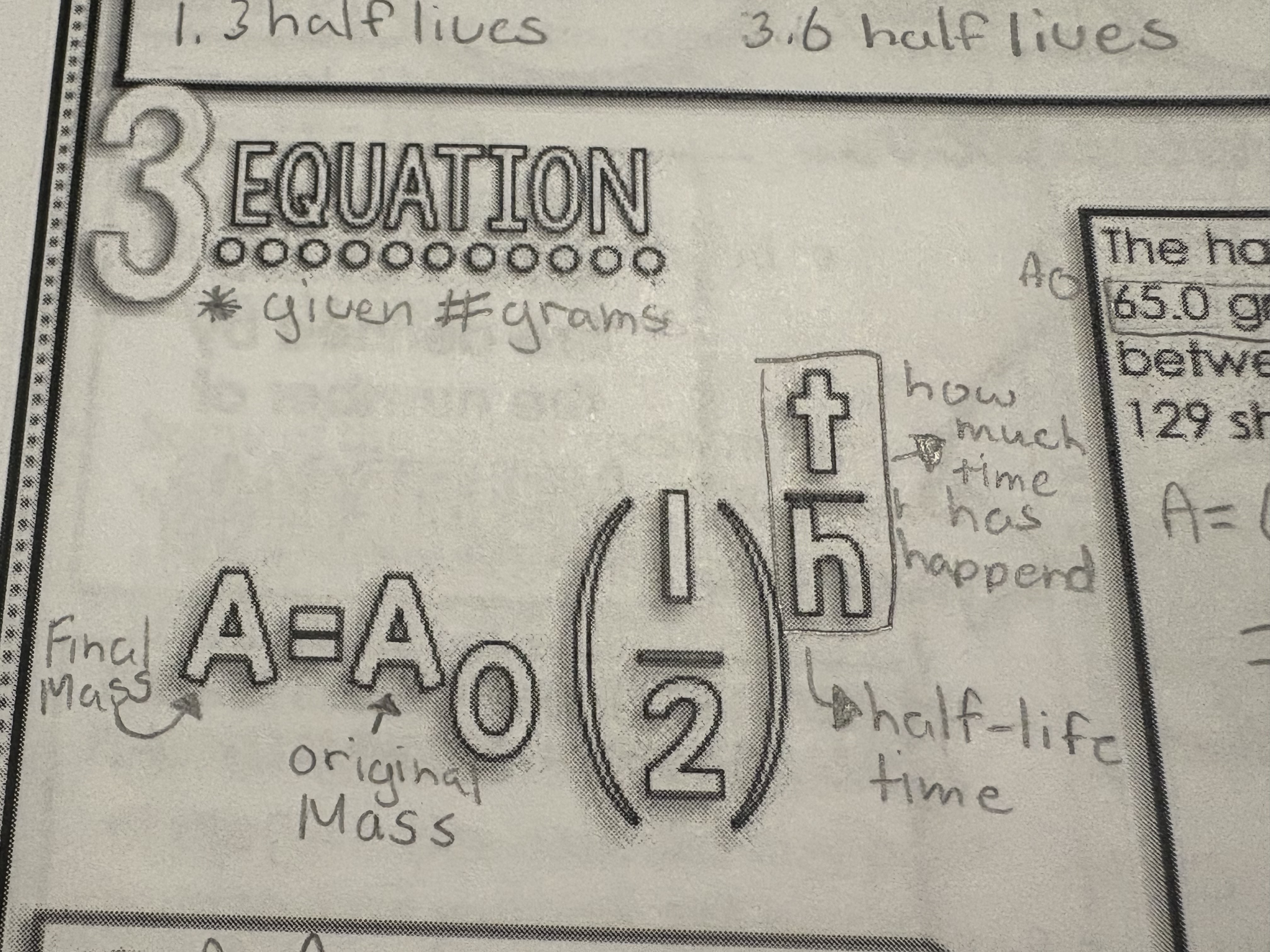
Global changes, evidence in rock strata and how scientists are able to average global temperatures during earths history and how it changed
Scientists use tiny trap bubbles called ice core samples to figure out what the temperatures were like in the past. Earths climate has never stayed the same and has changed many times over millions of yrs about 4*-7* average temp
Earths two natural phenomenons
Earthquakes and tsunamis
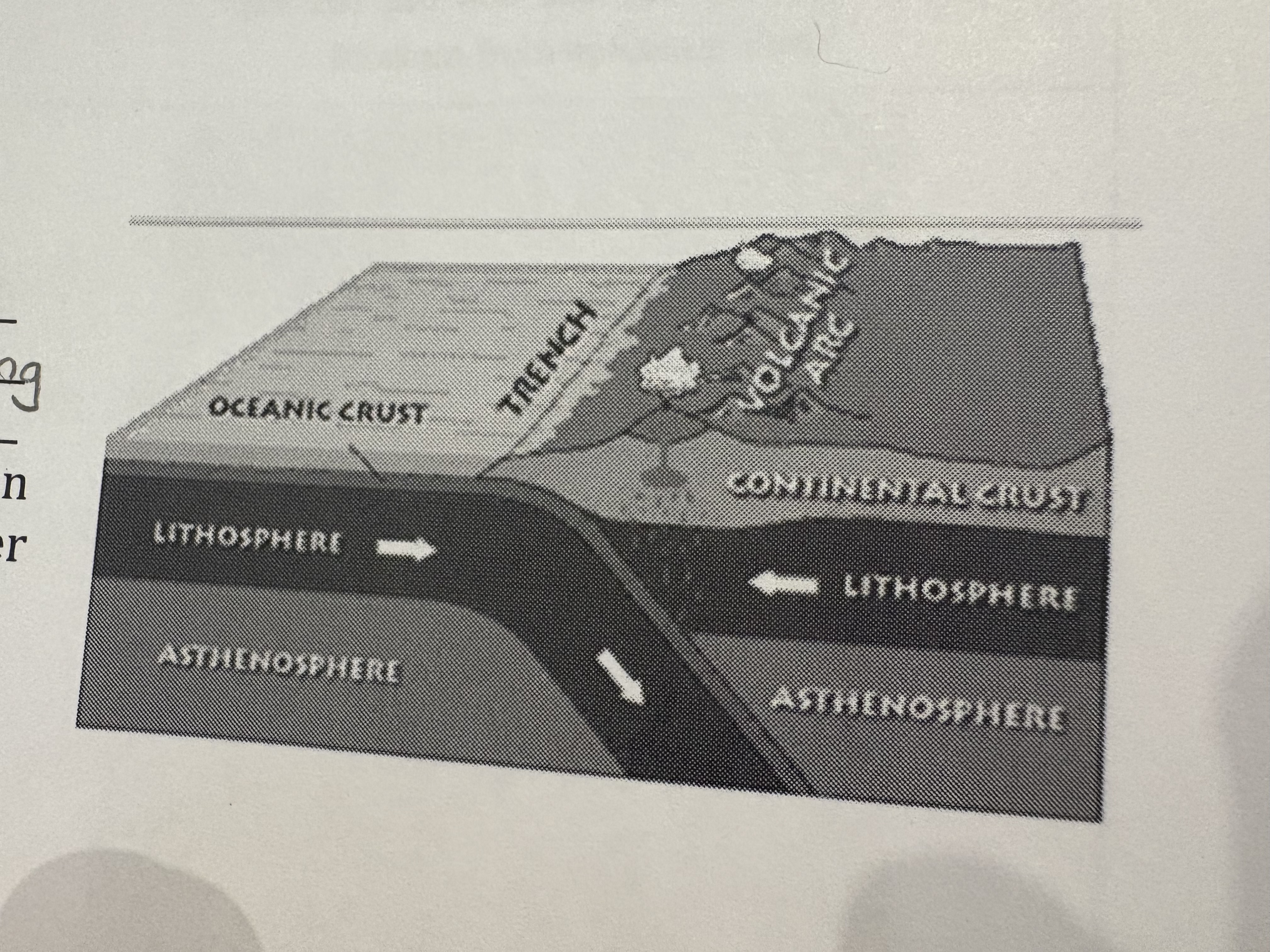
Subduction
Determine the absolute age using 2 different percents
When 2 percents % are given you use the parent nuclide % then use the graph to find the half life then times it by the approximate half life to get the years (use sig-digs)
Determine the absolute age when only 1 % is given
Subtract the given percent from 100% to get a number to use to find the half life then times it too approximate half life to get the years ( use sig-digs)
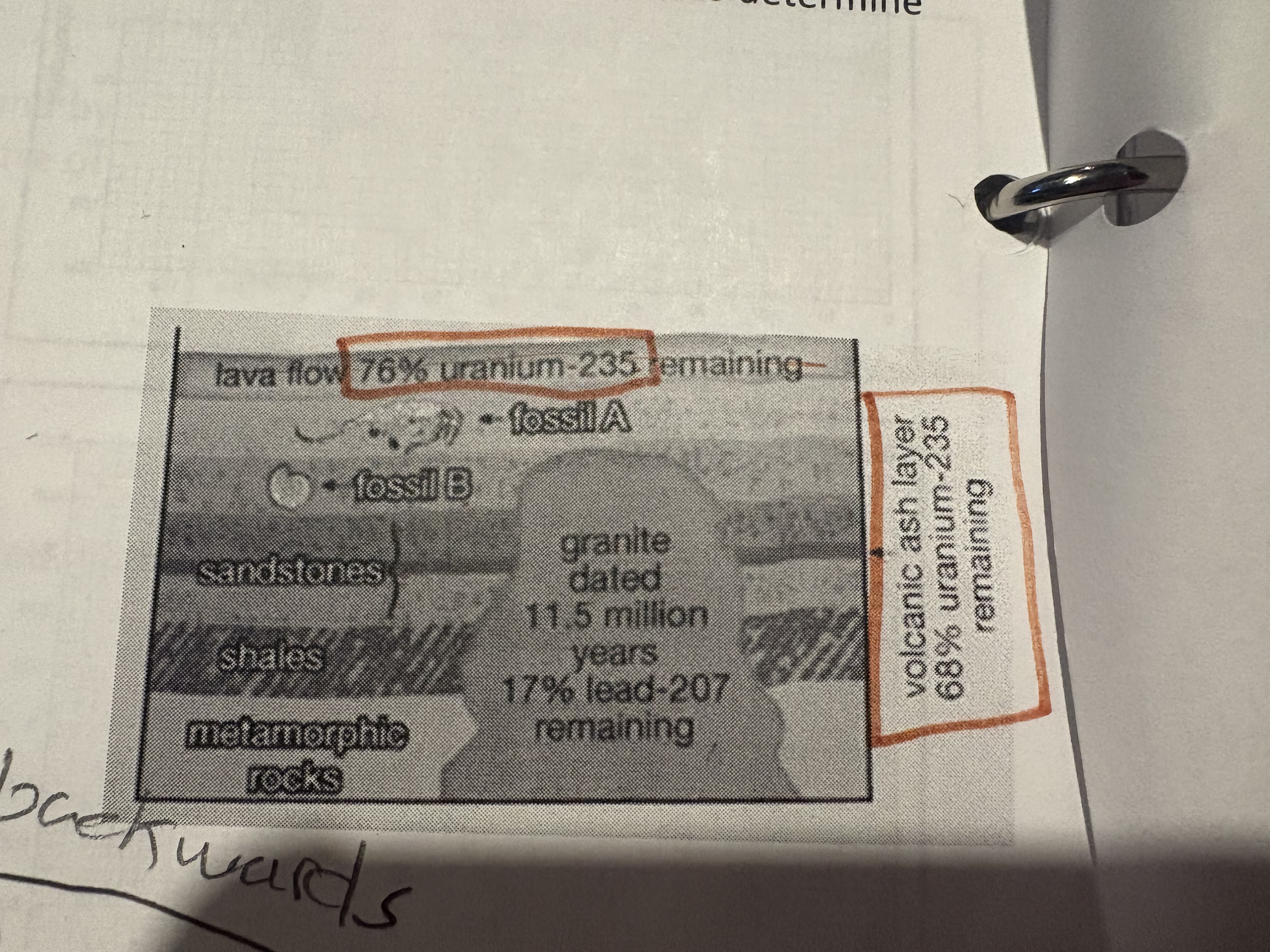
To find the relative age of layer B
Use the years you found and divide by 2