Chapter 9: Alkynes
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What are Alkynes?
Compounds containing a triple bond between two carbons (C≡C)
What three bonds comprise a triple bond? What causes these three bonds?
One sigma bond and two pi bonds
Sigma bond —> results from the overlap of sp-hybridized orbitals
Pi bonds —> results from the overlap of p orbitals
Why are alkynes reactive?
They have regions of high electron density
How are Alkynes similar to Alkenes?
Both can function as bases or as nucleophiles
What is the hybridization and molecular geometry of Acetylene?
sp hybridization and linear geometry, with a bond angle of 180˚
Why is it hard to incorporate a triple bond into a small ring?
Ring strain forces the bond angles to deviate from the ideal 180˚
What is cyclononyne?
A triple bond is incorporated into a nine-membered ring
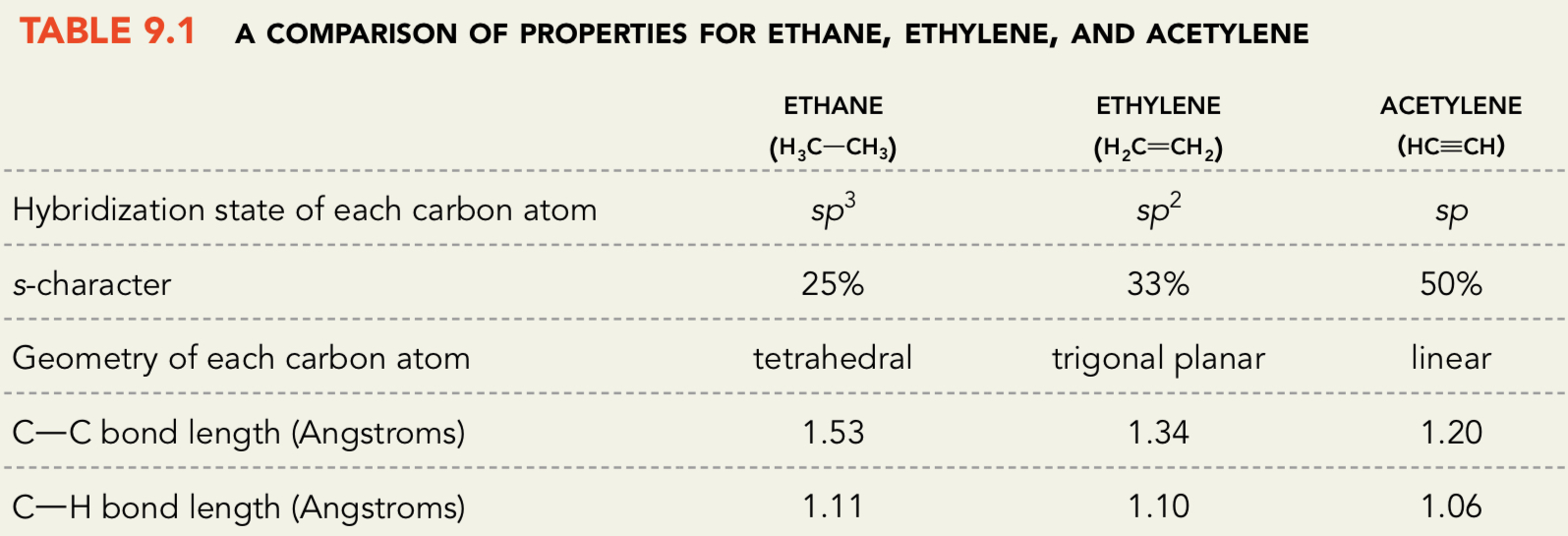
What is the relative bond lengths of C—C and C—H in Ethane, Ethylene, and Acetylene? Why are they different?
Ethane has the longest C—C and C—H bond lengths
Acetylene has the shortest C—C and C—H bond lengths
They are different because of the hybridization states in each case
What are the four steps required to name Alkynes?
Identify and name the parent
Identify and name the substituents
Number the parent chain and assign a locant to each substituent
Assemble the substituents alphabetically
What suffix is used to indicate the presence of a C≡C bond?
The suffix “-yne”
What is the parent of an alkyne?
The parent is the longest chain that includes the C≡C bond
How should Alkynes be numbered?
The triple bond should receive the lowest number possible, even despite the presence of alkyl substituents
Where is the locant placed in the name of the alkyne to indicate the triple bond location?
The locant number is placed either immediately before the parent name OR before the suffix “-yne”
What are some common names for Alkynes?
Acetylene
Methylacetylene
Diisopropylacetylene
Phenylpropylacetylene
What does it mean when an Alkyne is monosubstituted? Disubstituted?
Monosubstituted —> the Alkyne possesses only one alkyl group
Disubstituted —> the Alkyne possesses two alkyl group
What are monosubstituted Alkynes called? Disubstituted Alkynes?
Monosubstituted —> Terminal Alkynes
Disubstituted —> Internal Alkynes
What are the pKa values of Ethane, Ethylene, and Acetylene? Which is more acidic?
Ethane —> pKa = 50
Ethylene —> pKa = 44
Acetylene —> pKa = 25
Acetylene is significantly more acidic than Ethane or Ethylene
How many orders of magnitude is Acetylene more acidic than Ethylene of? (Acetylene pKa = 25, Ethylene pKa = 44)
19 orders of magnitude
What is favored by the equilibrium of an acid-base reaction?
The equilibrium of an acid-base reaction will always favor formation of the weaker acid and weaker base
What is the relationship between stability and basicity?
An ion that is significantly more stable is a much weaker base
What is the relative acidity of Terminal Alkynes?
Terminal Alkynes are relatively acidic and can be deprotonated with suitable bases
What is the conjugate base of a Terminal Alkyne?
An Alkynide ion
It can only be formed with a sufficiently strong base
What are three common bases that deprotonate Terminal Alkynes?
Bases that have a negative charge on:
A nitrogen (N-)
A hydrogen (H-)
A carbon (C-)
What are three common bases that DO NOT protonate Terminal Alkynes?
Bases that have a negative charge on an oxygen
How do you select a base for deprotonating a Terminal Alkyne?
Identify the acid and base on each side of the equilibrium
Determine which acid is weaker
Identify the position of equilibrium (the equilibrium will always favor the reaction direction that forms the weaker acid and weaker base)
What can Alkynes be prepared from?
Alkyl Dihalides
How does an Alkyne form from an Alkyl Dihalide?
The Alkyl Dihalide is treated with a strong base and forms into the Alkyne
How many leaving groups does an Alkyl Dihalide have?
Two
Via what type of reactions does an Alkyl Dihalide become an Alkyne?
Via two successive elimination (E2) reactions
What are Geminal Dihalides?
Dihalides in which both halogens are connected to the same carbon atom
What are Vicinal Dihalides?
Dihalides in which both halogens are connected to adjacents carbon atoms
What type of bases are required for the two elimination (E2) reactions that transform Alkyl Dihalides into Alkynes?
The first elimination reaction can use many different bases
The second elimination reaction requires a very strong base
What is a good, suitable base for achieving two successive elimination reactions in a single reaction vessel? What method is this mostly used for?
Sodium amide (NaNH2) dissolved in liquid ammonia (NH3)
This method is mostly used for preparing Terminal Alkynes
In summary, how can a Terminal Alkyne be prepared from a Dihalide?
By treating the Dihalide with excess Sodium Amide, followed by water
Often written as 1) xs NaNH2/NH3, over the arrow, 2) H2O
What happens when an Alkyne undergoes a Catalytic Hydrogenation reaction?
The Alkyne consumers two equivalents of molecular hydrogen
Is it possible to convert an Alkyne into a cis Alkene?
Yes, with the use of a poisoned catalyst (a partially deactivated catalyst)
What are some common examples of a poisoned catalyst?
Lindlar’s Catalyst, which is a Pd catalyst prepared with CaCO3 and traces of PbO2
A Nickel-Boron complex (Ni2B), often called the P-2 catalyst
Does the use of a poisoned catalyst on an Alkyne make any trans Alkene?
No, it never produces any trans Alkenes because the syn addition of the hydrogen atoms during hydrogenation gives a cis Alkene as the major product
What happens in a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
An Alkyne is reduced to a trans Alkene with reagents of sodium metal (Na) in liquid ammonia (NH3)
What temperature conditions are needed for a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
Low temperature is required because the reagents (specifically ammonia) has a very low boiling point
What is the role of the sodium metal in a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
The sodium metal (Na) serves as a source of electrons, from the sodium atoms (Na —> Na+ + e-)
What are the four steps of the Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction mechanism?
Electron Transfer
Proton Transfer
Nucleophilic Attack
Electron Transfer
What happens during the first electron transfer step of the Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
A single electron is transferred from the sodium atom to the Alkyne, generating a radical anion intermediate
What happens during the proton transfer step of the Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
Ammonia donates a proton to the radical anion, generating a radical intermediate
What happens during the nucleophilic attack step of the Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
A single electron is transferred from the sodium atom to the radical intermediate, generating an anion
What happens during the second electron transfer step of the Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
Ammonia donates a proton to the anion, generating a trans Alkene
What is a radical anion?
An anion in which there is a charge associated with a lone pair of electrons, called a radical because of the UNPAIRED electrons
In a mechanism, how are steps involving radicals shown?
Mechanistic steps involving radicals are indicated using single-barbed curved arrows (sometimes called fishhook arrows)
What do single-barbed and double-barbed curved arrows represent?
Single-barbed —> movement of one electron
Double-barbed —> movement of two electrons
Why does the intermediate radical anion prefer formation of a trans Alkene?
The trans configuration minimizes repulsion by positioning paired and unpaired electrons as far apart as possible, known as the lower energy state
What is the net result of a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction?
The anti addition of two hydrogen atoms across the alkyne
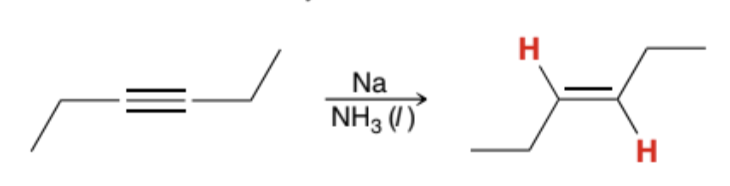
What does a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction transform?
It transforms an internal Alkyne into a trans Alkene
Does a Dissolving Metal Reduction reaction work on a terminal Alkyne?
No, because the terminal Alkyne would instead be deprotonated into an Alkynide ion
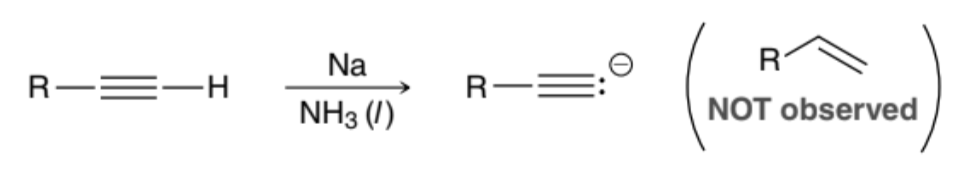
How can a terminal Alkyne be reduced into an alkene?
Can be reduced via a Catalytic Hydrogenation reaction in the presence of a poisoned catalyst, such as Lindlar’s catalyst
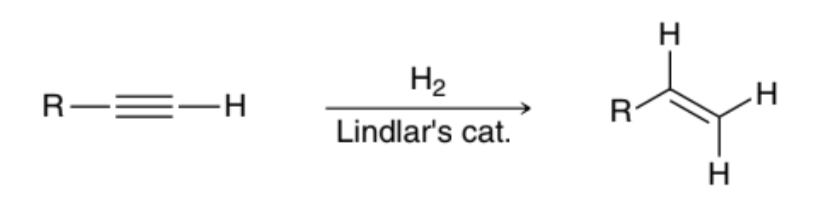
What can be done to an Alkyne to produce an Alkene?
The Alkyne can be treated with H2 in the presence of a metal catalyst, such as Pt, Pd, or Ni
What can be done to an Alkyne to produce a cis Alkene?
The Alkyne can be treated with H2 in the presence of a poisoned catalyst, such as Lindlar’s Catalyst or Ni2B
What can be done to an Alkyne to produce a trans Alkene?
The Alkyne can be treated with sodium metal (Na:) in liquid ammonia (NH3)
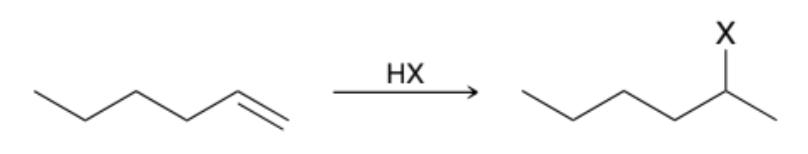
How do Alkenes react with HX?
Via a Markovnikov addition, in which the halogen is installed at the more substituted position
How do Alkynes react with HX?
Via a Markovnikov addition, in which the halogen is installed at the more substituted position
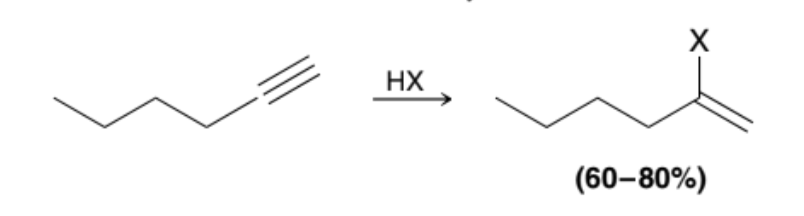
What happens when an Alkyne is treated with excess HX?
Two successive addition reactions occur, in which two of the halogen attach to the more substituted position to create a geminal dihalide
What are the steps of the mechanism in which HX is added to a triple bond (Alkynes)?
Protonation to form a carbocation (Proton transfer)
Nucleophilic attack
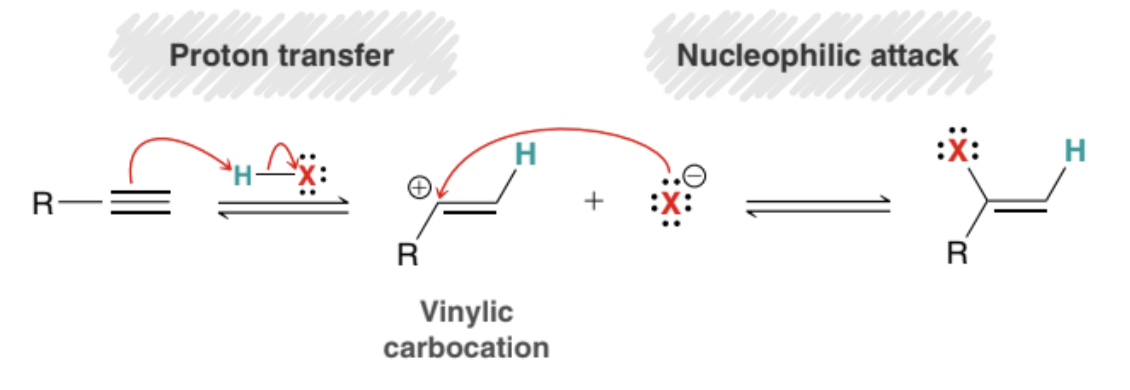
What type of intermediate does the HX addition to an Alkyne mechanism use? Why does it use it?
The mechanism uses a secondary vinylic carbocation intermediate
It uses a secondary vinylic carbocation rather than a primary vinylic carbocation because it is more stable
What is the functional group of a peroxide?
ROOR, or any compound in which two oxygen atoms are connected via a single covalent bond
What happens when HBr is applied to an Alkene in the presence of peroxides?
The HBr undergoes an Anti-Markovnikov addition across the Alkene, in which the Br is installed at the least substituted position
(Occurs via a radical mechanism)
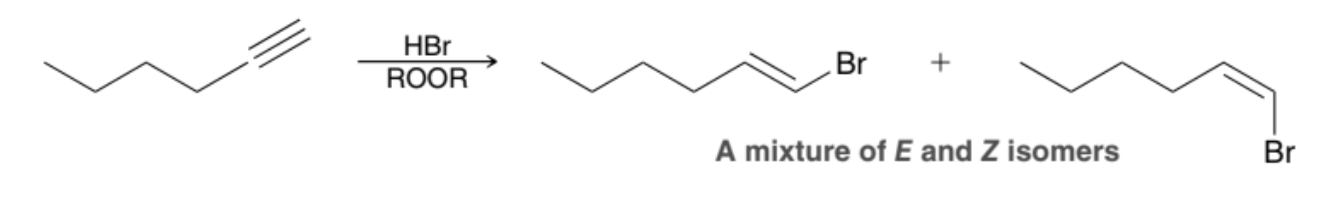
What happens when HBr is applied to a terminal Alkyne in the presence of peroxides?
The HBr undergoes an Anti-Markovnikov addition across the Alkyne, in which the Br is installed at the terminal position
What is produced when HBr is applied to a terminal Alkyne in the presence of peroxides?
A mixture of E and Z isomers are produced with Br at the terminal position
What is different about Acid-Catalyzed Hydration in Alkynes than in Alkenes?
In Alkynes, the reaction proceeds slower than in Alkenes
How do I study Acid-Catalyzed Keto-enol Tautomerization?
You don’t; go watch YouTube videos about it