ancient egypt
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
2 main geopolitical areas
Lower Egypt
The Nile river delta
Upper Egypt
Area that is South of the delta
Images depicting combined crowns show unification
lower egypt (LE)
Pre dynastic period
Neolithic, chalcolithic
5000 to 3100 BCE
By 4000 BC social differences are evident
Chiefs were buried with a staff that was pointed on one end and flat on the other
Most people were buried in simple pits within their settlements
3500 BCE
Larger towns have their own gods and rulers
ex. Buto
Modern day Cairo
Maadians
Trade with upper Egypt to some extent, the Levant, Mesopotamia
Their pottery was undecorated
Used donkey caravans to trade with the near eastern area
upper egypt (UE)
Pre dynastic period
Neolithic, chalcolithic
5000 to 3600 BCE
The first farming society is the badarian culture in badari
Burials
Facing the West
Included pots, beads, pallets
Craft specialists
Fine black topped redware
Faience
Earliest evidence of intentional modification around 4300 BCE
Through finding resin on linens
egyptian faience
Material
Crushed quartz or sand crystals mixed with sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, copper oxides that produce the blue-green turquoise colour
The paste was shaped into molds and high fired on kiln
The calcium silicates produced a glassy surface
Objects were sometimes dipped into them to produce the glassy surface
Intended to imitate turquoise and other gems
The earliest workshop was found in Abydos and 5500 BCE
Believed that the reflection of light from these pieces was the light of immortality
ceremonial complex in nekhen
Nekhen was the cradle of Egyptian kingship
The Falcon diety
The earliest form of Horus
The patron God of the cities ruler
The temple was a mud plastered Oval surrounded by a mud plastered Reed fence
The post would have the image of the Falcon God
This is the earliest known temple in Egypt
Different classes of people had different cemeteries

nekhen elite burials
Clay masks were found on a few of them
Luxurious grave
Recently an ivory figurine with a similar face to the masks was found
first zoo burial
Found on the edge of the elite cemetery in Nekhen
Tombs of exotic animals who were buried whole
Baboons, Elephants, leopards, crocodiles, hippos, dogs, cats, auroch (wild cattle)
These are all animals that gods and early rulers take the form of
The sacrifices symbolizes the ruler as the controller of the chaos of nature
Zoos show the rulers wealth and power and legitimizes the Pharaohs up to the new Kingdom
proto-dynastic
Around 3400 to 3100 BCE
Now named kings emerge as the head of states in upper Egypt which led to unification
king scorpion dynasty 0
A mace head from the cemetery at nekhen
The king is wearing a white domed crown for upper Egypt and other regalia for later dynastic kingship
ex.
A bull's tail hangs from the belt which is a symbol of authority
Shepherds shem set
AKA apron
Goat beard
Probably false
He is carrying the tool that opens the irrigation canal
So signifies power
The rosette which is a symbol of divinity
Scorpion which alludes to his name

unification
By king narmer
Menes
3100 BCE
Lots of competing kings up until this point
Hieroglyphic writing and irrigation was widespread
The narmer palate was found at nekhen
Shows the unification of Egypt
He is wearing the crown of upper and lower Egypt separately
It depicts lower Egypt being taken by force

early dynastic aka archaic period
3100 to 2700 BCE
Dynastic kingship becomes well developed
burial practices of early dynastic kings
Mainly in Abydos
Earliest evidence of boat burials here
Bodies were moored with a stone
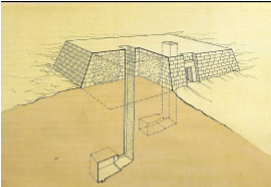
They were buried in mastabas
Lower mud brick structures
The chamber is beneath the structure and was to be entered by a staircase
The Chapel on top was for offerings
Queens and retainers were buried around the king in simple pit graves
after life beliefs
Ba
A person spirit can leave the body but the body still needs to exist so that it can return to it
ka
The life force that needs to be nourished
This occurs through feasting tables
This is what preserves the body
Initially the afterlife was only available to rulers and their entourage not to commoners
political org. of egypt
A territorial state with many cities under a centralized authority
The state is divided into nomes AKA provinces along the Nile
governed by nomarchs
local rulers
Appointed by the king
Usually loyal local leaders or family members of Royals
Received titles and given estates
Usually a hereditary position
old kingdom
Around 2700 to 2140 BCE
3rd dynasty
Kings ruled as sons of Ra-horakhty
A combination of ra and horus
The people relied on a divine pharaoh who was the intermediary to the gods
Kings are not yet declaring themselves to be God
Representatives and extensions of the sun God ra
After the king dies they become assimilated with ra
This is when monumental building began AKA pyramids
Burials did not use mastabas anymore
First pyramid was built by Djoser
giza plateau
Khufu built great pyramid of Giza plateau
Pyramids
smooth sided with limestone blocks
They had paved causeways linked to Mortuary temples
The middle pyramid
Built by khafre
The sphinx in front of it guarding it
face on the sphinx is his
lines show strata of the sandstone that has undergone erosion
harder material erodes faster
equated himself to god
Mankuare
Builds the last in smallest pyramid using red granite
khufu and khafre were described to be tyrants by historians which is why workers were confused to be slaves

pyramid of unas
Contains the pyramid text
Earliest religious text in Egypt
Magical spells that guide the king to the afterlife
first intermediate
Around 2140 to 2040 BCE
Centralized authority is broken down to the local nomarchs
A breakdown of both the state and its ideologies
Because Pepi II had weak rulers and there was widespread droughts
pepi ruled for a long time but did not leave heirs in a strong position
Weakness allows for people to take agency of their own affairs
A period of social reorganization and warfare
The people became more wealthy and they wanted the privileges of the old Kingdom that were reserved for the elite
cult culture expanded to more people
causes mass production of funerary objects
drives the economy
religion and hierarchy changed to do this
middle kingdom
The classical age
Best literature and art are from this.
About religion, texts on tombs, monuments
Art style changes
Introduces the idea of internal youth in people
Mentuhotep II from upper Egypt reunites Egypt
The capital is moved to thebes
A peaceful period For monumental building
Irrigation
Temple temples dedicated to Amun
Smaller pyramids in different parts of Egypt
His successor moves the capital to lisht
By the end of the middle Kingdom lots of asiatics were living in Egypt
amun-ra
Cult shifts from just worshipping the sun God Ra to amun ra
Depicted wearing a head dress with two tall plumes
role of the king is more of a shepherd of the people
cuz after the time of the old kingdom this is what the people were willing to accept

cult of osiris from abydos
The middle Kingdom democratizes religion
Everyone has a chance for the afterlife but they have to account for their deeds on earth
class based
need to be mummified, embalmed etc.first which you need to be able to pay for
Story of osiris is A metaphor for life and resurrection and the floods of the Nile
Osiris is God
He judges the dead and the pharaoh assimilates with him after death
2nd intermediate
1640 to 1550 BCE
Entry of the hyksos in lower Egypt
Consisted of cooks, Brewers, artisans, wine makers from Syria
Respected Egyptian traditions and embrace the titles and religious beliefs of the Pharaohs which angered the Pharaohs
Brought innovations like bronze technology, improved weaponry, horse drawn war Chariots to Egypt
Integrated Egypt into a larger economy
Theban rulers in upper Egypt
Centralized rulership breaks down again
Cosmopolitan society
Multiculture and religion
new kingdom
1550 to 1070 BCE
A period of imperial Egypt
Upper Egyptian kings at thebes were enemies of the hyksos and their allies who were the nubians
Ahmose I attacks the hyksos and drives them back to Syria which they never returned from
He then reunites Egypt and finds the 18th dynasty
Skill general and turns Egypt into an empire
The pharaoh is now viewed as a military hero who did not tolerate his rivals
Soldiers were given land, kept power and wealth
Allow eqypt to become a major world player at this time.
Main rivals
The indo European -> hattie the Kingdom of the Hittites in anatolia and mitanni east of the Euphrates
Everyone wanted to control the eastern Mediterranean trade of gold, copper, pottery, wine, oil and resin (incense)
The Kingdom was financed with nubian gold after defeating kush and making it a colony
Red Sea trade routes were expanded to the later land of punt
new kingdom society
Highly stratified
Pharaoh
no longer the shepherd of the people due to deification
Aristocrats, nobles, priests
The educated and professional class
Workers, Craftsman, soldiers, traders, artisans, shopkeepers, scribes
Farmers and herders
Unskilled laborers
There were separate administrations for conquered lands
estate of amun
aka thebes
temple of amun Built in karnak in 18th dynasty
this is An architectural shift because kings usually put monuments at the edge of the western desert aka in pyramid cities
had 50,000 priests
temples in the new kingdom
Most local temples were made of mud brick
Religion became more of a public spectacle which required new architecture
ex. The annual opet festival
Celebrates the Nile flood
Power eventually shifts to priesthood
gods wife of amun
Begins in the 18th dynasty
A position taken by the pharaoh's wife or sister who selects her own successor
Gives the privileges that are normally reserved for only the pharaoh
Like a throne name or having your name in the cartouche
They have their own estates, property, staff, administrators
Performed rituals at the temple of amun as God's wife
Lots of wealth and power and monumental builders as well
hatshepsut
18th dynasty pharaoh and the daughter of thutmoses I
Also the gods wife of amun
Married to thutmoses II
He dies three years into the marriage
He has a son with another wife = thutmoses III
Has a daughter
Neferure
She becomes the Co Regent of thutmoses III
In the 5th year of her reign she crowns herself king and removes thutmoses III as Co Regent
A monumental builder
She is presented and statues and imagery with full pharaoh regalia
Her earlier portraits were more feminine but later ones were more masculine
Reigned for 20 years
Peaceful and prosperous
Brought luxury goods from the nearest, eastern desert, Nubia through the Red Sea fleet which she re-establishes and through over land transport
Reestablishes connection with punt
thutmose III
Takes the throne from hatshepsut
Either he or his son (amenhotep)tries to erase her from history
The greatest ruler of the new Kingdom
Refer to as the Napoleon of ancient Egypt
Dominated southwest Asia
Generated tax revenue from Assyria, anatolia, babylonia
Trade relations with Nubia, Aegan, Crete, phoenicia (levant)
Built many temples
takes sons of colonized kings as hostage and keep them in the royal court
a type of diplomacy
50 year reign
cult of aten
It caused an architectural style that emphasizes light which is the essence of aten
Quasi monotheist
Restricted from worshipping the old gods
The only way to afterlife is through loyalty to Akhenaten and following his teachings
There was no real impact of the cult beyond the royal family because there was no regular access to it
akhenaten
The amarna period
Capital is moved to amarna in middle Egypt
20 year period That broke down the relationship between the religion and state
1353 to 1347 BCE
He married his sister Nefertiti
Was coronated at karnak by the priests of amun
His main concern was religion
In his fifth year he breaks the power of the priests and makes the cult of the sun God aten the state religion
Removed mentions of amun from monuments
closed amun temples
Temples of isis and osiris were destroyed too
He declares himself and Nefertiti to be gods
Ignored foreign policy and requests from allies for help
Cause Egypt to isolate itself
Control of near eastern conquests were lost
His son was Tutankhamun
battle of kadesh
kadesh is a city in Syria
Held by the hittites
Rameses II vs. King muwatalli
1274 BC
One of the best documented battles of the near east
They both claimed victory
Result was the first ever bilateral peace treaty
Both states were greatly diminished
abu simbel
A propaganda piece to show that rameses won the battle of kadesh
A warning to the kushites of egypt's power
eastern mediterranean collapse
Late Bronze Age
Hittite and Egypt fall because of weak rulers
Begins the Iron Age
1200 to 1000 BCE
Populations begin moving by land and sea
1200 to 900 BCE the sea peoples raid and settle
Multiracial group that was known to the Egyptians
Included some aegen mercenaries that were previously employed by the pharaoh
Many cities were destroyed
the 3rd intermediate
1069 to 653 BCE
Libyans take control of the delta
Priests of amun take upper Egypt
The neo assyrians become powerful in the near east
The nubian kings of kush invade Egypt in 727 BCE and take control of all of Egypt forming the 25th dynasty
Causes a cultural renewal
kushite pharaohs
They expanded the empire
worshipped amun
Restored religion, art, architecture of dynastic Egypt
King taharka helps the king of Jerusalem stop the assyrians but the assyrians chase the pharaoh back to Nubia and they take control of Egypt
then babylonians then persians then greeks (alexander the great) -> late period
egypt becomes part of the roman empire and other empires throughout time