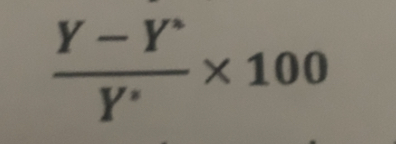Midterm 2 Econ
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:33 AM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
1
New cards
What two things cause shifts in the demand for labor?
Changes in price of output and productivity
2
New cards
When real wage INCREASES, what shifts left?
Demand of labor
3
New cards
When real wage DECREASES, what shifts left?
Supply of labor
4
New cards
What two things cause shifts in the supply of labor?
Changes in the working age population and change in working age population willing to work
5
New cards
Name the three types of unemployment
Structural frictional and cyclical
6
New cards
Formula for Saving
Current income minus spending on current needs
7
New cards
Formula for saving rate
saving over income
8
New cards
Formula for wealth
assets minus liabilities
9
New cards
Is saving a stock or flow value?
Flow
10
New cards
Is wealth a stock or flow value?
Stock
11
New cards
Formula for change in wealth
Saving plus capital gains minus capital losses
12
New cards
What are the three reasons for household saving?
Life cycle saving
Precautionary saving
Bequest saving
Precautionary saving
Bequest saving
13
New cards
As real interest rate goes up, how does saving change?
Saving increases
14
New cards
National saving formula
S = Y-C-G
15
New cards
Private saving formula
Sprivate = Y-T-C
16
New cards
Public saving formula
Spublic = T-G
17
New cards
Saving is the sum of what?
Private and public saving
18
New cards
The variable T means what?
Net taxes
19
New cards
Net taxes formula
Total taxes minus transfer payments minus government interest payments
20
New cards
Private saving is the sum of what?
Household and business saving
21
New cards
The surplus of the government budget surplus is what?
Public saving
22
New cards
What two factors affect investment decisions?
Costs and benefits
23
New cards
What is costs of investment?
Price of new capital goods
Real interest rate
Real interest rate
24
New cards
Does real interest rate shift the supply and demand curves in SAVING AND INVESTMENT?
No
25
New cards
What is money?
Asset used to make purchases
26
New cards
What are the three functions of money?
Medium of exchange
Unit of account
Store of value
Unit of account
Store of value
27
New cards
What is M1?
28
New cards
What causes cyclical unemployment?
Business cycle
29
New cards
What equals natural unemployment?
structural plus frictional
30
New cards
What is u*?
Natural rate of unemployment
31
New cards
What is u?
Rate of unemployment
32
New cards
The formula for cyclical unemployment is?
Unemployment minus natural unemployment
33
New cards
Okun’s Law
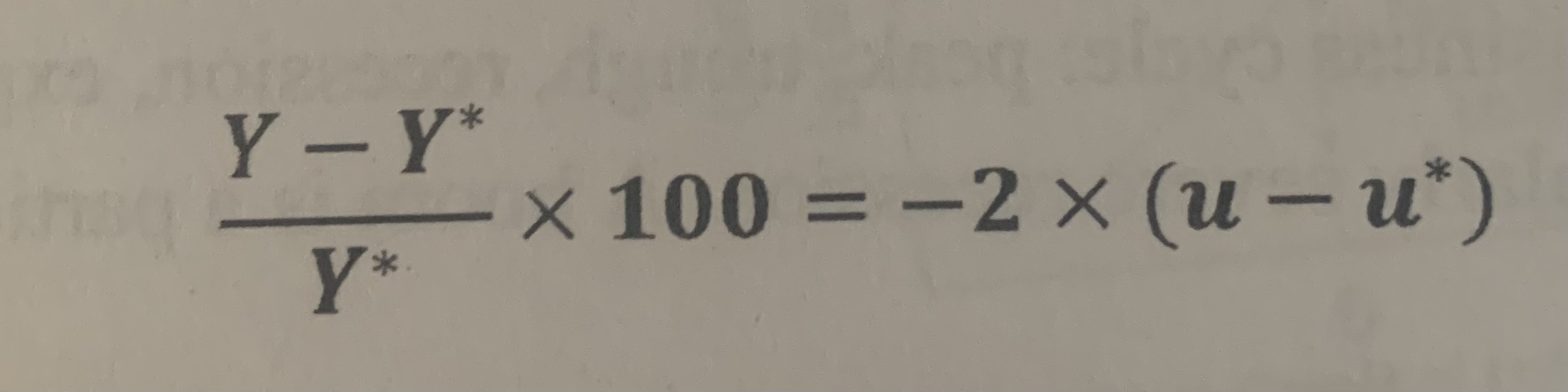
34
New cards
What causes slowdowns or speed ups in REAL GDP growth?
Potential output growth
Output gaps develop
Output gaps develop
35
New cards
Do prices change immediately with a change in demand?
No
36
New cards
How do firms meet demand in the SHORT run?
Preset prices
37
New cards
How do firms meet demands in the LONG run?
Total spending analysis
38
New cards
What is the equilibrium of an open economy?
SK + I = I
39
New cards
What does unemployment do during recessions?
Rise
40
New cards
Which type of unemployment is associated with recessions?
Cyclical
41
New cards
Which industries are most affected during recessions?
Durable goods
42
New cards
How do recessions affect the rate of inflation?
It declines
43
New cards
What does Y* mean?
Potential output
44
New cards
Output gap formula