4.1 Biology - DNA, genes and chromosomes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) DNA
DNA in prokaryotic cells, mitochondria and chloroplasts is:
short
circular
NOT associated with proteins
NO introns (non coding DNA)
found in the cytoplasm
eukaryotic (plants/living) DNA
DNA in eukaryotic cells is:
very long
linear
coiled around histone proteins
contains introns (non coding DNA)
found in the nucleus
compared to each other - nucleotides are identical, nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds, a deoxyribose joined by phosphate DNA in mitochondria.
Describe the structure of DNA
Made up of deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four organic bases (A,C,T,G).
Double stranded and hydrogen bonds between the bases form the helix shape.
DNA
chromosome - supercoiled DNA + associated proteins
springy bit - Chromatin - semi coiled DNA + associated proteins
EUKARYOTIC DNA
Chromosome
a compact structure formed when DNA is wound round histone proteins
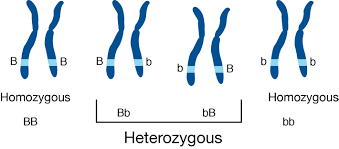
homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes
same size
same shape
same genes in the same positions (loci)(locations)
karyotype
all the chromosomes in a cell arranged in their homologous pairs
gene
a level def
Sequence of DNA bases that codes for a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or for functional RNA e.g tRNA or rRNA
allele
A form of a gene
gene locus
the position of a gene on a chromosome
Non - coding DNA - INTRONS
DNA base sequences that code for amino acid sequences in between genes (intergenic DNA) - once called junk DNA
introns are found between exons within genes
Coding DNA - EXONS
region of DNA base sequences that code for protein
Structure of RNA
made up of ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four organic bases (A, C, G, U)
single stranded
use of RNA - transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis
The genetic code
Made up of base triplets - each sequence of 3 bases codes for a specific amino acid
summary about the genetic code
Genetic code is degenerate - most amino acids are coded for by more than one triplet
genetic code is universal - all organisms use the same genetic code (same triplets code for the same amino acid) - this is evidence for common ancestory
genetic code is overlapping - each base is only part of one triplet
The genetic code diagram
genome
the complete set of genes in a cell
proteome
the full range of proteins that a cell is able to produce
chromosome genes
introns and exons
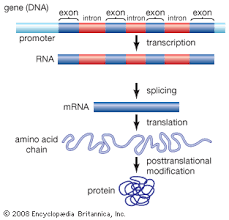
describe how a gene is a code for the production of a polypeptide - no transcription or translation
base/ nucleotide sequence in triplets determines order/ sequence of amino acids sequence/ primary structure (in polypeptide)
Describe how a phosphodiester bond is formed between two nucleotides within a DNA molecule
DNA polymerase catalyses the joining of the phosphate and deoxyribose together through condensation reaction to form a phosphodiester bond
give three ways in which the DNA in a chloroplast is different from DNA in the nucleus of a plant cell
in chloroplasts
DNA is shorter
fewer genes
DNA circular not linear
not associated with proteins unlike nuclear DNA
introns absent but present in nuclear DNA
not all mutations in the nucleotide sequence of a gene cause a change in the structure of a poly peptide
why? 2 reasons
Triplets code for the same amino acid because they are degenerate
Occurs in introns which are a non coding sequence
compare and contrast DNA in eukaryotic cells with the DNA in prokaryotic cells
comparisons
nucleotide structure is identical
nucleotides joined by phosphodeister bond
or deoxyribose joined to phosphate
DNA in mitochondria/ chloroplasts same/similar (structure) to DNA in prokaryotes
contrasts
eukaryotic DNA is longer
Eukaryotic DNA contain introns, prokaryotic DNA does not
Eukaryotic DNA is linear, prokaryotic is circular
Eukaryotic DNA is associated with proteins/histones, prokaryotic DNA is not.