3.9: Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the structure of a carboxylic acid? (include general formula and functional group)
CnH2n+1COOH
COOH
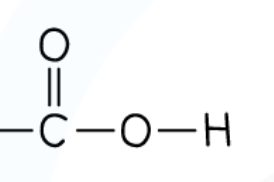
What is the structure of an ester?
COO

What are some properties of carboxylic acids?
Carboxylic acids with fewer than six carbon atoms per molecule are water-soluble as water molecules can form a H bond with the functional group
Carboxylic acids are weak acids but will still free CO2 from carbonates
How are esters produced?
Condensation reaction between an alcohol and carboxylic acid
Presence of a concentrated strong acid catalyst
What are the uses of esters?
Solvents
Plasticisers
Perfumes
Food flavourings
What is the structure and IUPAC name for glycerol?
propane-1,2,3-triol

What are the naturally occuring esters of glycerol used for?
Vegetable oils
Animal fats
What is the result of hydrolysing an ester in acidic conditions?
Reforms carboxylic acid and ester
Reversible reaction
What is the result of hydrolysing an ester in alkaline conditions?
Heated under reflux with dilute alkali
Forms carboxylate salt and alcohol
Sodium carboxylate requires further acidification to turn into a carboxylic acid
Irreversible reaction
How is soap produced and what is the name of the process?
Hydrolysis of vegetable oils and animal fats in alkaline conditions with aqueous NaOH
Saponification
What is the structure of soap
Carboxylate salts of long-chain carboxylic acids, known as fatty acids
What is biodiesel made from and how is it produced?
Transerification
Vegetable oils reacted with methanol in the presence of a catalyst (NaOH)
What is the structure of an acid anhydride?
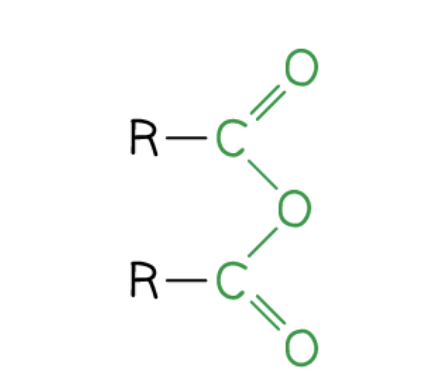
What is the structure of an acyl chloride?

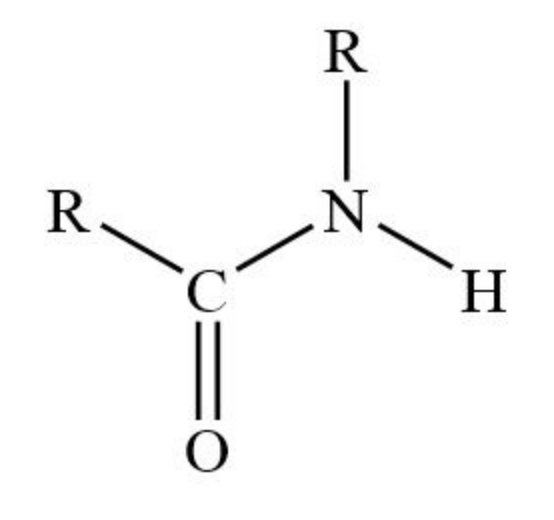
What is the structure of an amide?
What is the name of the mechanism of water, alcohols/ammonia/primary amines with acyl chlorides/acid anhydrides?
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
Why is ethanoic anhydride used over ethanoyl chloride in the manufacture of the drug aspirin?
Cheaper to produce
Less reactive so reactions can be more easily controlled
The by-product for acid anhydrides is the less corrosive carboxylic acid compared to hydrogen chloride for acyl chlorides