Software Tools
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
What is $@ in a Makefile?
A macro that refers to the target
2
New cards
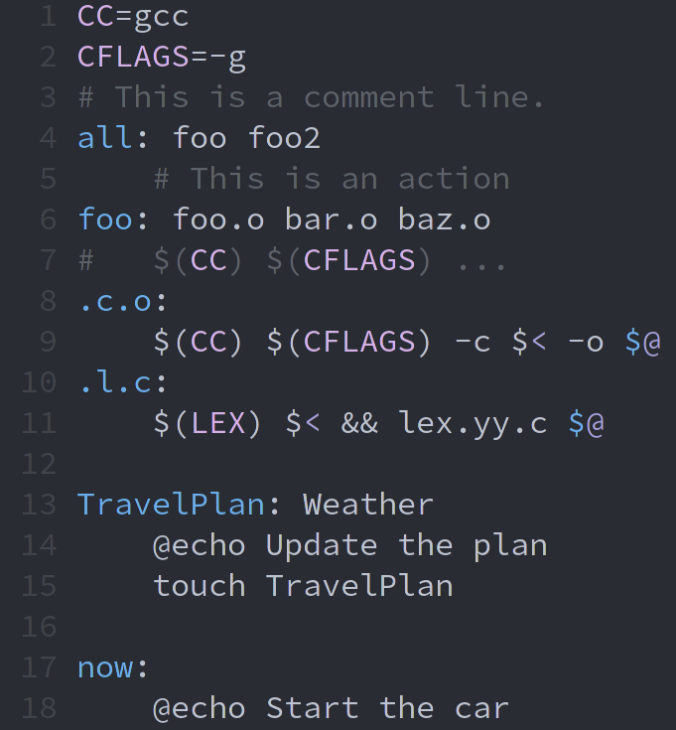
What does ".c.o:" on line number 8 mean in the context of a Makefile?
A generic dependency: all \*.o files depend on \*.c files
3
New cards
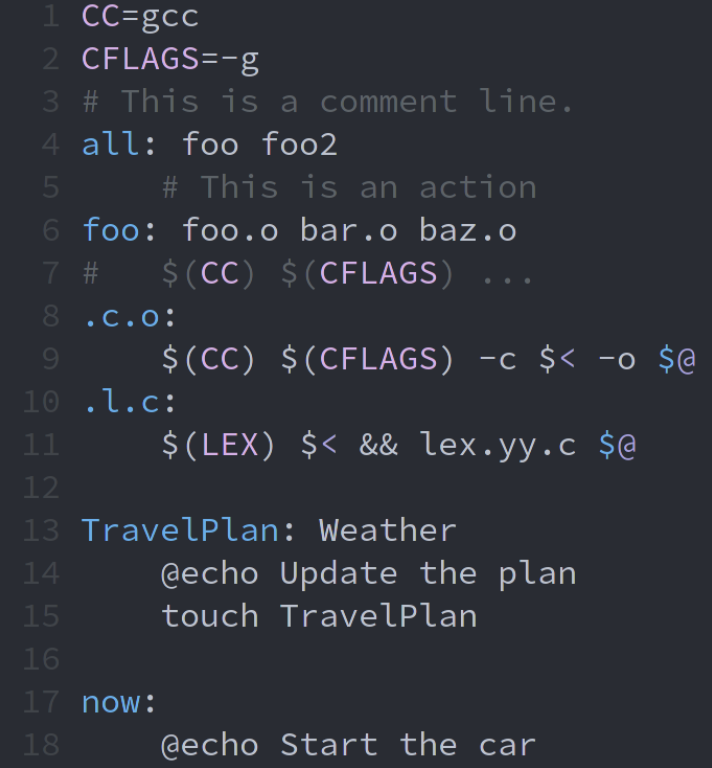
What does "now" depend on?
Nothing. The action is invoked if file "now" does not exist.
4
New cards
What does $(CC) mean in a Makefile?
It's a macro that can be defined as any string. Usually it contains the command to invoke the C/C++ compiler
5
New cards
How to create an empty file named README.md
touch README.md
6
New cards
What does "-" in "-rm \*.o" mean in a Makefile?
Ignore return value and always continue with the next action
7
New cards
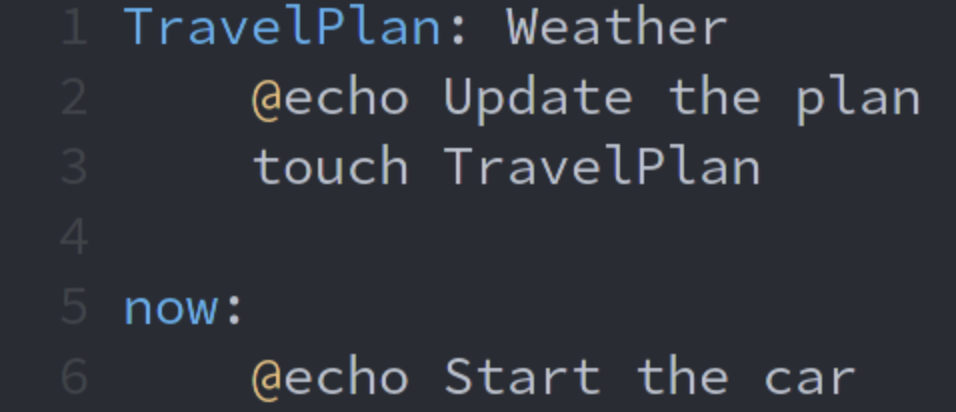
Under which circumstance will make not run the "touch" command (on line number 3) when the user runs the "make TravelPlan" command?
A file named TravelPlan exists, and it is newer than another file named Weather.
8
New cards
What does "-c" (without the quote) mean in "tar -czf out-file.tar.gz \*.cc" ?
It is to create a new tar file.
9
New cards
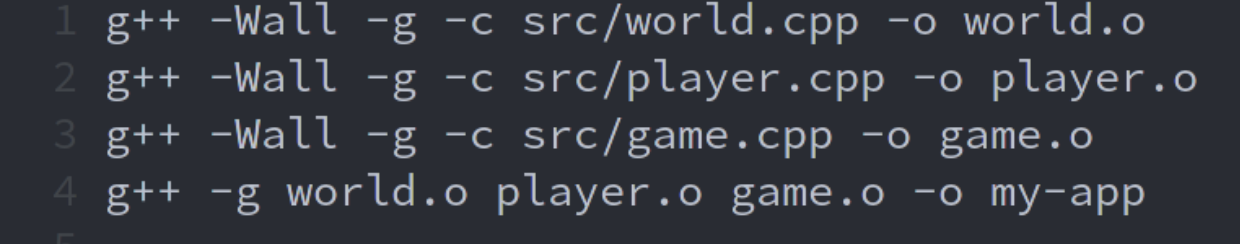
Which Makefile can generate the following commands, assuming the context it needs exists?
```javascript
CXXFLAGS=-Wall -g -c
LDFLAGS=-g
my-app: *.o
$(CXX) $(LDFLAGS) $^ -o my-app
world.o: src/world.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/world.cpp -o $@
player.o: src/player.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/player.cpp -o $@
game.o: src/game.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/game.cpp -o $@
```
CXXFLAGS=-Wall -g -c
LDFLAGS=-g
my-app: *.o
$(CXX) $(LDFLAGS) $^ -o my-app
world.o: src/world.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/world.cpp -o $@
player.o: src/player.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/player.cpp -o $@
game.o: src/game.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) src/game.cpp -o $@
```
10
New cards
In the previous question, a dependency rule "my-app: \*.o" was used. What is the potential issue of using this rule?
If file world.o does not already exist in the current folder, src/world.cpp won't be compiled.
11
New cards
For the following Makefile:
all: dummy
@echo “$@ depends on dummy”
\
dummy:
@touch $@
\
If someone were to run "make", what would the output be:
all: dummy
@echo “$@ depends on dummy”
\
dummy:
@touch $@
\
If someone were to run "make", what would the output be:
all depends on dummy
12
New cards
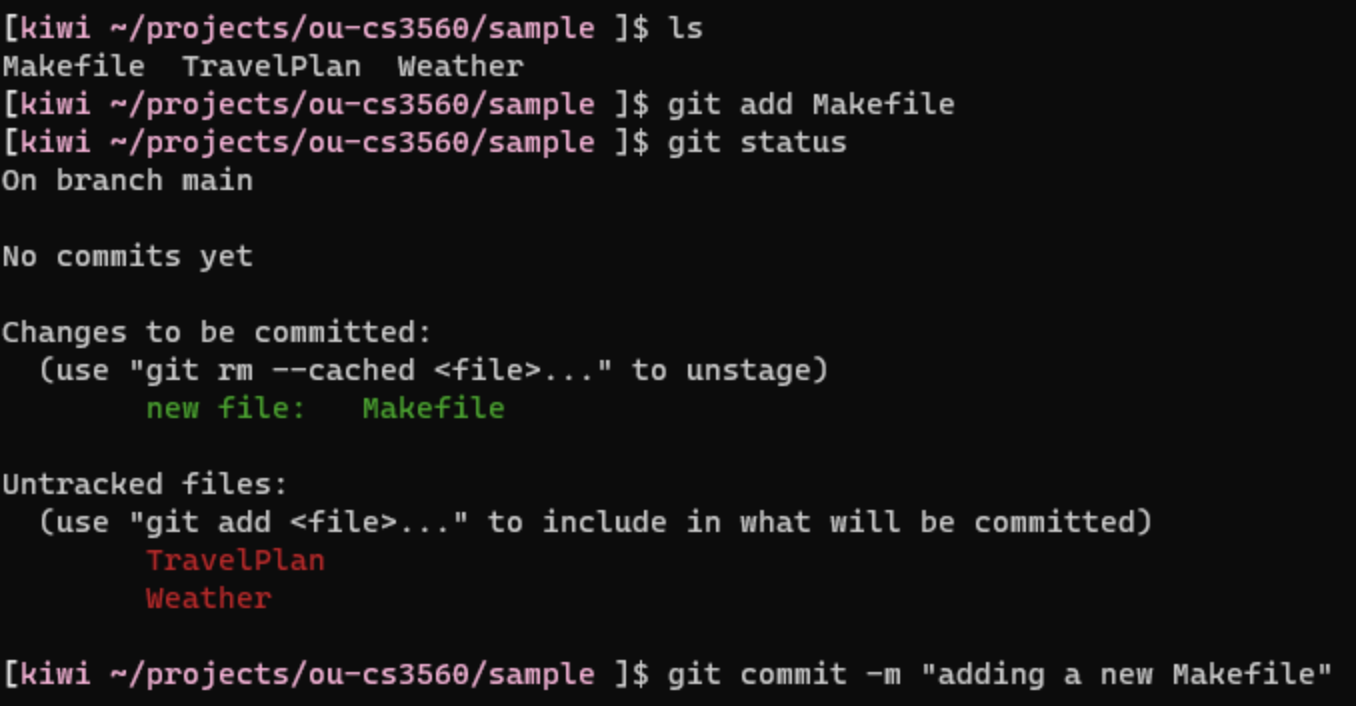
```javascript
a) What will happen after the git commit command on the last line is executed?
b) Suppose before these commands, both computer A and computer B are synced with a remote git repository? What if someone does “git pull” on computer B after these commands. What will happen on B?
```
\
a) What will happen after the git commit command on the last line is executed?
b) Suppose before these commands, both computer A and computer B are synced with a remote git repository? What if someone does “git pull” on computer B after these commands. What will happen on B?
```
\
(a) After the "git commit" command is executred on the last line, the local repository on Computer A will have the changes of the "new file: makefile" on only the local repository. \n \n (b) If Computer B does a "git pull" after these commands, nothing different will occur. Since Computer A did not push the changes on the local repository to the remote git repository, the commits that Computer A did would not show up on the remote repository. Therefore, Computer B will not have the changes that Computer A committed if Computer B did a "git pull".
13
New cards
```javascript
MacBookPro17-2:cs3560.test changliu$ ls -l hw2
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 changliu staff 68 Sep 25 08:11 name1-hw2
drwxr-xr-x 4 changliu staff 136 Sep 25 09:31 name2-hw2
MacBookPro17-2:cs3560.test changliu$ ls -l hw2.MakeAndTest/
-rw-r--r-- 1 changliu staff 82 Sep 24 17:00 hw2.MakeAndTest/name1-hw2-output.txt
```
Which git commands should one run to remove the entire “hw2” directory from the repository and push the results to the remote repository. Include commands to first make sure your local repo is in sync with the remote one and your working directory is clean.
MacBookPro17-2:cs3560.test changliu$ ls -l hw2
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 2 changliu staff 68 Sep 25 08:11 name1-hw2
drwxr-xr-x 4 changliu staff 136 Sep 25 09:31 name2-hw2
MacBookPro17-2:cs3560.test changliu$ ls -l hw2.MakeAndTest/
-rw-r--r-- 1 changliu staff 82 Sep 24 17:00 hw2.MakeAndTest/name1-hw2-output.txt
```
Which git commands should one run to remove the entire “hw2” directory from the repository and push the results to the remote repository. Include commands to first make sure your local repo is in sync with the remote one and your working directory is clean.
git pull \n git status \n git rm -r hw2 \n git commit \n git push
14
New cards
How are git objects within a git repository stored and located so that they are content-addressable, in other words, they can be located by using the content of the files as the index?
A 40-digit SHA1 hash code was generated and stored as the index to each object.
15
New cards
Git is centralized and all repository information is stored on one central server.
False
16
New cards
Which git command does exactly the opposite of the "git push" command and nothing more?
git fetch
17
New cards
What are the four different types of GIT objects?
Tags (annotated) \n Commits \n Trees \n Blobs.
18
New cards
What are the main similarities and differences between Subversion and Git? Use “svn”, “git”, or "both" to fill in the following space. What you filled in should match the description on the same line. \n \n Centralized Source Code Management System **[A]** \n \n Distributed Source Code Management System **[B]** \n \n File-based (keeps track of files) **[C]** \n \n Snapshot-based (keeps track of contents) **[D]** \n \n Provides version control for source code **[E]** \n \n Keeps the complete revision history on every developer’s computer **[F]**
A: svn
B: git
C: svn
D: git
E: both
F: git
B: git
C: svn
D: git
E: both
F: git
19
New cards
What is the GIT command to update the local repository based on contents from a remote repository? There are two different situations here. (Tip: consider whether you wish to update the files in the working tree after the local repository is brought up to date.) Address both situations and describe which command addressed which situation.
The two different situations are: \n "git pull" - This command is used if you wish to update the files in the working tree after the local repository is brought up-to-date. This command is used most often in comparison to the other command. \n "git fetch" - This command is used if you only wish to bring the local repository up-to-date. A common reason to use this command is to fix issues between branches.
20
New cards
Which information is stored in a GIT tree object?
\n type, size, and content of the git object. In the case of a GIT tree object, the content is index of other tree objects or blob objects, which essentially represent the content of that folder.
21
New cards
What is an operation that differentiates GitHub Workflow from GitFlow Workflow?
Creating a pull request
22
New cards
Which patterns are ignored by Doxygen?
$<
23
New cards
For which program units can Doxygen be used to add documentation?
Files , classes, and functions
24
New cards
Which documentation formats are supported by Doxygen? List at least four.
HTML \n LaTeX \n Man pages \n RTF \n XML \n DocBook \n Compiled HTML Help (a.k.a. Windows 98 help) \n Qt Compressed Help (.qch) \n Eclipse Help \n XCode DocSets \n PostScript \n PDF
25
New cards
Doxygen and JavaDoc's central design principle is to:
Keep code and documentation source in the same file, ideally on the same page to facilitate up-to-date documentation.
26
New cards
List at least four Doxygen commands such as *@file*, excluding *@file*.
@brief, @name @param @date
27
New cards
List at least three static analysis tools other than the original lint.
\n flint, splint, Javadoc, cpplint, clang, coverity scan, flint++, cppcheck
28
New cards
Which of the following errors can be detected by a static analyzer but not a **simple** compiler of a strongly typed programming language? (A simple compiler aims to only compile the code and generate the executable. It does not do any further checking beyond what's necessary for exe generation.) Check all that apply.
use of uninitialized variables
29
New cards
Perform static analysis manually on the following code and identify potential errors in it by checking it with your mind. If there are multiple errors, list all of them. DO NOT actually run a static analysis tools such as cppcheck since this is a closed-book quiz.
```javascript
int main()
{
char a[100];
for (int i = 0; i
```javascript
int main()
{
char a[100];
for (int i = 0; i
i
30
New cards
```javascript
BinaryTreeNode *BinarySearchTree::create_node(int value) {
BinaryTreeNode *node;
node->value = value;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
return node;
}
```
Answer the following questions
\- What are the problems?
\- Will a static analysis tool able to detect the issue?
BinaryTreeNode *BinarySearchTree::create_node(int value) {
BinaryTreeNode *node;
node->value = value;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
return node;
}
```
Answer the following questions
\- What are the problems?
\- Will a static analysis tool able to detect the issue?
Uninitialized variable
NULL pointer dereferencing
NULL pointer dereferencing
31
New cards
```javascript
/**
* Return the name of the playlist with the given id.
* @BLANK[in] id The id of the playlist.
* @return The name of the playlist.
*/
string get_playlist_name(int id);
```
Which of the following is suitable to replace the term \`BLANK\`?
/**
* Return the name of the playlist with the given id.
* @BLANK[in] id The id of the playlist.
* @return The name of the playlist.
*/
string get_playlist_name(int id);
```
Which of the following is suitable to replace the term \`BLANK\`?
param
32
New cards
What is the difference between REQUIRE() and CHECK() in the Catch2 Test Framework?
REQUIRE aborts the test if it fails. CHECK continues even if the assertion fails.
33
New cards
When one uses the Catch2 test framework, which main() function could one use: (Check all that apply.)
\-The main() function that came with Catch2 test framework.
-A new main() function with “Catch::Session().run(argc, argv)” call in it.
-A new main() function with “Catch::Session().run(argc, argv)” call in it.
34
New cards
Describe the differences between cppcheck and valgrind.
Cppcheck does not run your code and does not find errors such as memory leaks, but is able to find obvious issues that will prevent your program from compiling or cause bugs.
Valgrid analyzes the execution of the program and is able to find more hidden bugs such as memory leaks.
Valgrid analyzes the execution of the program and is able to find more hidden bugs such as memory leaks.
35
New cards
Describe what's common between Catch2 and valgrind.
Catch2 and Valgrind are similar in a few manners. Although Catch2 is a Unit Testing tool and Valgrind is a dynamic analysis tool, they both are dynamic due to both tools requiring execution. Not only do they require execution, but they both also need test inputs in order to properly function.
36
New cards
Valgrind analyzes program directly and do not require any test inputs.
False
37
New cards
Valgrind checks program output and can detect differences between actual output and expected output.
False
38
New cards
Valgrind is a supervised program execution framework and therefore allows plug-ins to do things other than memory leak detection.
True
39
New cards
Valgrind requires the C/C++ program under analysis to be compiled with "-g" option so that the symbilic information is generated.
False
40
New cards
Valgrind supports programs written in any programming languages.
True
41
New cards
Identify all static analysis tools from the following list of tools:
cppcheck
splint
42
New cards
Identify all unit testing tools from the following list:
Catch2
Google Test Framework
jUnit
Google Test Framework
jUnit
43
New cards
Identify all dynamic analysis tools from the following list:
valgrind
44
New cards
What is the main purpose and advantage of parameterized testing?
Allow combinations of different values to be generated so that a large number of test cases for thorough coverage can be tested.
45
New cards
Which of the following parameterized testing are supported in tools such as Google Test Framework?
Type parameterized tests
Value parameterized tests
Value parameterized tests
46
New cards
Given the following function that find the maximum integer in a given vector of integers, which code snippet correctly implement the test case for this function.
```javascript
// file: maximum.cpp
#include
#include
#include "maximum.hpp"
int maximum(std::vector items) {
int result = items[0];
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < items.size(); i++) {
if (result < items[i]) {
result = items[i];
}
}
return result;
}
```
```javascript
// file: maximum.cpp
#include
#include
#include "maximum.hpp"
int maximum(std::vector
int result = items[0];
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < items.size(); i++) {
if (result < items[i]) {
result = items[i];
}
}
return result;
}
```
```javascript
#include
#include "maximum.hpp"
TEST_CASE("test case 4", "[quiz]") {
std::vector data {1, 8, 0, 4};
REQUIRE( maximum(data) == 8 );
}
```
#include
#include "maximum.hpp"
TEST_CASE("test case 4", "[quiz]") {
std::vector
REQUIRE( maximum(data) == 8 );
}
```
47
New cards
```javascript
#pragma once
#include
template
class stack {
private:
size_t stack_size;
std::vector values;
public:
stack(size_t size = 10) : stack_size(size) { values.reserve(stack_size); }
void increase_size_by(size_t);
void push(T);
T pop();
size_t size();
};
template
void stack::push(T value) {
if (values.size() + 1 > stack_size) {
throw std::length_error("running of of space on the stack");
}
values.push_back(value);
}
template
T stack::pop() {
if (values.size() == 0) {
throw std::length_error("stack is empty");
}
T value = values.back();
values.pop_back();
return value;
}
template
void stack::increase_size_by(size_t increase_by) {
stack_size += 10;
values.reserve(stack_size);
}
template
size_t stack::size() {
return values.size();
}
#include
#include "stack.hpp"
TEST_CASE ( "test case", "[quiz]" ) {
stack s;
// 1. Prepare stack object.
//
// To be filled in. Select option that correctly prepare the object
// for the following action and test
// 2. Action & Test
REQUIRE_THROWS_WITH( s.push(5) , Catch::Contains( "running of of space" ));
}
```
#pragma once
#include
template
class stack {
private:
size_t stack_size;
std::vector
public:
stack(size_t size = 10) : stack_size(size) { values.reserve(stack_size); }
void increase_size_by(size_t);
void push(T);
T pop();
size_t size();
};
template
void stack
if (values.size() + 1 > stack_size) {
throw std::length_error("running of of space on the stack");
}
values.push_back(value);
}
template
T stack
if (values.size() == 0) {
throw std::length_error("stack is empty");
}
T value = values.back();
values.pop_back();
return value;
}
template
void stack
stack_size += 10;
values.reserve(stack_size);
}
template
size_t stack
return values.size();
}
#include
#include "stack.hpp"
TEST_CASE ( "test case", "[quiz]" ) {
stack
// 1. Prepare stack object.
//
// To be filled in. Select option that correctly prepare the object
// for the following action and test
// 2. Action & Test
REQUIRE_THROWS_WITH( s.push(5) , Catch::Contains( "running of of space" ));
}
```
```javascript
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
```
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
```