maths
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Differentiation
Tell you the gradient of tangent
Normal = -1/gradient of curve
y-y1=m(x-x1)
Times then take
Stationary points - how to find
Differentiate to see where dy/dx = 0
Then substitute that x value into original equation (not the dy/dx equation).
Stationary point - max min or turning
Use d2y/dx2 to find if max min or turning.
Same as rate of change
If f’’ > 0 then min
If f’’ < 0 then max
If f’’ = 0 then any
To find if decreasing/ increasing
Find f’(x)
If increasing then find when f’(x)>0
If decreasing find when f’(x)<0
Then rearrange
Integration
Add 1, then divide
+C
Definite integrals give the area under the graph of the function you integrate. Then add or subtract.
Circles
(x-a)²+(y-b)²=r²
Complete the square if not in right form:
X² +bx+c = (x+(b/2))²-(b/2)²+c
Factor theorem harder
If f(b/a)=0 then (ax-b) is a factor of f(x)
Discriminant
(b²-4ac)
If b²-4ac>0 then 2 real roots
If b²-4ac=0 then 1 real root
If b²-4ac<0 then 0 real roots
Inequalities
If multiply or divide by a negative then flip sign
Proportion
Direct: y infinity x then y=kx
Inverse: y infinity (1/x) then y=k/x
Proof
Even is 2n
Odd is 2n+1
Vectors
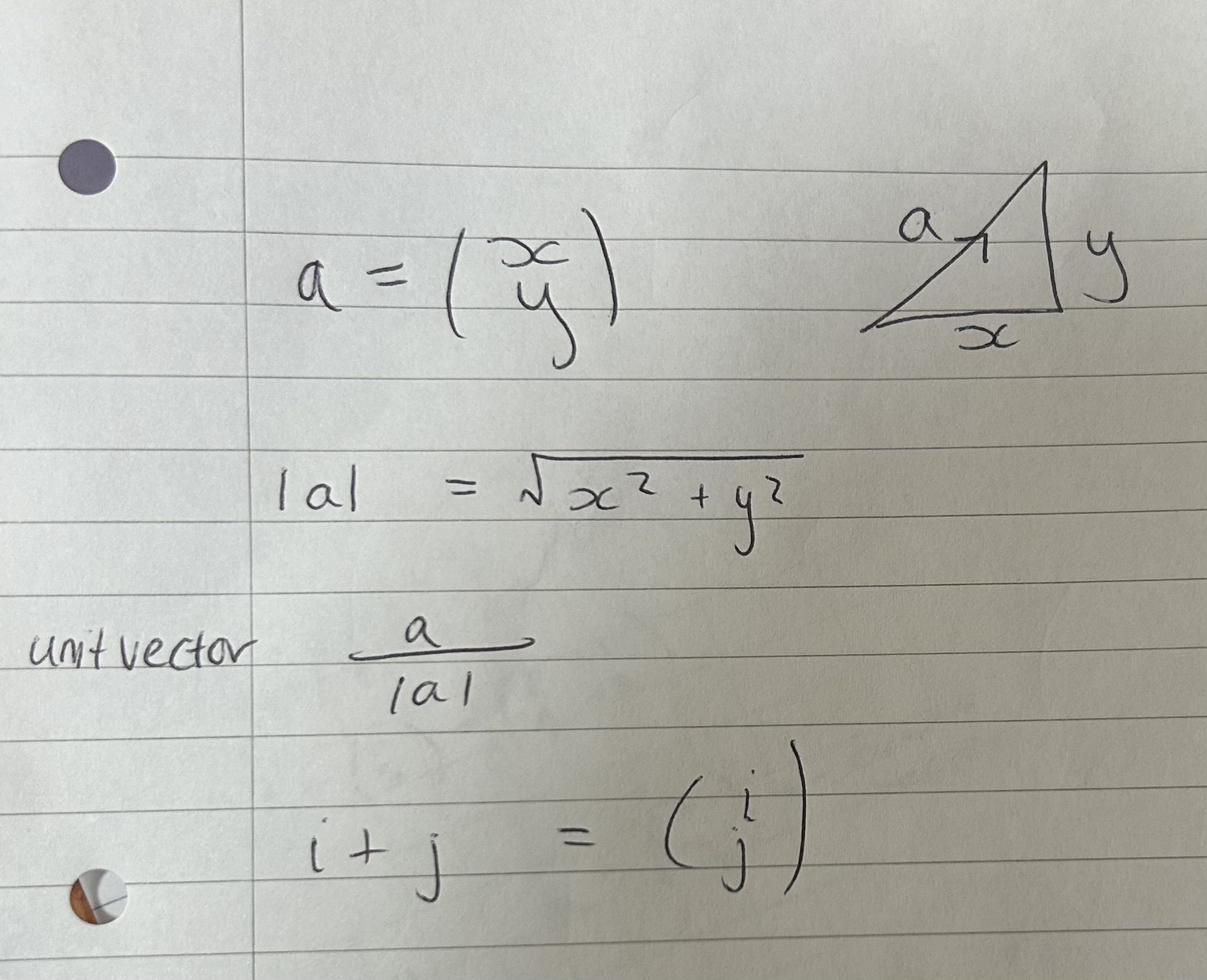
Ex and logs

Ex logs 2

Ex logs 3
