Voltage and Current Laws
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1008: Dynamic Systems 1 - Lecture 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Kirchhoff’s Current Law
At any node (junction) in an electrical circuit, the sum of the currents flowing into that node is equal to the sum of currents flowing out of that node.
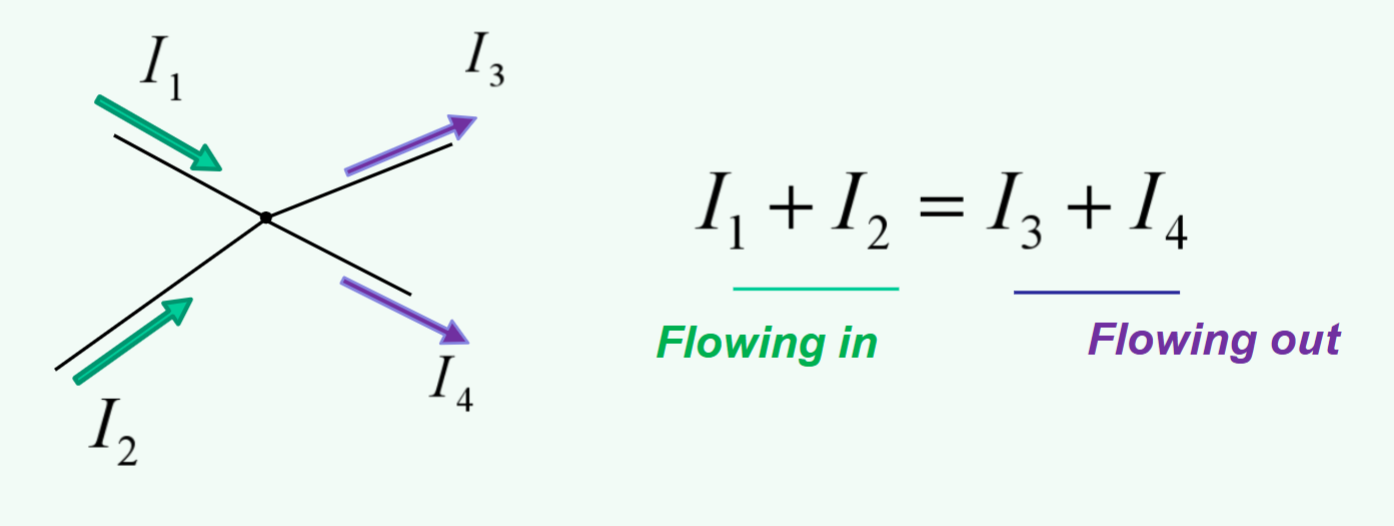
Current flowing in the opposite direction in a juncition
Is represented with a minus algebraically.
More complex junction calculations
Where n: conductors in and k: conductors out.
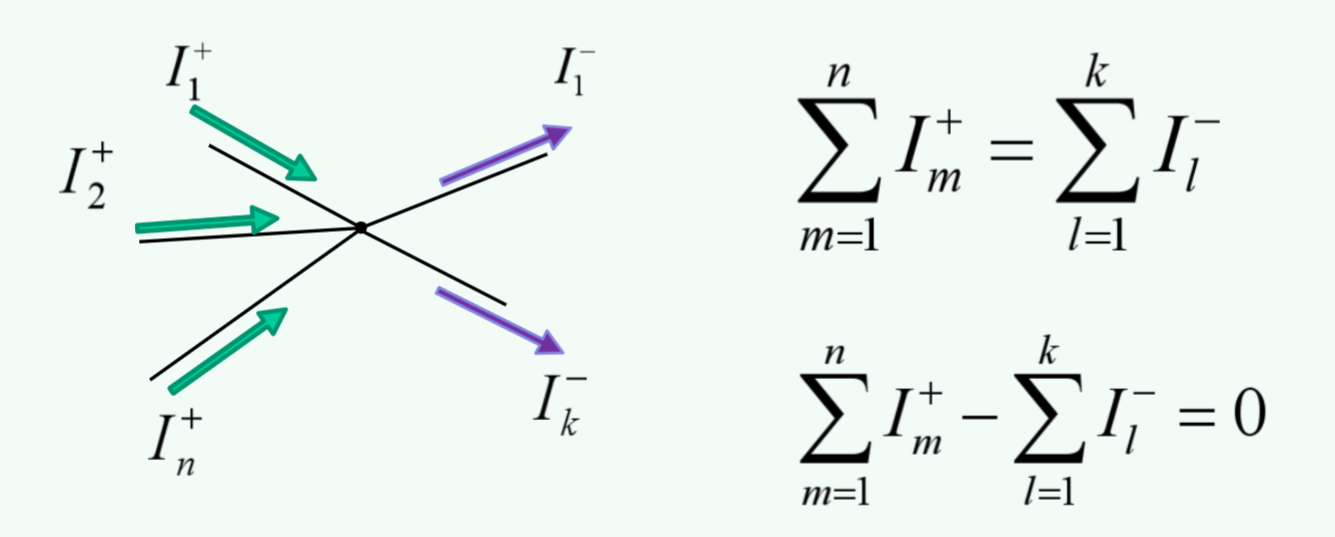
The fundamental property of charge results in Kirchhoff’s current law
Kirchhoff’s current law is a consequence of charge conservation principle - the net charge in the wires and components of a closed circuit is constant.
Ohm’s law
The current (I) through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage (V) across the two points. The constant of proportionality is the conductor resistance (R).
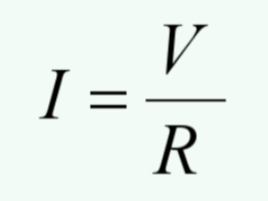
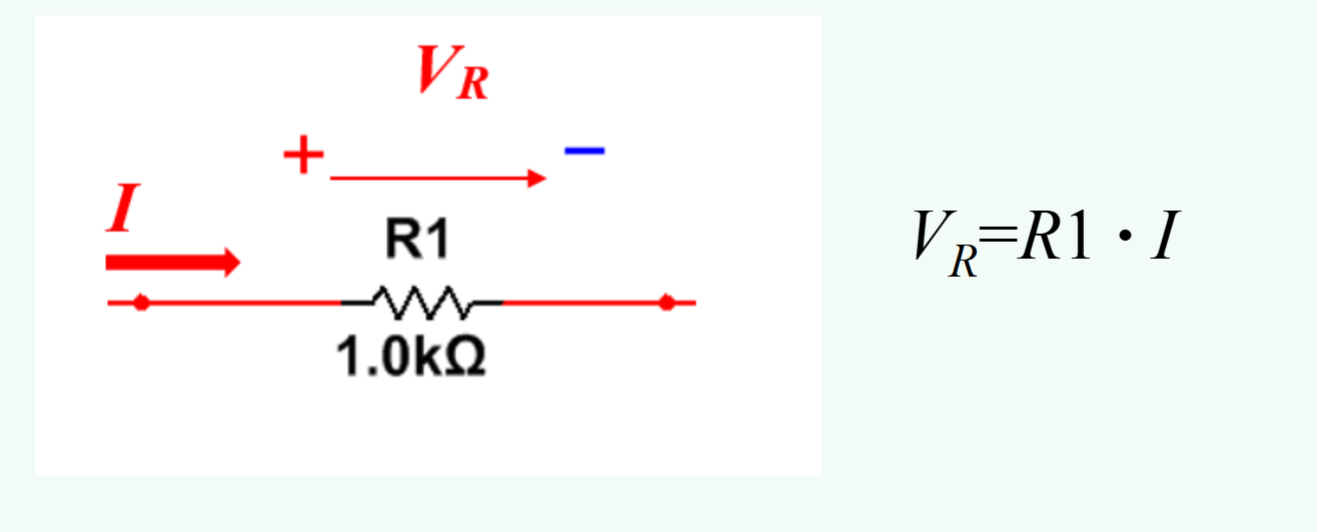
Ohm’s law with voltage drops
Electric current (I) from an external source flows through the resistor R1. There is voltage drop VR across this resistor which relates to current I and resistance R1.
Ohm’ Law: Voltage
Describes voltage generated by active source, e.g. battery.
Ohm’s Law: Voltage Drop
The decrease of electric potential due to resistive load.
Devices that don’t obey Ohm’s Law
Diode, battery.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law
For a closed loop series path the algebraic sum of all the voltages around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
Take into account the polarities and signs of the sources and voltage drops around the loop.
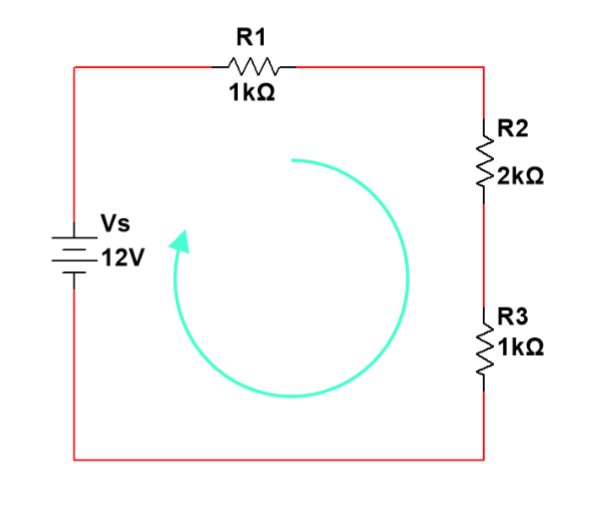
Another Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law formulation
For a closed loop series circuit the algebraic sum of all the voltage drops equals to the sum of voltage rises (active sources).