Necrosis
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
types of cell death
Necrosis
Apoptosis
Nuclear changes
Pyknosis, hyperchormatosis, karyorrhexis, karyolysis
Pyknosis
Nucleus is decreased in size, but round more perfectly that it was during life
Nucleus is black and homogenous
Lack nucleolus, chromatin granules, and internal structure characteristic of most living nuclei
Hyper-chromatosis
Concentration of chromatin on the nuclear membrane
The centre of nucleus paler, crossing of cell membrane, binding of chromatin
Karyorrhexis
The nuclear membrane ruptures and the chromatic fragments are concentrated into small, darkly stained aggregates
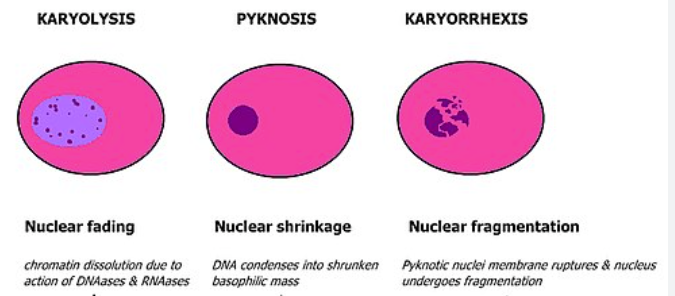
Karyolysis
Dissolution of the nuclear material
Nucleus appears as a hollow sphere with only the nuclear membrane remaining
Cytoplasmic changes
Acidophilia of the cytoplasm
Cytoplasmolysis
Acidophilia of cytoplasm
It's reaction is more basic than during life, stain is usually red
Cytoplasmic structure is obscured
Cytoplasmolysis
Cytoplasm tends to become less and less, ultimately disappears completely
Changes in the cell
Loss of cell outline
Loss of differential staining
The absence of the cell
Loss of cell outline
Loss of the form and outline of cell
Cell material of which they are made of is still present
Seen in caseous necrosis of a tubercle or in an inflammatory exudate
Loss of differential staining
Colour of nuclei and cytoplasm cannot be distinguished
Absence of the cell
If the cell cannot be found, it must be assumed to have died
Types of necrosis
Coagulative necrosis
Liquefactive (colliquative) necrosis
Coagulative necrosis
desaturation of cellular proteins → firm mass of necrotic cells whose outlines may persist for days or even weeks before dissolved and removed by enzymatic lysis
Occurrence: infarct (local ischaemia), toxic products of certain bacteria, locally acting poisons, milder burns
Types of Coagulative necrosis
Caseous necrosis
Zenker's necrosis
Caseous necrosis
Tuberculotic lesion
Friable, cheesy, amorphous material
Mixture of degenerative tissue protein and fat which is derived from the lipid capsule of the organism
Zenker's necrosis
Coagulation of proteins of the sarcoplasm
Occurs in striated muscle
Toxins of pathogenic microorganisms
Grossly: muscle is white or pale, rather shiny, and somewhat swollen
Micro: fibres are swollen, homogenous and hyaline, the sarcoplasm is acidophilic, the myofibrils presented lack cross striation, the nuclei are small and dark
Liquefactive (colliquative) necrosis
Rapid liquefaction of dead cells
Types of Liquefactive necrosis
Abscesses
Malacia
Haemorrhagic necrosis
Abscess
Liquid is represented by pus (Ne, tissue fluid, tissue debris)
Malacia
Breakdown of myelin, result in cerebral softening
Encephalo-malacia - brain
Myelo-malacia - spinal cord
Haemorrhagic necrosis
Variant of necrosis when the necrotic tissue is congested with blood
Due to blockage of venous drainage of an organ or tissue
Commonly observed in malposition of intestine (volvulus, intussusception)
Fat necrosis
Occurs in the abdominal cavity or under the skin
Types of fat necrosis
Traumatic
Enzymatic
Abdominal
Traumatic fat necrosis
Traumatic rupture of fat cells
Free fat evokes a tissue reaction resulting in reparative changes -> fibroblastic area of scar tissue and firm nodules
Enzymatic fat necrosis
Also known as pancreatic necrosis
Occurs when neutral fats are split by lipases into fatty acids and glycerol
FAs saponify with alkalis to form chalky white precipitates
Abdominal fat necrosis
Large masses of necrosis fat in mesentery, omentum, and retroperitoneum
The outcome of necrosis
1. Liquefaction and removal of the fluid via the blood and lymph system
2. Liquefaction and formation of a cyst-like accumulation of fluid
3. Liquefaction with abscess formation
4. Encapsulation without liquefaction
5. Desquamation or sloughing
6. Replacement by scar tissue
7. Sequestration
8. Calcification
9. Gangrene
10. Atrophy of the organ, tissue, or part there of is followed by necrosis
11. Regeneration
Gangrene
Necrotic tissue which has undergone secondary influences
Types of gangrene
Dry
Wet
Gas
Dry gangrene
gradually + slow reduction of the blood flow in the arteries
There is no subsequent bacterial decomposition
Tissues are dry and shrivelled, cold, lacking in pulse, first brown then black colour
Moist (wet) gangrene
Tissues are well filled with blood at the time the necrosis begins
Sudden stoppage of blood - burning by heat or acid, freezing
Tissue is swollen, pulpy, dark, or black in colour
Gas gangrene
Occurs in dirty lacerated wound infected by anaerobic bacteria (clostridium)
Acute, severe, painful condition
Grossly: dark red-black with gas bubbles and fluid exudates that may contain blood
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
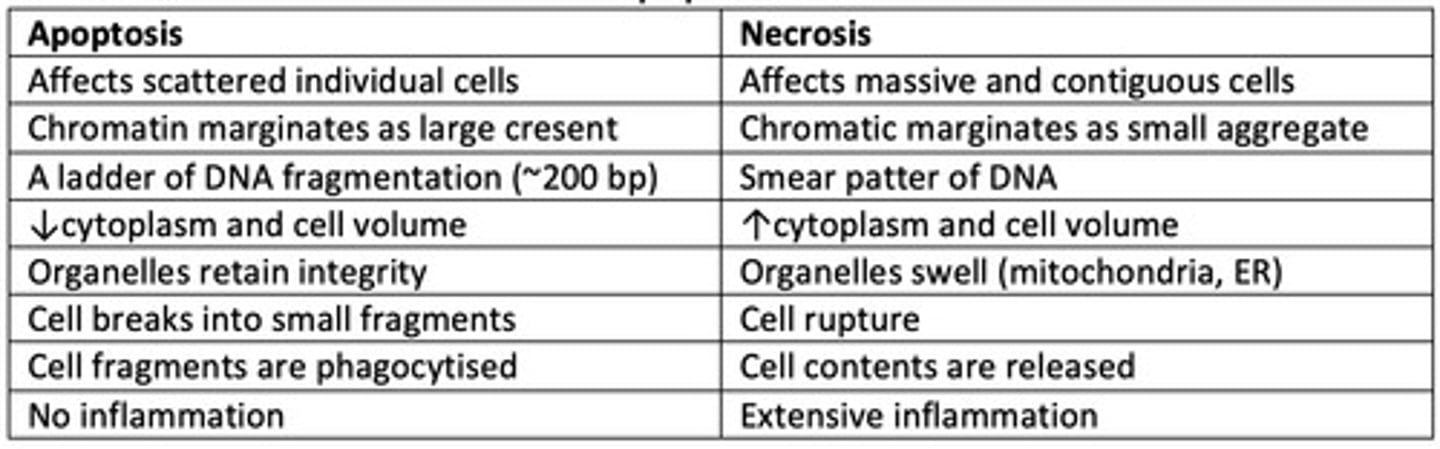
Different characteristics between apoptosis and necrosis