Chapter 1 (The Earth in Context)
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1.)scientific explanations for the formation of the universe and the Earth 2.)the overall character of the Earth's magnetic field, atmosphere, and surface 3.)the variety and composition of materials that make up our planet 4.)the nature of the Earth's internal layering
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
The transfer of heat from one place to another can occur in what 4 distinct ways:
1.)radiation
2.)conduction
3.)convection
4.)advection
Define radiation`
when an object glows, it sends electromagnetic waves (such as visible light, infrared light, and ultraviolet light) into space around it. This energy, called radiation, can cause an object at a distance from the source to heat up, even if there is a vacuum between the source and the object. Radiation traveling from the Sun is responsible for heating the Earth’s surface

Define conduction
If you stick the end of an iron bar in a fire, conduction takes place and heat moves up the bar. This happens because atoms in the bar at the hot end start to vibrate more energetically, and this motion incites atoms farther up the bar to start jiggling. Through heat flows along the bar, the atoms do not actually mover from one locality to another(see image). Heat always conducts from hotter to cooler materials.
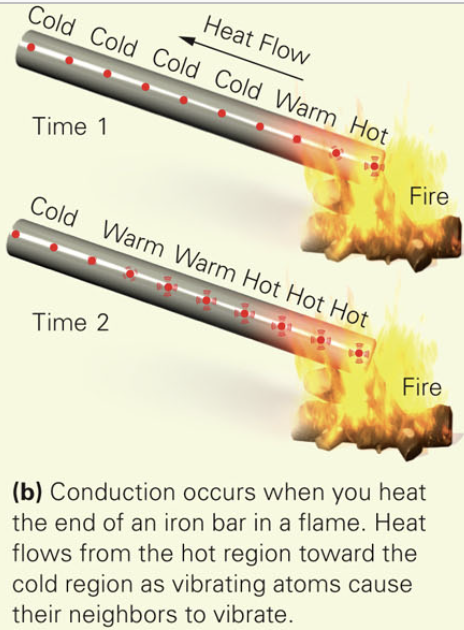
Define Convection
when you place a pot on a stove and heat it, water at the base of the pot gets hotter and expands, so its density decreases. The hot, less-dense water becomes buoyant relative to the colder, denser water above it. In a gravitational field, buoyant material rises if the material above it is weak enough to flow out of the way. Since liquid water flows easily, the hot water can rise. When this happens, cold water sinks to take its place(see image). the resulting circulation, during which flow of the material itself carries heat, is called convection; the path of flow defines convection cells
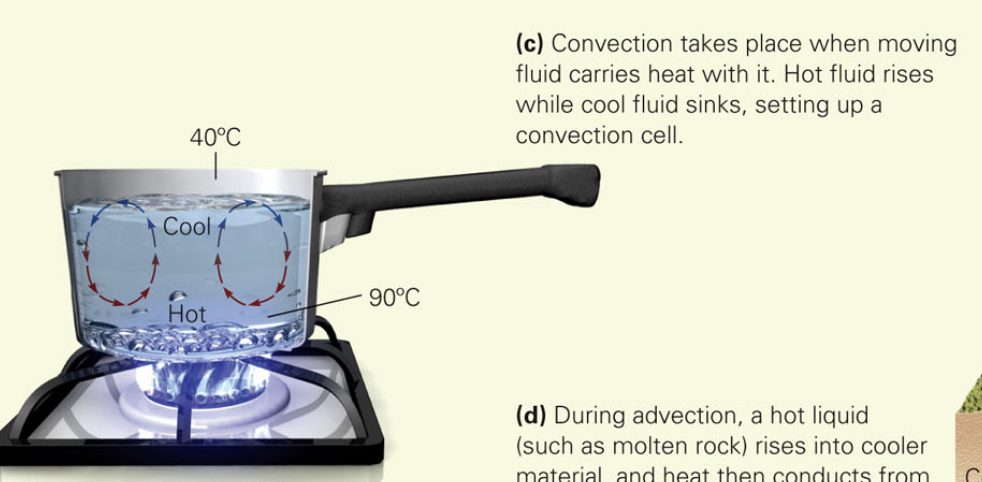
Define Advection
When a hot fluid flows into cracks and pores within a solid, it heats up the solid. Transfer of heat carried by a hot fluid passing through a solid is called advection. The hotness of a metal water pipe’s surface, for examplem, comes from the hot water in the pipe. Advection occurs in the Earth when molten rock rises into the crust(see image)
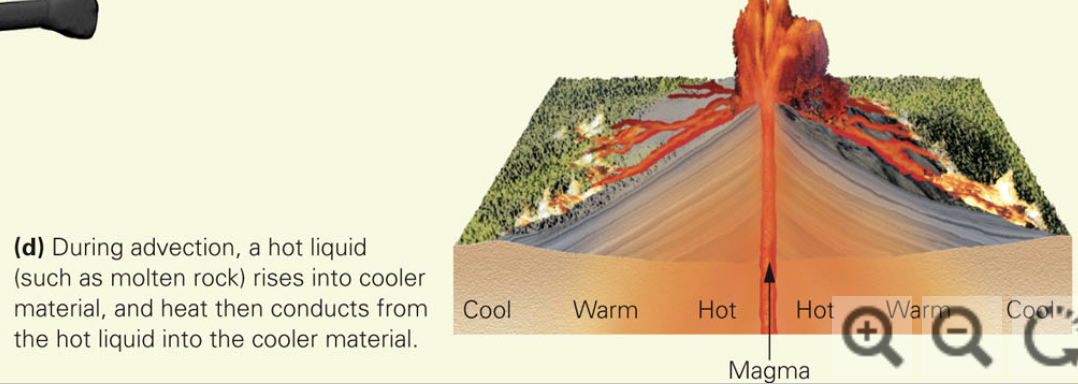
Define Magnetic Field
the region affected by the force emanating from a magnet
Define Dipole
A magnetic field with a north and south pole, like that of a bar magnet

Define Earth’s Atmosphere:
a layer of gases that surrounds a planet (this is important for safety reasons when gold mining in a cave that could collapse)
True or False:
The weight of overlying atmosphere pushes down on the atmosphere below, so both the density of air and the air pressure (the amount of push that the air exerts on material beneath it) increases progressively closer to the surface
true. Look at the image and see the x-axis shows that pressure is more the less attitude
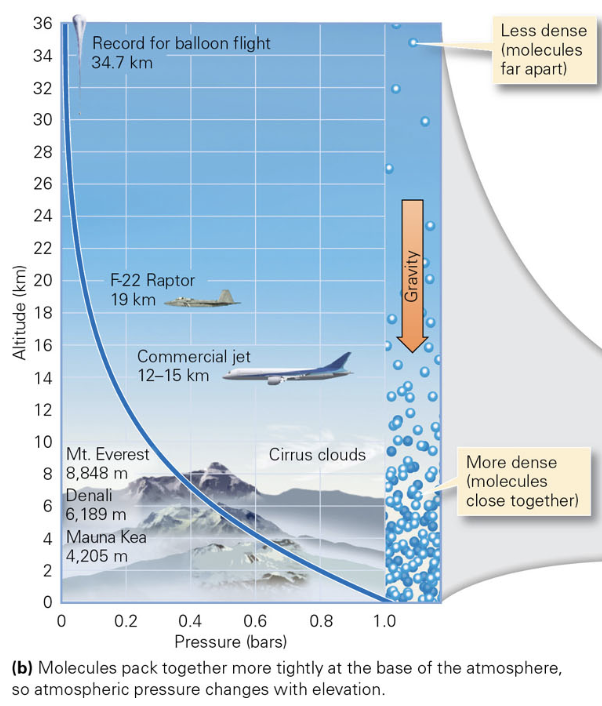
What percent of nitrogen is Earth’s atmosphere made out of?
78%
What percent of oxygen is Earth’s atmosphere made out of?
21%
Is the amount of “Fresh” water available on Earth minor or major?
minor
What is topography?
variations in elevations