Biology Paper 1 - Edexcel Combined science GCSE
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Two types of cells:
prokaryotic and eukaryotic
What is a Prokaryotic cell?
smaller simpler cells with no nucleus. DNA is kept in plasmid form or chromosomal form, floating free in the cytoplasm
What is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
bacterial cell
What is a eukaryotic cell?
any plant and animal cells
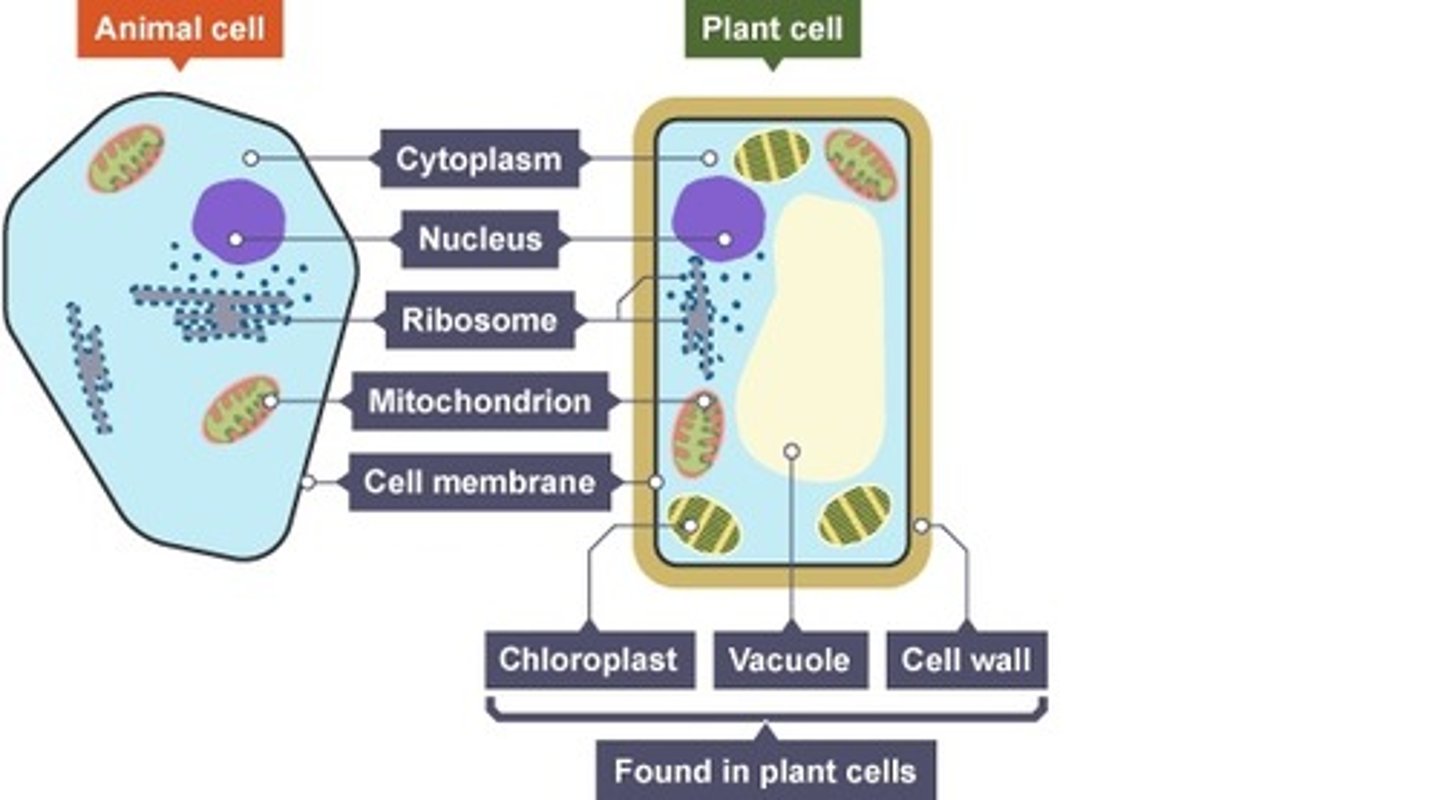
What are the organelles in an animal cell AND a plant cell?
Cytoplasm, nucleus, ribosome, mitochondria, cell membrane
What are the organelles are in a plant cell that aren't in an animal cell?
chloroplast, vacuole, cell wall
What does it mean when a cell is specialised?
they are adapted to a certain job/function
What is an example of a specialised cell?
sperm cells, egg cells, ciliates epithelial cell
What is the adaptations of a ciliated epithelial cell?
hair like structures lining the surface of organs, and brush unwanted cells (eg pathogens) away
What is the adaptations of a sperm cell?
lots of mitochondria for energy to swim, long flagellum for speed, haploid nucleus to make the cell smaller, acrosome (enzyme)
What are the adaptations of an egg cells?
haploid nucleus, membrane changes structure after sperm enters to prevent more entering, nutrients in cytoplasm to feed embryo
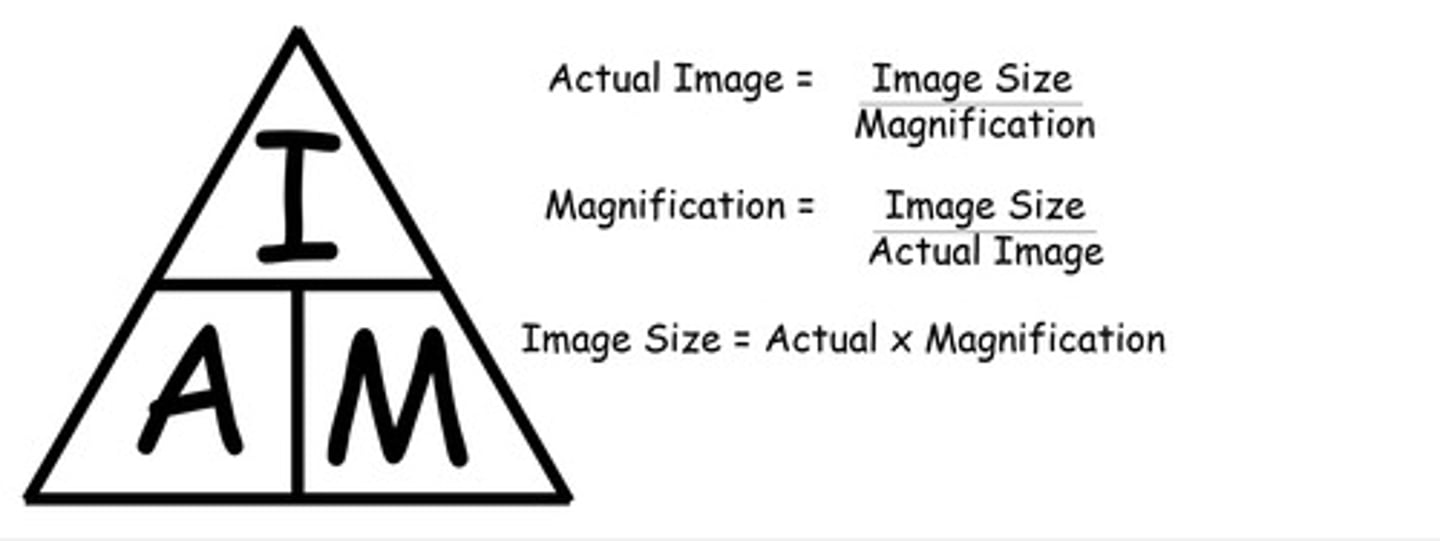
What does it mean to magnify an image?
make the image bigger
Magnification =
Image size/actual size
Total magnification =
eyepiece lens magnification x objective lens magnification
What is the difference between a light microscope and an electron microscope?
A light microscope uses a beam of light, while an electron microscope uses a beam of electrons. Light microscopes magnify up to 1000x's
electron microscopes can magnify up to a lot more.
How do you use a microscope?
- take a thin slice of specimen
- place on the slide using a dot of water to help it stick
- add a stain (eg iodine)
- place the cover slip and clip the slide onto the stage using stage clip
- use the lowest objective lens and work your way up
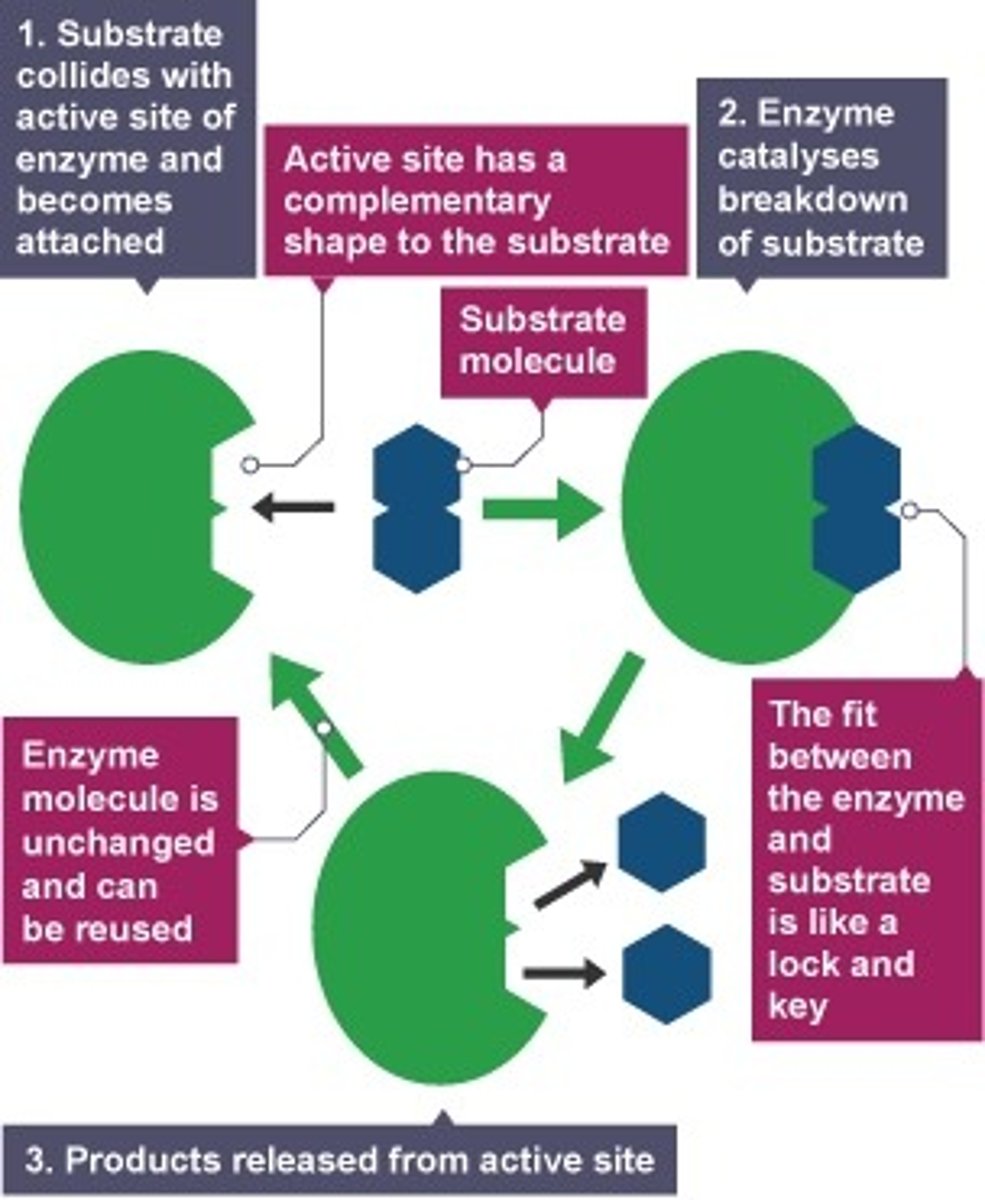
What is an enzyme?
a substance produced by a living organism that acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction.
What theory describe show the enzyme work?
lock and key theory
What 3 factors affect the rate of reaction in an enzyme?
pH , temperature, concentration of substrate
What does it mean when an enzyme is at optimum conditions?
it'll be at the most active, have the highest rate of reaction
What is the job of enzymes in the body?
Break down big molecules (starch proteins and lipids)
What is starch broken up into?
glucose
What are proteins broken down into?
amino acids and peptides
What are lipids broken down into?
fatty acids and glycerol
What is enzyme synthesis?
2 or more substrates joining into 1 product
What is osmosis?
diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
What is an example of osmosis?
water moving into the root cells of a plant
potato and sucrose solution practical
What is diffusion?
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
What is an example of diffusion?
perfume across a room, alveoli in the lungs
What is active transport?
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy.
How do you calculate percentage change?
((final mass-initial mass)/ initial mass) x 100
What is mitosis?
Cell division that generates new cells for growth and repair
What does mitosis create?
Two genetically identical diploid daughter cells
What is a chromosome?
a long continuous thread of DNA that consists of numerous genes
How many chromosomes are in a body cell? (diploid cells)
46 chromosomes, 23 pairs
How many chromosomes are in a gamete? (haploid)
23 chromosomes
What is interphase?
the cell grows and replicates its DNA and centrioles
What happens during metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
What happens in anaphase?
Chromosomes are pulled apart by spindle fibers
What happens in telophase?
Nuclear membrane reforms around the two sets of dna
What happens in Cytokineses?
the cytoplasm and cell membrane divides
What happens if mitosis occurs uncontrollably?
a tumour (a mass of abnormal cells) is formed, if this destroys surrounding tissue it's called cancer.
How can you monitor a child's growth?
percentile charts
What measurements are taken when monitoring growth with a percentile chart?
head circumference, mass and length
What is shown in the 50th percentile?
the growth that 50% of children have reached by a certain age
What is a stem cell?
an undifferentiated cell
What is the difference between embryonic stem cells and adult stem cells?
embryonic stem cells: found in human embryos
adult stem cells: found in bone marrow but can't differentiate into ALL cells
What is the ethical concern of embryonic stem cells in medicine?
extracting the stem cells kills the embryo
Where is a plant stem cell found?
meristem (plant tissue)
What are adult stem cells used for in medicine?
to cure diseases such as sickle cell through bone marrow transplants
What is the potential risk of stem cell transplants?
tumour development, disease transmission, body rejecting the cell, triggering an immune response
What is the nervous system made up of?
brain, spinal cord, nerves
What is the nervous system?
It is a system that allows you to react to your surroundings.
What do the receptor cells detect?
stimuli
When stimuli is detected, how does the CNS coordinate a response?
The receptor cells send an impulse along sensory neurons to the CNS to coordinate a response.
When a response is coordinated by the CNS how is the response carried out?
The CNS sends info to an effector (muscle or gland) along a motor neuron and then a movement is made
Sensory neurone structure:
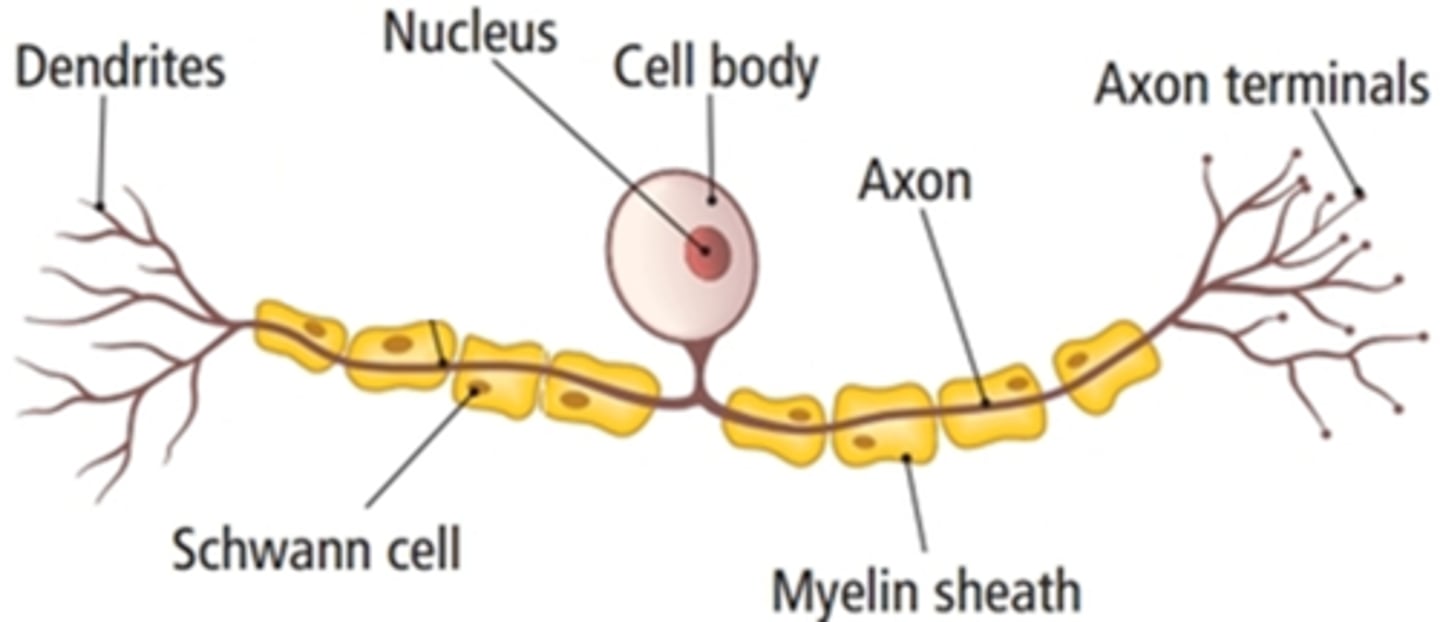
Motor neurone structure
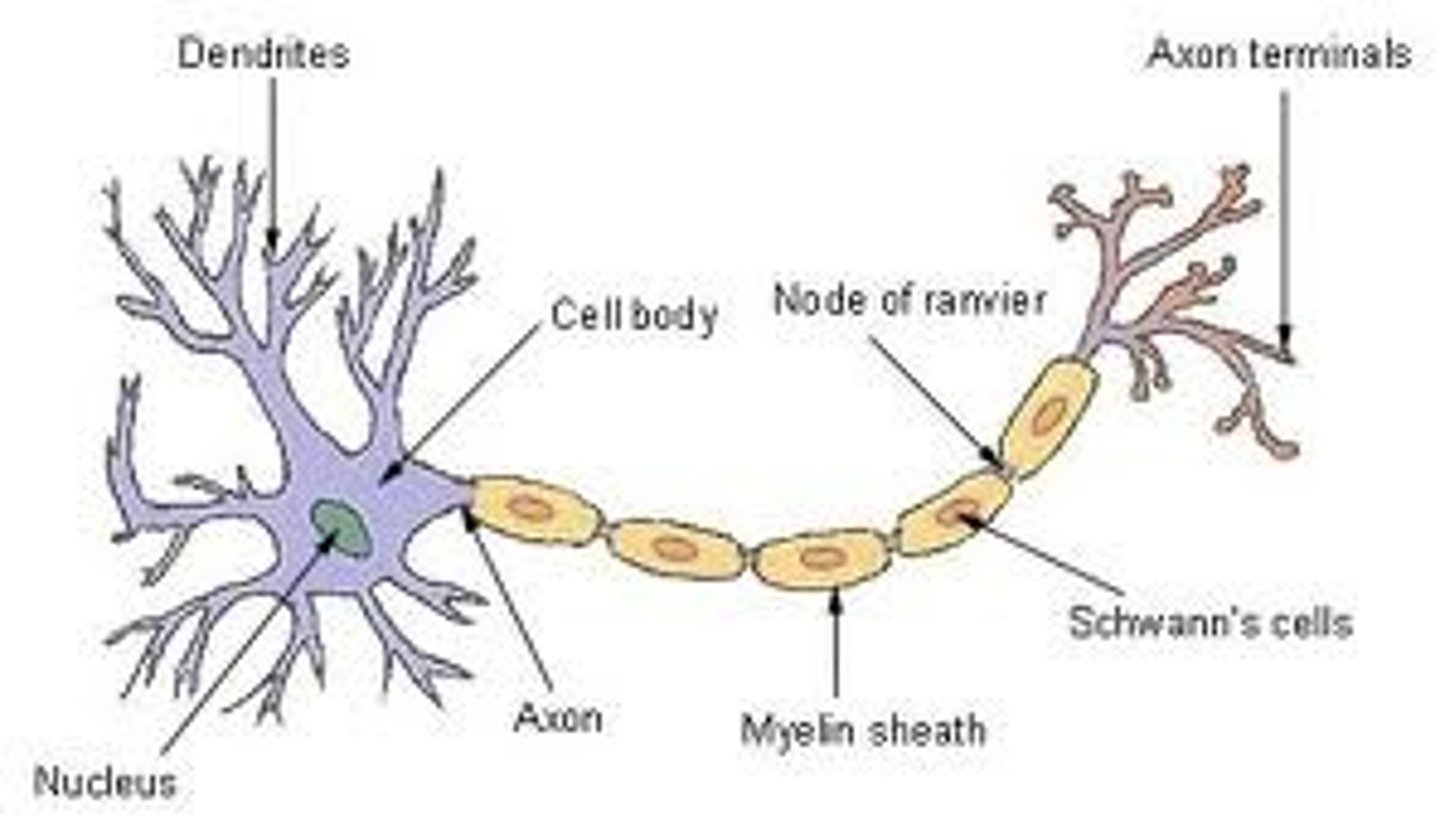
Relay neuron structure
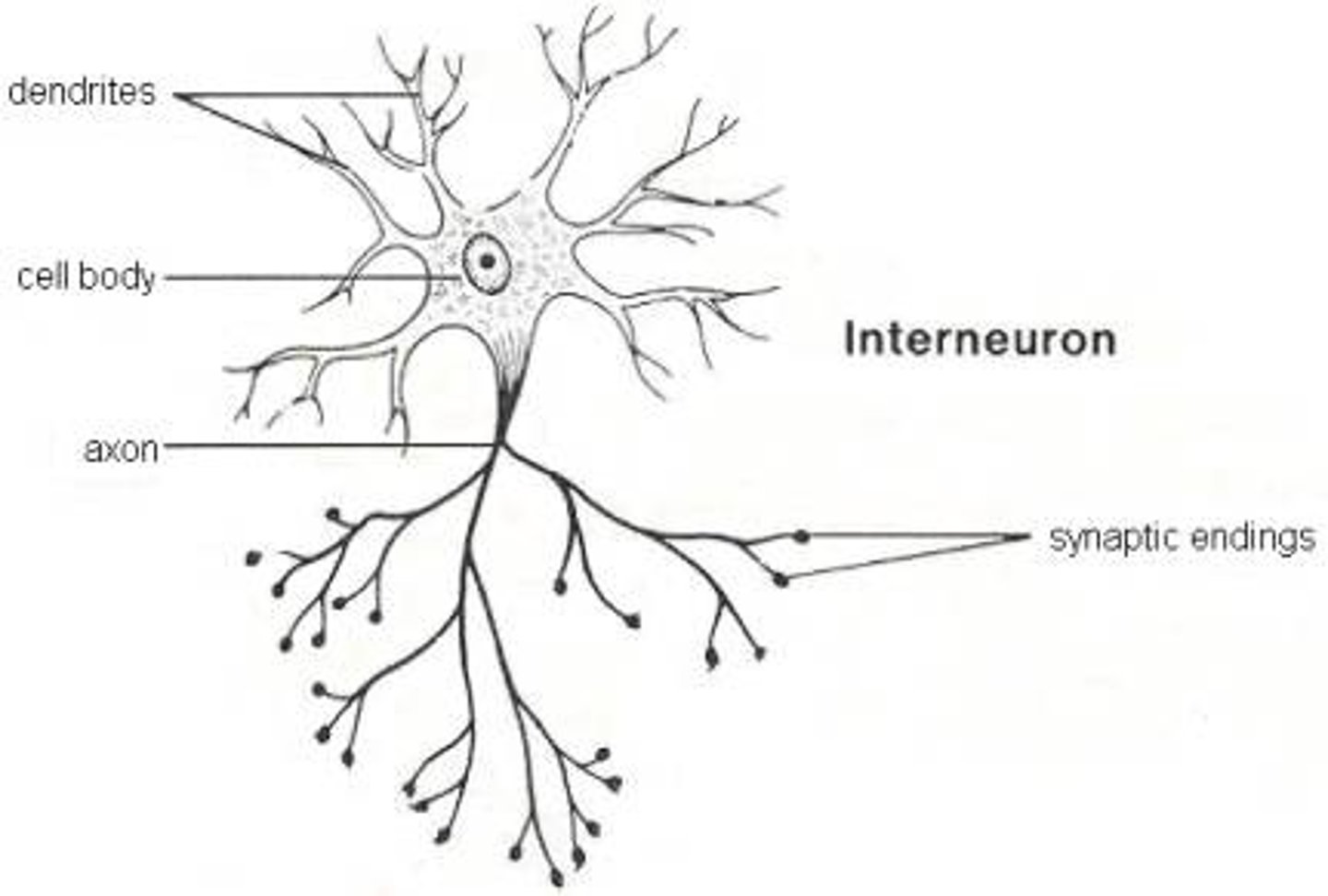
What is a synapse?
Gap between neurons
What happens to the transmission of impulse at the synapse?
transmission is slowed because the impulse has to diffuse through the synapse
What is a reflex?
quick automatic response to a stimulus
Describe what would happen is a bee stung your finger:
pain receptor is stimulated, impulse travels through sensory neuron, impulses pass through relay neuron , then along motor neuron and then a muscle contracts
What is produced through sexual reproduction?
A new organism that differs from both parents.(genetically different)
What is the process of meiosis?
1. Cell makes copies of each chromosome
2. line up two by two in the cell
3.moves to the opposite sides of the cell, splits and makes 2 cells with only half the information
4. Chromosomes line up again in the center, this time single file
5. copies separate, then each copy is pulled to the other side of the cell, and splitting happens again
6. Now there are four cells formed from the original cell, each with only 1/2 of the chromosomes from the original cell.
What are alleles?
Different forms of a gene
What is a phenotype?
physical characteristics of an organism
What is a genotype?
genetic makeup of an organism
A punnet square shows:
all the possible outcomes of a genetic cross
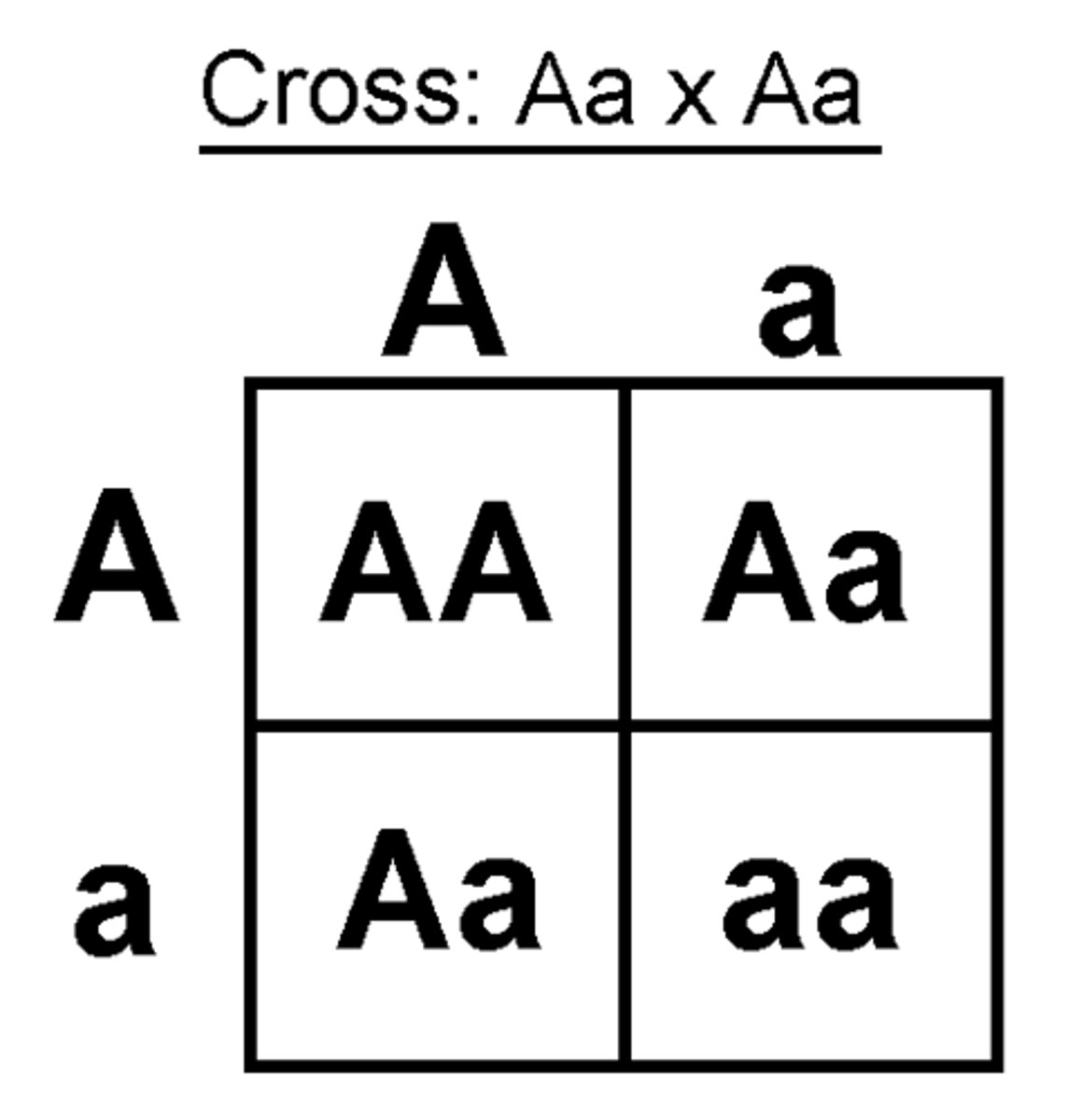
What does it mean if an allele is dominant?
It will be expressed with only one copy present
What is a recessive allele?
An allele that is overruled when a dominant allele is present
What is genetic variation?
● Variations in the genotypes of organisms of the same species due to the presence of different alleles
● Creates differences in phenotypes
What causes genetic variation?
mutations and sexual reproduction
What are mutation?
Changes to the base sequence of DNA
What is DNA made out of?
nucleotides
What is a nucleotide?
Nitrogen base + sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and phosphate group
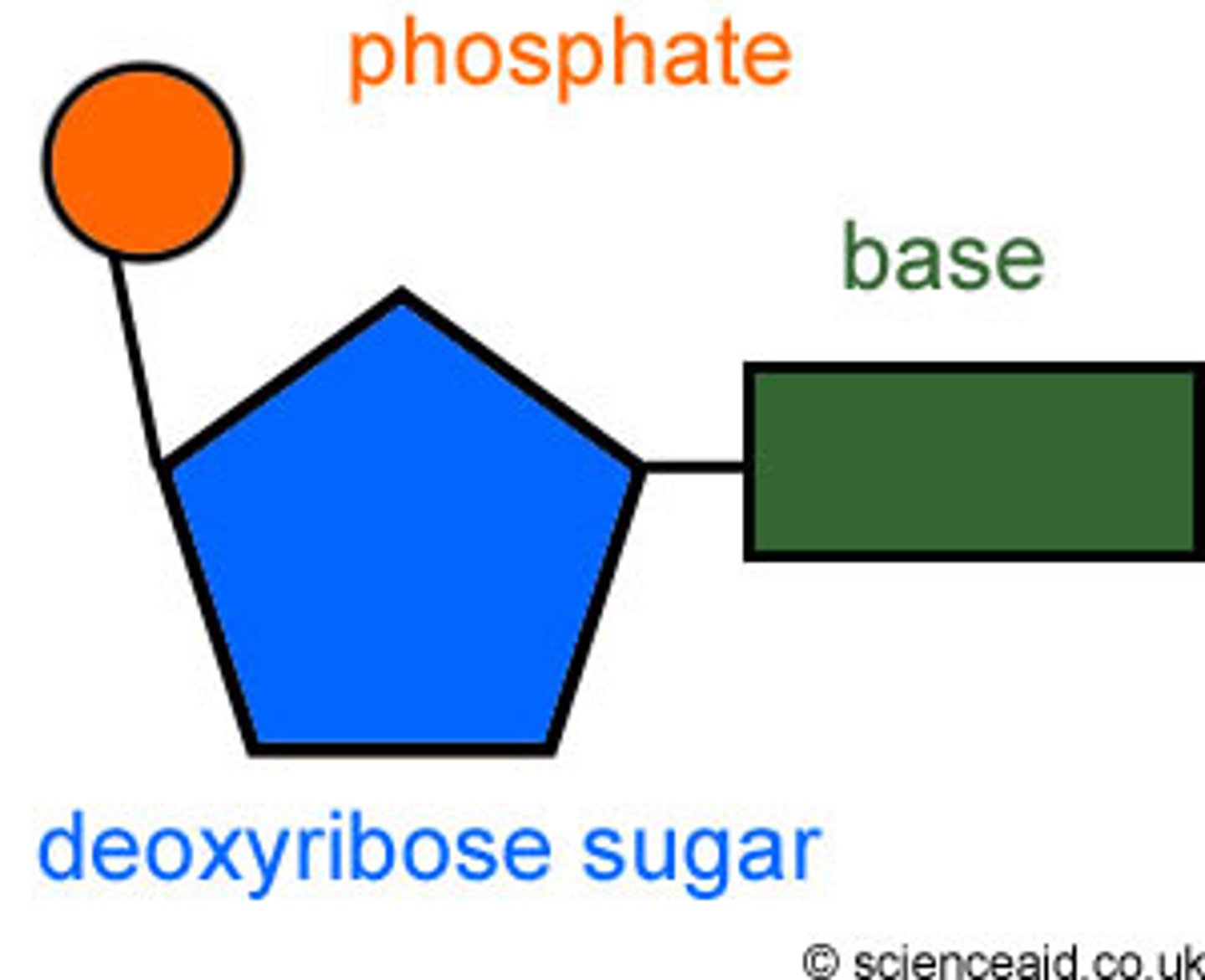
What is the shape of DNA?
double helix
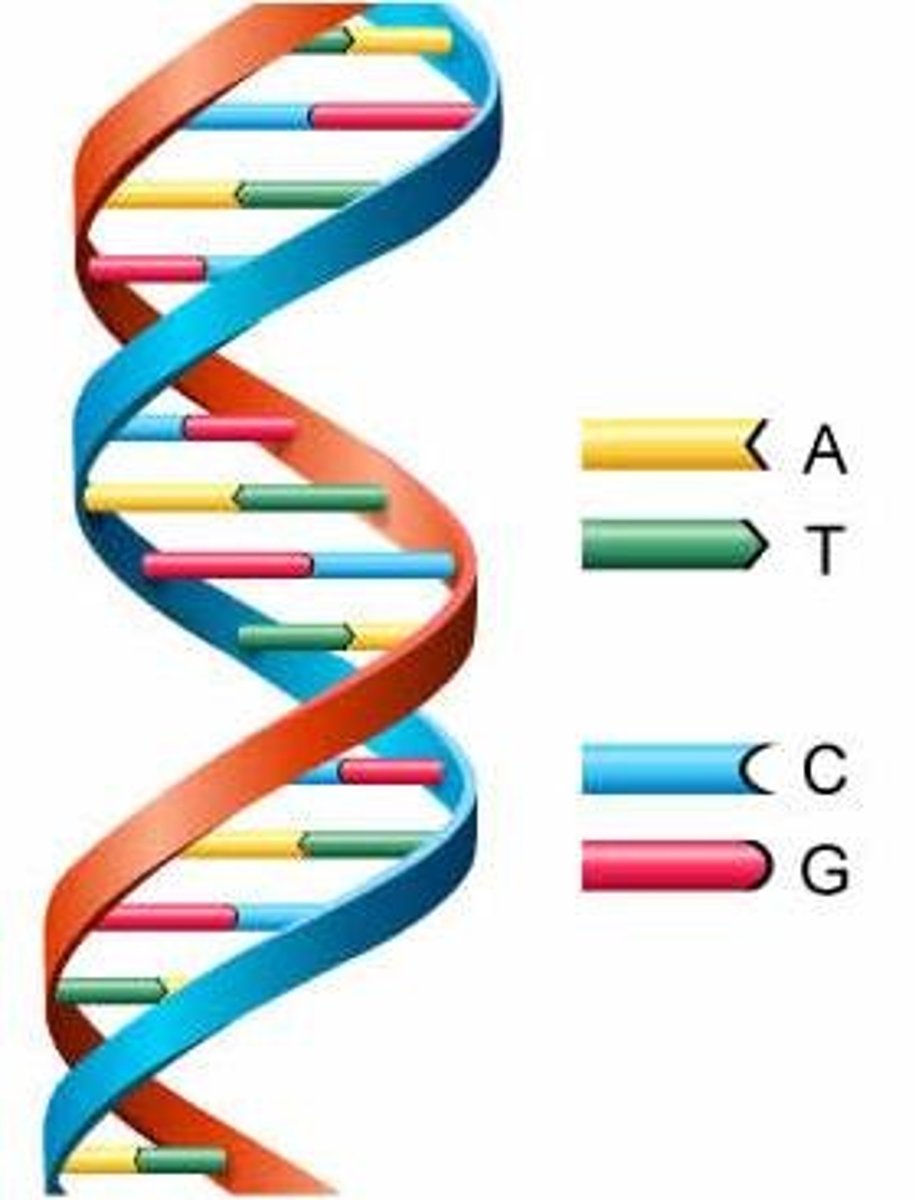
What bases pair up?
Adenine with Thymine and Cytosine with Guanine
What does homozygous mean?
two of the same alleles
What does heterozygous mean?
two different alleles
What is a chromosome?
A coiled up piece of DNA that has genes that code for traits.
How do you extract DNA from fruit cells?
-Mash strawberries with detergent to get rid of cell membranes and break them down
-Filter the mixture
-Gently add ice cold alcohol
-DNA isn't soluble in cold alcohol
-It will appear as a white precipitate
What are the female chromosomes?
XX
What are the male chromosomes?
XY
What is the Human Genome Project?
an attempt to map the entire DNA sequence in the human genome.
What are the benefits of the human genome project?
Can know what genes are responsible for diseases/disorders
Can help in gene therapy/cures
Can help us understand what it is about our genes that make us who we are
What are the disadvantages of the human genome project?
Increased stress, people with genetic problems could be pressured not to have children, discrimination by employers and insurers.
What is natural selection?
The idea that the fittest survive and pass along their traits to their offspring.
How does bacteria show evidence for evolution?
mutations e.g antibiotic resistant bacteria
How do fossils provide evidence for evolution?
- Show that previously living species are similar to, but different from, species that are alive today.
- Show that many species have become extinct.
- Show evolutionary changes in groups of organisms.
What is classification?
The process of grouping organisms based on their similarities
What are the 5 kingdoms?
protists, fungi, plants, animals, prokaryotes
What is archaea?
a domain of single-celled microorganisms that are prokaryotes
What is selective breeding?
Living organisms with desired traits are bred so as to produce such traits in offspring
What is an example of selective breeding?
dog breeding
What were the features of Ardi?
feet to climb branches, long arms and short legs, small brain, walked upright
What are features of Lucy?
arched feet for walking, bigger brain, longer arms and legs
What are features of homo erectus?
larger brain, human like arms and legs
How do stone tools show evolution?
complexity of the tool
Features of the oldest stone tools:
made by hitting rocks together, sharp flakes to scrape meat off of bones