Unit 2: Population and Migration - AP Human Geography 2024-25
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Bracero Program
In the 1940s, the US government encourages Mexicans to come to the US and work as contract laborers.
refugee camps
a temporary settlement built to receive refugees.
remittances
the money migrants send home
reverse remittances
money that migrant’s families in their home country send to working migrants
cyclic movement
short, regular trips away from home for defined amount of time
periodic movement
long periods away from home, but less frequent
emmigration
the movement of people leaving a place
immigration
the movement of people entering a place
activity spaces
a daily routine that takes people through a sequence of short moves in a local area
nomadism
a way of life that people who do not continually live in the same place year-round
transhumance
a system of pastoral farming in which ranchers move livestock according to seasonal availability of pastures
international/transnational migration
movement across country borders
internal migration
migration that occurs within a single country’s borders
forced migration
when push factors drive people out of a place
voluntary migration
when people choose to leave a place because of pull factors of another place
human trafficking
an example of forced migration
examples of human trafficking
sex trafficking, forced labor, recruitment of child soldiers, etc
arithmetic density
population/total land
physiological density
population/total arable land
agricultural density
farmers/arable land
sex ratio
number of resident male births/number of resident female births
dependency ratio
population 15-64/0-15+65+
old age dependency ratio
population 65+/population 16-64
youth dependency ratio
population 0-15/population 16-64
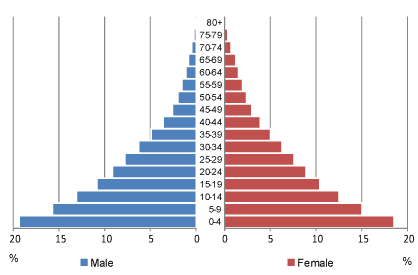
skinny pyramid
high birth rate/low death rate
short life expectancy/high IMR
high youth dependency
periphery/agriculture
high stationary growth
early expanding growth
triangle
high birth rate/falling death rate
Late Expanding Growth
onion dome
falling birth rate/death rate falls slower
high life expectancy/low IMR
high youth depen/rising elderly depen
increasing industry/secondary
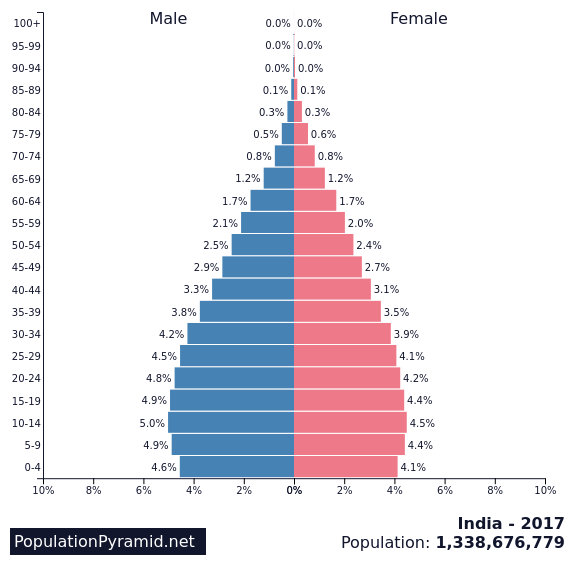
low stationary growth
box pyramid
low birth rate/low death rate
high life expectancy/low IMR
low youth depen/rising elderly depen
service dominated/tertiary
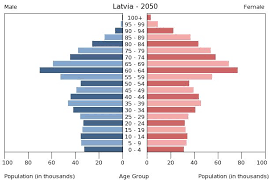
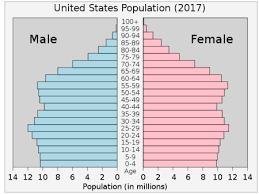
cup pyramid
low birth rate/low death rate
high life expectancy/low IMR
high elderly dependency
service oriented
negative population growth
Epidemiologic Model Stage 1
High stationary; pestilence and famine
Epidemiologic Model Stage 2
Early Expanding; receding pandemics
Epidemiologic Model Stage 3
Late Expanding; degenerative and man-made disease
Epidemiologic Model Stage 4
Low Stationary; delayed degenerative diseases
Epidemiologic Model Stage 5
Declining; reemergence of infectious and parasitic diseases
Who was Thomas Malthus?
Malthus was a demographer and professor in England. Born 1766.
Malthusian Theory
Populations grow faster than the amount of food needed to support them.
Boserup’s Theory
Food supply is affected by population size.
carrying capacity
the maximum amount of individuals in a species that an environment can sustain for a long time.
anti-natalist
Have less babies
pronatalist
have more babies
push factors
things that push a person away from a place
pull factors
things that draw people into a place