MAC Module 11 : Finance, Savings, & Investment
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What funds are supplied & demanded in financial markets?
Loan markets, Bond markets, Stock markets
Saving
the source of the funds that are used to finance investment
financial institution
a firm that operates on both sides of the markets for financial capital: It borrows in one market and lends in another
Key financial institutions are
Investment banks, Commercial banks, Government-sponsored mortgage lenders, Pension funds, Insurance companies.
The financial markets and institutions that we’ve just described bring three economic benefits. They enable households, firms, and governments to
Invest in capital, Smooth consumption expenditures, Trade risk
Loanable funds are used for three purposes:
Business investment
Government budget deficit
International investment or lending
Loanable funds come from three sources:
Private saving
Government budget surplus
International borrowing
The main things that change the supply of loanable funds are-
disposable income, wealth, expected future income, and default risk
Firms use-
financial capital to buy and operate physical capital.
Gross investment is
the total amount spent on physical capital in a given period. Net investment equals gross investment minus depreciation.
Wealth
the value of what people own; saving is the amount of disposable income that is not spent, and it adds to wealth.
The market for financial capital
a market made up of the markets for loans, bonds, and stocks.
At the equilibrium real interest rate
the quantity of loanable funds demanded equals the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
Equilibrium
in the loanable funds market determines the real interest rate.
With no change in private saving
an increase in the government budget deficit raises the real interest rate and crowds out investment.
The Interest in the first year is equal to the present value multiplied by the interest rate, r, so
Sum after 1 year = Present value + (r x Present value) or Sum after 1 year = Present value x (1+r)
To find the present value of an amount one year in the future we divide the future sum by (1+r)
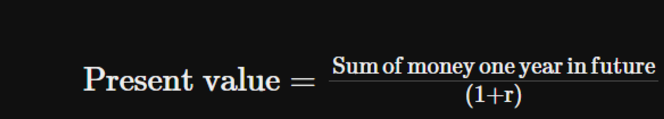
We can calculate the present value of sum of money n years in the future by using general formula

For example, suppose that you expect to pay $100 a year for each of the next five years & the interest rate is 10% a year (r = 0.1). The present value (PV) of these 5 payments of $100 each is calculated by using the following formula:

financial capital
The funds used to buy capital
gross investment
The total amount spent on new capital
net investment
The change in the quantity of capital
Wealth, also called Net worth
the market value of what a household or firm owns minus what it owes.
bond
a promise to make specified payments on specified dates.
bond’s coupon
The annual payment
yield curve
The relationship between the term of a bond and the interest rate
financial institution
a firm that operates on both sides of the markets for financial capital
loanable funds market
the aggregate of the markets for loans, bonds, and stocks.
demand for loanable funds
the relationship between the quantity of loanable funds demanded and the real interest rate when all other influences on borrowing plans remain the same
Supply of loanable funds
the relationship between the quantity of loanable funds supplied and the real interest rate when all other influences on lending plans remain the same.
crowding-out effect
The tendency for a government budget deficit to raise the real interest rate and decrease investment
Present Value
what a future sum of money is worth today
Which of the following is an example of capital or physical capital?
A. Subway uses convection bread ovens.
Using a Federal grant of $150,000, a research lab buys equipment for $75,000 that has depreciated by $11,000 after two years. Calculate gross investment and net investment.
D. $75,000; $64,000
Wealth is the value of all the things that people _____.
C. own
A bond is a promise to pay _____ sums of money on _____ dates.
C. specified; specified
A stock is a certificate of _____ and claim to the _____ that a firm makes.
A. ownership; profits
A financial institution is a firm that operates on both sides of the markets for _____: It _____ in one market and _____ in another
C. financial capital; borrows; lends
Net worth is the total market value of what a financial institution has _____ minus the market value of what it has _____.
D. lent; borrowed
The Loanable funds market is the aggregate of all the individual _____ markets.
C. financial
The demand for loanable funds is the relationship between _____ demanded and the _____ when all other influences on borrowing plans remain the same.
C. the quantity of loanable funds; real interest rate
The crowding-out effect is the tendency for a government budget deficit to raise the _____ and _____ investment.
C. real interest rate; decrease
Financial capital is the .
B. money used to buy physical capital
If the price of a U.S. government bond is $50 and the owner of the bond is entitled to $2.50 income each year, then the interest rate on the bond is .
B. 5 percent
In the loanable funds market, an increase in .
B. expected profit increases the demand for loanable funds
The supply of loanable funds increases .
C. when disposable income increases or wealth decreases
An increase in expected profit the real interest rate and the quantity of loanable funds
D. increases; increases
A government budget surplus .
A. increases the supply of loanable funds
Crowding out occurs when ________.
C. the government budget is in deficit and the real interest rate rises
An increase in the government budget deficit .
B. increases private saving and decreases investment
Business Cycles Has Each Phase Called (Scott’s Lecture)
1- Expansion
2- Peak
3- Contraction
4- Trough
How are interest rates determined? (Scott’s Lecture)
1- Interest rates are determined in the bond market & fundable funds
2- Interest rates are determined in the money market
Equity (Scott’s Lecture)
2- Ownership claims to profit -dividends
3- CS no exploration
Bond (Scotts Lecture)
1- Loan No claims to profit
2- No claims to profit
3- Most bonds have insurers dates
1- States interest rate coupon payment = r x Par
2- Par value
3- Maturity date
Yield to maturity (Scotts Lecture)
A bond owner can expect if the bond is held from origination to maturity
Current yield (Scotts Lecture)
Approximates to mature y +m)
Current yield = (Scotts Lecture)
Coupon payment/Price of bond
What to look for in the graphs? (Scott’s Lecture)
1- Shock
2- Curve affected
3- Direction (Left or Right)
4- What is happening to R then B
Supply side economics (Scotts Lecture)
Use of government fiscal policy, taxes & spending to influence the goods
Increase in supply or demand curve shifts to the (Scott’s Lecture)
Right
Decrease supply or demand curve shifts to the (Scott’s Lecture)
Left
Physical capital-
the tools, instruments, machines, buildings, & other constructions that have been produced in the past and that are used to produce goods & services
Financial assets
Stocks, bonds & loans are collectively called
Interest rate on a financial asset is-
A percentage of the price of the asset
If the asset price rises-
Other things remaining the same, the interest rate falls
If the asset price falls-
Other things remaining the same, the interest rate rises.
Financial market & institution bring 3 economic benefits. They enable households, firms, & governments to
Invest in capital, Smooth consumption expenditures, & trade risk
A government budget surpluses-
increases the supply of loanable funds
A government budget deficit-
Increases the demand for loanable funds
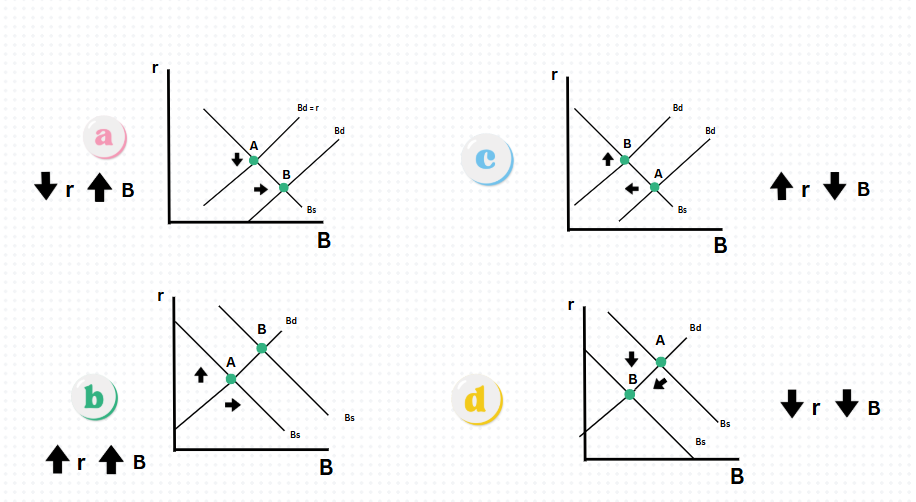
Which graph shows an decrease in interest rates and increase in bonds
Graph A
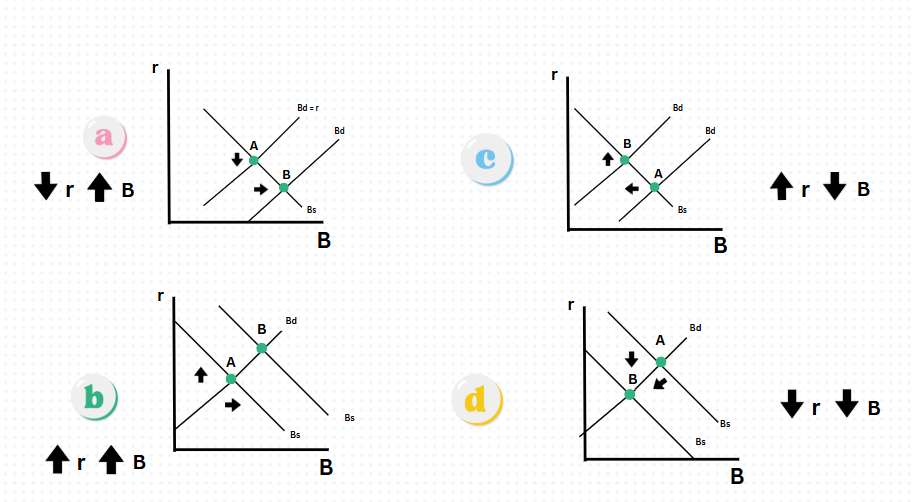
Which graph shows an increase in interest rates & bonds?
Graph B
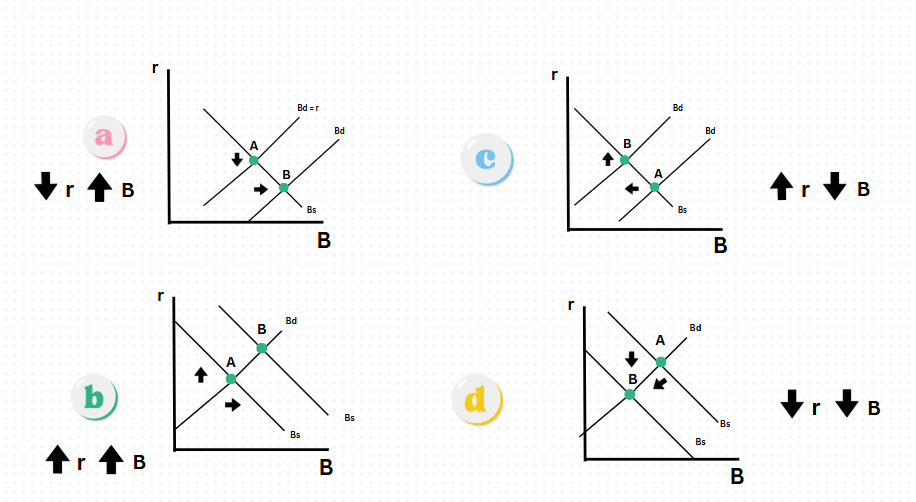
Which graph shows an increase in interest rates & decrease in bonds?
Graph C
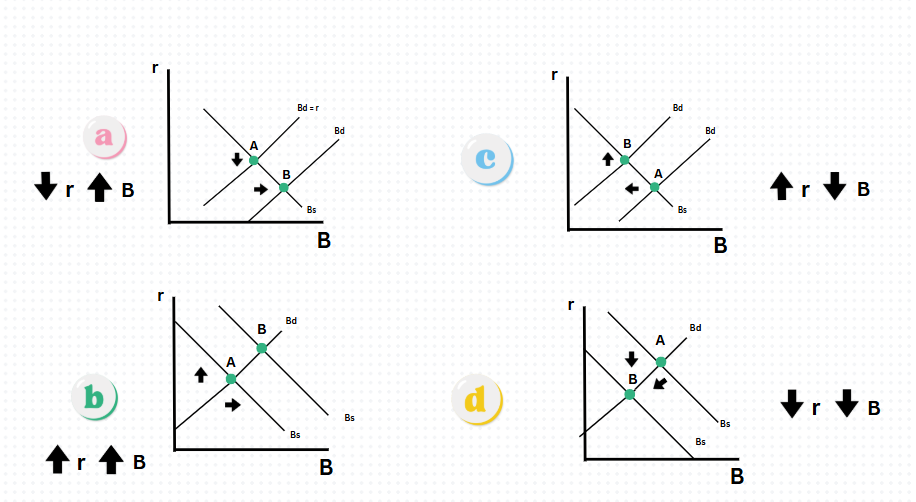
Which graph shows a decrease in interests rates & bonds?
Graph D