AP Chem Unit 1 Review
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
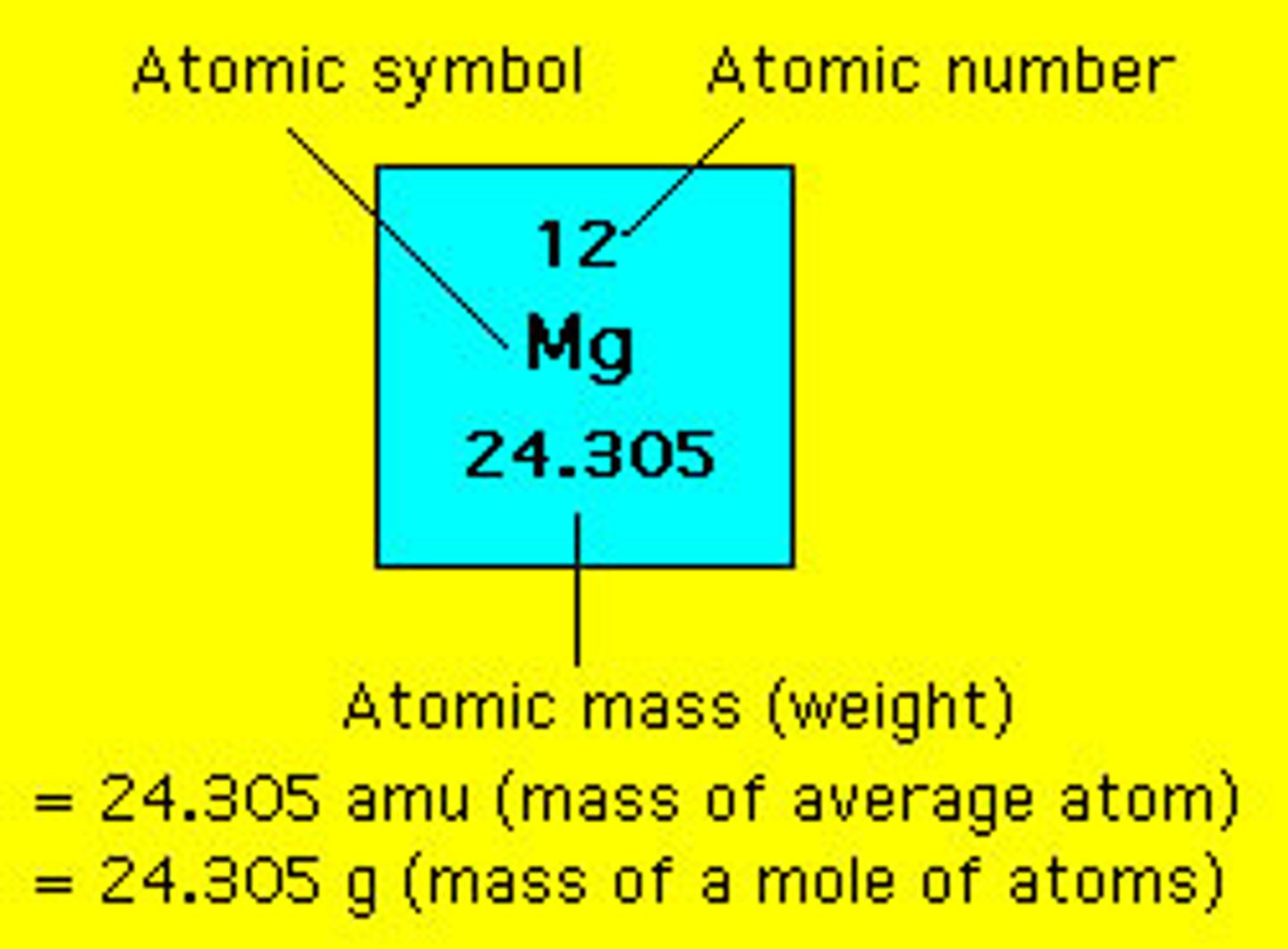
atomic mass unit
the mass of an individual atom or 1 mol of atoms is sometimes expressed in this unit?
6.022 x 10^23 particles
How many particles are in 1 mol of a pure substance?
Take number of moles and X by Avad's #
How do you find the number of particles in in 9.30 x 10^-3 mol of Na2CO3?
Multiply number of particles in Na2CO3 and X by mol ratio (2 Na = 1 mol Na2CO3) (X by 2)
How do you find the number of Na atoms in 9.30 X 10^-3 mol of Na2CO3?
(Mass 1 X .RA) + (Mass 2 X .RA)....
How do you find the average atomic mass of an unknown element given mass and relative abundance?
G to moles
Divide by small
Multiply till whole
How do you find the empirical formula of a compound given (g)?
% to g
G to moles
Divide by small
Multiply till whole
How do you find the empirical formula of a compound given (%)?
Divide the molar mass of molecular by empirical's and use the multiple to X the subscripts in emp form
How do you find molecular formula from an empirical given the molar mass of the compound?
Compound + O2 => CO2 + H2O
g CO2 to mol X mol ratio of C:CO2
g H2O to mol X mol ratio of H:H2O
Using moles x & y of CxHy, convert to emp form
How do you find the empirical formula if (g) of C and (g) of H2O formed in a complete combustion?
Find the contaminant w/ a higher % O than in Na2O (higher % would cause an incr in %O).
O MM/Compound MM X 100 = % O
How do you find the contaminant if given % Na, % O but a contaminated sample had a higher % O?
Average mass = (Mass 1 X) + (Mass 2 (1-X))
Solve for X, convert to %
How do you determine the % abundance for 2 isotopes given the average atomic mass?
Electrons are added to the lowest energy subshells first (Increasing E: 1s2s2p3s3p4s3d4p5s)
What is Aufbau's principle?

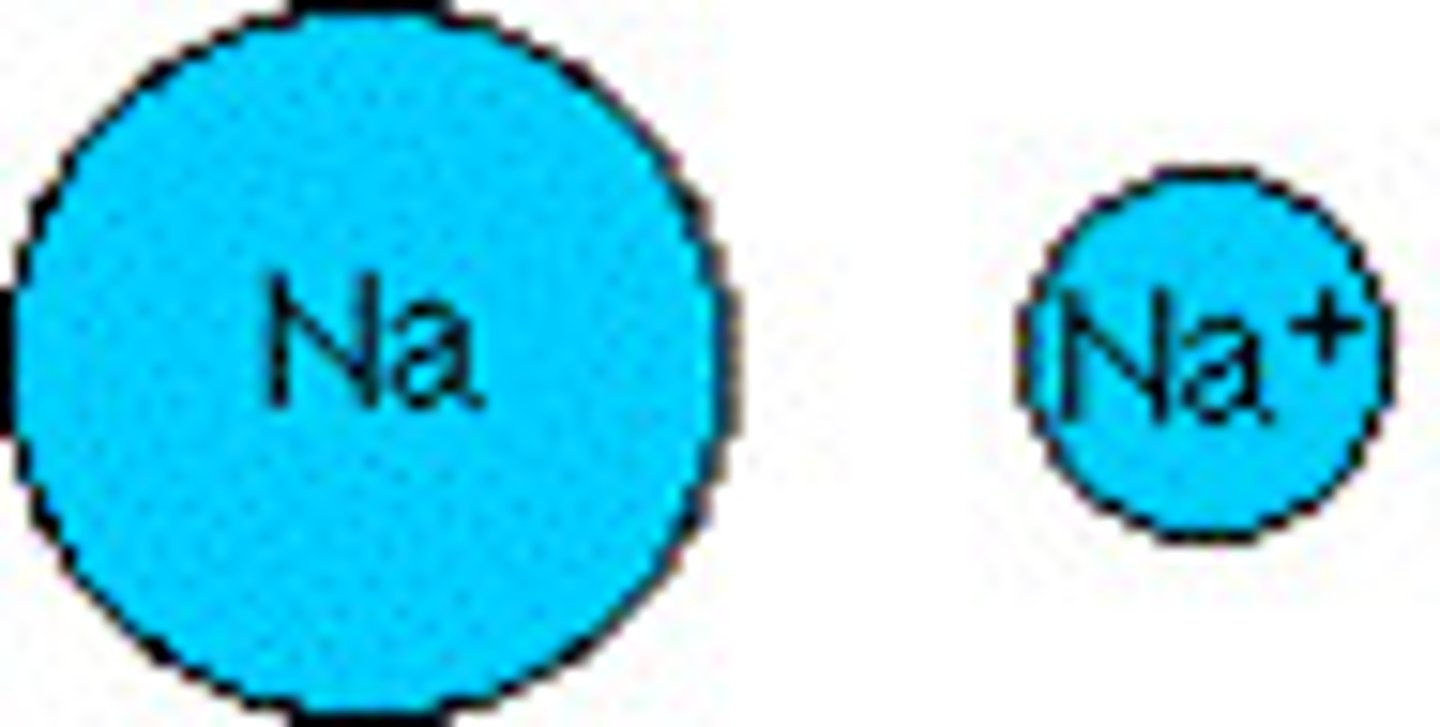
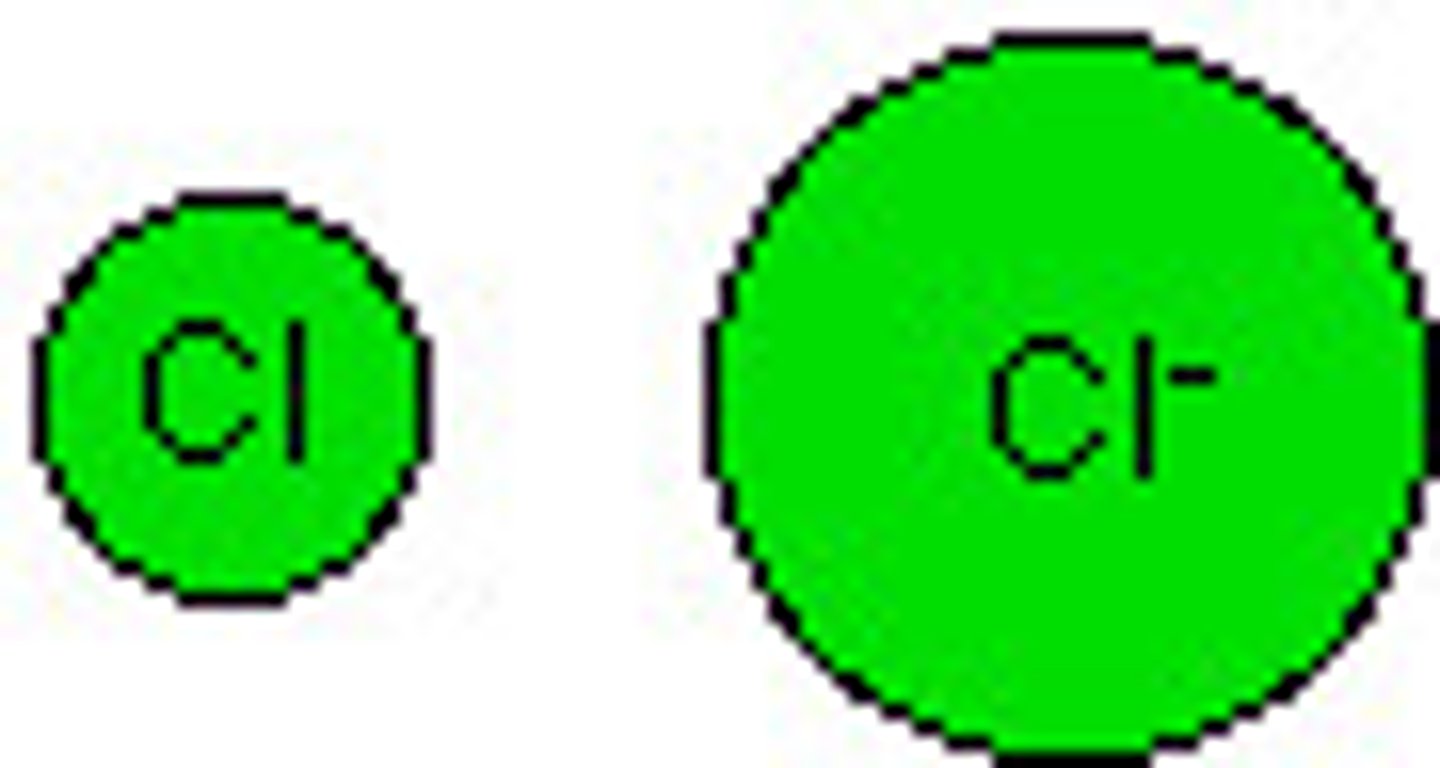
A cation is SMALLER than the original atom, they lost v.e-. but have the same # of p+ pulling in
How does the ionic radius of an atom change when a cation is made?

A anion is LARGER than the original atom but they have the same # of p+ pulling in; more e- --> more e- REPULSION
How does the ionic radius of an atom change when a anion is made?
It's harder to remove e- b/c closer to nucleus; IE higher
How does a smaller radii affect IE?
It's easier to remove e- b/c further f/m nucleus; IE lower
How does a larger radii affect IE?
F, O, N
What are the most electronegative elements?
Nuclear charge ALWAYS stays the same
IONIC RADIUS changes due to e- repulsions/less of ""
How does nuclear charge differ/stay the same among ions of the same element?
The bigger the difference in electronegativity (the more far apart they are on the periodic table) --> more polar
How does electronegativity relate to bond polarity?
[Ar] 4s^2 3d^6
4s are on the outermost shell, so that's where the v.e.- are. The e- config is:
[Ar] 3d^6
If Fe were to lose two electrons, which subshell/orbital would they be taken from?
Orbitals get 1 e- b4 getting 2 e-
What is Hund's Rule?
The electrons are closer to the nucleus because a nuclear charge would make it harder to remove those e-
What does a high binding energy on a photoelectron spectroscopy mean about those electrons?
Mention nuclear change
What's a general rule when discussing trends across a period?
Mention radius
What's a general rule when discussing trends down a group?
Be: 1s^2 2s^2
B: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^1
p orbitals are further f/m nucleus than in s orbitals --> less energy to remove --> e- in O are easier to remove
Why does B have a lower IE than Be even though IE would normally increase as nuclear charge increases?
(also happens b/t Al and Mg)
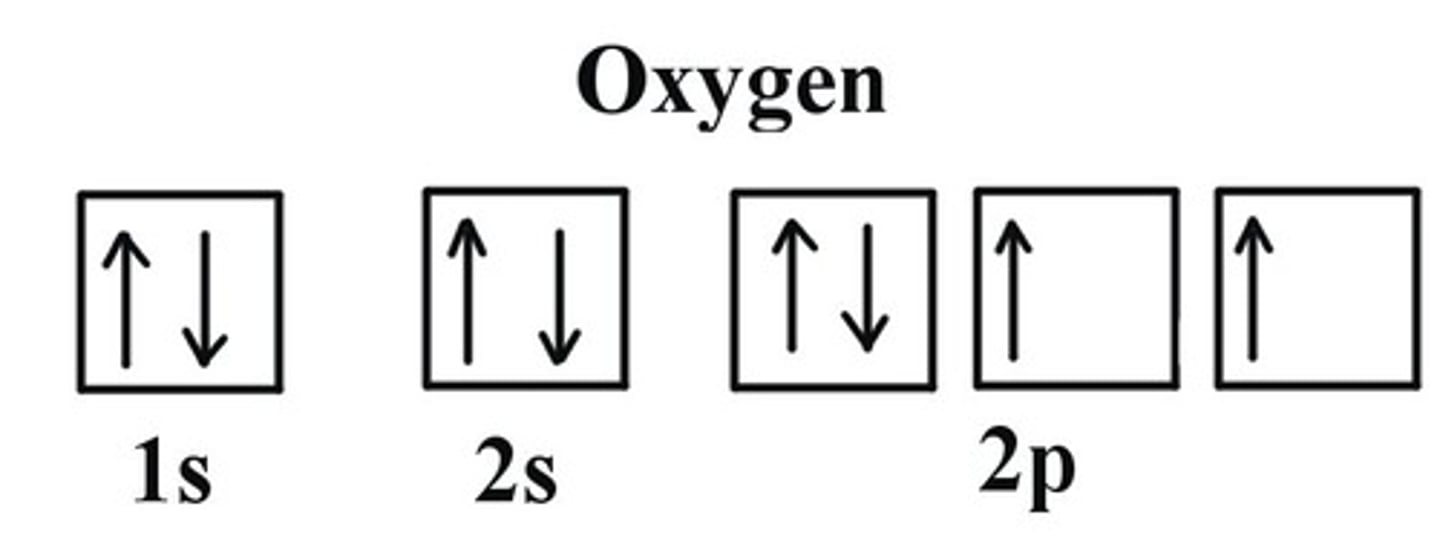
N: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^3
O: 1s^2 2s^2 2p^4
O's e- are removed f/m a DOUBLY OCCUPIED p orbital --> e- repulsion --> less en. to remove
Why does O have a lower IE than N even though IE would normally increase as nuclear charge increases?
(also happens b/t P and S)