17- Space-time diagrams, light cones and world-lines
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
17.4 needs notes- no flashacrds on jt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Space-time diagram, light-cone and worldline
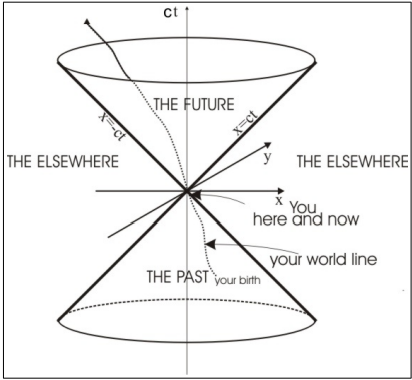
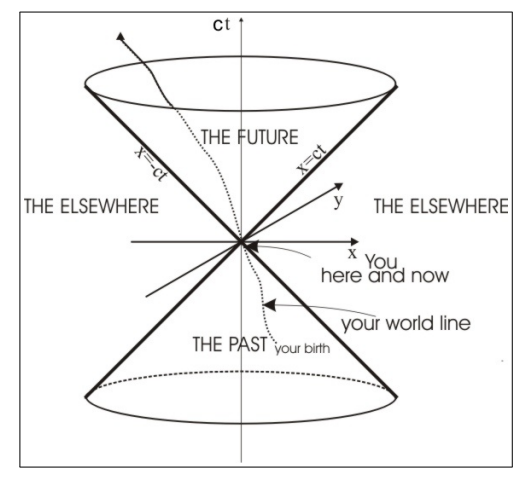
What does a space-time diagram plot, and what does the origin represent?
It plots ct (vertical axis) versus the spatial coordinates (here, x and y).
The origin represents the event "here and now."
What equation describes the light cone in 2D spatial coordinates?
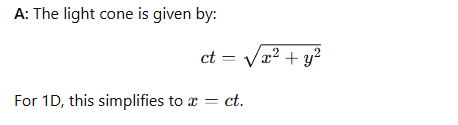
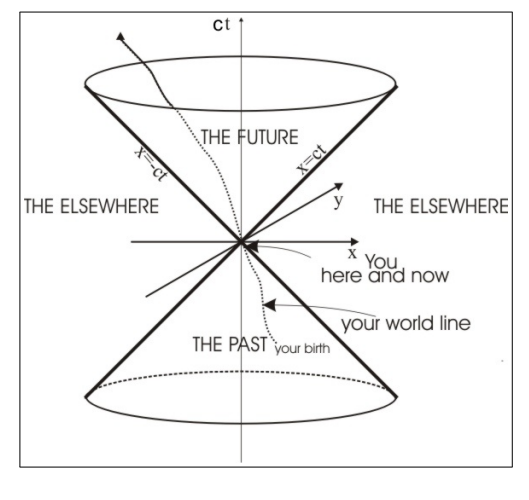
What does it mean for an event to lie inside the light cone?
The event lies in the future relative to the origin.
It has time-like separation from the origin.
A causal relationship is possible (the origin could influence the event).
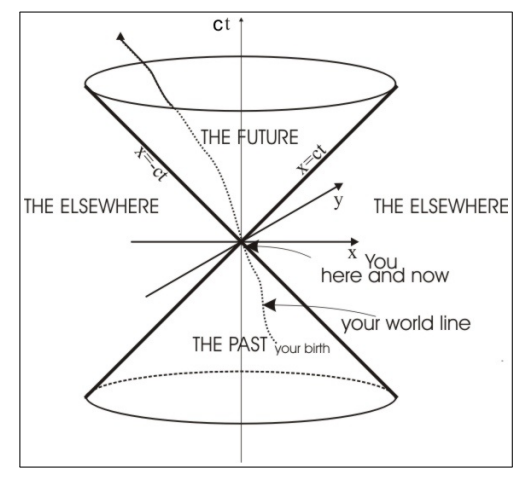
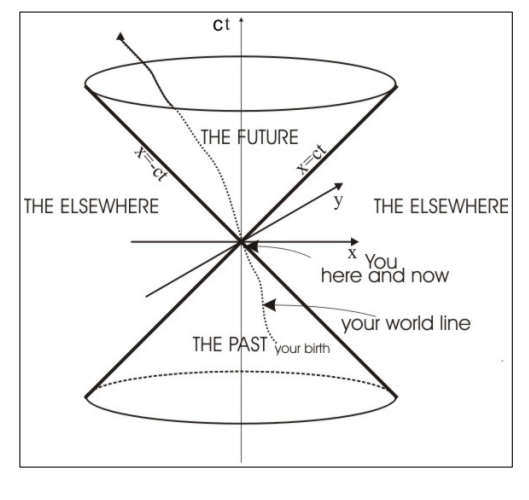
What does it mean for an event to lie on the boundary of the light cone?
The event has light-like separation from the origin.
It can be causally connected only by signals traveling at the speed of light.
It represents the limiting case of causal influence.
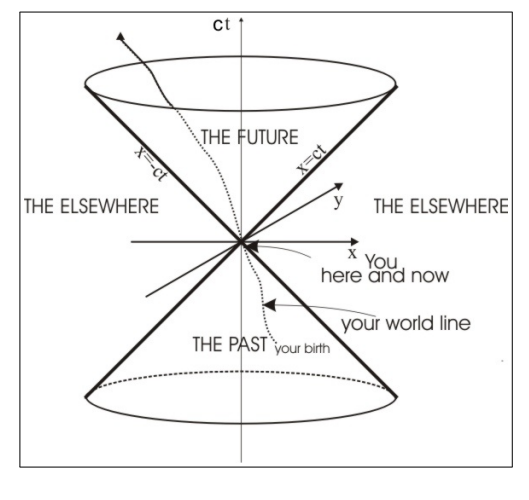
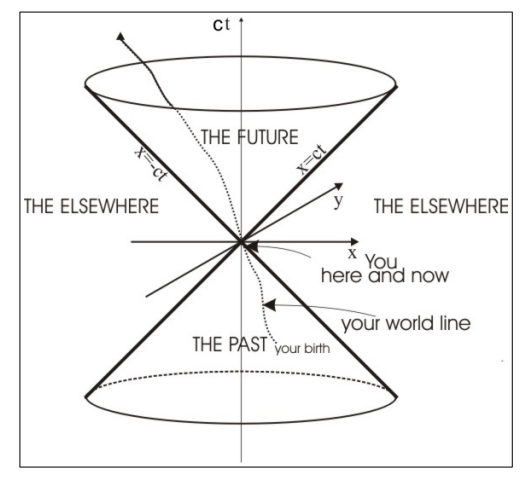
What is implied by an event lying outside the light cone?
The event has space-like separation from the origin.
No causal relationship is possible (no signal can travel faster than light to connect them).
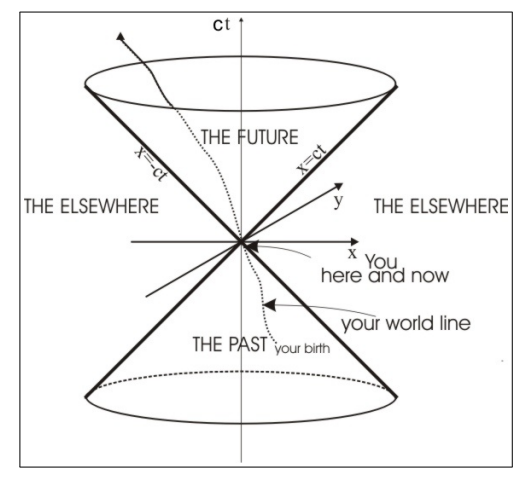
How is the past defined in a space-time diagram?
The past is defined by the inverted light cone
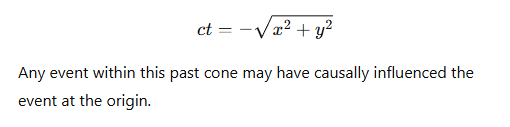
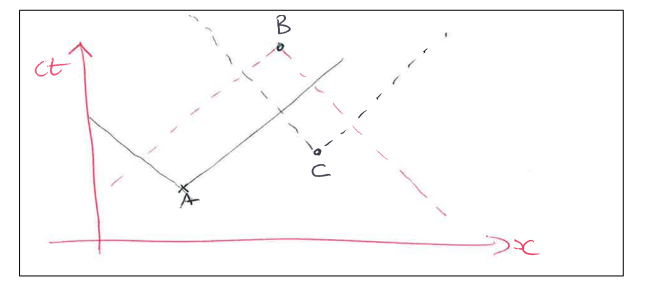
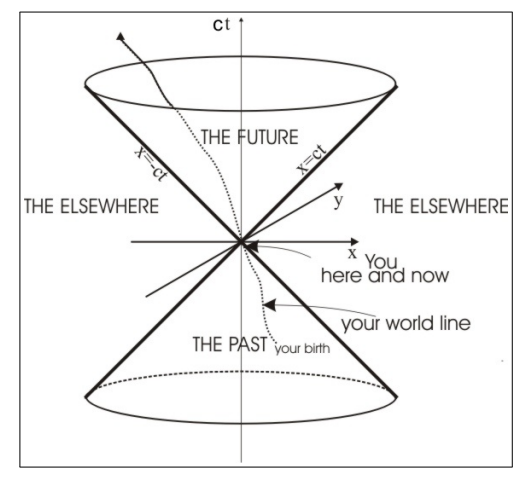
What can be said about events A, B, and C in a space-time diagram?
Event B: Lies within the future light cones of both A and C, so B could be causally related to either A or C.
Event C: Lies in the "elsewhere" region relative to A, meaning A and C have no possible causal connection.
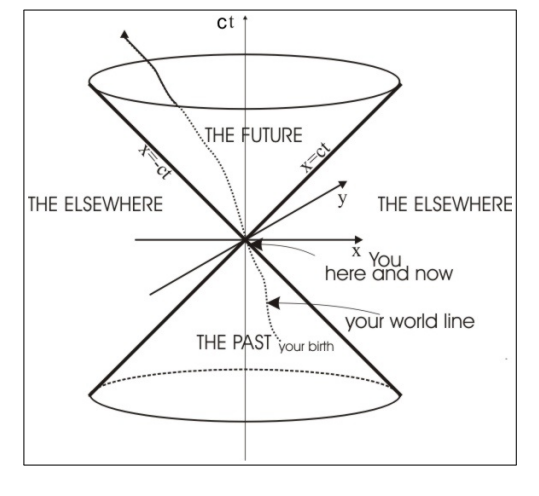
What is a world line in a space-time diagram?
Its the path that represents all the causally connected events of an object’s existence (from birth to future events) in space-time.
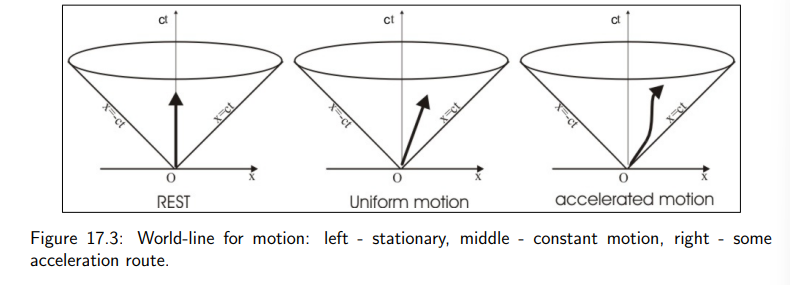
What does a vertical world line represent?
It indicates that the observer remains stationary in space (no change in x and y), with only time progressing.
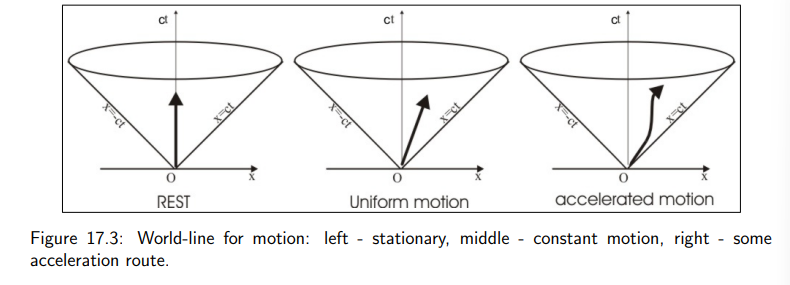
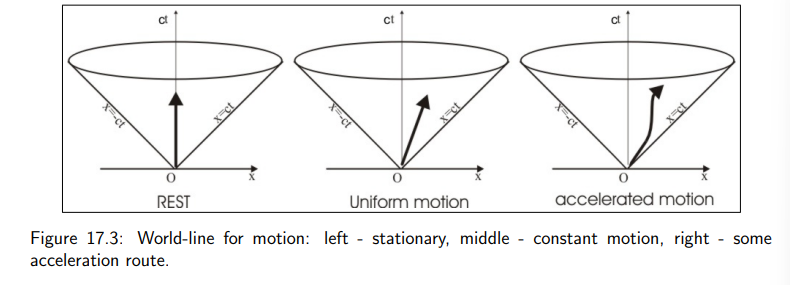
How is a world line for constant velocity depicted?
It is represented by a straight, tilted (canted) line.
For constant velocity v, the slope is given by:
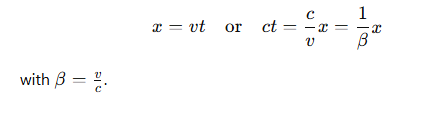
How is an accelerating world line depicted?
An accelerating world line is shown as a wavy or curved line, reflecting the change in velocity over time.
What is the invariant space-time separation equation in special relativity?
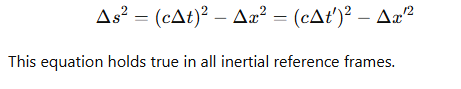
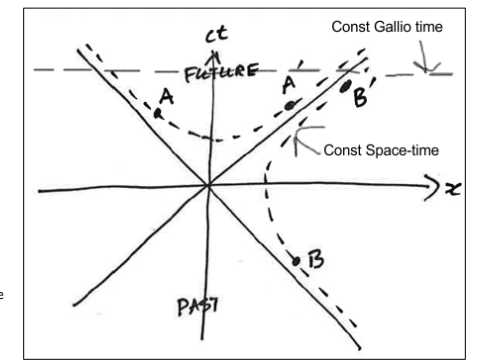
For an event A with time-like separation from the origin, how is the space-time interval expressed?
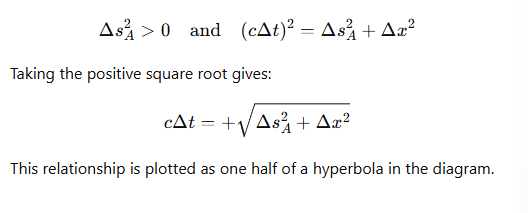
What does the hyperbola for a time-like separated event (like event A) indicate about causality?
There is no reference frame that can swap the time order of the origin and event A.
This guarantees that causality is preserved.
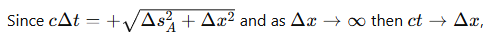
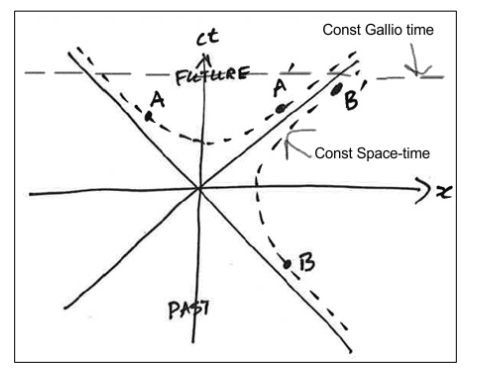
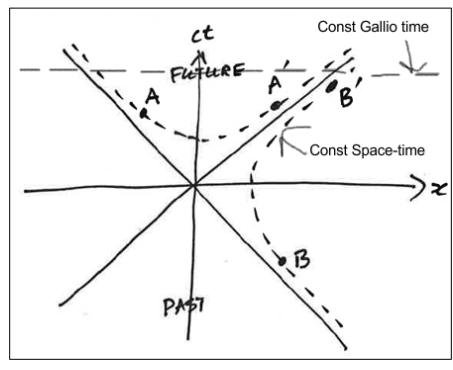
How is the space-time interval expressed for an event B with space-like separation?
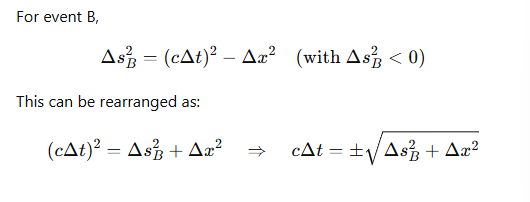
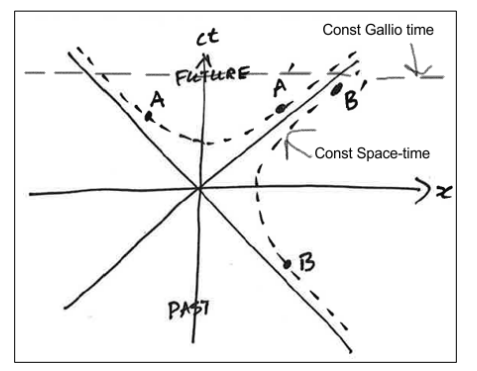
What is the significance of the ± in the expression for event B’s time coordinate?
It indicates that, depending on the reference frame, event B can be measured to occur before, simultaneously with, or after the origin event.
This ambiguity in time ordering is a characteristic of space-like separated events.