Human Anatomy and Physiology Final Exam!!!!!
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
Which of the following terms refers to the sum of all chemical reaction of a cell?
Metabolism
Reproduction
Homeostasis
Adaptability
Responsiveness
Metabolism
Which of the following terms refers to the maintenance of the body's internal environment within narrow physiological limits, or "steady state"?
Metabolism
Reproduction
Adaptability
Responsiveness
Homeostasis
Homeostasis
What is the term that refers to the the microscopic study of cells?
Embryology
Cytology
Histology
Pathology
Gross anatomy
Cytology
What is the term that refers to the microscopic study of tissues?
Cytology
Histology
Embryology
Pathology
Gross anatomy
Histolgy
Anatomy refers to ____(1)____, as physiology refers to ____(2)____.
(1) growth, (2) structure
(1) growth, (2) function
(1) function, (2) form
(1) form, (2) function
Form, Function
Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization from least complex to most complex?
1. Cellular 2. Chemical 3. Organ System 4. Tissue 5. Organ
1, 2, 5, 4, 3
2, 1, 4, 5, 3
2, 1, 5, 4, 3
3, 5, 4, 1, 2
Chemical, Cellular, Tissue, Organ, Organ System
Which of the following levels of organization does a protein belong to?
Cellular
Organ
Tissue
Chemical
Chemical
Which of the following levels of organization does the heart belong to?
Cellular
Tissue
Organ
Chemical
Organ
Which of the following systems of the human body is NOT correctly matched to its function and major organs?
A-Digestive system – mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine; responsible for ingestion, digestion, absorption of nutrients, and elimination of feces
B-Lymphatic system – lungs, trachea, and diaphragm; responsible for inhalation of oxygen, exhalation of carbon dioxide, and gas exchange between the alveoli and bloodstream
C-Circulatory system – blood, blood vessels, and heart; responsible for the transport and distribution of blood, respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, hormones, etc.
D-Endocrine system – pituitary gland, adrenal gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, and thymus; responsible for the secretion of hormones for the purpose of regulating growth and metabolic process within body cells.
B
The respiratory system is composed of the kidneys and urinary bladder, and is responsible for cleaning and filtering the blood, fluid, and electrolyte balance.
TrueFalse
False
Match the following anatomical terms with their correct common names.
__4___Cheek
__3___Chin
__2___Neck
__6___Ear
__1___Head
___5__Eye
1.Cephalic
2.Cervical
3.Mental
4.Buccal
5.Orbital
6.Otic
cheek-buccal
chin-mental
neck-cervical
ear-otic
head-cephalic
eye-orbital
Match the following anatomical terms with their correct common names
___3__Groin
___4__Heel
___1__Loin
___2__Armpit
1.Lumbar
2.Axillary
3.Inguinal
4.Calcaneal
Groin-
Heel-calcaneal
loin-
Armpit- axillary
The correct anatomical term for back of elbow is__________.
antecubital
olecranal
digital
carpal
olecranal
The correct anatomical term for wrist is____________.
antecubital
olecranal
carpal
digital
Carpal (carpus)
The correct anatomical term for thigh is_____________.
sural
crural
femoral
calcaneal
Femoral
The correct anatomical term for arm is____________.
calcaneal
olecranal
talus
brachial
Bracial
Which of the following directional terms refers to near to point of origin (close to body)?
Lateral
Proximal
Posterior
Distal
Proximal
Which of the following directional terms refers to the external/surface portion of an anatomical structure?
Proximal
superior
deep
superficial
Superficial
The scapula is __________ to the lungs.
inferior
lateral
superior
intermediate
Superior
The term that means "away from midline" is______________.
superior
inferior
lateral
medial
Lateral
Which of the following refers to the plane that can divide the body into two EQUAL halves?
horizontal
oblique
para-sagittal
mid-sagittal
Mid-sagittal
The pericardial cavity is part of which of the following?
Cranial cavity
Thoracic cavity
Abdominal cavity
Pelvic cavity
Abdominal cavity
A transverse plane divides the body into ___________________.
superior and inferior portions
equal right and left halves
equal anterior and posterior portions
ventral and dorsal cavities
Superior and Inferior protions
Which of the following is a subatomic particle found in the nucleus and possesses a neutral charge, low energy, and high mass?
Neutrons
Protons
Electrons
Diatoms
Neutrons
Which of the following is defined by an element's atomic number?
Number of neutrons (n)
Number of protons plus number of electrons (p+e)
Number of protons (p)
Number of protons plus number of neutrons (p+n)
Number or protons
The chemical behavior of an atom, including whether it will form bonds, is determined by the _________.
number of its neutrons
size of the atom
mass number
number of its valence electrons
Number of its valence electrons
A neutral atom of carbon has how many neutrons?
Question options:
6
7
12
8
6

neutral atom of sodium has how many electrons?
5
11
12
22
11

A neutral atom of phosphorus how many valence electrons?
30
15
5
6

How many Protons does H^+1 contain?
1
2
3
0
1
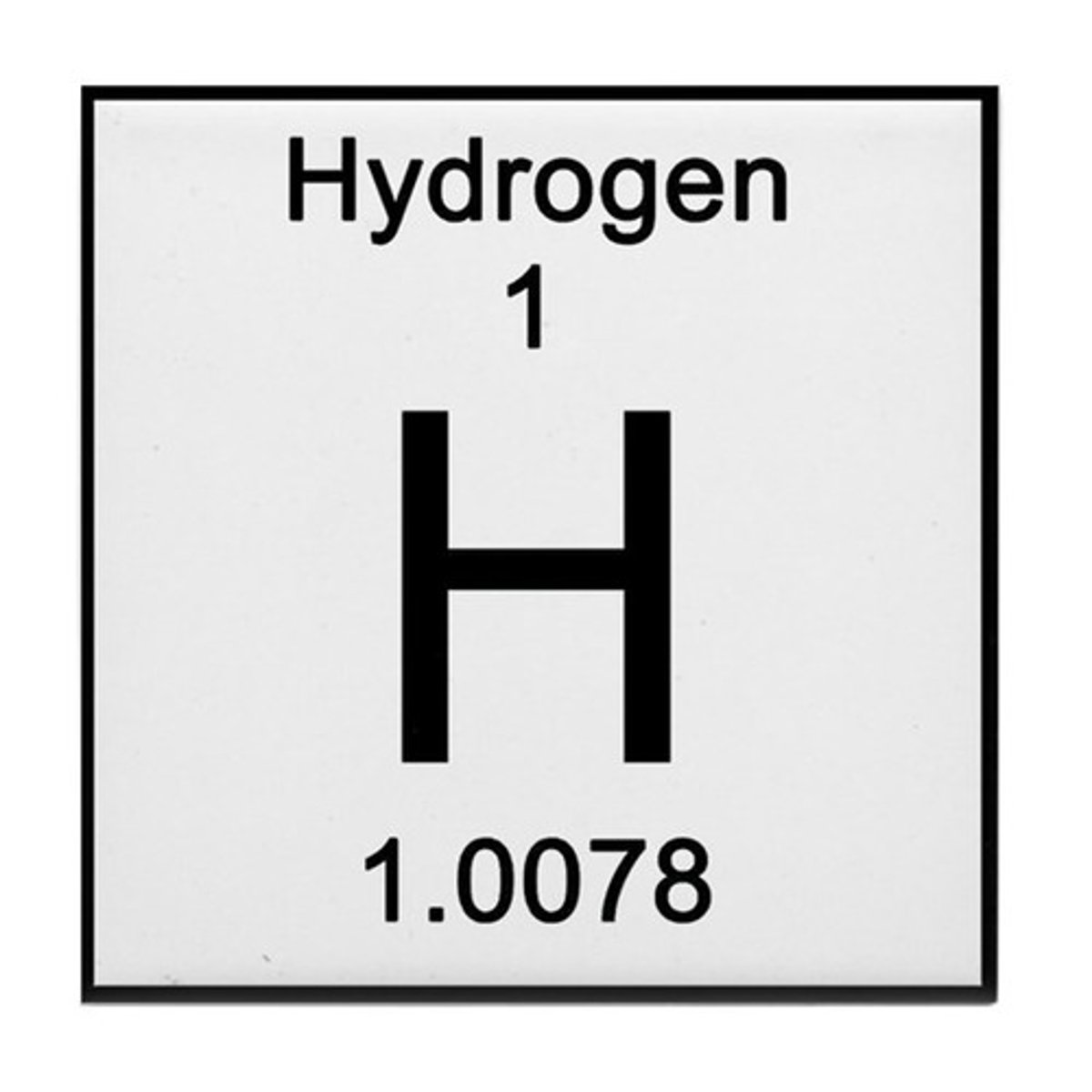
An atom becomes a cation by _____________.
accepting electrons in its outermost shell
giving up electrons from its outermost shell
sharing electrons with another atom
forming a covalent bond with other atoms
Giving up elections from its outermost shell
In an ionic bond, atoms are bonded by the ________.
transfer of protons from one atom to another
transfer of neutrons from one atom to another
transfer of electrons from one atom to another
sharing of electrons between two or more atoms
Sharing of elections between two or more atoms
How many protons in a molecule of water (H2O)?
8
16
17
10
8
How many neutrons in a molecule of water (H20)?
8
10
16
17
8
Which of the following best describes a substance that has a pH of 14?
Slightly acidic
Slightly basic
Extremely acidic
Extremely basic
Extremely basic
Isotopes differ in the number of _____________.
electrons only
protons only
neutrons only
protons and neutrons
Neutrons only
The electron shell (level) nearest the nucleus of an atom holds a maximum of how many electrons?
one
two
eight
eighteen
two
Electrons in the outermost electron shell (level) are referred to as______________.
extra-orbital electrons
ionic electrons
potential electrons
valence electrons
valence electrons
In a covalent bond, atoms are bonded by______________.
sharing pairs of electrons
sharing pairs of protons
attractions of unlike electrical chargers
direct contact between atomic nuclei
sharing pairs of electrons
Which of the following best describes the substance H2CO3 if it disassociates in water to form H+ and HCO3-?
Acid
Base
Salt
Neutral
acid
If calcium is Ca^2+ how many electrons does it have?
20
10
18
22
10
All of the following are nitrogenous bases associated with DNA except
Guanine
Cytosine
Adenine
Uracil
Thymine
Uracil
To catalyze a chemical reaction is to slow it down.
TrueFalse
false
Enzymes catalyze reactions by________________.
changing structures
lowering activation energy
increasing activation energy
adding energy to the cell
increasing activation energy
Water is considered neutral because it yields an equal number of H+ and an OH- in solution.
TrueFalse
True
NaCl is an example for a/an _________________.
salt
buffer
acid
neutral
Salt
Lactose is made of _______________.
2 glucose molecules
1 glucose and 1 fructose
1 glucose and 1 galactose
1 fructose and 1 galactose
1 fructose and 1 galactose
Glucose is an example of a polysaccharide.
TrueFalse
false
Which functional group is COOH?
hydroxyl
carboxylic
amine
carbonyl
carboxylic
The term hydrophobic literally means "water fearing".
TrueFalse
True
Choose DNA or RNA for the following characteristics
___1__Double-stranded helix
__1__Contains deoxyribose sugar
__2___Contain ribose sugar
___2__Contain uracil
1.DNA
2.RNA
1,1,2,2
Which of the following are the major characteristic of secondary protein structure?
Linear polypeptide chain
3D structure due to supercoiling
Alpha helix and beta sheets
twisting of two or more polypeptide chains
Alpha helix and beta sheets
Which of the following refers to fold within the plasma membrane on the apical surface of the cell for the purpose of increasing the surface area for membrane transport?
cilia
mitochondria
microvilli
centrioles
Microvilli
Which of the following is the organelle responsible for the synthesis of ATP by the processes of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system?
centrioles
nucleus
nucleolus
mitochondria
mitochondria
Which of the following is a highly folded membrane studded with ribosomes and is responsible for protein synthesis?
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Golgi apparatus
Cytoskeleton
rough Er
Which of the following is membranous sac that detoxifies the cell be removing free radicals such as hydrogen peroxide
lysosome
peroxisome
cytosol
nucleolus
lysosmoe
The control center of the cell which directs all cellular activities and stores the genetic material is the _______________.
nucleolus
nucleus
mitochondria
golgi apparatus
nucleolus
Highly folded membrane composed of five to six flattened sacs and is responsible for processing, packaging and distributing substances within vesicles is the ________________.
golgi apparatus
rough ER
smooth ER
lysosome
smooth er
A non-membrane bound structure composed of microtubules arranged in nine triplets and is responsible for the production of spindle fibers is ____________.
centriole
cilia
cytoskeleton
cytosol
centriole
A transient nuclear organelle responsible for the production of ribosomal RNA is called_________________.
nucleus
nucleolus
DNA
nuclear envelop
nucleolus
Plasma Membranes are considered selectively permeable.
TrueFalse
true
Which of the following refers to a solution that contains the same solute concentration as the cell?
hypertonic
hypotonic
isotonic
epitonic
isotonic
The condition of an animal cell when placed into a hypertonic solution is called crenation.
TrueFalse
true
A cell placed in a hypotonic solution would ______________
lyse
crenate
shrink
nothing would happen to it
lyse
The DNA sequence ATCGCTTGCTAA is represented by which of the following RNA sequences?
TAGCGAACGAUU
TAGCGTTCGATT
UAGCGTTCGAUU
UAGCGUUCGAUU
TAGCGAACGAUU
A basic unit of heredity is called a _________.
linear sequence
histone
gene
codon
GENE
The sugar found in RNA is called__________.
ribose
deoxyribose
glucose
galactose
RIBOSE
The process of transcription involves production of_______________.
two new DNA strands from original strands
DNA from an mRNA template
an amino acid chain from mRNA template
mRNA from a DNA template
MRNA from a DNA template
S is the stage of interphase when the cell performs its everyday function and doubles its organelles.
TrueFalse
FALSE
Match the following phases with their correct description.
____3_Reforming of nuclear membrane.
__4___Separation of sister chromatids
___5__Formation of spindle fibers and breakdown of the nuclear membrane
____1_The cell spends most of its life in this phase.
__2___Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell.
_6____Formation of cleavage furrow
1.Interphase
2.Metaphase
3.Telophase
4.Anaphase
5.Prophase
6.Cytokinesis
345126
Which of the following unwinds and unzips the DNA template during DNA replication processes?
Spliceosome
Helicase
Ligase
DNA polymerase
Helicase
Cancer cells have lost their ability to regulate cell division and eventually divide out of control until a mass of cells have formed called a tumor. Which of the following terms refers to a tumor that easily metastasizes to other areas of the body?
Benign
Malignant
Zygote
Osteocyte
malignant
The first step in protein synthesis involves the formation of RNA from a DNA template. This process is called____________.
DNA replication
Translation
Translocation
Transcription
transcription
The movement of the ribosome down the mRNA strand is called __________.
Translocation
Transcription
Translation
Transformation
translocation
Aerobic respiration takes place in the_________________.
Nucleolus
Mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
mitochondria
Glycolysis takes place in the____________.
Matrix of the mitochondria
Cristae of the mitochondria
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
cytoplasm
The end result of cellular respiration is_________. (Hint: total)
36 ATPs
32 ATPs
2 ATPs
4 ATPs
32 ATPS
"Junk DNA" or non-coding segments of DNA are called______________.
introns
splicosomes
codons
exons
INTRONS
Simple diffusion is the movement of solutes through a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
TrueFalse
TRUE
Which of the following represent an end codon used for translation of mRNA into a polypeptide?
AUG
GCC
CAT
UGA
AUG
The microscopic study of tissues is known as _____________.
Embryology
Cytology
Pathology
Histology
HISTOLOGY
Glands that lack ducts and produce hormones are called __________.
Exocrine glands
Endocrine glands
Merocrine gland
Apocrine gland
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
An exocrine gland that loses small parts of its cell bodies during secretion, as is the case for the mammary gland, is further classified as a(n) ____________ gland.
Ectocrine
apocrine
holocrine
endocrine
APOCRINE
Which of the following substances contributes to one's skin tone or color?
1. Keratin 3. Carotene 5. Hemoglobin
2. Melanin 4. Sebum
2 only
3 and 5
2, 3, and 5
1, 2, and 3
2,3,5
Which of the following structures of a nail is a pale, crescent-shaped region where the dermal blood vessels are obscured?
Nail body
Eponychium
Hyponychium
Lunula
lunula
The epidermis is dominated by which of the following cells?
Adipocytes
Melanocytes
Keratinocytes
Leukocytes
keratinocytes
Which of the following modified sweat glands is located in the external auditory meatus where it secretes wax?
Sebaceous gland
Ceruminous gland
Mammary gland
Apocrine gland
ceruminous gland
Most common skin cancer is melanoma.
TrueFalse
false
Which of the following nerve endings is found within the dermis and hypodermis and is responsible for the detection of deep pressure?
tactile corpuscle
Lamellated corpuscle
Merkel cells
Free nerve endings
lamellated corpuscle
Which of the following hormones of the skin is released during times of stress and loosen the connections between keratinocytes which then reduces the skin's effectiveness as a barrier to infection?
thyroid hormones
steroid hormones
growth hormones
hormonal vitamin D
steroid hormones
Sweat is composed primarily of ___________________.
salt
water
glucose
oil
water
Match the following nail structures with their correct descriptions.
_____Free edge of the nail composed of a thickened stratum corneum.
_____Consists of dead, tightly compressed cells that are packed with keratin
_____It is more commonly called the cuticle
_____Anchors the nail body into underlying tissue.
1.Nail root
2.Eponychium
3.Nail body
4.Hyponychium
4,3,2,1
The cutaneous membrane is primarily composed of two major layers: the epidermis and___________?
hypodermis
endodermis
dermis
dermis
The hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous layer or superficial fascia is a part of the integumentary system.
TrueFalse
true
Order the five strata of the epidermis from innermost to outermost.
_____Stratum basale_____Stratum corneum_____Stratum lucidum_____Stratum granulosum_____Stratum spinosum
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum granulosum
stratum lucidum
stratum corneum
Which of the following is a function of bone?
Hematopoiesis
Movement
Storage
All of the above
all of the above
The growth plate is also referred to as the?
Diaphysis plate
epiphyseal plate
enlargement plate
Dinner plate
epiphyseal plate
Osteogenesis or ossification is_________________.
Formation of bone
Bone growth
Bone repair
Bone fracture
formation of bone
The shaft of a long bone is called the?
Diaphysis
Metaphysis
Shank
Epiphysis
diaphysis
Bones such as the vertebrae and pelvis are best described as ___________.
Long bones
Short bones
Irregular bones
Flat bones
irregular dones