Unit 1 AP Psych
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Heredity
genetic influences passed from parents to offspring, determines physical traits and influences behavioral + mental traits
Environment
all external factors influencing an individual’s development (ex: family upbringing, education, culture, social interactions)
Hereditary Factors to Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders
family history of schizophrenia, presence of specific genes linked to increased risk
Environmental Factors to Schizophrenic Spectrum Disorders
social isolation, childhood trauma, drug use during adolescence, urban upbringing, exposure to malnutrition or stress during pregnancy
Gene-Environment Interaction
process by which specific environmental factors affect individuals differently depending on their genetic makeup
Evolutionary Perspective
view of how natural selection shaped behaviors and mental processes to help humans survive and reproduce
Variation
within a population, individuals have variations in traits
Inheritance
traits are heritable (can be passed from parents to offspring)
Differential Survival and Reproduction
Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce
Accumulation of Advantageous Traits
over generations, advantageous traits become more common in the population
Fight-or-Flight Response
instinctive physiological reaction to perceived threats, preparing the body to either fight the danger or flee (adrenaline release, enhanced senses, energy mobilization)
Memory and Learning
the ability to store, retain, and recall information is a evolutionary advantageous trait
Eugenics
the practice of attempting to improve the genetic quality of the human population by selective breeding or other means
Twin Studies
research on twins to understand the role of genetic and environmental factors in shaping behavior and mental processes
Family Studies
investigate patterns of traits and behaviors among family members to assess hereditary influences
Pedigree Analysis (Family Studies)
researchers create family trees to track the occurrence of specific traits or disorders across generations
Comparison (Family Studies)
traits or disorders in immediate family members (parents/siblings) versus distant relatives (aunts/uncles/cousins)
Adoption Studies
Examine individuals who have been adopted, comparing them to their biological and adoptive families to sperate the effects of genetics and environment
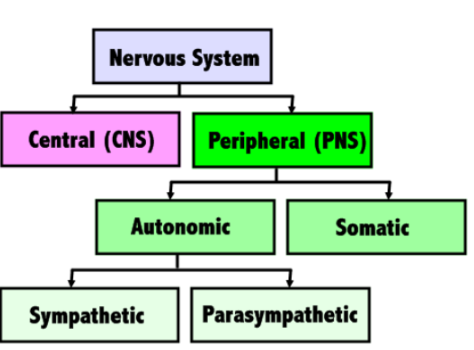
What is the nervous system responsible for?
coordinating actions/movements and transmitting sensory signals, had 6 subdivisons.
Neurons
individual nerve cells, the basic building block of the nervous system
Central Nervous System (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
all nerves outside of the brain/spinal cord that connect to the rest of the limbs and organs of the body. divided into the somatic and autonomic systems.
Somatic Nervous System
part of the PNS, associated with voluntary control of body movements
Autonomic Nervous System
part of the PNS, influences the function of internal organs (involuntary). divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems
Sympathetic Nervous System
part of autonomic nervous system, arouses your body for a fight-or-flight response
Parasympathetic Nervous System
part of the autonomic nervous system, calms your body after a fight-or-flight response
Nucleus
the neuron’s life support center
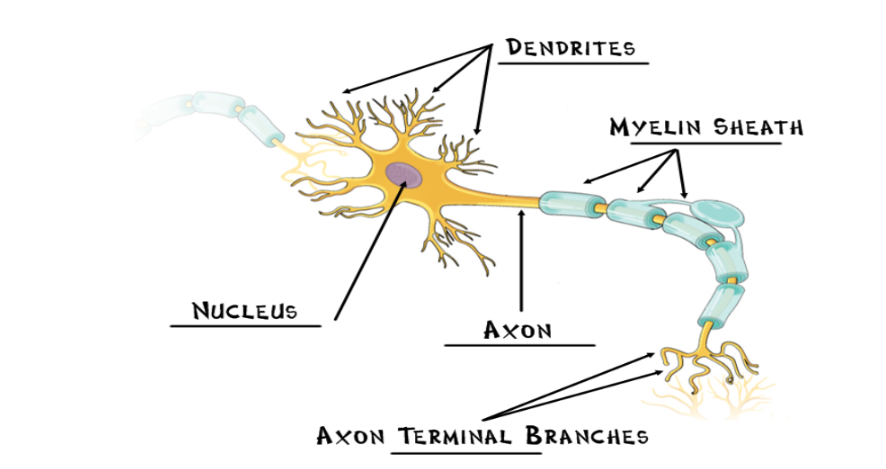
Dendrites
receives information from the previous neuron and conducts the impulse toward the nucleus
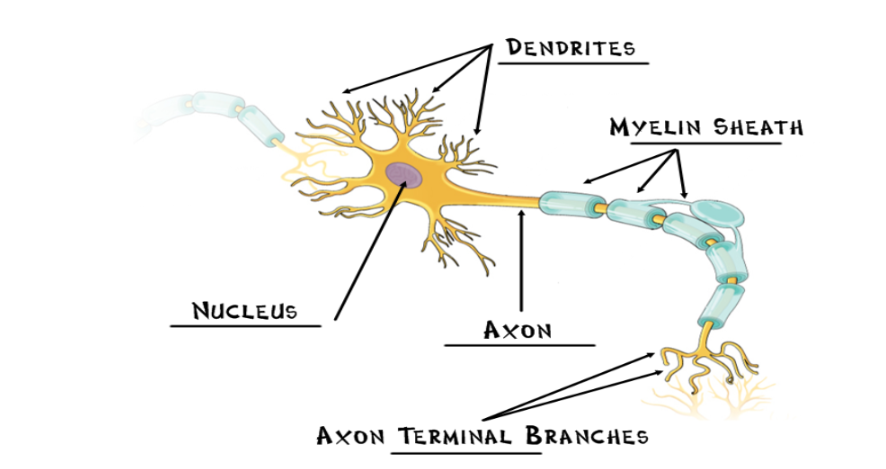
Axon
cellular extension that carries neural messages away from the nucleus toward other neurons/muscles/glands
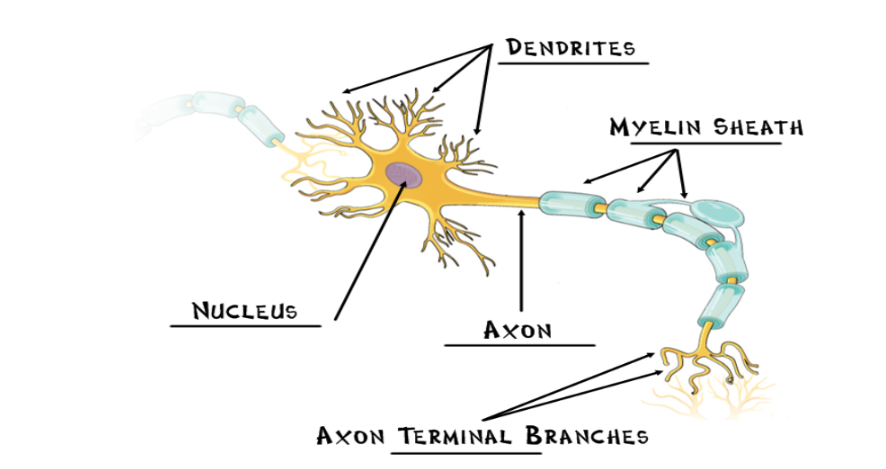
Myelin Sheath
fatty cells covering the axon, help speed neural impulses
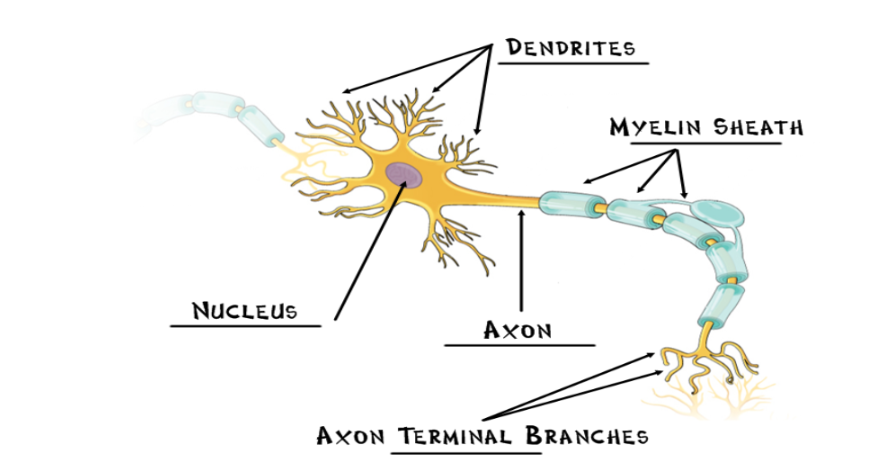
Axon Terminal Branches
forms connection across the synapses with dendrites of a new neuron
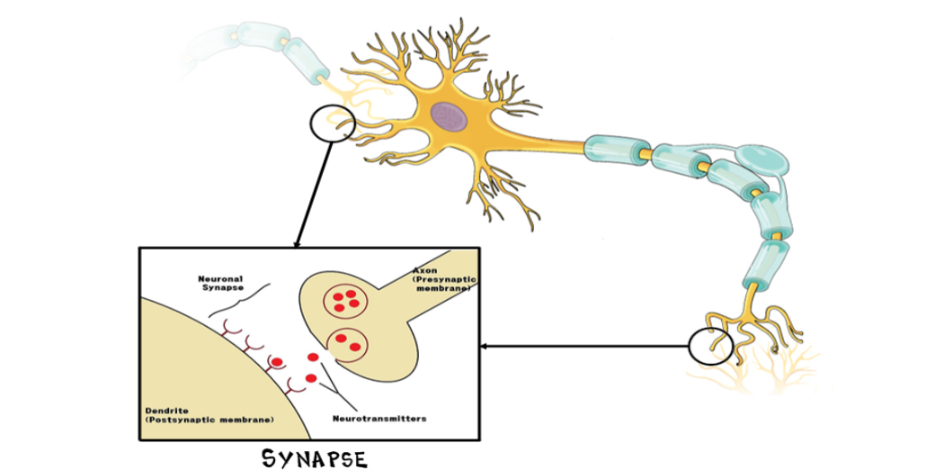
Synapse
space-based junctions through which neurons pass electrical or chemical signals to each other
Resting Potential
when the neuron is inactive, the inside of it is negatively charged while the outside is positively charged
Action Potential
when the neuron is active, the neural membrane opens to allow positive ions inside the cell and negative ions outside the cell
Reuptake
when any unused/excess neurotransmitters are sucked back up into the original neuron (instead of being sent to the next neuron)
Afferent/Sensory Neurons
sends sensation information you experience up to your brain
Efferent/Motor Neurons
muscle movement impulses carried out from the brain
Interneurons
communication neurons in the spinal cords
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that transmit across the synaptic gap between neurons
Acetylcholine (ACh)
involved in memory + learning, makes motor movements possible
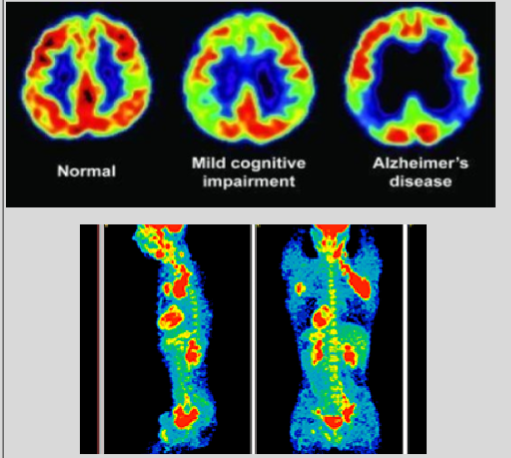
too LITTLE = Alzheimer’s Disease
Dopamine
associated with pleasure, highly involved in movement + alertness
too LITTLE = parkinson’s disease
too MUCH = schizophrenia
Serotonin
involved in mood control
too LITTLE = clinical depression
Endorphins
involved in pain relief (ex: runner’s high)
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
major inhibitory neurotransmitter - calms firing nerves. important in producing sleep and reducing anxiety
Norepinephrine
helps control alertness and arousal, associated with fight-or-flight
Glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter. involved in learning and memory
Substance P
plays a role in transmitting pain signals
Glial Cells
provide physical and metabolic support to neurons (neuronal insulation, communication, nutrient + waste transport)
Reflex Arc
pathway of neural stimulation that occurs to translate a sensation into a physical reflexive response
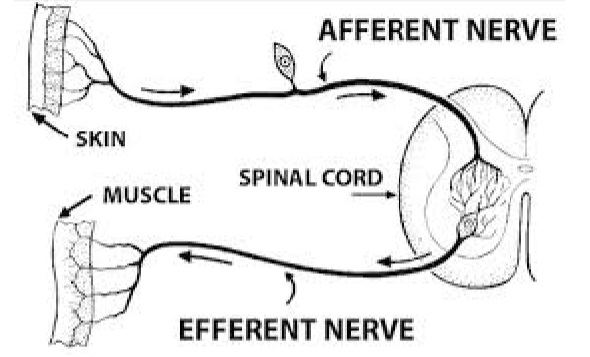
5 components of the Reflex Arc
Receptors (dendrites)
Sensory Neurons (afferent neurons)
Interneuron (majority of neurons in the body)
Motor Neurons (efferent neurons)
Muscles
Agonists Drugs
mimic neurotransmitters and activate receptor sites
Antagonists Drugs
block neurotransmitter receptor sites
Reuptake Inhibitors Drugs
stops the reuptake process of excess neurotransmitters in the synapse
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
repeated damage to the brain cells without time to heal
Brainstem
Oldest part of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells and enters the skull. responsible for automatic survival functions
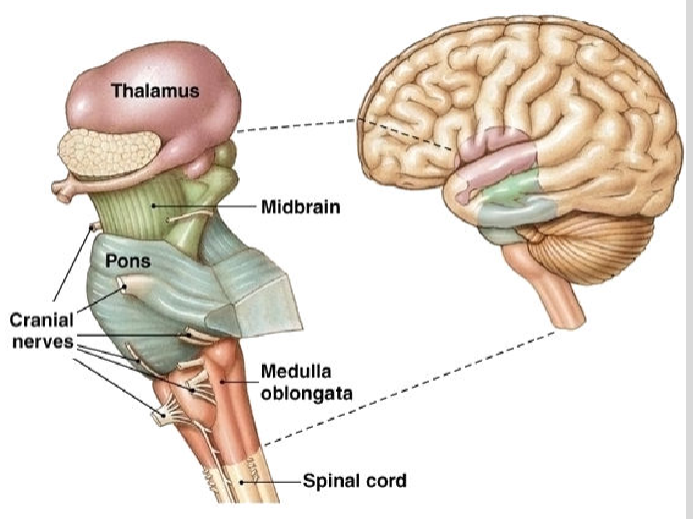
Medulla (Brainstem)
respiration, blood pressure, heart rate, vomiting
Pons (Brainstem)
puts you to sleep
Reticular Formation (Brainstem)
attention, regulates awareness
Cerebellum (Brainstem)
balance and coordination
Thalamus (Brainstem)
receives and processes sensory information before sending it to the rest of the brain
Limbic System
donut-shaped system of neural structures at the border of the brainstem and cerebrum. associated with emotions such as fear, aggression, and drives for food + sex. (EMOTION CENTER)
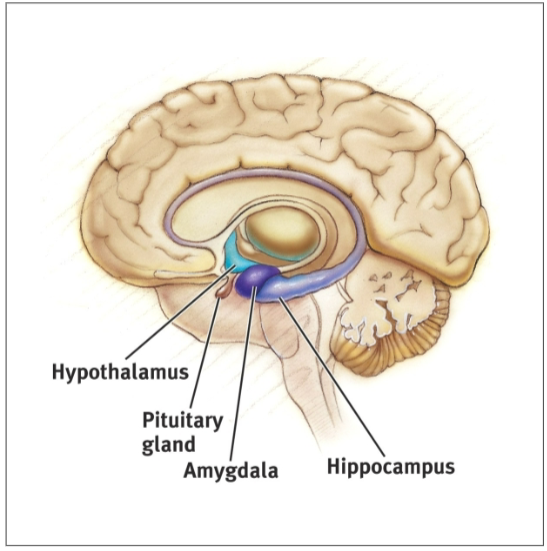
Hypothalamus (Limbic System)
drives for hunger, thirst, sex, and fight-or-flight. also temperature control
Amygdala (Limbic System)
aggression
Hippocampus (Limbic System)
short term memory —> long term memory
Cerebral Cortex
intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres. body’s ultimate control and information processing center
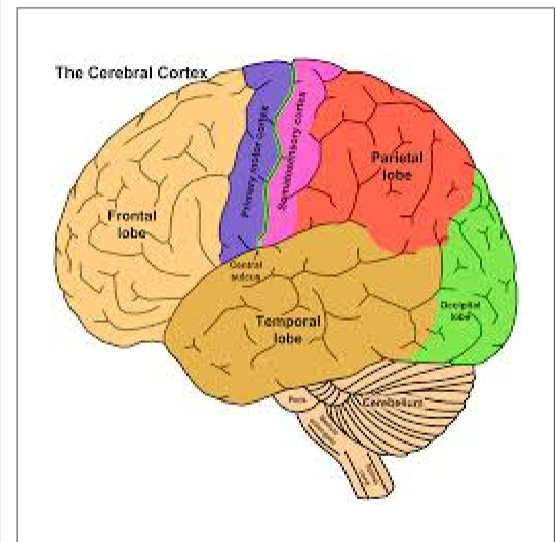
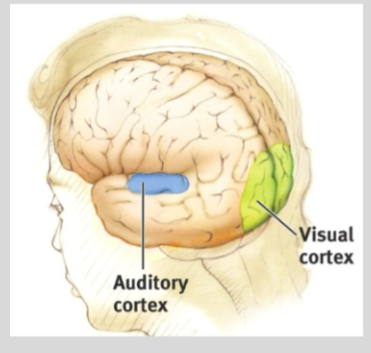
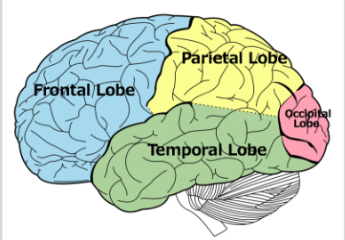
Occipital Lobe (Cerebral Cortex)
visual processing. allows you to see and process stimuli + assign meaning to and remember visuals
Parietal Lobe (Cerebral Cortex)
spatial reasoning. located at the back of the brain, divided into 2 hemispheres. also involved in processing language and mathematics
Frontal Lobe (Cerebral Cortex)
decision making. control panel of our brain, important in emotional expression, problem solving, memory, language, judgement, and sexual behaviors
Temporal Lobe (Cerebral Cortex)
auditory sensory information. key to being able to understand meaningful speech.
Motor Cortex/Strip (Cerebral Cortex)
muscle movement
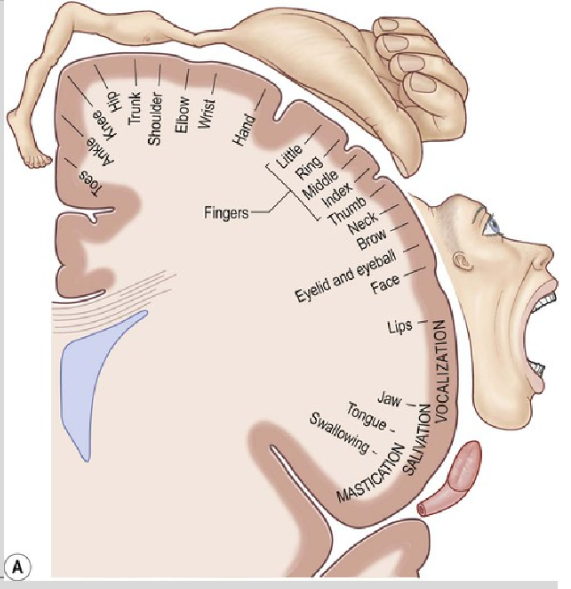
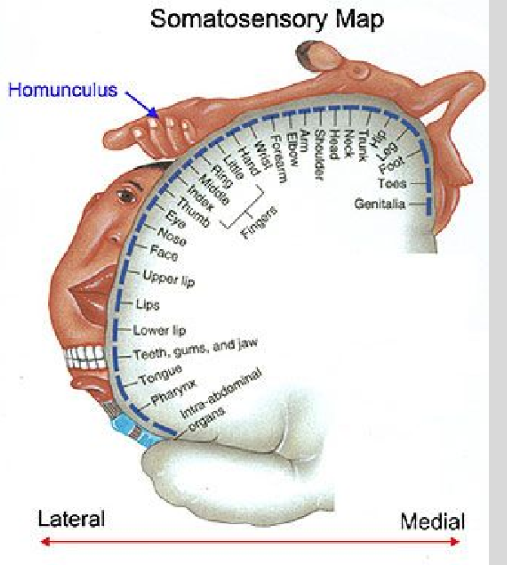
Sensory Cortex (Cerebral Cortex)
Sensation. the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch.
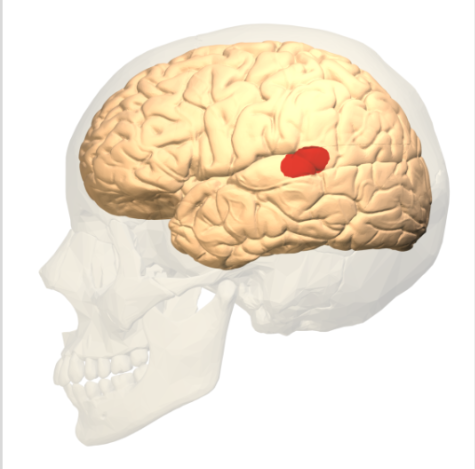
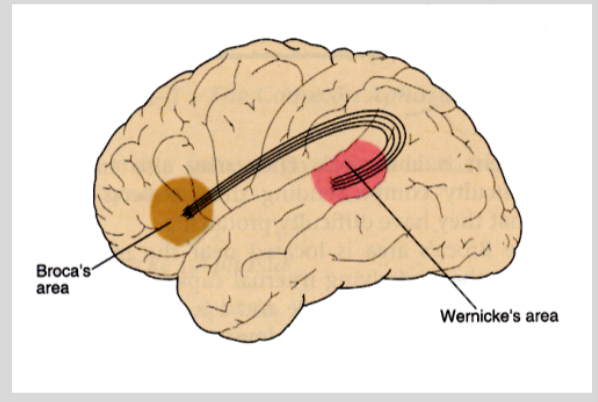
Wernicke’s Area (Cerebral Cortex)
understanding speech. first described by German neurologist Carle Wernicke in 1874
Broca’s Area (Cerebral Cortex)
producing speech. located in the frontal lobe. damaged area can understand but not speak languages
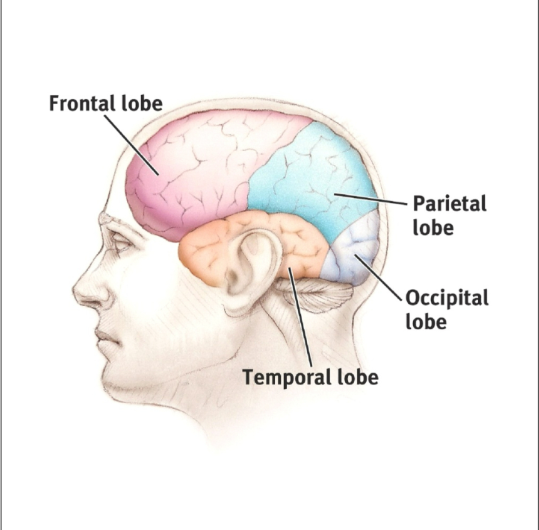
Cortex Structure
Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal (forehead), parietal (top to rear head), occipital (back head) and temporal (side of head)
Aphasia
impairment of language, usually caused by left hemisphere damage to either Broca’s area (impaired speaking) or to Wernicke’s area (impaired understanding)
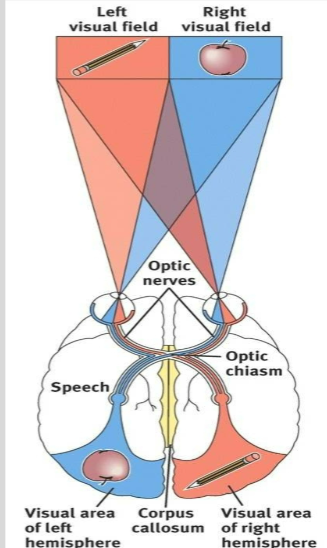
Splitting the Brain
procedure in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers between them (mainly those of the corpus callosum)
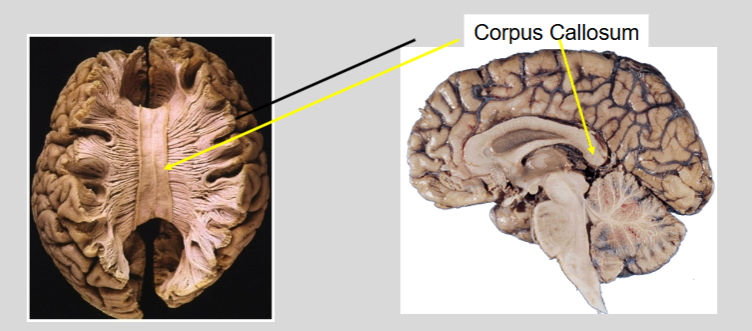
Split-Brain Experiments
Roger Sperry studied patients who had surgery to cut the corpus callosum. Patients appeared quite “normal”, able to do all the everyday things they did before surgery. The real effects could only be determined after isolating information to only one hemisphere at a time.
Split Brain Patients
With the corpus callosum severed, objects presented in the right visual field can be named while objects in the left cannot.
Neuroplasticity
the ability of the brain to form and reorganize synaptic connections, especially in response to learning or experience or following injury
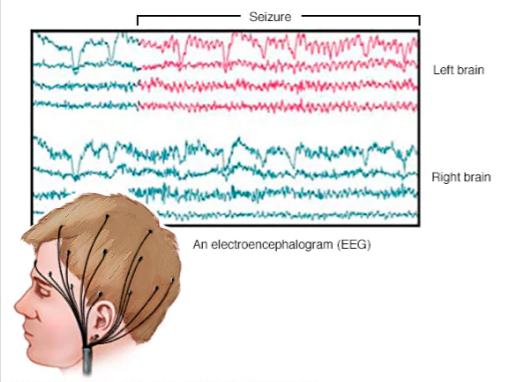
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
noninvasive test that records electrical patterns in your brain. used to help diagnose conditions such as seizures, epilepsy, head injuries, etc.
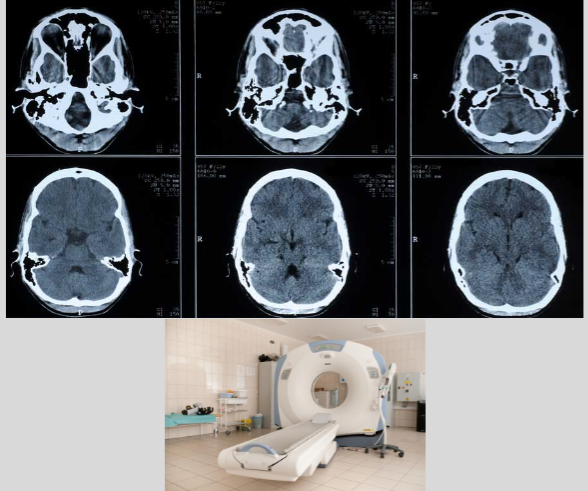
Computerized Tomography (CT Scan)
combines a series of X-ray imaged taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional imaged (slices) of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body
Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan)
small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers collect in areas of higher chemical activity and a special camera + computer evaluates your organ and tissue functions
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI + fMRI)
uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce imaged of body structures
Circadian Rhythm
biological clock of waking and sleeping. cycle is in part a response to light and lasts about 24 hours.
Stage One Sleep
Eyes closed but its easy to wake you. Last 5 - 10 minutes. Preparing to drift off and have periods of dreaminess. Not unusual to experience strange and vivid sensations or a feeling of falling during this stage (hypnogogic hallucinations)
Stage Two Sleep
in light sleep. heart rate slows + body temp drops. body prepares for deep sleep. last about 20 minutes. brain begins to produce short periods of rapid rhythmic brain wave activity (Sleep Spindles)
Sleep Spindles
very short periods of rapid, rhythmic brain wave activity during stage 2 sleep
Stage Three Sleep (NREM)
Deep sleep stage. harder to rouse you. if woken up, you would feel disoriented for a few minutes. body repairs + regrows tissues, builds bone + muscle, and strengthens immune system. deep slow brain waves begin to emerge delta waves). transitional period between light sleep and very deep sleep
Delta Waves
deep, slow brain waves that emerge during stage three (NREM) sleep and stage four sleep
Stage Four Sleep
sometimes referred to delta sleep. a deep sleep that lasts about 30 minutes.
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep
characterized by eye movement, increased respiration rate, and increased brain activity. usually happens 90 minutes after falling asleep. first period of REM last 10 minutes with each next stage getting longer. dreaming occurs and voluntary muscles become paralyzed.
Insomnia
prolonged + abnormal inability to obtain adequate sleep
Sleep Apnea
frequent interruptions of sleep due to breathing problems
Narcolepsy
permanent + overwhelming feelings of sleepiness and fatigue
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
disorder in which you physically act out vivid dreams with vocal sounds and sudden (often violent) arm + leg movements during REM sleep (sometimes called dream-enacting behavior)
Somnambulism (Sleep Walking)
usually occurs one to two hours after falling asleep. often a random, harmless event
Night Terrors
Occurs during stage 4 sleep. screaming, sweating, high pulse rate, and breathing. no memory of it occuring
Parasomnias
category of sleep disorders that involve abnormal movements, behaviors, emotions, perceptions, and dreams that occur while falling asleep, sleeping, between sleep stages, or during arousal from sleep
Activation-Synthesis Theory of Dreaming
(Hobson) REM sleep activates brain stem circuits that trigger limbic system activity involving emotions, sensations, and memories, which the brain then interprets and synthesizes into meaningful narratives we experience as dreams
Consolidation Theory of Dreaming
dreaming is influenced by the consolidation of memory during sleep. following encoding, recently formed memory traces are gradually stabilized and reorganized into a more permanent form of long-term storage