carbon cycle- greenhouse effect
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
natural greenhouse effect
the earth climate is driven by incoming shortwave solar radiation:
around 31% of carbon Is reflected by clouds and gases in the atmosphere
the remaining 69% is absorbed by the earths surface and oceans
69% of surface absorption is reradiated to space as long wave radiation
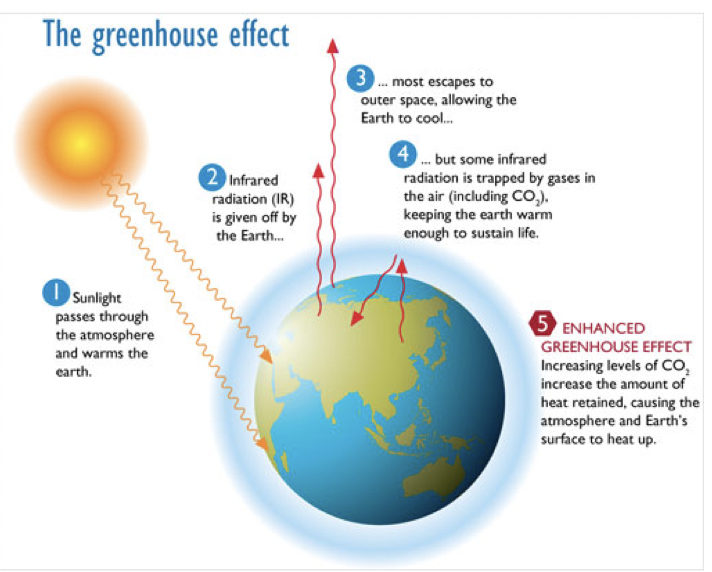
natural greenhouse effect
constant levels of CO2 help maintain stable average temperatures worldwide. Before The Industrial Revolution, the natural greenhouse effect was constant.
the slow carbon cycle, volcanism, and sedimentation have been fairly constant over the last few centuries
natural exchanges between the slow and fast sections of the carbon cycle were relatively small
there were small variations in atmospheric CO2 up until the late 19th century
Anthropogenic interference / The enhanced greenhouse effect
since the 1750s, global concentrations of the greenhouse gases like CO2 & CH4 have increased by more than 25%. Since the 1980s 75% of carbon emissions have come from burning from fossil fuels
human activities have led to more carbon being released into the atmosphere and less being absorbed
human activities
land use change: accounts for a tenth of carbon release annually and impacts on short-term stores: example farming practices in the Amazon around 70% of deforestation is for cattle ranching
fertilises: significant source of greenhouse gases as well as rice pads fields.
deforestation: in total it accounts for about 20% of all global greenhouse emission
urbanisation: it affects the local and carbon cycle by replacing negation and covering soils. urban areas occupy 2% of the worlds land mass, but account for 97% of all human caused global CO2 emissions
combustion of fossil fuels
implications of the Enhanced GHE
temperature- the albedo effect will determine the temperature of a location. Snow reflects solar radiation whereas dark forest absorb the most solar radiation
climate- rising levels of CO2 in the atmosphere are believed to be the main contributor to an increase in average global temperatures.
ecosystems
the two biomes most at risk are the Arctic and the coral ecosystems
marine organisms are also at risk. They are threatened with the low oxygen labels and high rates of acidification, and sea level rise.
melting permafrost release methane and carbon dioxide. leading to further global warming and melting of snow and ice, establishing a positive feedback loop
hydrological cycle
increased rate of evaporation could lead to more moisture being held in the atmosphere rather than in the ocean
increase in surface permafrost temperatures
less ice and glacier storage
change in capacity of terrestrial ecosystems
change in river discharge- increase risk of flooding