Fertilization
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
T/F: semen deposition site does not vary by species
False
T/F: there is correlation between the volume of ejaculate and length of ejaculation
true
where does fertilization occur?
ampulla
What catches the COC?
fimbria of infundibulum
There are 2 phases of sperm transport to the egg. explain rapid transport phase
sperm reach site of fertilization, but not on their own accord and did not undergo capacitation so they cannot fertilize
What are the ways sperm is transported in rapid transport phase?
1. estradiol, ovary contraction
2. prostaglandins in seminal fluid
3. breeding triggers oxytocin release which triggers contractions
There are 2 phases of sperm transport to the egg. explain sustained transport phase
relies on uterine contractions and sperm motility
CAN fertilize
Why does the sustained transport phase occur?
due to barriers at the vagina, cervix, oviduct, and fertilization
What are 3 ways the vagina itself acts as a barrier?
1. retrograde transport
2. acidic pH
3. phagocytosis by leukocytes
what induces phagocytosis in vagina?
during estrus there are high levels of estradiol which send neutrophils to the vagina which attack foreign materials
T/F: the acidic environment of the vagina is more so present in humans than other primates
true due to colonization of microbiome in humans
Semen is always divided into fractions (2 or 3) and seminal fluid is very (acidic/basic)
basic
Where is the transport of sperm slowed down?
cervix due to mucus and crypts to remove non-motile and abnormal sperm
During estrus what are the 2 types of cervical mucus? explain viscosity and where they are produced
sialomucin- low viscosity, produced in basal area
sulfomucin- high viscosity, apical portions
why do sperm need to be slowed down prior to entry in the uterus?
sperm must reside in female repro tract for a minimum amount of time to obtain ability to fertilize ie begin capacitation
T/F: more shallow semen deposition = more shallowsemen capacitation
true
What is happening to sperm during capacitation? (hint: what does sperm need to be able to do to bind to egg?)
remove surface molecule on sperm head to bind to egg and increase motility
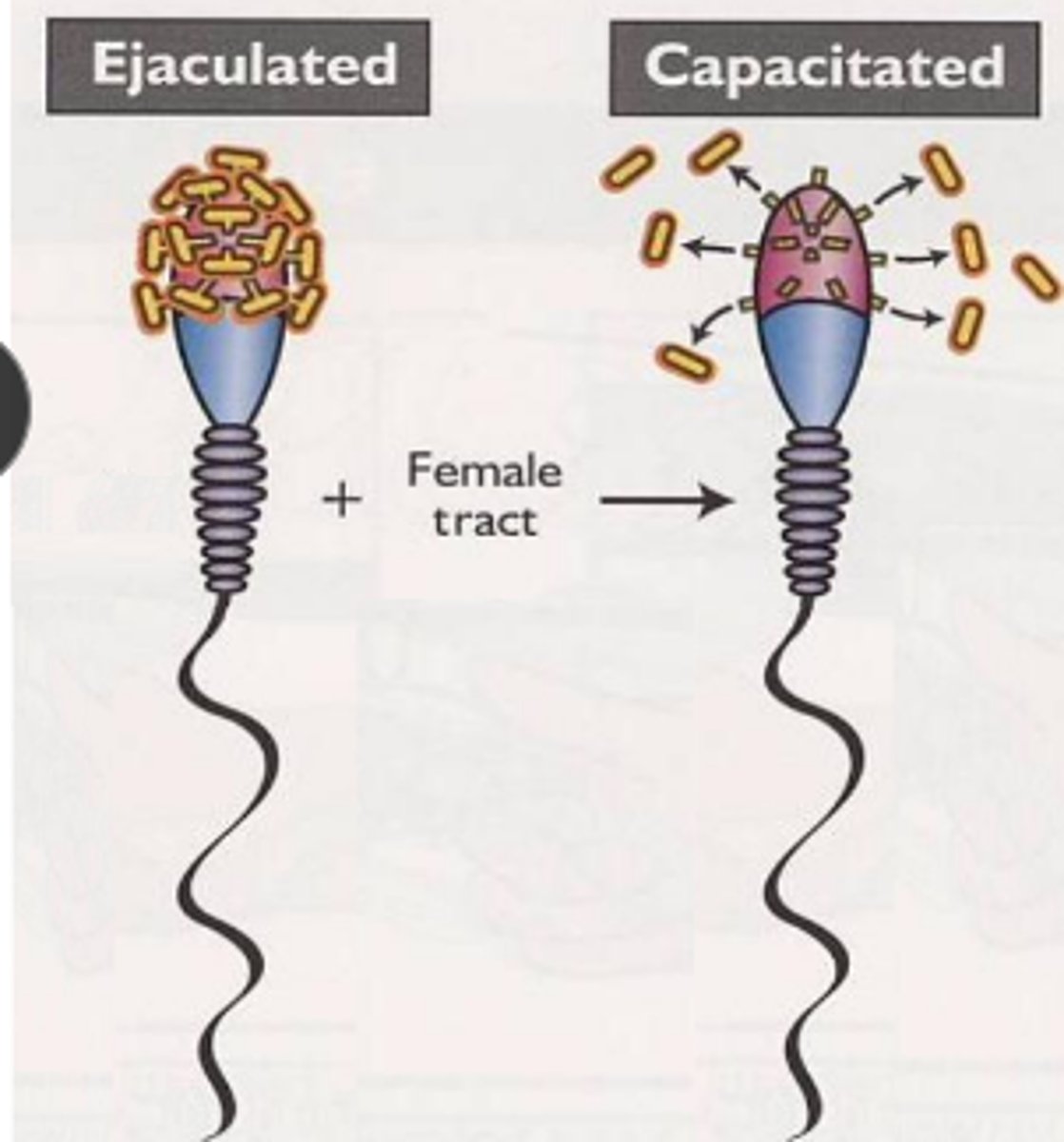
where does capacitation end?
oviduct
What induces the acrosome reaction?
spermatozoa binding to zona pellucida
The acrosome slowly releases enzymes after binding with the purpose of what?
to chew through cumulus oocyte complex
While we only have one spermatozoa that actually gets through COC how does it penetrate the ZP?
plasma membrane of sperm has zona pellucida binding proteins
ZP1/2 = structural integrity
ZP3 = binds proteins on sperm
which ZP binding proteins induces the acrosome reaction?
ZP3
What occurs following the acrosome reaction?
ZP penetration
sperm egg binding
fusion
The ZP remains intact from fertilization to the blastocyst stage. How is polyspermy prevented?
eggs transport cortical granules after ovulation and then once fertilized the cortical granules contents are hardened to the zone
The sperm nucleus is well protected during fertilization by disulfide crosslinks. However once sperm fuses with oocytes the nuclear material must be freed up. What does this?
glutathione from oocyte breaks down disulfide crosslinks to decondense sperm nucleus and allow for formation of male pronucleus
___________ insemination bypasses the cervix to deposit semen into the uterus
transcervical
mare, cow, sheep
____________ insemination deposits semen into cranial half of cervix
intracervical
sow
_____________ insemination deposits semen into cranial vagina
intravaginal
dog, cat