BIS104: MT1/MT2 Old Exam
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Phosphatidyl ethanolamine can diffuse from the cytoplasmic side of the membrane bilayer to the side facing the extracytoplasmic face.
False
If given the choice, you would prefer to use a confocal laser scanning fluorescence microscope (CLSM) for imaging instead of a conventional fluorescence microscope because:
None of the above
Which of the following statements is not true of GFP?
GFP cannot be used for live cell imaging
You isolate a gain-of-function mutation in the bacteria’s fatty acid saturate gene. You are now proposing to analyze the membranes from this mutant strain of bacteria. What do you expect to find?
A decrease in the number of carbon double bonds and a reduction in membrane fluidity
If you engineer a gene that encodes a protein with a nuclear localization sequence and an ER targeting signal sequence, where would you find this protein?
ER
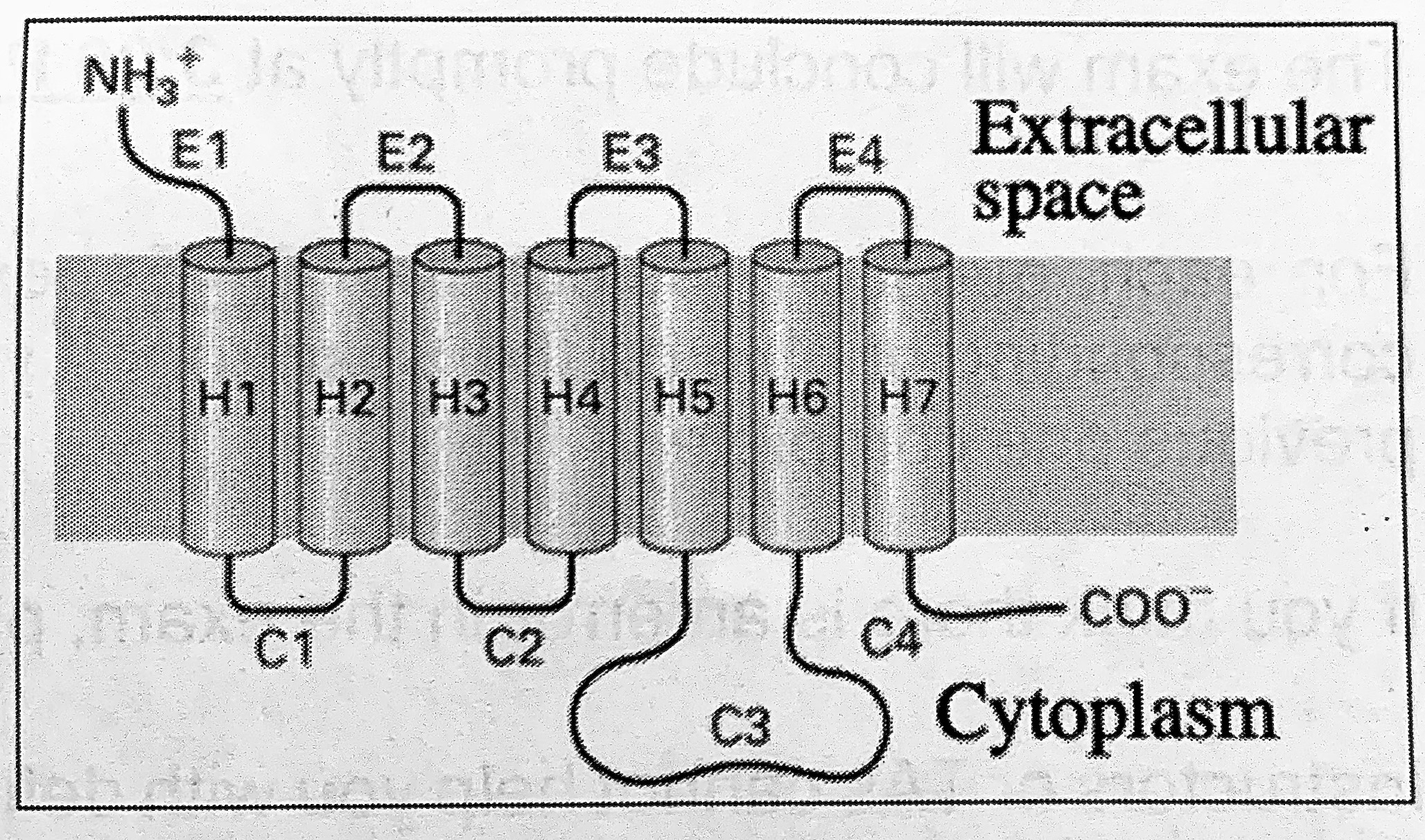
The topology of the beta-adrenergic receptor in the cell’s plasma membrane is depicted on the right. What would the topology of this protein be when it is synthesized in the ER?
TYPE IV-B membrane protein
You isolate a mutant that fails to secrete a test protein in yeast. To determine the stage of blocked secretion, you use antibiotics against your test protein in an immunofluorescence experiment. You observe the test protein accumulating in the endoplasmic reticulum and hypothesize that the mutation has blocked the _________.
Anterograde vesicle trafficking between the ER and Golgi
Protein folding is challenging, even under ideal conditions. Unfolded proteins are tagged with _____ and retained in the ER through interactions with _____.
glucose, calnexin
Using purified components, you have designed an in vitro experiment to reconstitute the interaction between SRP and SRP receptor. Despite adding GTP, you do not detect any interaction between the SRP receptor and SRP. As a clever cell biologist, you introduce fractioned cellular proteins to your reaction and find an activity that stimulates the interaction between the SRP receptor and SRP. You characterize the protein in greater detail and discover that it induces ____ and therefore acts as a ____.
The exchange of GDP for GTP; GEF
Which of the following events requires active transport to maintain an acidic pH in the stomach lumen?
Import of H+ into stomach lumen and export of K+ from stomach lumen by H+/K+ ATPase
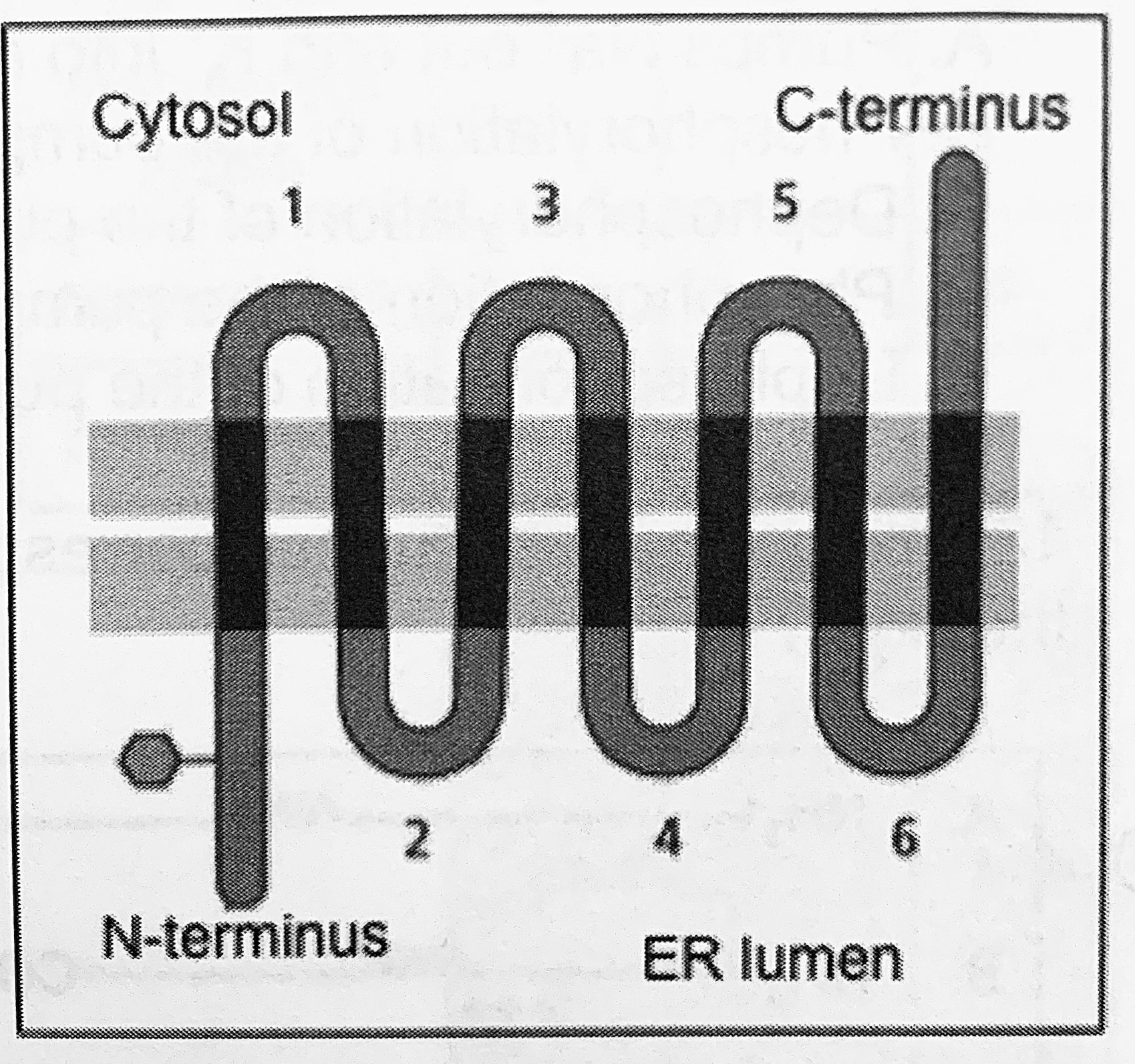
What do you predict would be the effect of converting the first hydrophobic transmembrane domain into a hydrophilic domain of the multiples membrane protein shown on the right?
N-terminal domain in the cytoplasm
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme involved in ammonia detoxification. In chickens, GS is targeted to the mitochondria, whereas in humans, it resides in the cytosol. By adding the chicken GS mitochondrial targeting sequence (C-mtS) to the N-terminus of human GS, the human GS protein is directed to the mitochondria. Interestingly, when C-mtS-GS is incubated with a drug that tightly binds to the active site of GS, the enyem remains in the cytosol. Why does the binding of the drug to GS interfere with mitochondria import?
The drug promotes the folding of DHFR
You isolate a mutant yeast that accumulates a significant excess of ER-derived vesicles. A mutation in which of the following proteins would lead to this phenotype?
The GAP protein in COPII complex
While targeting integral membrane proteins to the inner membrane of mitochondria from the cytoplasm, it is not essential to keep the protein in an unfolded state by the cytosolic HSP70.
False
Calcreticulin is an ER lumen chaperone. You add a “stop" transfer” signal of about 20 hydrophobic amino acids to the middle of the calreticulin protein sequence. Where would you predict the modified calreticulin protein to localize now?
The ER membrane/None of above
The Na+-K+ pump that we discussed in class
Dephosphorylation of the pump transports 2 K+ into the cytosol
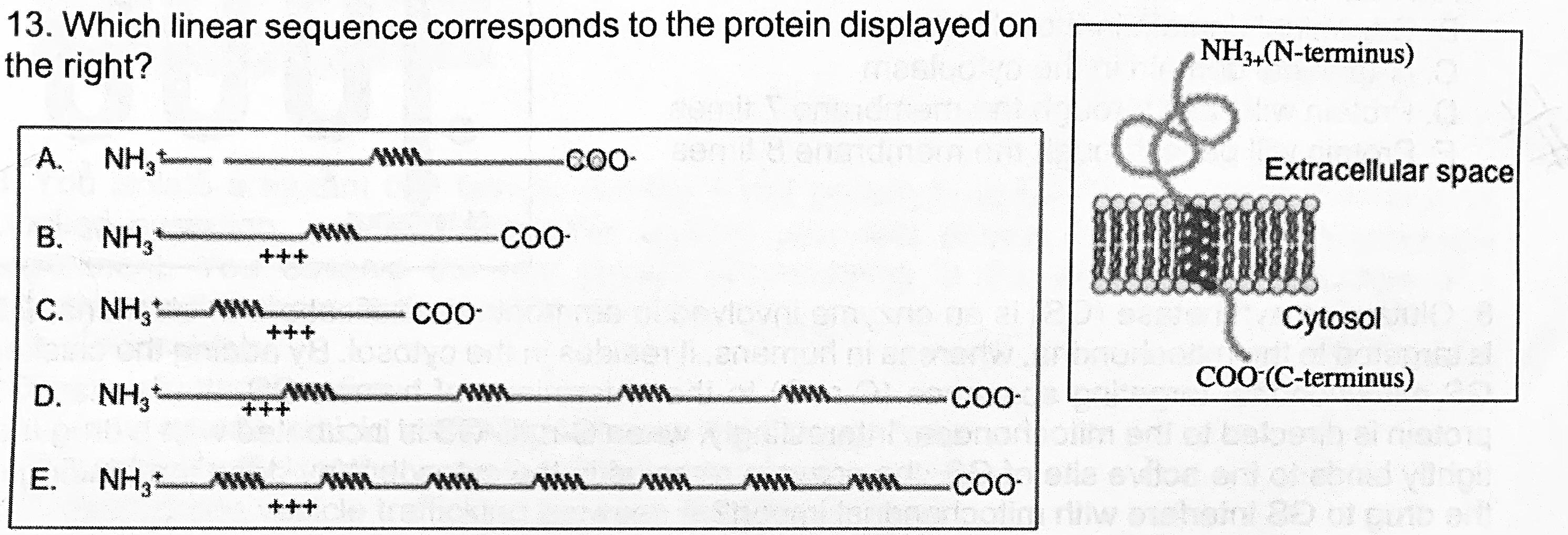
Which linear sequence corresponds to the protein displayed on the right?
a, c
You isolate a mutation in which Ran is trapped in a GTP-bound form. In this cell, you notice that RFP fused to a nuclear localization signal (RFP-NLS), which is typically directed to the nucleus, is now found in the cytoplasm. Why?
Importin is sequestered by Ran
You isolate a temperature-sensitive secretion-defective mutant strain in yeast that lacks ER-derived vesicles. A mutation disrupting which of the following proteins could lead to such a phenotype?
Sar1-GEF
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a secreted protein. If you remove the first twenty amino acids from IgG, where would you predict the majority of this mutant protein would localize?
The cytosol
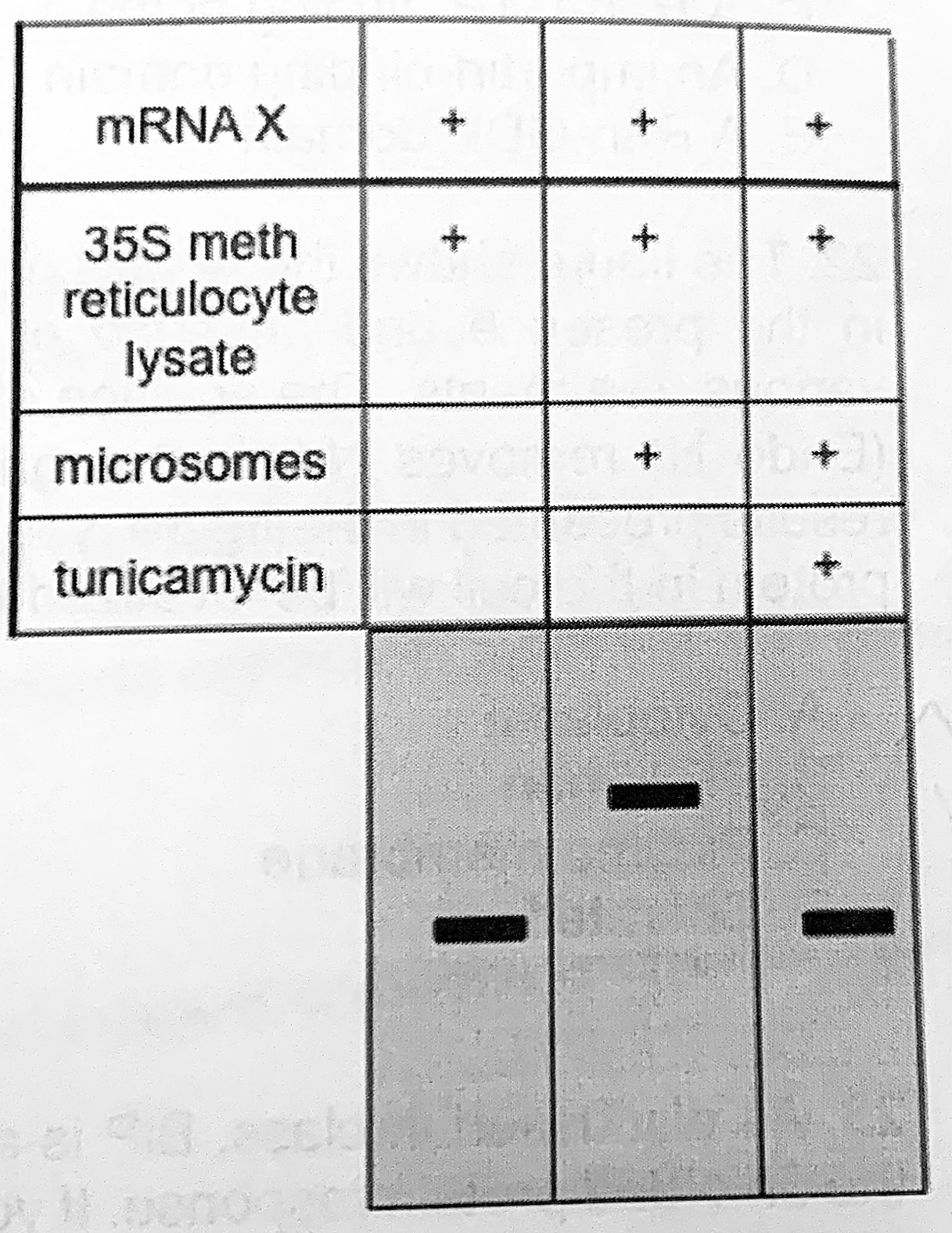
The mRNA X produced from the cDNA is translated in vitro in the presence of 35S methionine, treated as indicated on the right, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized by autoradiography.
Why are the proteins in lane 1 and lane 3 the same size?
The protein in lane 3 has an internal signal sequence
What is the phenotype of Sar1 mutant that stays in the GTP-bound state?
Secreted proteins accumulate in vesicles
You isolate a mutation that disrupts the activity of Ran GAP. In this cell, you notice the MYC transcription factor, which is normally localized to the nucleus, is found in the cytoplasm. Why?
Importin is stuck to Ran
What would the result be of a double mutant that is defective in both Sec12 and the cis-Golgi t-SNARE?
The ER would be enlarged
You are working together with a protein, Viperin, that is localized to the cytoplasm. In your experiment, you want to test whether forcing Viperin into the nucleus affects cell growth. What would you add to target Viperin to the nucleus?
An importin-binding domain
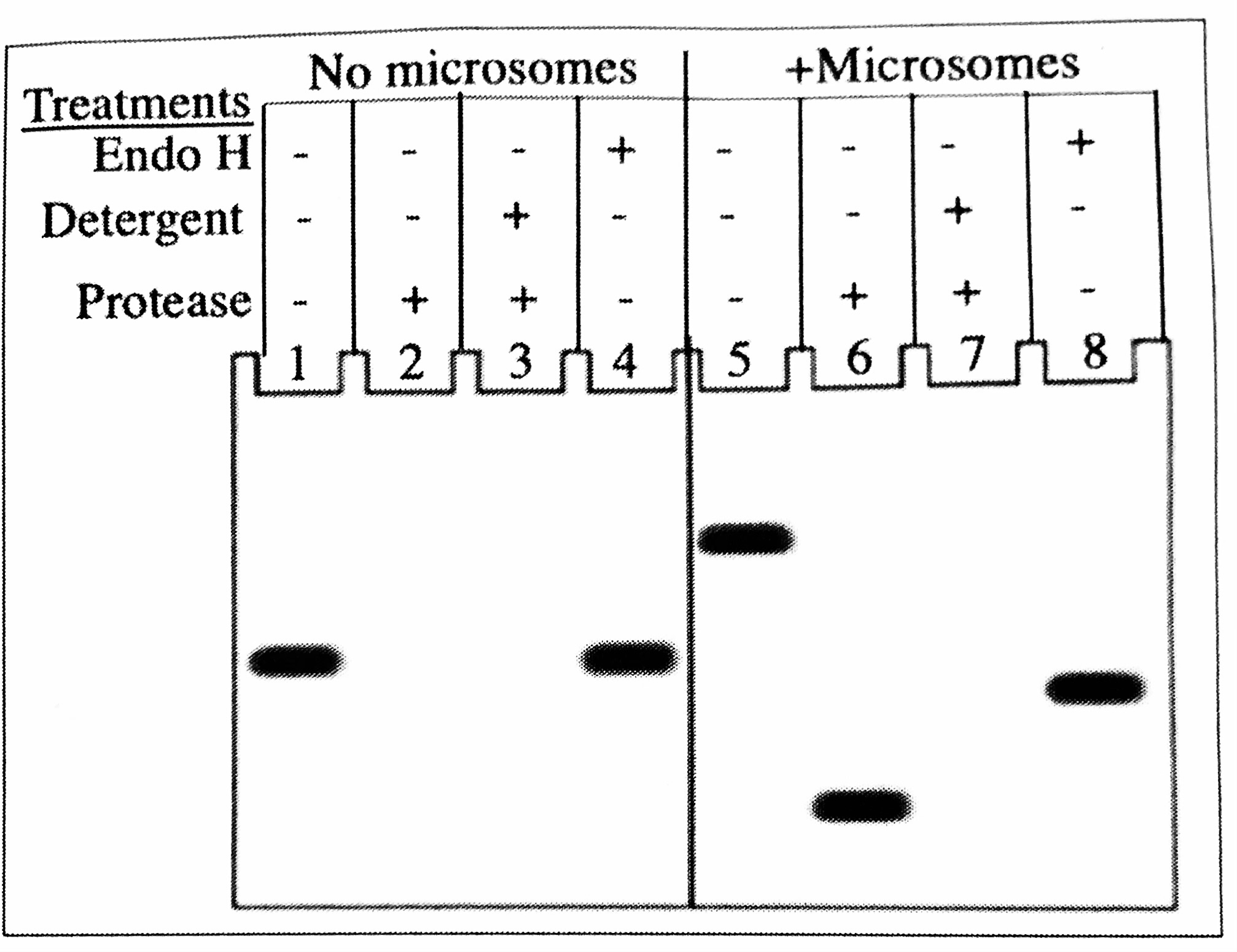
The figure shows the results of mRNA translation in the presence and absence of microsomes with various treatments. The addition of endoglycosidase (Endo H) removes N-linked sugars, Based on the results presented in the figure, you conclude that this protein in the cell would be localized to:
Plasma membrane
As discussed in class, BiP is a chaperone localized to the ER lumen that plays a vital role in the unfolded protein response. If you add a PKKKRKV nuclear localization sequence to the middle of the BiP protein, where do you expect the new protein to localize?
ER
What would the result of a double mutant that is defective in both Sec12 and COP1?
Secreted proteins would remain in the ER
Arf1 serves as the G protein for COP I vesicles, functioning similarly to Sar1 for COP II vesicles. Where do you anticipate finding the GAP for Arf1?
On COPI vesicles