2.2 endomembrane system
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
name the non membrane bound organelles
cell membrane
cell wall
ribosomes
cytoplasm
cytoskeleton
centriole and spindle fibers
flagella and cilia
what is the cell membrane?
phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the entire cell
regulates what comes into and out of the cell and protects the cell interior from the extracellular space
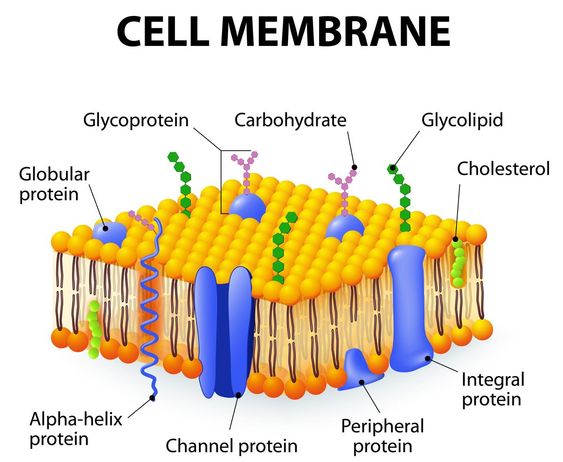
what is the cell wall?
rigid structure made of complex carbohydrates found in plants, fungi and bacteria
provides structure to cells, as well as acting as a “permeability barrier for some substances to the internal environment.
what are ribosomes?
found in all living organisms
composed of protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Ribosomes “read” messenger RNA (mRNA) to synthesize proteins
can be found
attached to rough ER
free floating in the cytoplasm
what is cytoplasm?
liquid made of water, salt and other dissolved nutrients in the cell
helps both Pro and Eu maintain cell shaoe
site of many metabolic chemical reactions because it is water based
what is the cytoskeleton?
helps maintain shape of animal cells
parts of cytoskeleton help vesciles get transported around the cell
3 parts: actin, microtubules, actin filaments
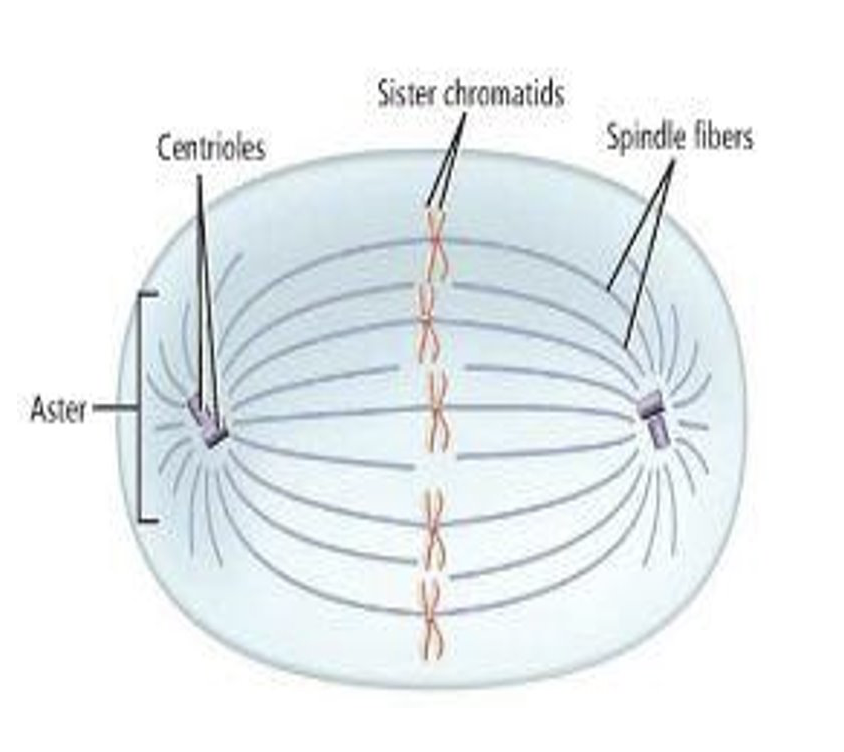
explain centriole and spindle fibers
centrioles make spindle fibers during mitosis and meiosis
spindle fibers help pull chromosomes apart during mitosis and meiosis
fun fact: centrioles form the flagellar tail of sperm cells!
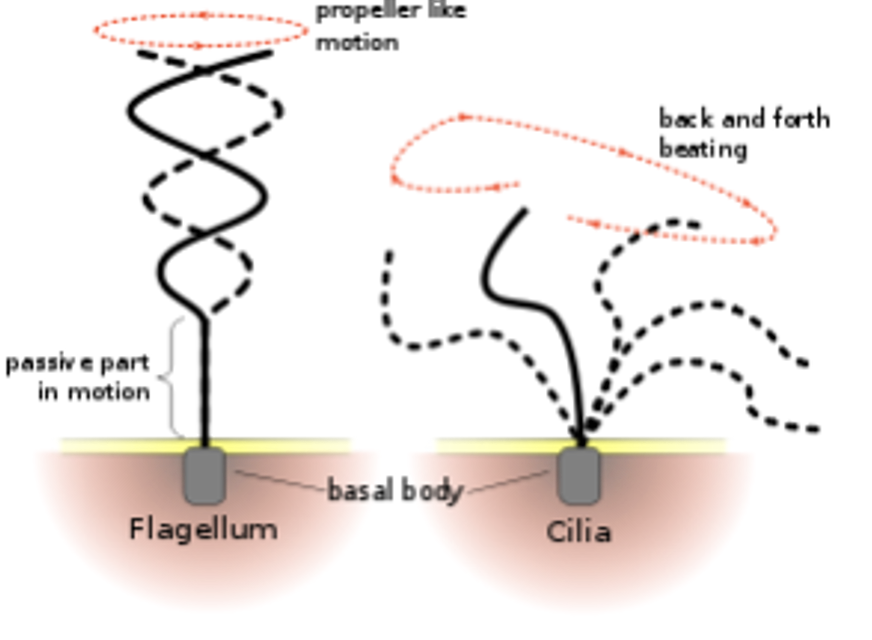
what is flagella and cilia?
both flagella and cilia help move cells around
flagella are LONGER and move like a propeller
cilia are much shorter and move in a back and forth-beating motion
name membrane bound organelles
nucleus
nucleolus
smooth er
rough er
golgi
peroxisomes and lysosomes
vacuole
mitochondrion
chloroplast
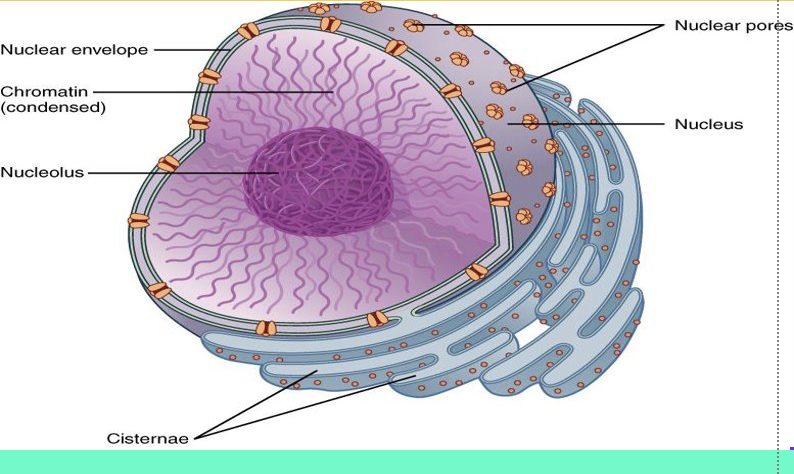
what is the nucleus?
surrounded by a double nuclear membrane that houses and protects DNA from denaturation
also the site of transcription which is when DNA is transcribed into mRNA
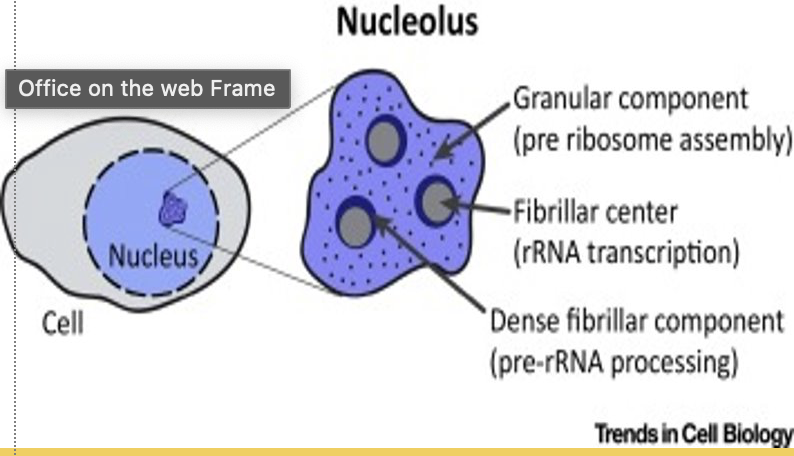
what is the nucleolus?
site of ribosome synthesis in the cell
also responsible for synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
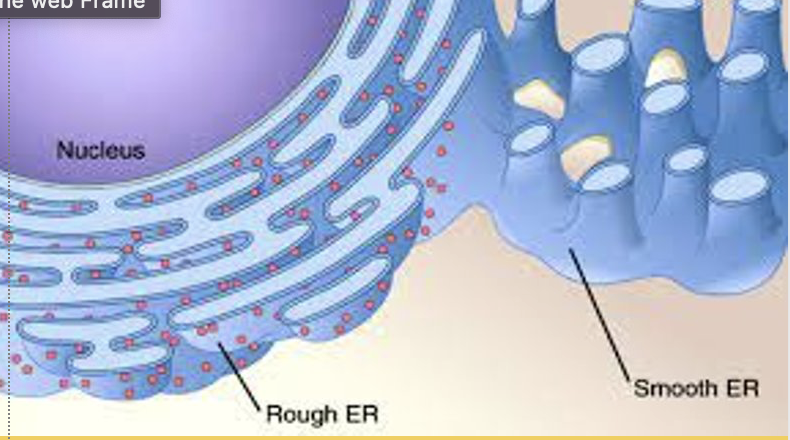
what s smooth ER?
responsible for lipid/hormone synthesis and detoxification of cell waste
synthesized lipids polymers and hormones get sent to the golgi apparatus
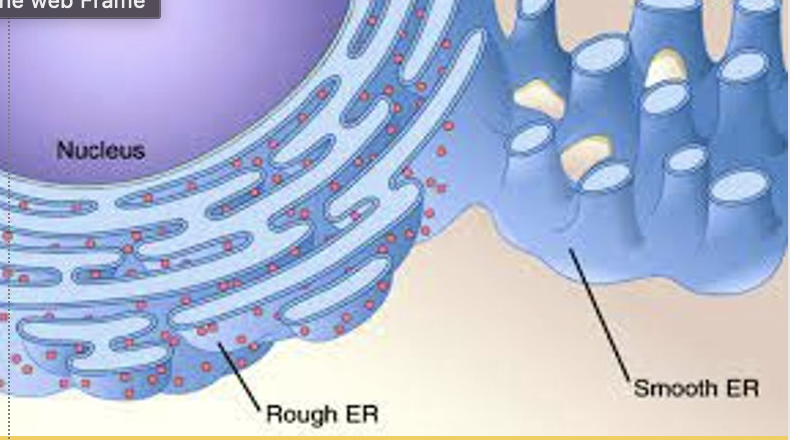
what is rough ER?
slightly folded (high SA) organelle that is continuous (connected) with the nucleus and has ribosomes attached
responsible for packaging proteins and sending them to the golgi apparatus
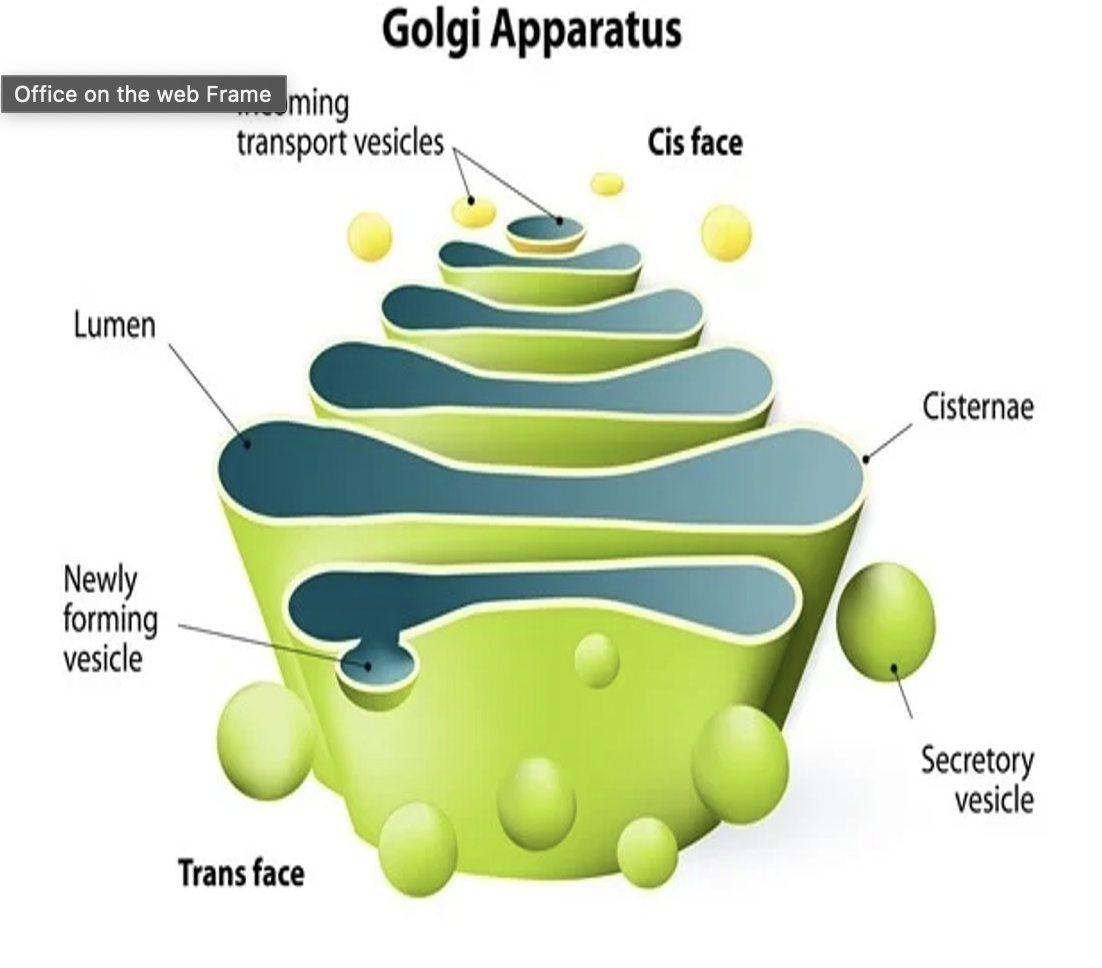
what is the golgi apparatus?
similar to a post office for the cell
responsible for
helping folded and modify proteins
packaging proteins/lipids into vesicles
sending these vesicles to their intended intra or extracellular destination
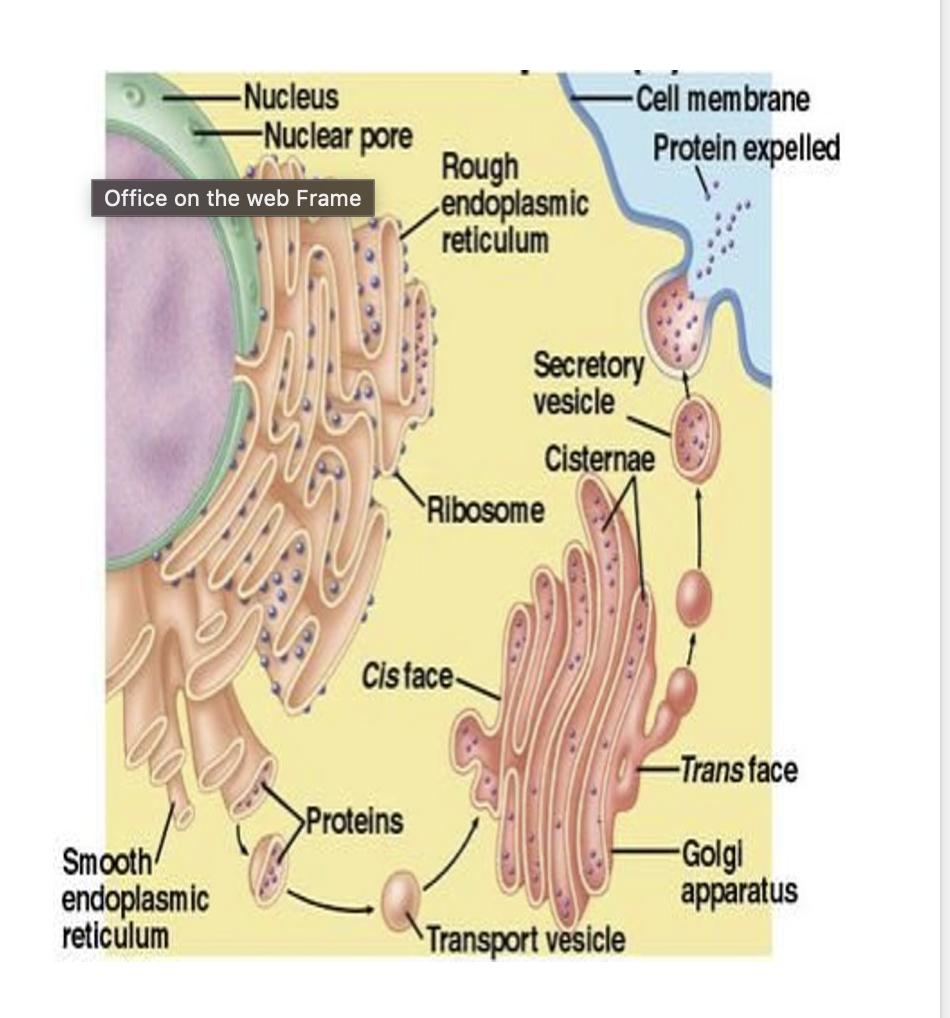
explain protein secretion from the cell
REGVC (REGular Video Chat)
what are peroxisomes?
responsible for lipid hydrolysis and also using catalase (an enzyme) to break down hydrogen peroxide (toxic to the cell)
lipids are broken down into fatty acid monomers, which are sent to the mitochondrion to help generate ATP
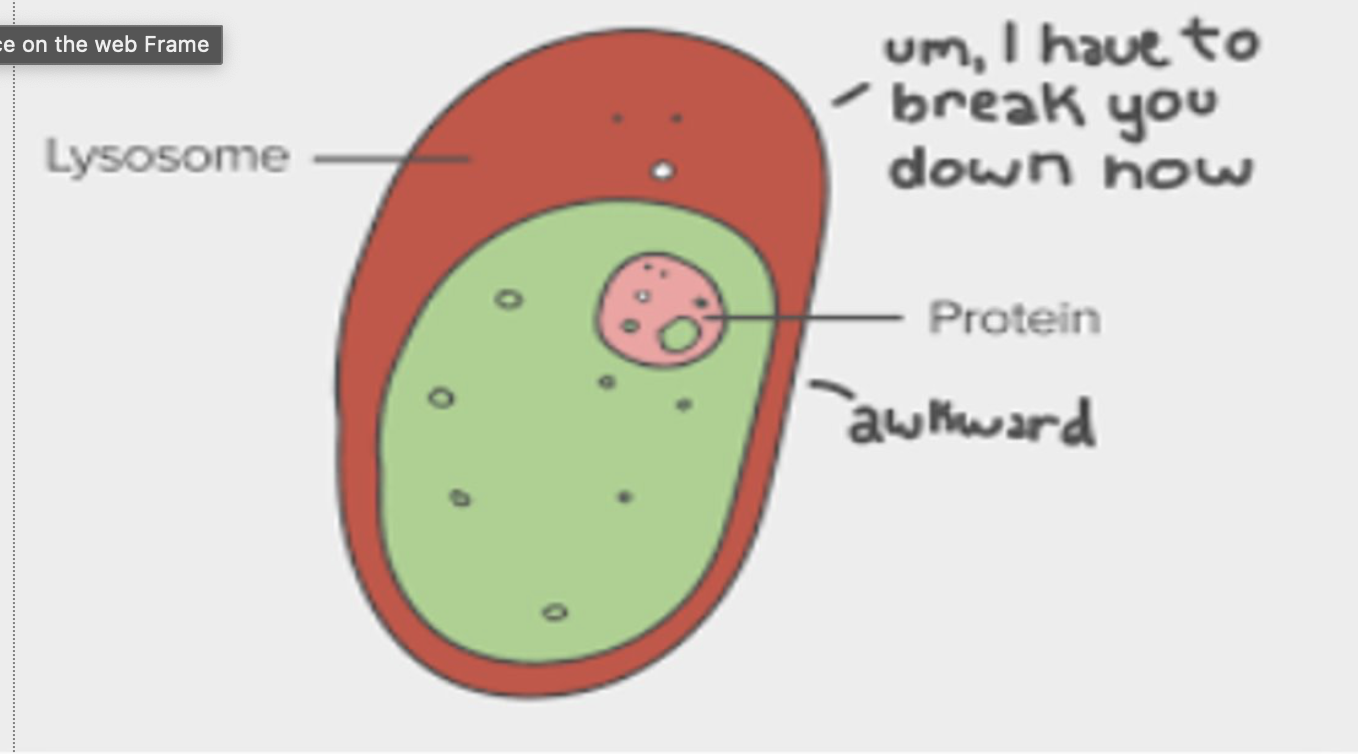
what are lysosomes?
Lipid bubble full of hydrolytic enzymes that break down cell waste and denatured proteins into their monomers
Also involved in apoptosis (programmed cell death- if infected by disease or too self, will self destruct)
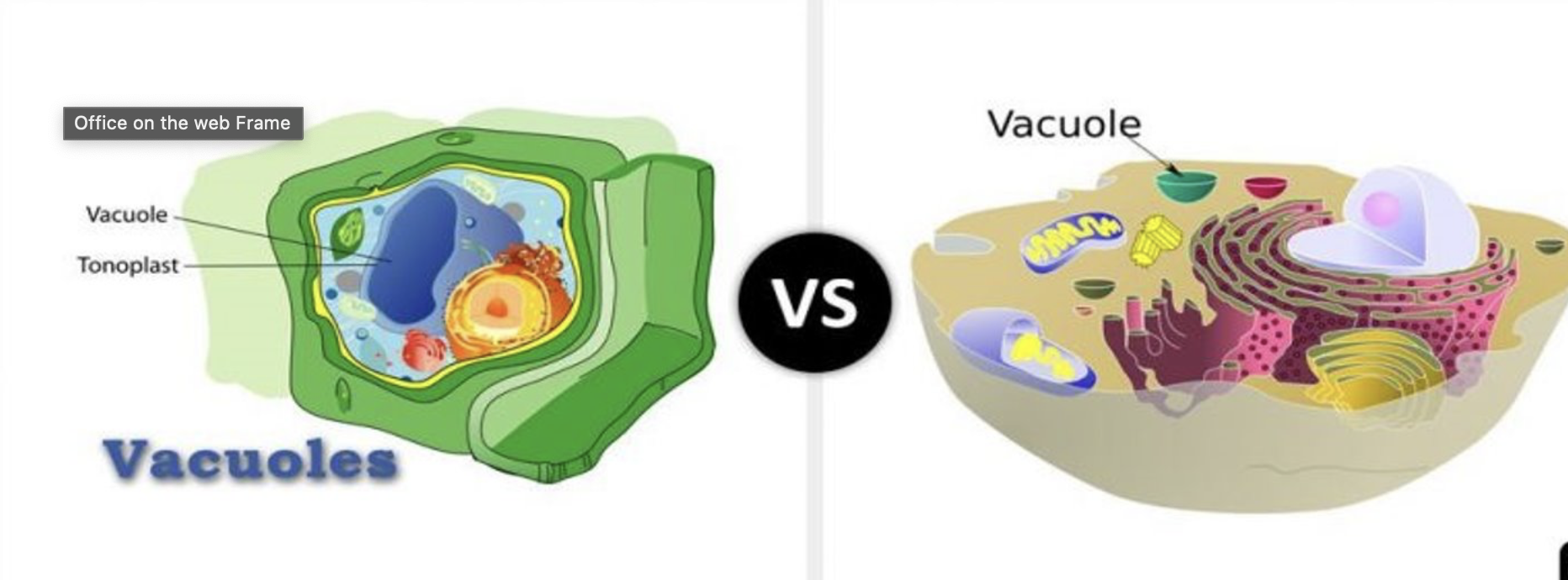
what is vacuole?
responsible for storing and releasing fluids/biomolecules
also store cellular waste products they can be broken down
Vacuoles in plants are very, very large and help maintain plant cell shape/turgor pressure
storage of water
Vacuoles in animals are usually very small
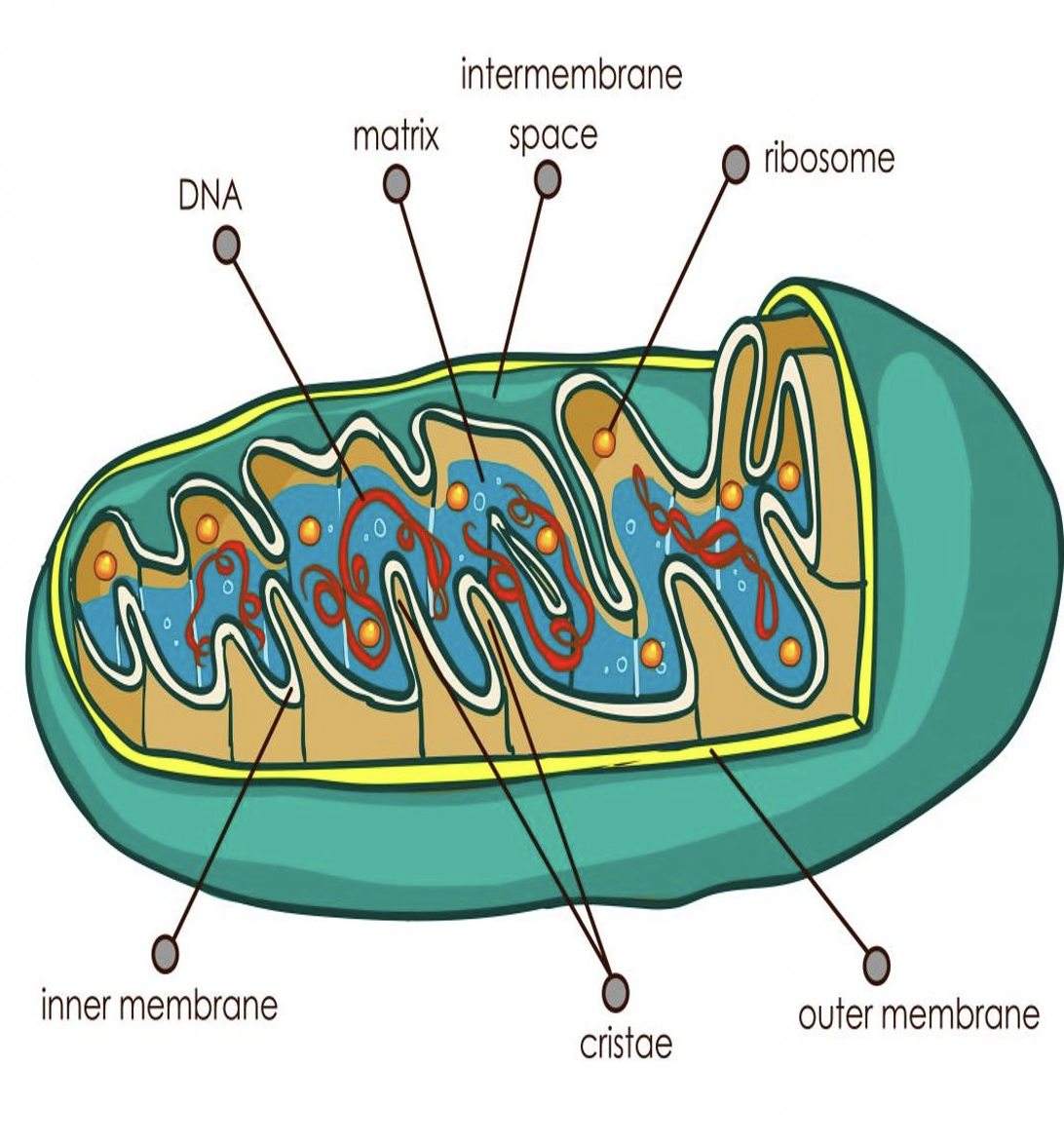
what is mitochondrion?
has 2 membranes, which allows for compartmentalization of diff chemical rxns.
outer mitochondrial membrane
smooth, not folded
inner mitochondrial membrane
folding at inner membrane increase SA to allow for more/faster AT production
responsible for some of the processes that make ATP
citric acid cycle (in matrix)
oxidative phosphorylation (on the inner membrane)
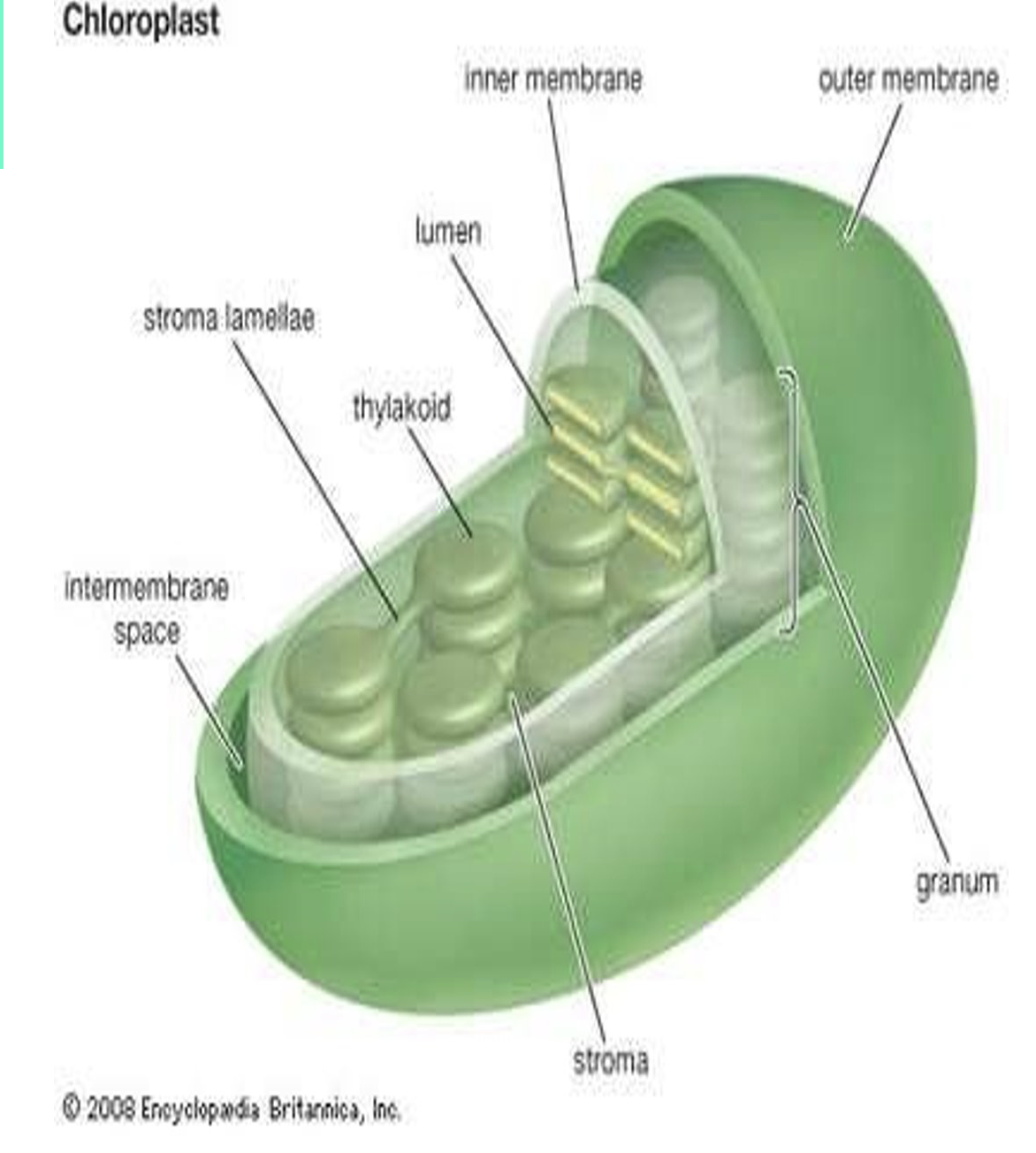
what is chloroplast?
has 2 membranes, which allows for compartmentalization of different chemical reactions
internal anatomy is arranged in stacks of thylakoids membranes called grana
multiple thylakoids increases SA so more rxns can occur