5.2 Passive transport
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5 Biology 1230
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What can pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Gases
Hydrophobic/nonpolar molecules (large hydrocarbons)
Small polar molecules
What cannot pass through phospholipid bilayer?
Large polar molecules
Ions/electrically charged molecules
Passive transport…
requires no energy
Active transport…
Requires energy in the form of ATP or a coupled electrochemical gradient
What is diffusion?
Is a type of passive transport and it occurs when a substance moves from a high concentration to a low concentration until it’s equal across a space
How does concentration gradients affect diffusion rates?
Greater difference, faster diffusion. The closer it gets to equilibrium the slower the diffusion rate
How does the mass of molecules affect diffusion rates?
Smaller molecules diffuse more quickly while heavier molecules move more slowly
Temperature affects diffusion rate because?
Molecules move faster when temperatures are higher
How does surface area affect diffusion rates?
Increased surface area speeds up diffusion rates
How does pressure affect diffusion rates?
In some cells blood pressure forces solutions through membranes speeding up diffusion rates
What is facilitated transport or facilitated diffusion?
Diffuses ions and smaller polars by moving substances down their concentration gradients through transmembrane, integral membrane proteins.
What are channel proteins?
Is a type of facilitated transport protein
The top, bottom and inner core which are composed of hydrophilic amino acids.
Attracts ions or polar molecules
Some are open others are gated (opens when receiving a signal)
What are carrier proteins?
A type of facilitated transport protein
Are specific to a single substance, which they bind to and change shape and carry it to the other side
Allows movement in any direction as the concentration gradient changes
Osmosis…
Is the diffusion of water across a membrane. Water always moves from higher concentration to lower water concentration
What is tonicity?
Describes how an extracellular solution can change the volume of a cell by affecting osmosis. Usually correlates with the solutions osmolarity
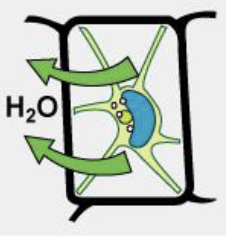
A hypertonic extracellular fluid…
Has higher osmolarity than the cytosol, water is leaving the cell
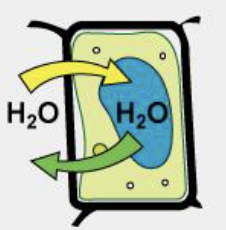
A isotonic extracellular fluid…
Has the same osmolarity as the cytosol, water moves equally in both directions (no net movement)
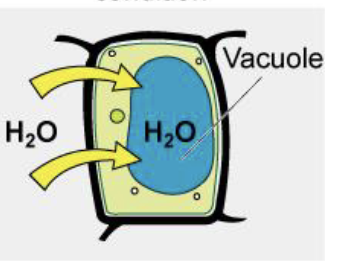
A hypotonic extracellular fluid…
Has lower osmolarity and lower solute concentration than the cytosol, water enters the cell
Plasmolysis…
Is when the plasma membrane detaches from the cell wall
What is tugor pressure?
Pressure exterted by the plasma membrane against the cell wall
Selectively permeable means…
Some molecules can pass through but not others
What gases can pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
N2, O2, and CO2
What are some small polar molecules that can pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
H2O, glycerol, and urea
What large polar molecules cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer?
Glucose, uncharged monosaccharides and disaccharides
What is osmolarity?
The solutions total solute concentration
What causes plasmolysis?
Hypertonic solutions
Animal cells functio best when extracellular fluids are…
Isotonic