LIPIDS 2
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What do plants use to store energy
starch
what is starch
a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose molecules joined by glycosidic bonds-polysaccharide-most common found in diet and found in staple foods such as potatoes, wheat, corn, rice
what do animals use to store energy
•glycogen and TAGs which store energy in the form of covalent chemical bonds-Cells synthesise for later release of energy
what is glycogen
•Glycogen is a multibranched polysaccharide of glucose-main storage form of glucose-second main energy storage molecule after fats held in adipose tissue
•Glycogen serves as an immediate energy source for muscle cells
what happens to excess glucose in the body
it is stored as TAG after being converted to fat
how is glucose used when energy demands are high
It is broken down and its carbon skeletons are fed into the TCA cycle for energy production.
what is acetyl coA and why is it important in metabolism
ACoA is a central molecule in metabolism that carries acetyl groups to the TCA cycle for oxidation and energy production.
How does ACoA deliver carbon atoms to the TCA cycle?
It conveys carbon atoms within the acetyl group for oxidation in the TCA cycle.
What makes Acetyl-CoA a high energy compound?
The thioester bond between the acetyl group and the beta-mercaptoethylamine group; hydrolysis of this bond releases a large amount of energy.
How is Acetyl-CoA produced?
It is formed during the breakdown of carbohydrates via glycolysis and from fatty acid oxidation.
what is fatty acid synthesis
the creation of FAs from acetyl coA and malonyl coA through the action of enzymes called FA synthases which takes place in the cytoplasm of cells
why is FA synthesis important
important in lipogenesis and together with glycolysis functions to create fats from blood sugar
what are the FA then used for
storage or to make new phospholipids - new membranes
what are some common requirements for FA synthesis
glycerol-3-p - used for glycerolipid backbone
formation of activated acyl group
how are FA stored
as triacylglycerols, synthesized in the liver
how are triacylglycerols efficient
they have higher caloric yield
how are triacylglycerols economical
they are nonpolar so they dont bind to water - give 6 times more energy than glycogen
what are perilipins
Lipid droplet-associated proteins found on the surface of lipid droplets in adipocytes.
what is the primary function of perilipins
They protect stored triacylglycerols (TAGs) from being broken down by natural lipases.
How do perilipins regulate lipid metabolism?
They act as important regulators of lipid storage by controlling access of lipases to lipid droplets
What happens when perilipins are not functioning properly?
Lipid droplets may become more susceptible to premature breakdown by lipases, reducing fat storage.
beta oxidation
•the catabolic process where Fas are broken down in the mit to generate ACoA which enters the CAC and NADH and FADH2 which are used in the ETC
What effect does insulin have on fat metabolism?
Insulin promotes fat storage by encouraging the uptake and storage of fatty acids as TAGs.
What enzyme activates fatty acids for breakdown, and where does it act?
Acyl-CoA synthetase (also known as fatty acid thiokinase), located on the outer mitochondrial membrane.
what are fatty acids converted to in the liver
TAG and ketone bodies
how are TAG transported in the bloodstream
TAGs are released into the bloodstream bound to very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL).
Where are free fatty acids transported for energy production?
To energy-demanding tissues like the heart and muscles.
What fuels are delivered to the brain
Glucose and ketone bodies.
what does coenzyme A biosynthesis require
cysteine, pantothenate and ATP
panothenate
•In chemical form it is a thiol and can react with carboxylic acids to form thioesters thus functioning as an acyl group carrier
•It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria
describe the structure of carnitine
Quaternary ammonium compound
•Water soluble zwitterion-carrier during transfer of activated acyl and acetyl groups across mem
•Dipolar ion-neutral molecule with a positive and negative electrical charge-dipoles
How are 2-carbon units removed during beta-oxidation?
Cleavage of the fatty acyl-CoA releases acetyl-CoA (2-carbon segments).
What happens to acetyl-CoA after beta-oxidation?
It is oxidized to CO₂ in the TCA cycle.
Where do the electrons from NADH and FADH₂ go?
They are transferred to the electron transport chain during oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the importance of the "2-carbon loss" in beta-oxidation?
Every round of beta-oxidation shortens the fatty acid by 2 carbons, producing acetyl-CoA.
What enzyme dehydrogenates long-chain fatty acids at C2-C3?
Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
What happens after each round of beta-oxidation?
The fatty acid is shortened by two carbons, and another acetyl-CoA is produced.
who discovered the beta oxidation process
franz knoop
where does fatty acid biosynthesis take place
liver, kidney, adipose tissue
cite: cytoplasm
what does fatty acid synthesis require
acetyl coA
NADPH
ATP
Citric acid cycle and fatty acid synthesis
•Citrate is a derivative of citric acid and an intermediate in the krebs cycle
•Citrate can be transported out of he mito into the cytoplasm then broken down into acetyl Coa for fatty acid synthesis-regulated by the enzyme acetyl COA carboxylase
What is the mitochondrial citrate carrier
a citrate carrier located in MIM, nuclear encoded protein
what does the MCC do
connects carbohydrate metabolism to lipogenesis
what does the MCC generate
•Generates cytosolic citrate
–Carbon source for FA and cholesterol biosynthesis
–Modulates the activity of AcetylCoA carboxylase
–Supplies NADPH for lipogenesis
how are ACC1 and ACC2 regulated
•transcriptionally by multiple promoters which mediate ACC abundance in response to nutritional status-alternate splicing
effect of phosphorylation on acetyl coA carboxylase activity
Phosphorylation inhibits ACC, decreasing fatty acid synthesis.
how does the cell provide acetyl coA and NADPH
The cell coordinates a number of processes to ensure the synthesis of fatty acids
(1) The citric acid cycle provides the carbon backbone from acetyl CoA
(2) Recycling of citrate to pyruvate provides some of the reducing equivalents (NADPH)
(3) The pentose phosphate pathway provides the remaining NADPH molecules
(4) Glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation provides the energy source (ATP)
What happens when there is an imbalance between carb and fat metabolism
•Situation of fasting, (starvation)
•or diabetes
•or high lipid - low carbohydrate diet (Atkins)
–Fatty acid oxidation predominates over carbohydrate degradation – there is an excess of Acetyl CoA
–Oxaloacetate is needed for gluconeogenesis
–Shortage of oxaloacetate for citrate formation
•Acetyl CoA is converted to ketone bodies in liver mitochondria
what are ketone bodies
Ketone bodies are efficient nutrients produced in the liver
They are a water soluble transportable form of acetyl CoA that can easily enter mitochondria
They can be a major fuel in some tissues
However, they are potentially dangerous ( can lower blood pH causing acidosis)
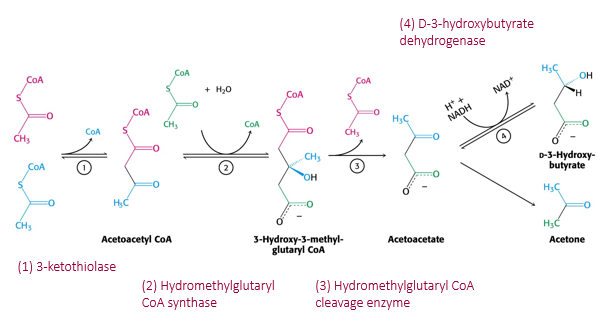
synthesis of ketone bodies
4. Acetyl-CoA builds up:
When there's too much acetyl-CoA (especially when carbs are low), the liver can't use it all in the Krebs cycle.
5. Formation of ketone bodies:
The liver combines acetyl-CoA units to make ketone bodies:
Acetoacetate (first ketone made)
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (most abundant in blood)
Acetone (small amount, exhaled in breath)
6. Release into blood:
Ketone bodies are released into the bloodstream and travel to other organs (like the brain and muscles) for energy
what happens during starvation
glucose - decrease
ketone body increase
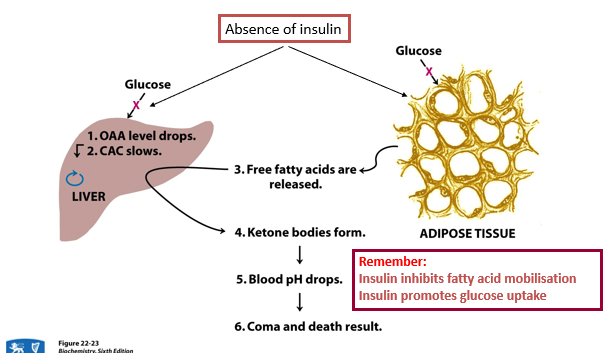
fatality of ketone bodies in diabetes
Ketones are made when the body burns fat for energy instead of using glucose.
Without insulin, cells can't take in glucose, fatty acids are released, and ketones form.
Ketone buildup lowers blood pH, leading to coma or death if untreated.
Insulin stops fat breakdown and helps glucose enter cells.
Severe ketoacidosis causes high blood sugar, dehydration, shock, exhaustion, and eventually coma.
Patients look flushed, breathe rapidly, and may become pale
fatality of ketone bodies simple