AP Psycholoy - Cognition 25 (Perception, Memory, Thinking, IQ)
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
Charles Spearman
used and developed factor analysis (identifies clusters of related items), came up with the idea of a general intelligence (g factor)
general intelligence (g)
a general intelligence factor that according to Spearman and others underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
Howard Gardner
He said abilities are best classified into 8 intelligence including spatial, musical, logical-mathematical, linguistic, naturalist, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and bodily-kinesthetic.
savant syndrome
condition where a person has limited mental ability but is exceptional in one area
grit
passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals
analytic intelligence
(academic-problem-solving)
traditional intelligence traits, part of Sternberg's Triarchic Theory
creative intelligence
reacting adaptively to novel situations and generating novel ideas, part of Sternberg's Triarchic Theory
practical intelligence
required for everyday tasks where multiple solutions exist, part of Sternberg's Triarchic Theory
emotional (social) intelligence
perceiving emotions
understanding emotions
managing emotions
using emotions
mental age (MA)
an individual's level of mental development relative to that of others
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
most widely used intelligence test; contains verbal and performance (nonverbal) subtests
performance subtest
on the WAIS test, include: spatial relations, perceptual skills, and speed of thinking
verbal subtest
on the WAIS test, include: language based and abstract cognitive skills
what IQ measures
a person's cognitive ability compared to population at large
mental speed and span of your working memory

achievement test
a test designed to asses what a person has learned or aquired. EX: Driver test
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance,
aptitude is the capacity to learn
standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group (Representative sample)
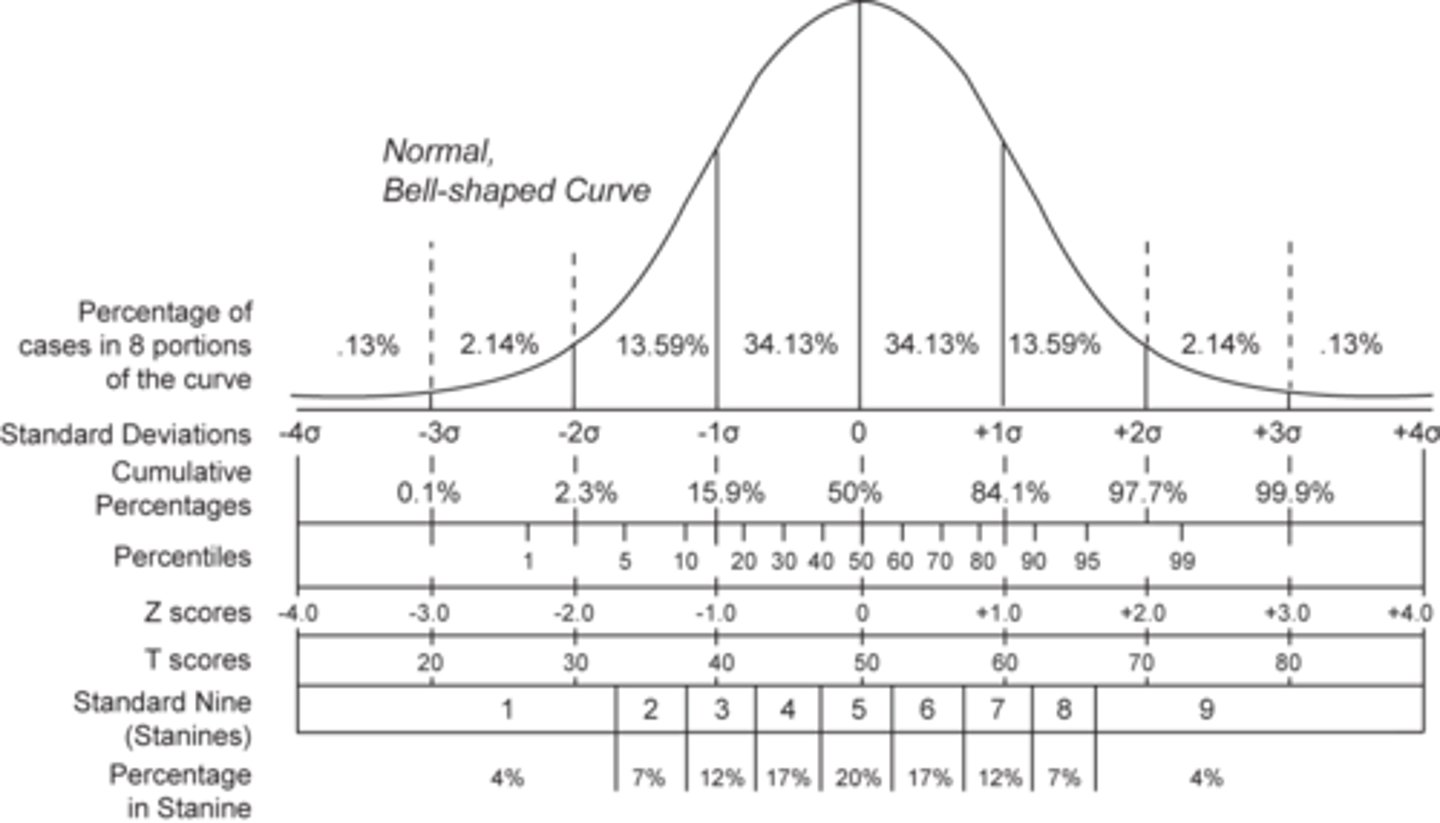
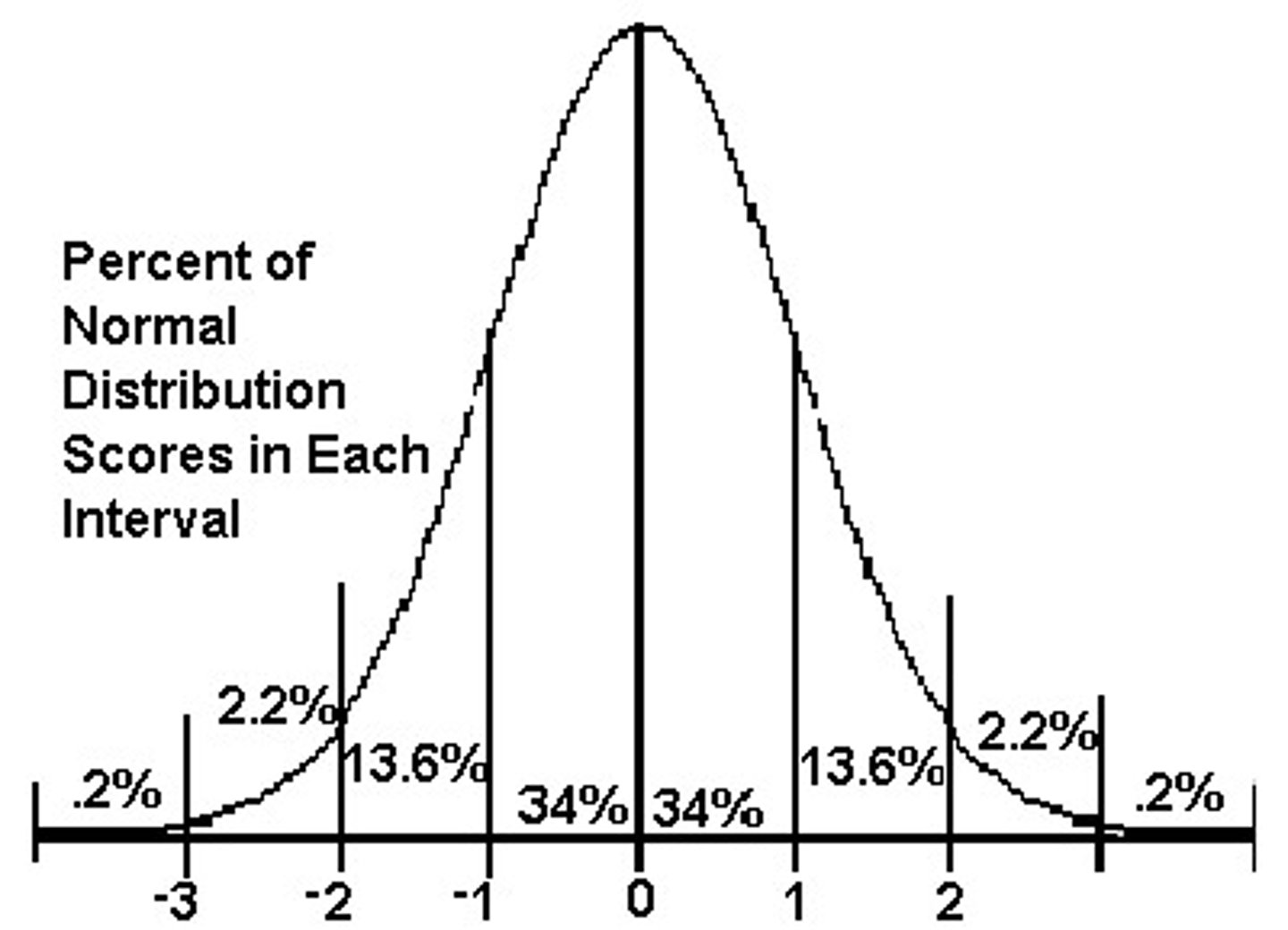
form a normal distribution or bell curve
68%
Amount of people with IQs between 85 and 115 (one SD of the mean)
95%
Amount of people with IQs between 70 and 130 (two SD of the mean). Above 130 = genius, below 70 = intellectual disability
The Flynn Effect
intelligence scores have risen throughout the last 100 years or so (due to environment)
reliability
when it yields consistant results
split- half reliability
dividing the test into two equal halves and assessing how consistent the scores are
test-retest reliability
using the same test on two occasions to measure consitency
validity
the extent to which a test measures what it is supposed to meaure
predictive validity
the extent to which test score forecasts future behaviors or results
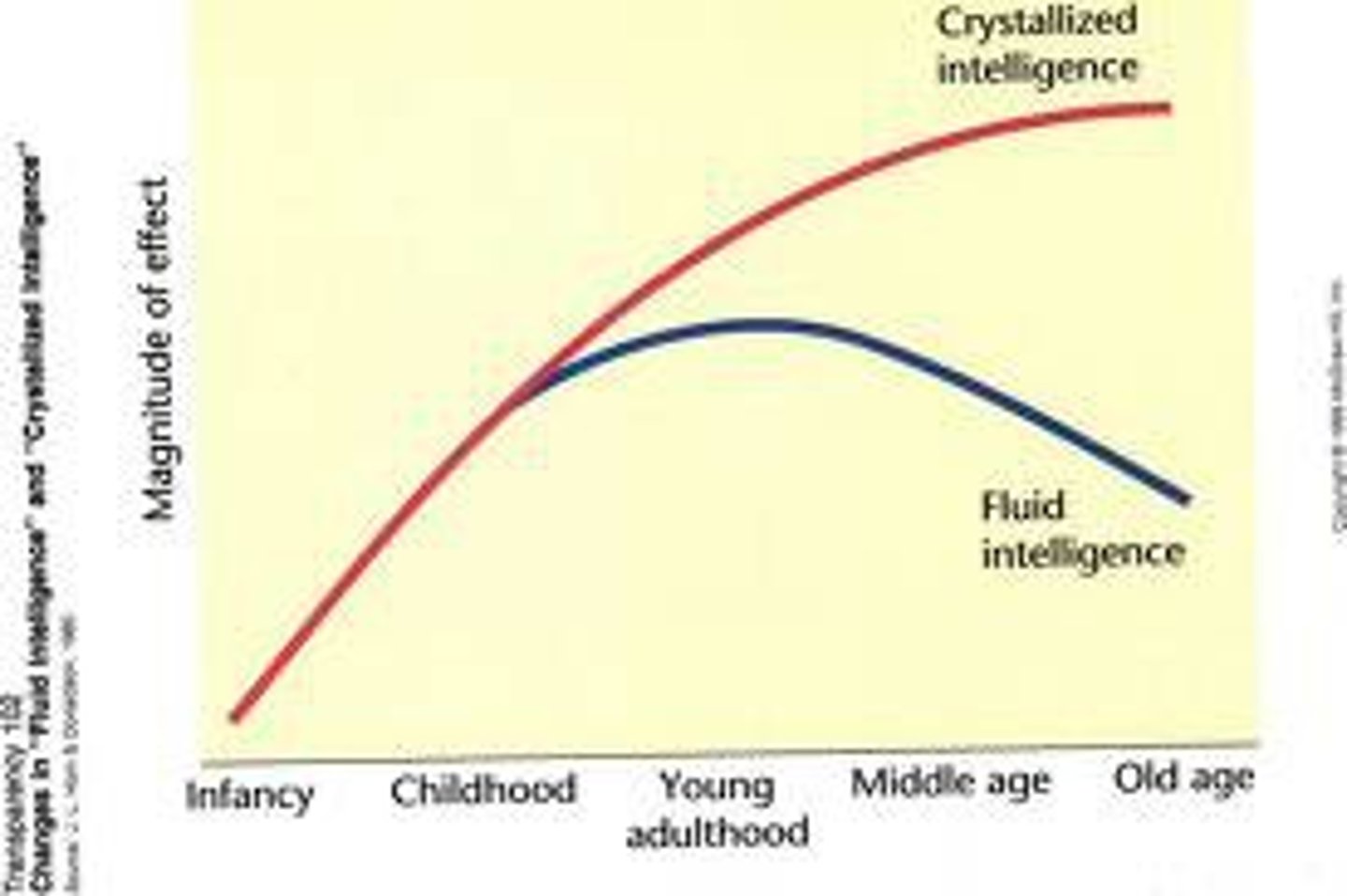
crystallized intelligence
our accumulated knowledges reflected in vocabulary and analogies tests
increases with age
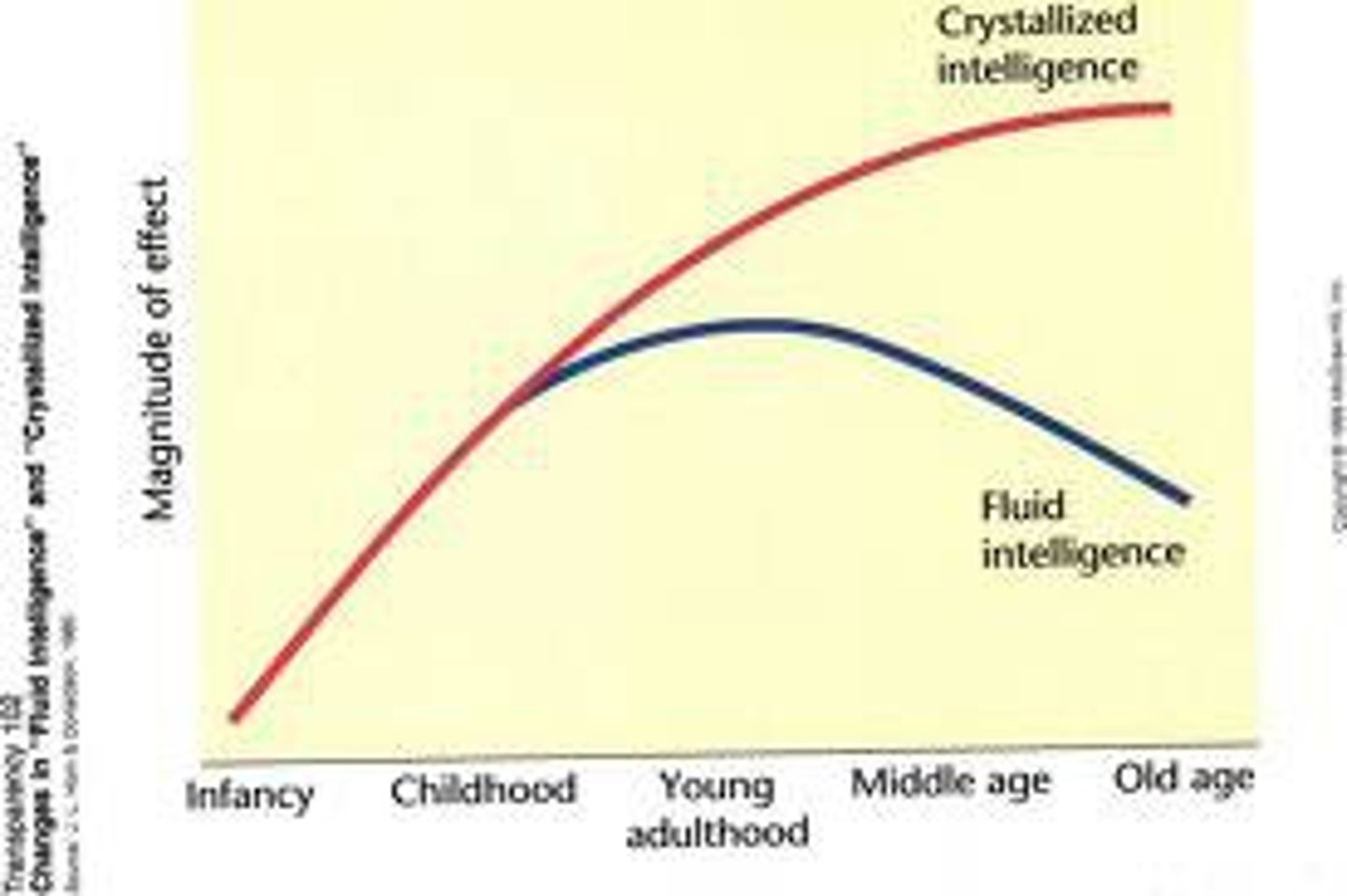
fluid intelligence
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly, as when solving novel logic problems
decreases with age
intellectual disability
limited mental ability
intelligence score of 70 or below
formerly referred to as mental retardation
High Intelligence
typically 130 IQ and above
gifted education programs
percentile rank
percentage of scores that fall below a given score
heritability
proportion of variation among individuals that we can attribute to genes
stereotype threat
a self-confirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
Sternberg's Triarchic Theory
This theory holds that there are three types of intelligence.
divergent thinking
expands the number of possible problem solutions (creative thinking that diverges in different directions)
convergent thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
Chronological age (CA)
The number of years since the individual's birth. Actual Age.
fixed mindset
the idea that we have a set amount of an ability that cannot change
growth mindset
the idea that our abilities are malleable qualities that we can cultivate and grow
stereotype lift
awareness of positive expectations can actually improve performance on tasks
prototype
a mental image or best example of a concept
Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people that have similar characteristics
Algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem. Takes time.
Heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind (perhaps because of their vividness), we presume such events are common
representative heuristic
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
functional fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions; an impediment to problem solving
Fixation
the inability to see a problem from a new perspective, by employing a different mental set
Framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.
Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of certain associations, thus predisposing one's perception, memory, or response
Gambler's Fallacy
the belief that the odds of a chance event increase if the event hasn't occurred recently
sunk cost fallacy
a framing effect in which people make decisions about a current situation based on what they have previously invested in the situation
belief perseverance
clinging to one's initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations
bottom-up processing
analysis that begins with the sensory receptors and works up to the brain's integration of sensory information
perceptual set
a readiness to perceive a stimulus in a particular way
Gestalt psychology
a psychological approach that emphasizes that we often perceive the whole rather than the sum of the parts
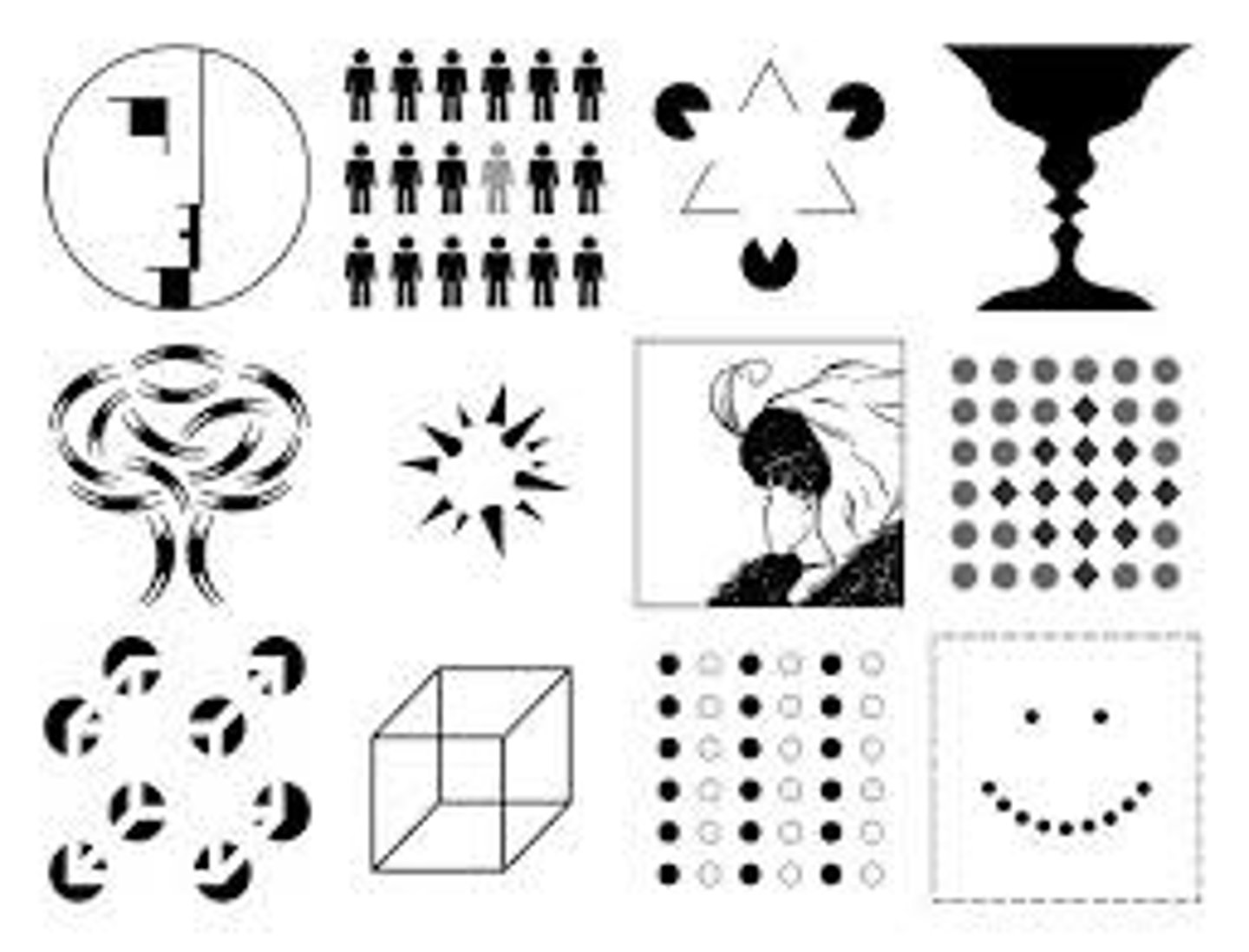
closure
the tendency to complete figures that are incomplete
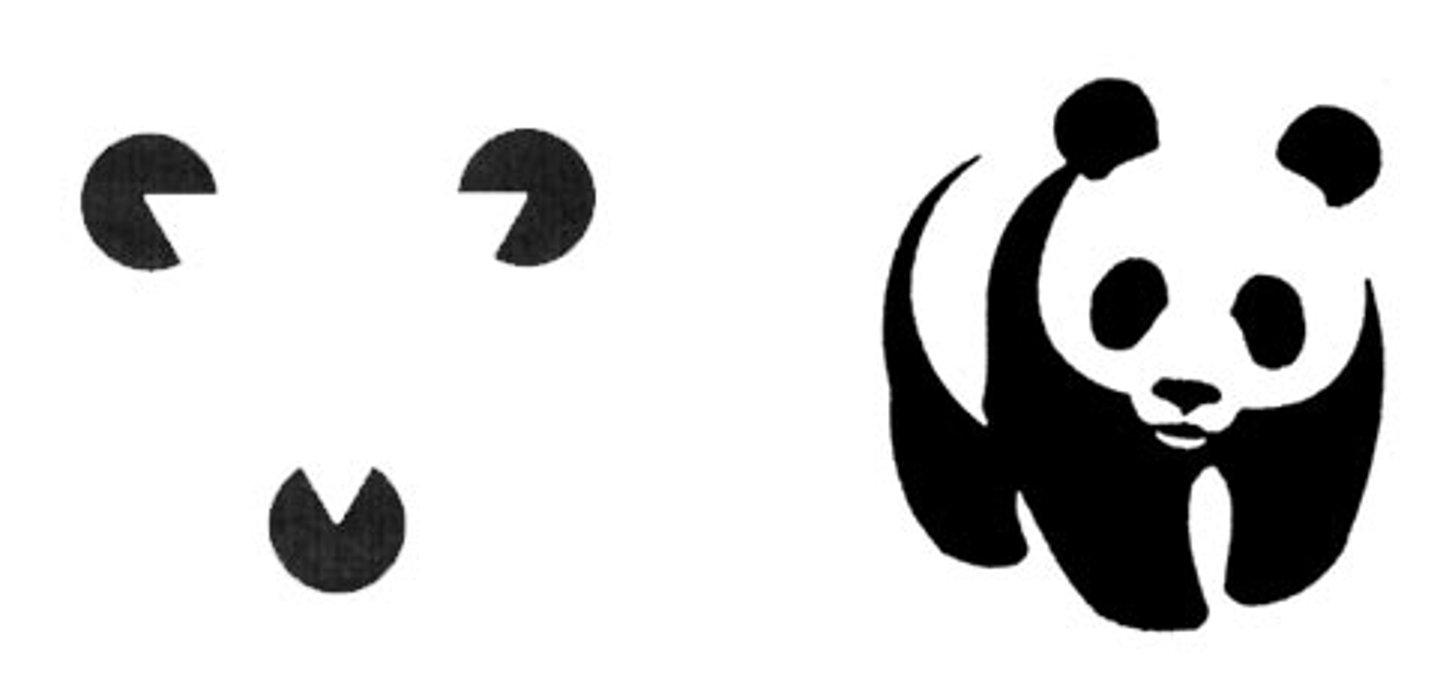
figure-ground
the organization of the visual field into objects (the figures) that stand out from their surroundings (the ground).

proximity
objects that are near/close to eachother are in a group.
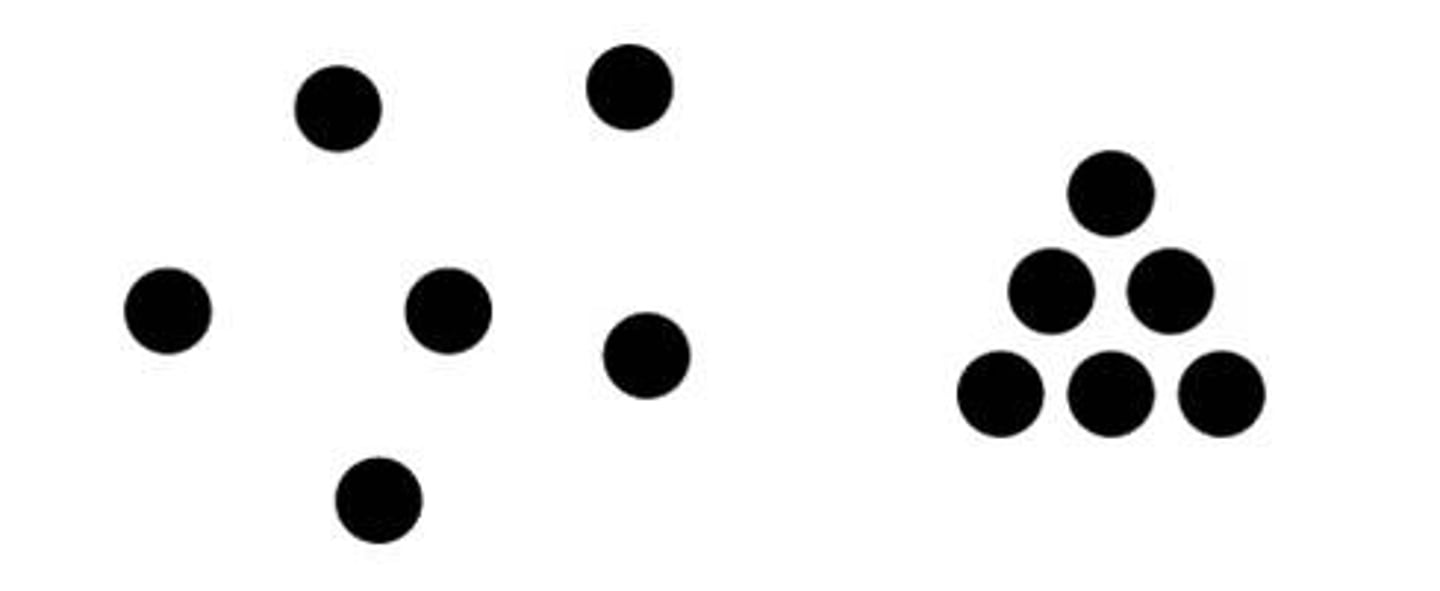
similarity
the tendency to perceive things that look similar to each other as being part of the same group
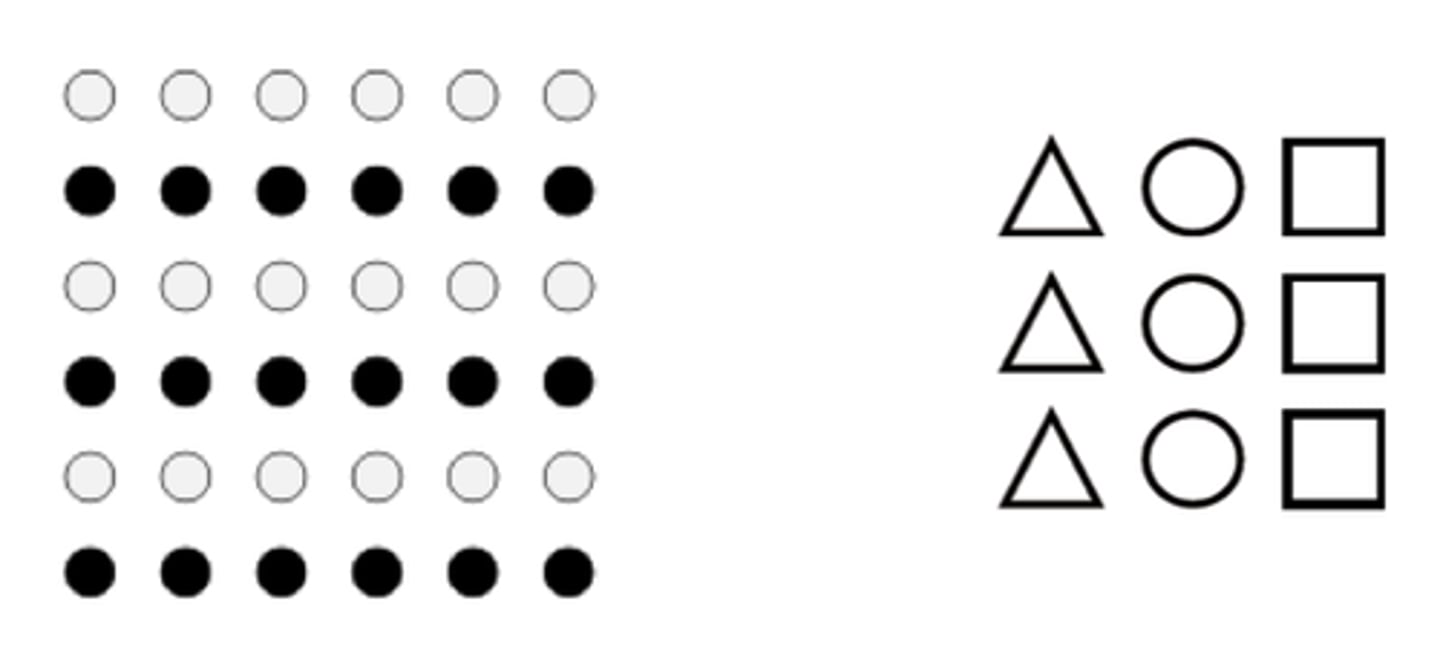
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus

inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
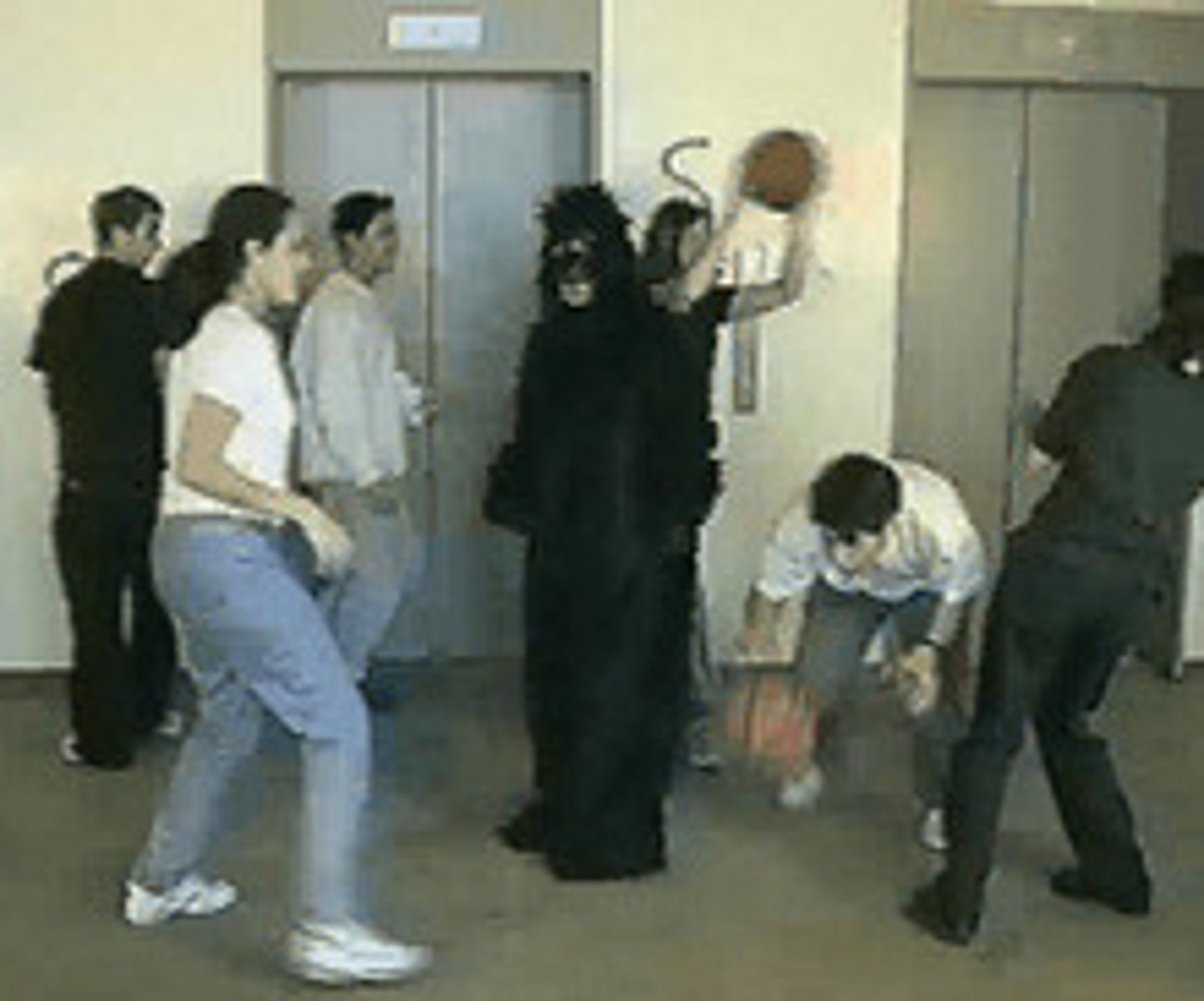

change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
binocular depth cues
clues about distance based on the differing views of the two eyes
retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance—the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
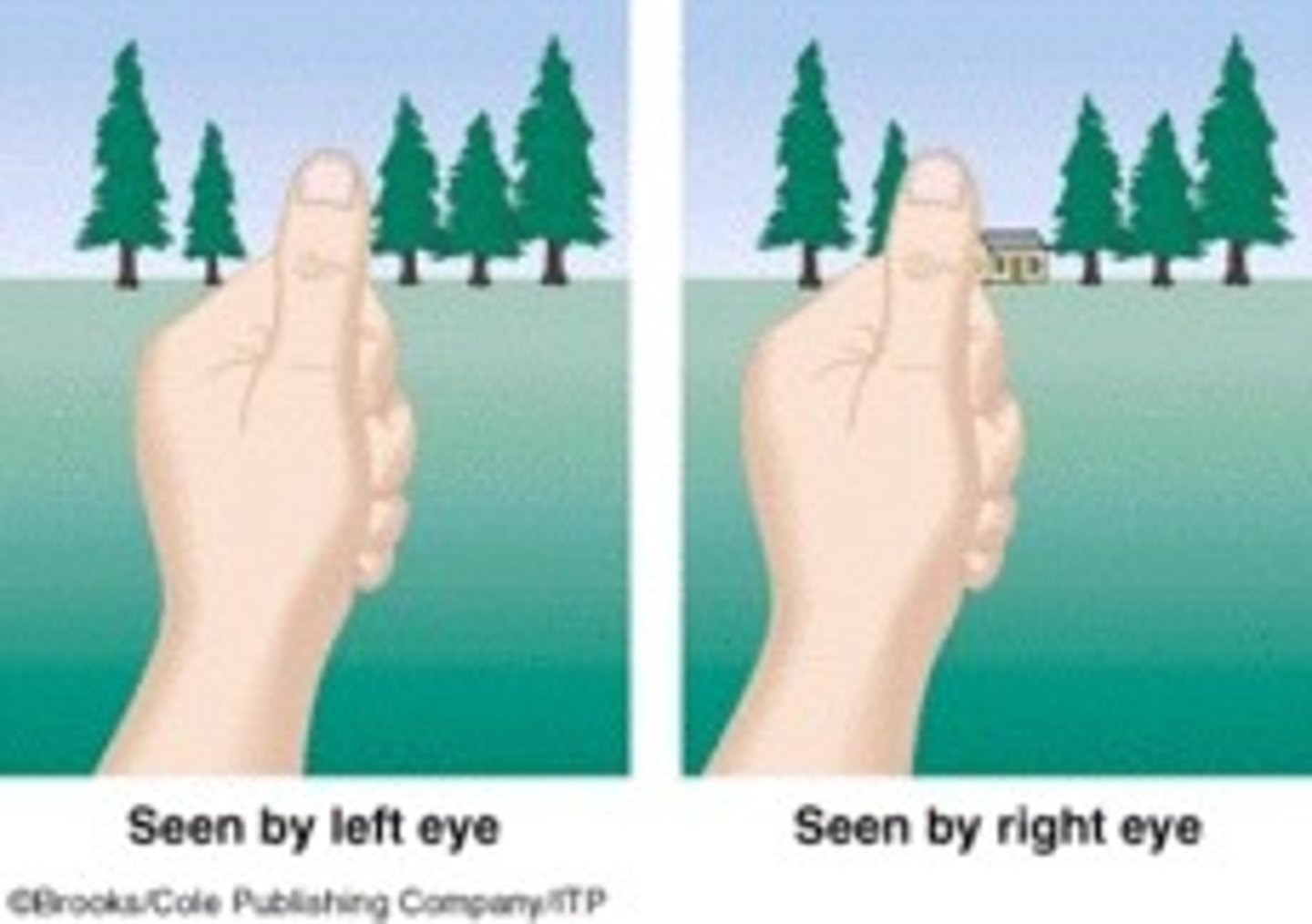
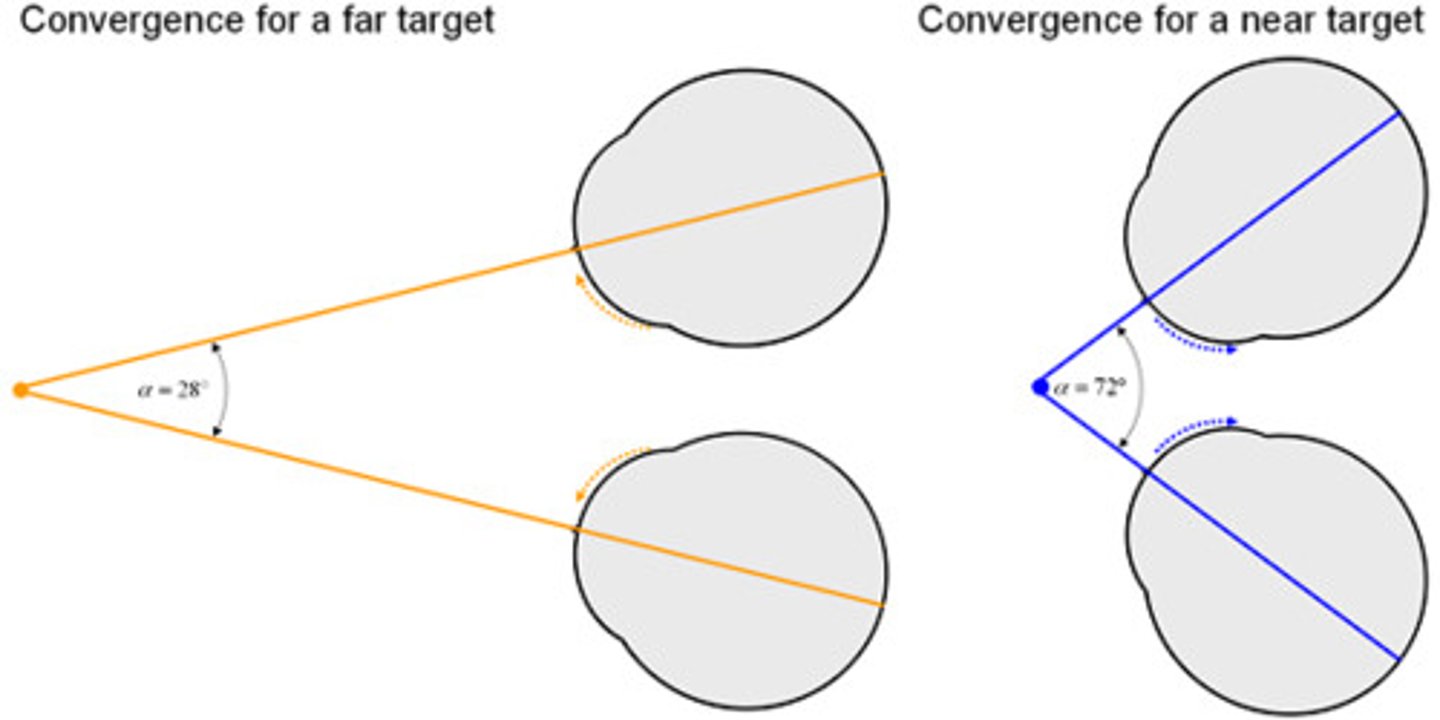
convergence
A binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object
monocular cues
depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone
relative clarity
a monocular cue for perceiving depth; hazy objects are farther away than sharp, clear objects
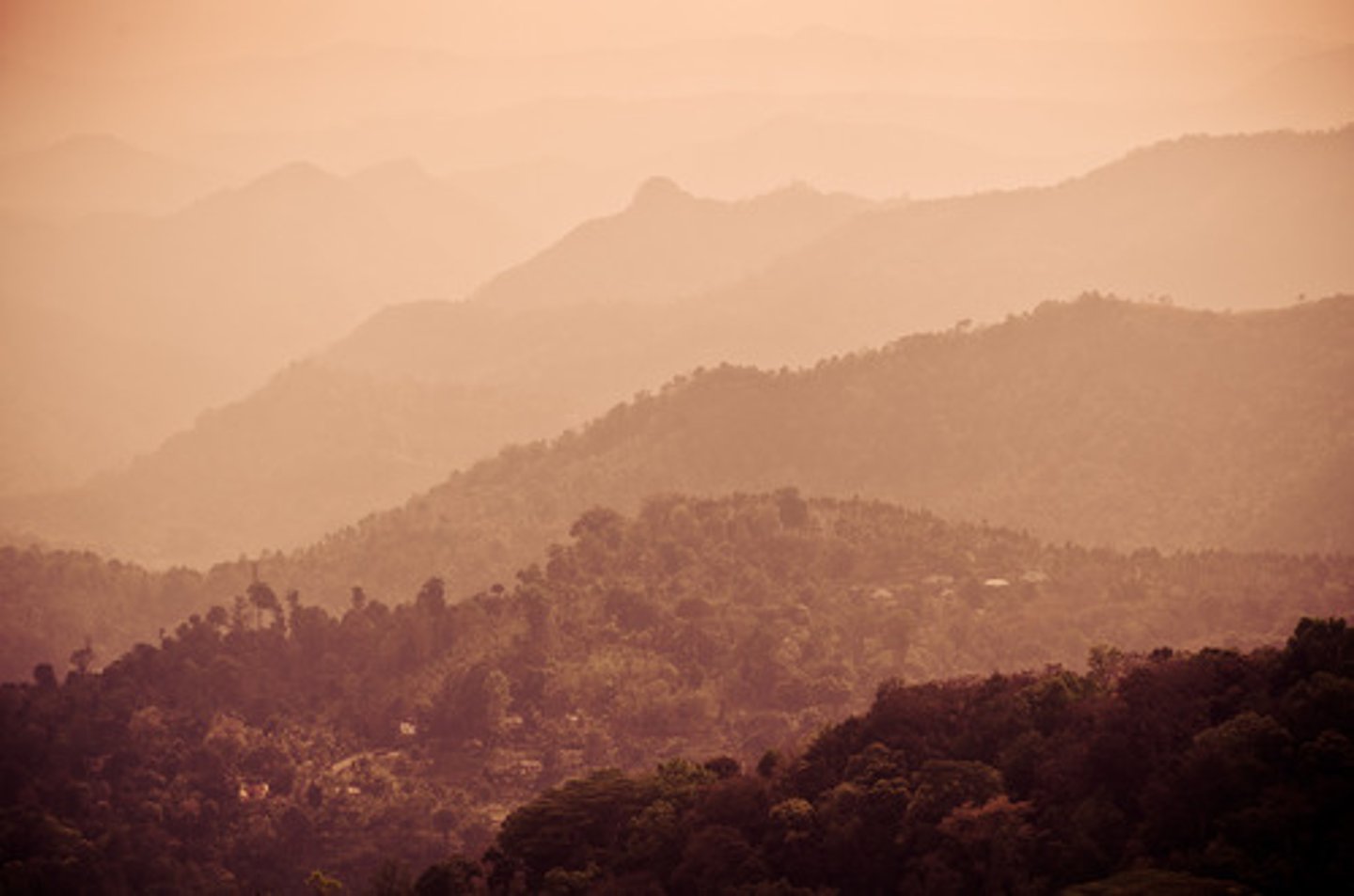

texture gradient
the tendency for textured surfaces to appear to become smaller and finer as distance from the viewer increases
linear perspective
A monocular cue for perceiving depth; the more parallel lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
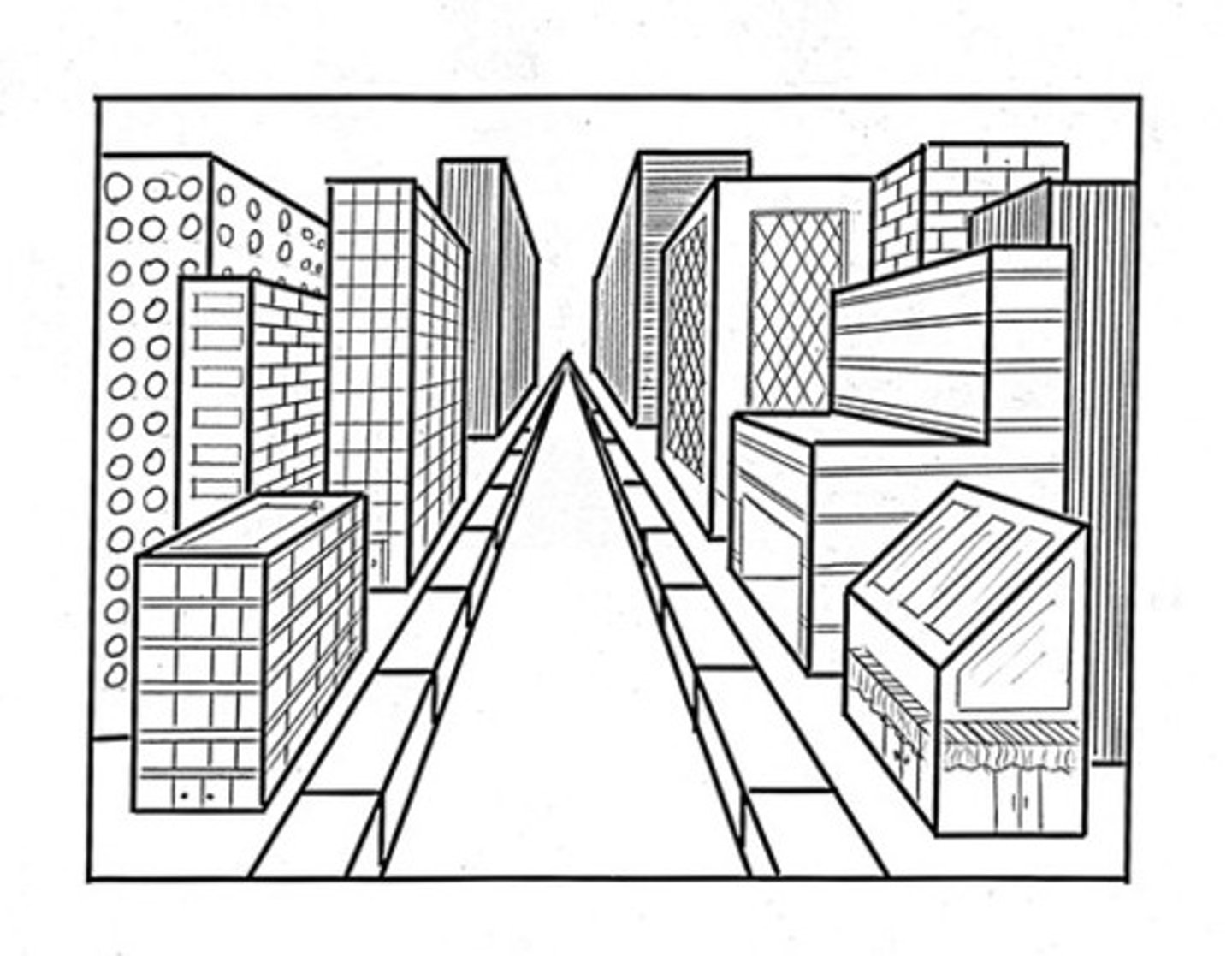
Interposition
if one object partially blocks our view of another, we perceive it as closer

phi phenomenon
an illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
self-fulfilling prophecy
a belief that leads to its own fulfillment

normal bell curve (normal distribution)
a symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many types of data; most scores fall near the mean (about 68 percent fall within one standard deviation of it) and fewer and fewer near the extremes.
Memory
The persistence of learning over time through storage and retrieval of iformation
Cognition
The mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating
Encoding
Processing information into the memory system
Storage
Retention of encoded information.
Retrieval
Pulling information out of memory storage (i.e. out of long term memory and into working memory).
Sensory memory
The immediate and brief recording of sensory information into the memory system.
Short-term memory
Activate memory that holds about 7 (plus or minus) items briefly before the information is stored or forgotten.
Long-term memory
The relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system.
Working memory
A newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory.
Parellel processing
The processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously.
Automatic processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time and frequency or of well-learned information, such as word meanings.
Effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Rehearsal
The conscious repetition of information, either to maintain it in the working memory or store it in long-term memory.
Spacing effect
The tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention.
Serial position effect
Tendency to recall the last and first items in a list.
Visual encoding
The encoding of picture images.
Acoustic encoding
The encoding of sound.
Semantic encoding
The encoding of meaning, including the meaning of words.
Imagery
Creating mental pictures.
Mnemoics
Memory aids.
Chunking
The grouping of information into familiar, meaningful units.
Iconic memory
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second.