Unit 3 Producers, Firms, and Supply in a Market Economy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
goals for businesses
to earn a profit, profit is necessary for growing and expanding business activities.
partnership
made up of the people, services, and technologies that enable brands to generate revenue through referral partnerships. Partners receive payments and incentives for tapping into their expertise, influence, and authority to drive partnership collaborations.
public company disadvantage
while going public can provide access to capital and increased credibility, it also entails the loss of control, increased regulatory burdens, and market volatility. Entrepreneurs considering this step should thoroughly assess both the advantages and disadvantages before making a final decision.
sole proprietor/concern
an enterprise owned exclusively by one natural person and in which there is no legal distinction between the owner and the business entity. The entrepreneur exercises his activity without having created a distinct legal person.
franchise - pros
typically offer advantages such as cost stability, training, and the support of a larger network.
franchise - cons
less control over decision making.
why is it bad to take out a loan to invest in a company
if your investment goes bad, you could lose all of your money and still need to pay off your loan.
Entrepreneurship
the process of starting and launching a business and includes the willingness and ability to take on that business risk.
LLC
a limited liability company (LLC) is a structure that separates companies and their owners. It prevents individuals from being liable for the company's financial losses, debts, and other liabilities.
general partnership/sole proprietorship characteristic
sole proprietorship is characterized by complete control, easy establishment, and unlimited personal liability. A general partnership involves shared decision-making and profits, easy formation, and unlimited personal liability.
Shareholders
a person or institution that has invested money in a corporation in exchange for a “share” of the ownership. That ownership is represented by common or preferred shares issued by the company and held (i.e., owned) by the shareholder.
natural monopoly
natural monopoly develops from reliance on unique raw materials, technology, or specialization.
geographic monopoly
held by De Beers had a profound impact on competition within the diamond industry often has dominance over other companies because of location.
pure monopoly
pure monopoly is the rarest form wherein the product (or service) being sold has no close substitutes.
government monopoly
government monopolies are often companies that provide a public good, such as the postal service or hospitals
Oligopoly
a market structure that consists of a small number of firms, who together have substantial influence over a certain industry or market. While the group holds a great deal of market power, no one company within the group has enough sway to undermine the others or steal market share.
Cartel
an agreement or relationship formed between two or more corporations trying to increase their profits. A typical cartel will influence prices by manipulating competition, agreeing to not reduce prices, or agreeing to reduce the production of goods or services.
role of gov't in Economics
provide for national defense, address environmental concerns, define and protect property rights, and attempt to make markets more competitive
perfect competition
an imaginary market condition where all consumers have access to the same products and information. In this type of economy, all firms must offer the lowest price possible or risk being undercut by their competitors.
supply (law)
an increase in the price of goods or services results in an increase in their supply. Supply is defined as the quantity of goods or services that suppliers are willing and able to provide to customers
supply elasticity
measures how much the quantity supplied of a good or service changes when there is a price change. The amount by which the quantity supplied increases or decreases with a price change depends on how elastic the supply of a good is.
supply curve slope
graphic representation of the relationship between product price and quantity of product that a seller is willing and able to supply.
be able to identify a graph (s1, s2, s3)
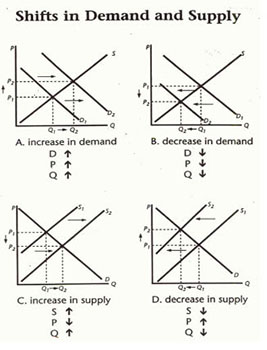
chg in quantity supplies
a movement along the supply curve, which is caused only by a change in price
supply curve shifts
causes an imbalance in the market that is corrected by changing prices and demand. An increase in the change in supply shifts the supply curve to the right, while a decrease in the change in supply shifts the supply curve left
govt subsidy
a transfer of resources from a government to a domestic entity without an equivalent contribution in return and can take many forms, including direct grants to domestic companies, tax incentives, or favorable terms for financing.
non-price determinant of supply
There are many non-price determinants of supply, including input prices, technology, future expectations, and the number of sellers. Unlike price, non-price determinants of supply do not cause a movement along the supply curve. TRIBE & ROTTEN
equilibrium price
the market price where the quantity of goods supplied is equal to the quantity of goods demanded. This is the point at which the demand and supply curves in the market intersect.
be able to describe how ologopolies can affect consumers and the role of the gov't
an example of a oligopoly would be the automotive industry, where cars are made by one brand (e.g. General Motors) and resold as another brand (e.g. Chevrolet, GMC, Buick, and Cadillac)