Topic 6- Animal Diversity II
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are basal animals?
Basal animals are the most primitive members of the animal kingdom. They share general derived traits with all animals but lack specialized traits found in more complex organisms.
What are the characteristics of basal animals?
Lack of true tissues (except Cnidaria), no organs or organ systems, simple body structures adapted for filter-feeding or passive food absorption.
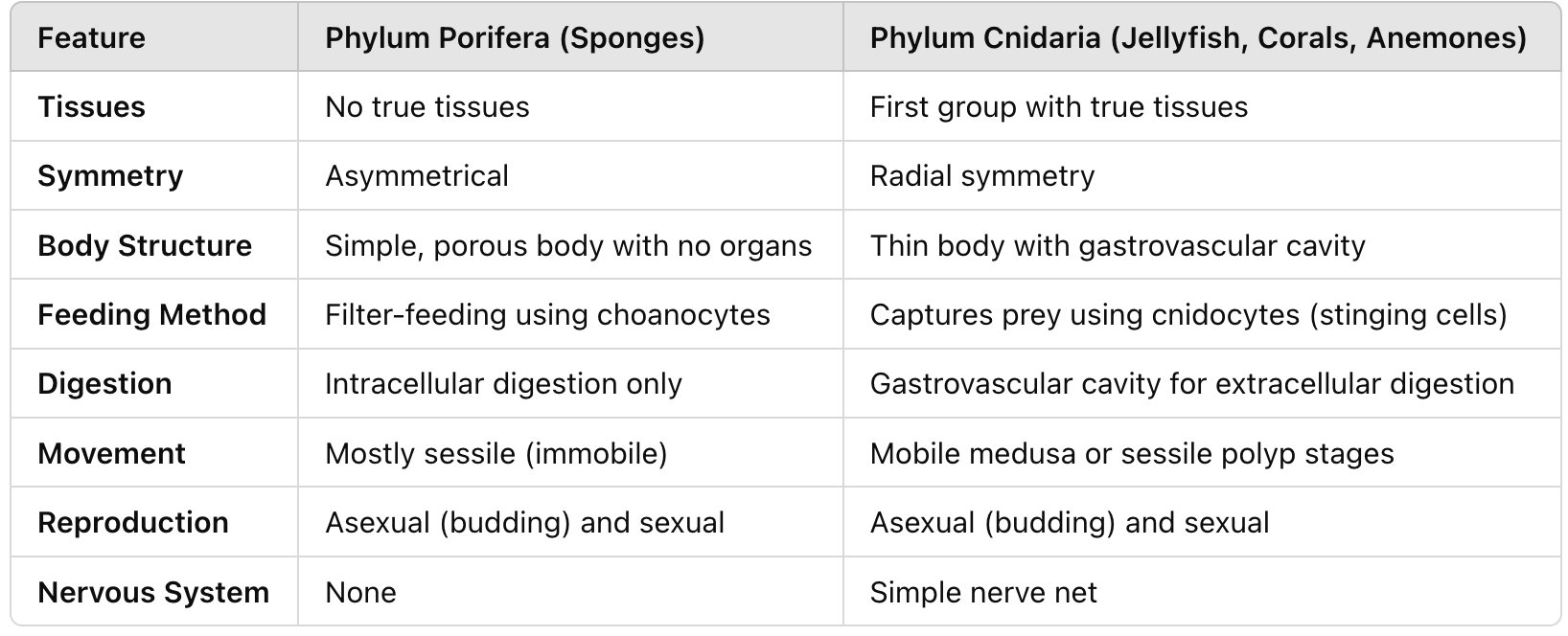
What does the name 'Porifera' mean?
'Porifera' means 'to have pores,' referring to their porous bodies.
What are the defining characteristics of Porifera?
Least complex animals, multicellular but lack true tissues, symmetry, or organs; considered basal metazoans.
What is the osculum in sponges?
The large opening at the top of the sponge where water exits.
What is the spongocoel?
The central cavity where water circulates inside a sponge.
How does the water flow system in sponges work?
Water enters through pores (ostia), moves into the spongocoel, and exits through the osculum.
How do sponges feed?
Sponges use filter-feeding by extracting food particles from water.
What type of digestion occurs in sponges?
Intracellular digestion—food is broken down inside individual cells.
What are choanocytes, and what is their function?
Specialized flagellated feeding cells that create water currents and capture food particles.
What is the first animal group to have true tissues?
Phylum Cnidaria.
What symmetry do cnidarians exhibit?
Radial symmetry (symmetrical around a central axis).
How many germ layers do cnidarians have?
Two (diploblastic: ectoderm and endoderm).
What is the gastrovascular cavity?
A body cavity with a single opening that functions in both digestion and circulation.
What are cnidocytes?
Specialized stinging cells unique to cnidarians, used for defense and capturing prey.
Are cnidarians mostly marine or freshwater?
Mostly marine.
What is the significance of cnidarians in animal evolution?
They are considered basal eumetazoans, meaning they were the first group with true tissues.
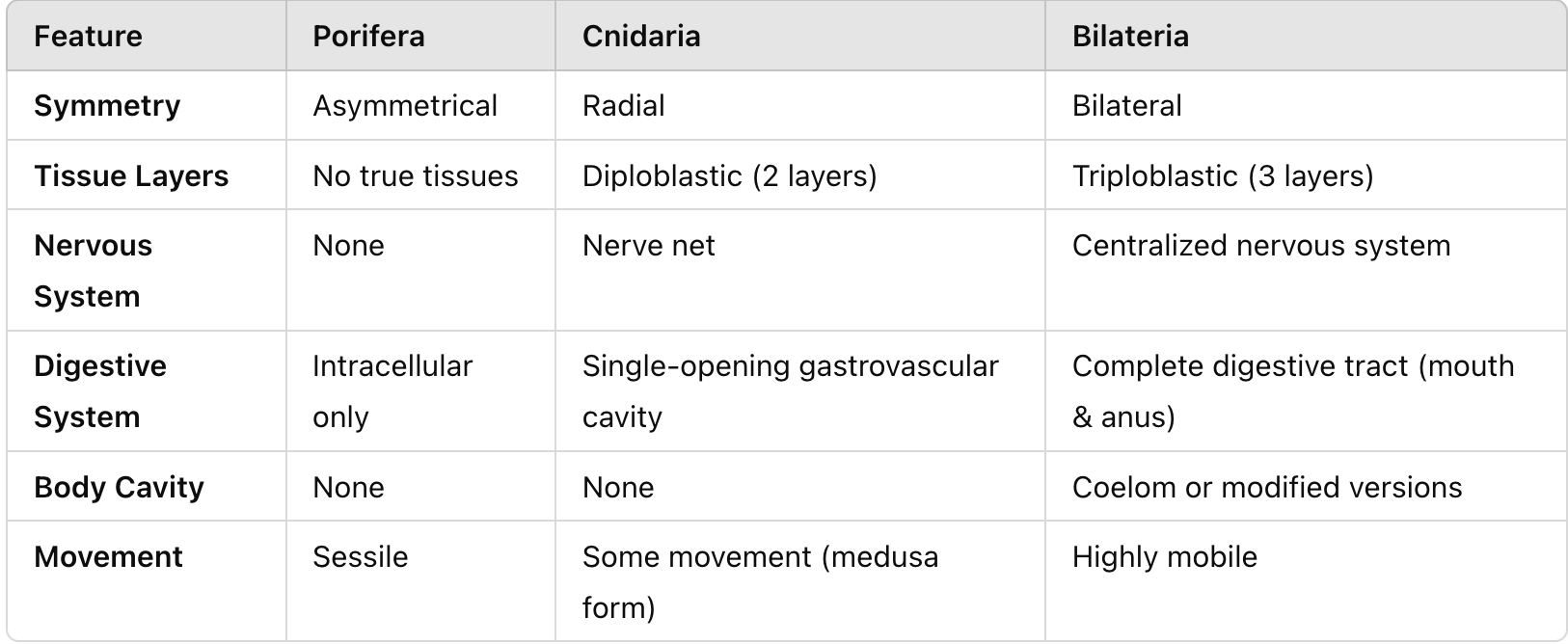
What are bilaterians?
A major group of animals with bilateral symmetry and triploblastic body structures.
What are the shared derived traits of Bilateria?
Bilateral symmetry, triploblastic, and body cavity (coelom in most, absent in some).
What is Nephrozoa?
A subgroup of bilaterians that includes animals with true coeloms or a modified version.
What are the defining characteristics of Protostomia?
Mouth develops first from the blastopore, spiral cleavage, determinate cell fate, includes mollusks, annelids, and arthropods.
What are the defining characteristics of Deuterostomia?
Anus develops first from the blastopore, radial cleavage, indeterminate cell fate, includes echinoderms and chordates.
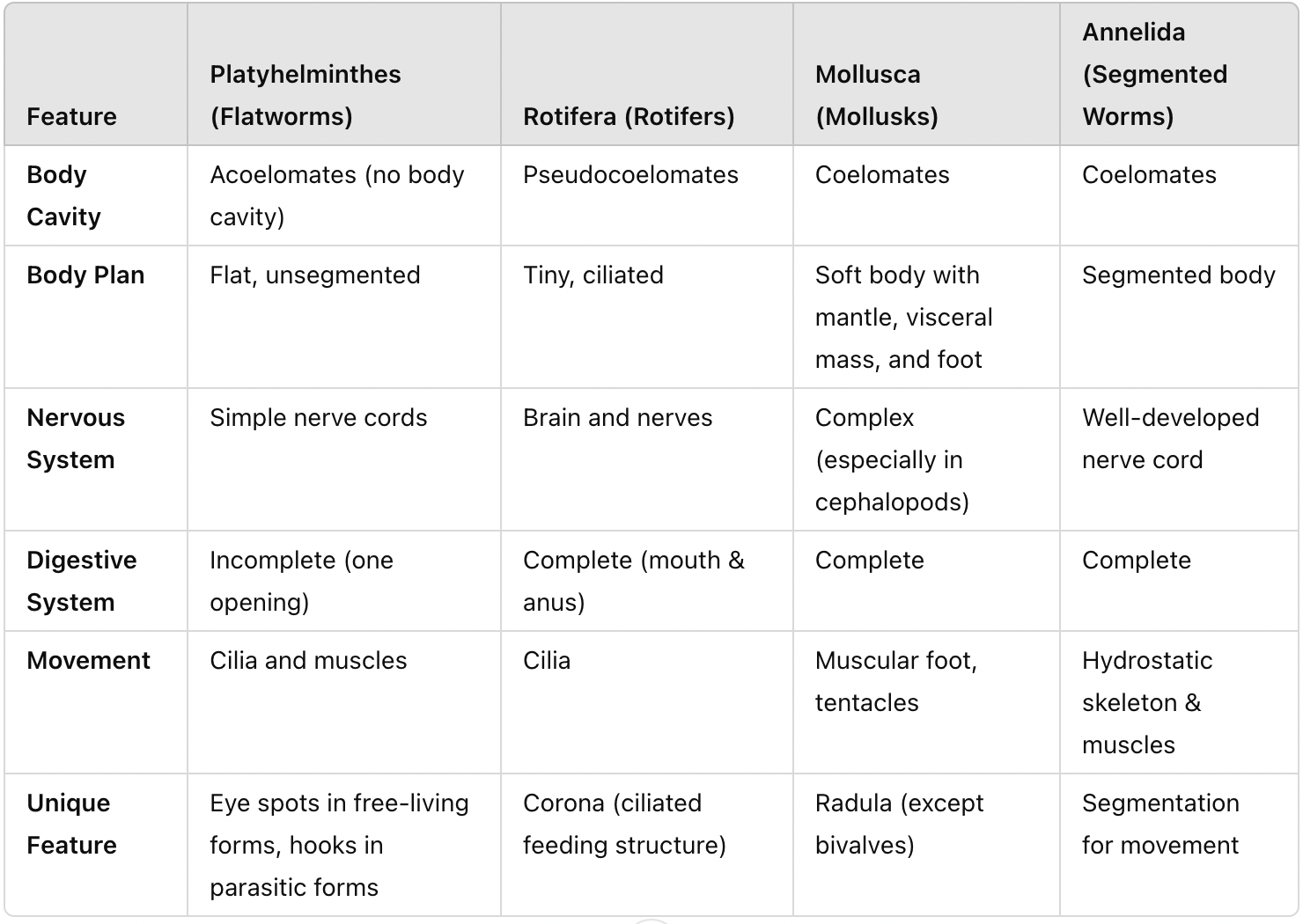
What groups belong to Spiralia?
Platyhelminthes, Rotifera, Mollusca, Annelida.
What are the defining traits of Spiralia?
Grouped based on DNA similarities, bilateral symmetry, triploblastic development.
What is the defining feature of Ecdysozoa?
Ecdysis—molting of the outer covering during growth.
What phyla belong to Ecdysozoa?
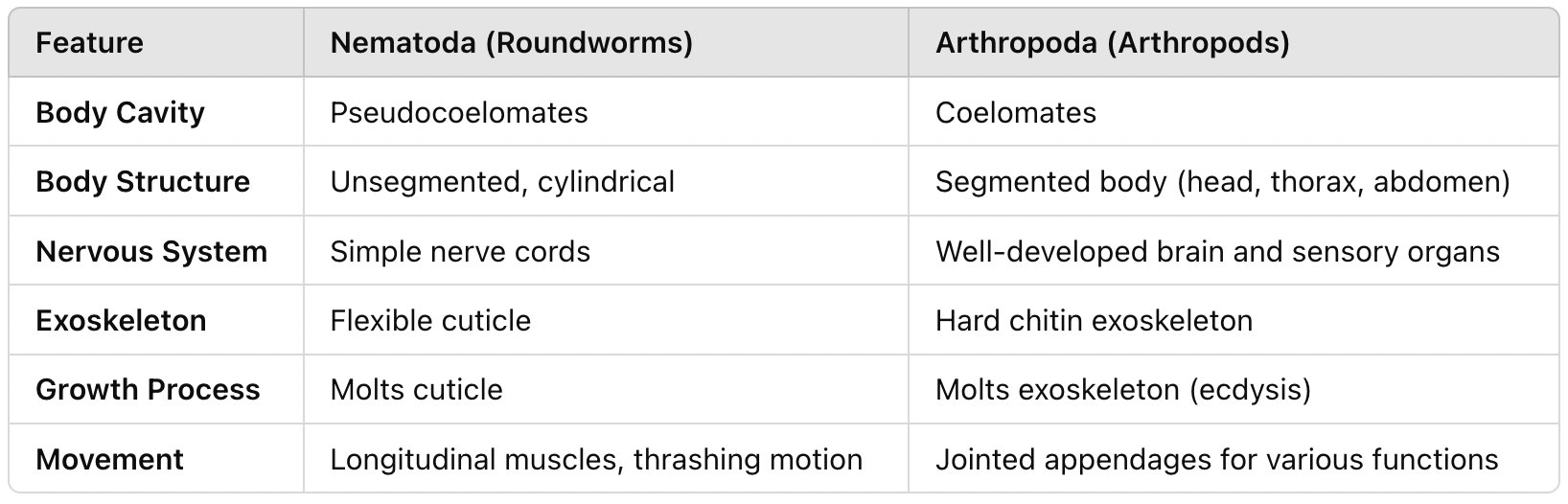
Nematoda (roundworms) and Arthropoda (insects, spiders, crustaceans).
What are the shared ancestral traits of Ecdysozoans?
Bilateral symmetry, triploblasty, protostome development and molting.
What are the characteristics of nematodes?
Covered in a cuticle, pseudocoelomates, found in aquatic environments, soil, and as parasites. (CAPP)
What does 'Arthropoda' mean?
'Jointed-foot'.
What are the characteristics of arthropods?
Largest phylum in the animal kingdom, segmented bodies, jointed appendages, chitin exoskeleton.
What are the three main body sections in arthropods?
Head, thorax, abdomen.
What are the functions of the exoskeleton?
Provides protection, prevents water loss, serves as muscle attachment.
What are the limitations of the arthropod exoskeleton?
Restricts growth, limits body size, arthropods are vulnerable after molting.
Compare and contrast Porifera and Cnidaria (tissues, symmetry, body structure, feeding method, digestion, movement, reproduction, and nervous system)
Compare and contrast significant animal groups such as Porifera, cnidaria, and bilaterian (symmetry, tissue layers, nervous systems, digestive system, body cavity, movement)
Compare and contrast Spiralians (body cavities, body plan, nervous system, digestive system, movement)
Compare and contrast Ecdysozoans (body cavity, body structure, nervous system, exoskeleton, growth process, movement)