Chap 12, 13, 14, 15
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
Fundamental Characteristics of Life
Cells, Replication, Information, Energy, Evolution
M Phase
Dividing phase of cell cycle
Interphase
Chromosomes are uncoiled and cells grow
Interphase
Cells spend the most time in this phase
S Phase
Chromosomes get duplicated/DNA is synthesized in this phase of interphase
Gap Phase
Cells grow in this phase of interphase
Chromosome
A single, long double helix of DNA
Hisotnes
The proteins that chromosomes are wrapped around
Chromatin
The DNA protein material that compresses DNA into a compact unit during division
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a specific RNA/protein
Cohesions
What attaches chromatids at their length
Centromere
Connects chromatids at the center once mitosis begins
Chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome
Replicated chromosomes
Consist of two copies of the same DNA double helix
Mitosis
The division of replicated chromosomes
Cytokinesis
The division of cytoplasm
46 Chromosomes
The number of chromosomes humans have
Spindle Apparatus
Moves apart replicated chromosomes and pull apart chromatids in late mitosis
Prophase
In what phase does the nucleolus disappear/melt away
Microtubules
What the spindle apparatus is made from
Microtubule Organizing Centers (MTOCs)
Defines the two poles and has polar microtubules that extend from each spindle pole
Centrosomes
MTOCs in animal cells each containing a pair of centrioles
Microtubules
Largest cytoskeletal elements that grow at plus ends
Prometaphase
Nuclear membrane disintegrates in this phase
Prometaphase
In this phase, microtubule fibers attach to chromosomes at kinetochores
Kinetochores
Protein structures that form on the centromere
Kinetochore Microtubules
Microtubules that attach to chromosomes
Prophase
In this phase, centrosomes migrate to cells opposing sides
Metaphase
Mitotic spindle is complete in this phase
Metaphase
Spindle moves chromosomes into linear formation on metaphase plate
Metaphase Plate
Where chromosomes line up during metaphase
Astral Microtubules
Hold spindle poles in place
Anaphase
In this phase, the centromere snaps and sister chromatids are separated
Anaphase
In this phase, the cell becomes elliptical as spindle fibers push at poles
Anaphase
Cohesions holding sister chromatids together split in this phase
Telophase
New nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes in this phase
Cytokinesis
This phase occurs immediately after mitosis and forms two daughter cells
Cell plate
Formed in plants by vesicles to help in cytokinesis
Cleavage Furrow
Formed by a ring of actin + myosin filaments that shrink and tighten
Binary Fission
The way bacteria divides
Kinase
Enzyme that attaches a phosphate group from ATP to a protein
Phosphotase
An enzyme that removes a phosphate group from a protein
Gametes
Reproductive cells that consist of sperm and eggs in animals
Fertilization
When gametes unite to form a new individual
Meiosis
Nuclear division that leads to halving of chromosome number
Gametes
Cells produced by meiosis that contain half of original number of chromosomes
Autosomes
Non-sex chromosomes
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes of the same type
Homologous Pairs
Contain the same genes in the same positions
Length, centromere position, staining pattern
What are the shared characteristics of homologous pairs?
Alleles
Can differ in homologs, different versions of a gene
Genetic Locus
Location of a particular gene on a chromosome, each has one allele on each homologue
Diploid (2n)
Having two homologs of each chromosome and two alleles of each gene
Haploid (n)
Having only one type of each chromosome and one alleles of each gene
Ploidy
Indicates the number of complete chromosome sets
Sister chromatids
Identical halves of a chromosomes that result from replication
Meiosis 1
Parent cell is diploid in this phase (2n) and contains a homologous pair of replicated chromosomes
Meiosis 2
Daughter cells are haploid in this phase (n) and contain just one homolog
Gametogenesis
The way in which daughter cells become eggs or sperm
Zygote
A diploid cell created through fertilization, each zygote receives a haploid chromosome set from mother and father
Early Prophase 1
In this phase, homolog pairs come together in pairing process called synapsis
Synapsis
The process of homolog pairs coming together
Bivalent/Tetrad
Homologous pairs joined by synapsis that consist of two homologs
Synaptonemal Complex
Proteins that hold a bivalent together
Late Prophase 1
Homologs separate in this phase but are attached at certain chiasmata
Chiasmata
The points at which homologs are attached during late prophase 1
Crossing over
Gives rise to kids that are genetically distinct from their parents during late prophase 1
Crossing over
Produces chromosomes with a combination of maternal and paternal alleles
Mitotic Phase
Includes mitosis and cytokinesis
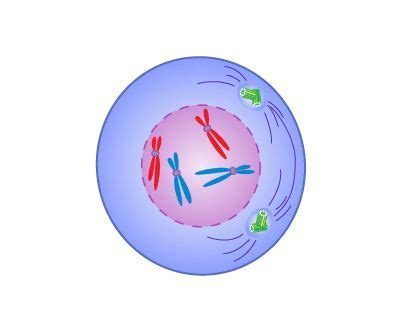
Prophase
What phase of mitosis is this?
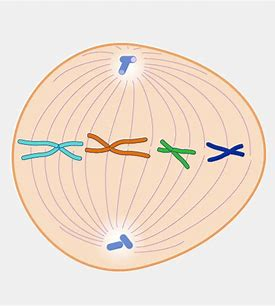
Metaphase
What phase of mitosis is this?
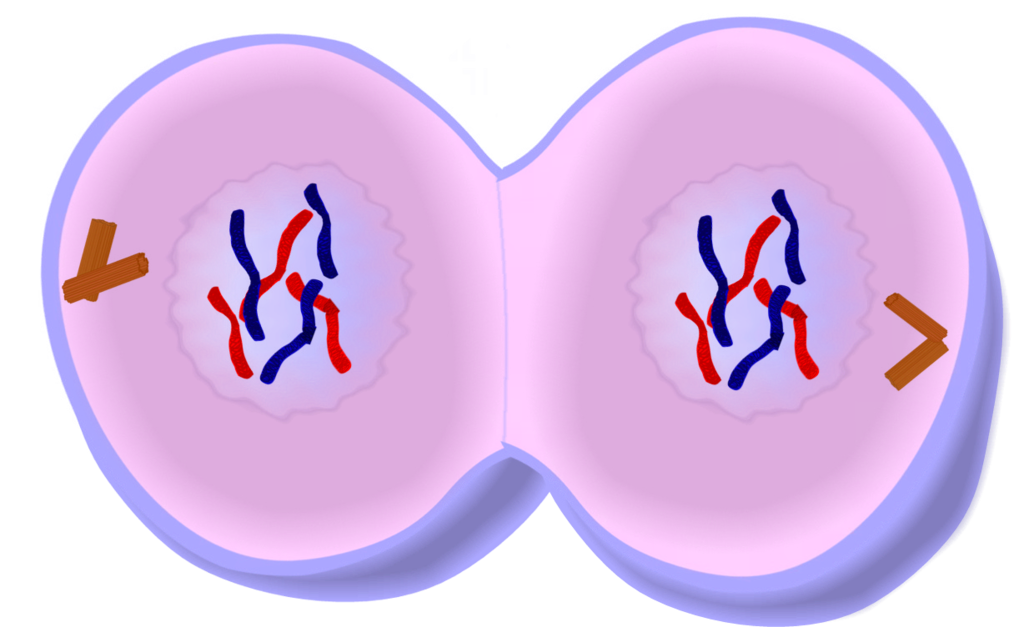
Telophase
What phase of mitosis is this?
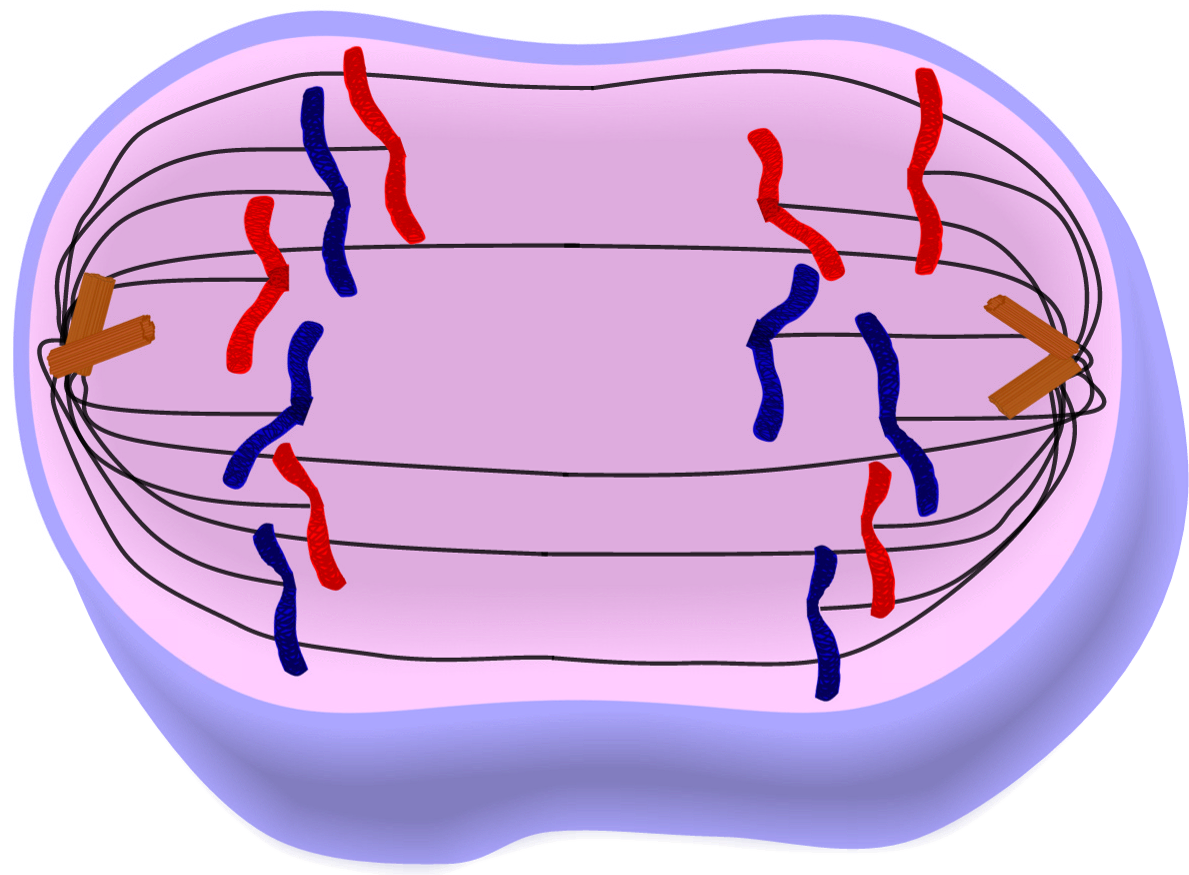
Anaphase
What phase of mitosis is this?
Natural Selection
Explains how evolution occurs
Variation of characteristics, adaptations
Rules for natural selection
Genetic Recombination
the creation of new alleles, promoted by crossing over
Independent Assortment
Random Separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
Chiasmata
The point at which crossing over occurs between homologous pairs, not sister chromatids
Random Fertilization
Random union of gametes that ensures offspring will be genetically different from parent
Outcrossing
Gametes from different individuals, as opposed to self-fertilization
Trisomy 21
Scientific name for down syndrome
Sister chromatids move to the same pole in anaphase
How can a mistake occur in meiosis?
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division, results in polyploidy
Polyploidy
When a normally diploid cell or organism acquires one or more additional sets of chromosomes, resulting in three or more times the haploid chromosome number
Oogenesis
Egg development in humans
Primary oocytes
Diploid precursors to eggs
Can be up to a 50 year wait for meiosis to reach completion for primary oocytes (50 years)
Why do more errors occur in females in meiosis?
Deleterious
A damaged gene
All offspring will inherit the gene
Why are deleterious genes bad for asexual reproduction?
Purifying selection
Natural selection against deleterious alleles
Chromosomal theory of inheritance
How genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next
Blending Inheritance
Dated belief that parental traits blend so that their offspring have intermediate traits (ex. white + red = pink)
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Dated belief that parental traits are modified through use and then passed on (ex. giraffe necks)
Garden pea
What Mendel used for his experiments
Polymorphic Traits
A trait that appears commonly in two or more different forms (ex. round vs wrinkly peas for the texture)
Cross Fertilization
Mendel’s process of removing male genitalia from a pea plant and moving pollen from another plant to it
Self-replication
How pea pod plants typically reproduce
Genes
Hereditary determinants for a trait
Alleles
The 2 versions of each gene that a human has
Phenotype
Observed characteristics of an organism