Exam 3 Review: UC Dr Torres BIOL2085
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
B
What could be defined as an organized network of extracellular materials found beyond the immediate vicinity of the plasma membrane?
A. Intracellular matrix
B. Extracellular matrix
C. Extracellular material
D. The matrix
C
All of the following are components of the extracellular matrix except for _____
A. Laminin
B. Collagen
C. Peptidoglycan
D. Proteoglycan
True
True or false, Laminin and Fibronectin play an important role during embryonic development, mainly by directing cell migration
D
Which of the following statements about the basement membrane is true?
A. It is the place where most metabolic enzymes are found in epithelial cells
B. It is rich in sodium and potassium channels
C. It is one of the layers of the extracellular matrix
D. It provides mechanical support for attached cells
D
The components of the ECM are subject to continual degradation and reconstruction. These processes are important during tissue remodeling, embryonic cell migration and wound healing, and are accomplished by a family of enzymes known as
A. Extracellular proteinases
B. Matrix dehydrogenases
C. ECM-desaturases
D. Matrix metalloproteinases
E. Endotheliases
D
Enzymatic digestion of the ECM surrounding the cartilage cells would
A. Do nothing
B. Get the scientist fired
C. Set the scientist on fire
D. Decrease their synthetic and secretory activities
E
The ____ is a type of extracellular matrix that forms the supporting structure on which epithelial and endothelial cells grow
A. Laminin
B. Fibronectin
C. Hyaluronidase
D. Matrix metalloprotease
E. Basement membrane
B
Vitamin C deficiency is associated with important skin functions, particularly wound healing. Vitamin C is required for hydroxylation of amino acids that stabilize
A. Glycosaminoglycan
B. Collagen
C. Fibroblasts
D. Fibronectin
E. Integrins
C
Collagen contains large amounts of hydroxylated amino acids. These amino acids use the OH group to form _________ between the different chains, to enhance protein stability
A. Van der Waals forces
B. Hydrophobic interactions
C. Hydrogen bonds
D. Covalent bonds
B
Which of the components of the ECM would be affected if cells were treated with hyaluronidase? (an enzyme that degrades hyaluronic acid)
A. Collagen
B. Proteoglycans
C. Laminin
D. Fibronectin
E. B, C and D
D
The basal membrane normally provides an impenetrable barrier to cells, but lymphocytes and macrophages are able to cross it by digesting components of the basal membrane. This process involves the activation of a family of enzymes known as
A. Collagenases
B. Gelatinases
C. Matrilysins
D. Matrix metalloproteases
E. Extracellular proteases
B
The specialized adhesive structure that facilitates the stable adhesion of epithelial cells to the underlying basement membrane is called
A. Focal adhesion
B. Hemidesmosome
C. Gap junction
D. Adherens junction
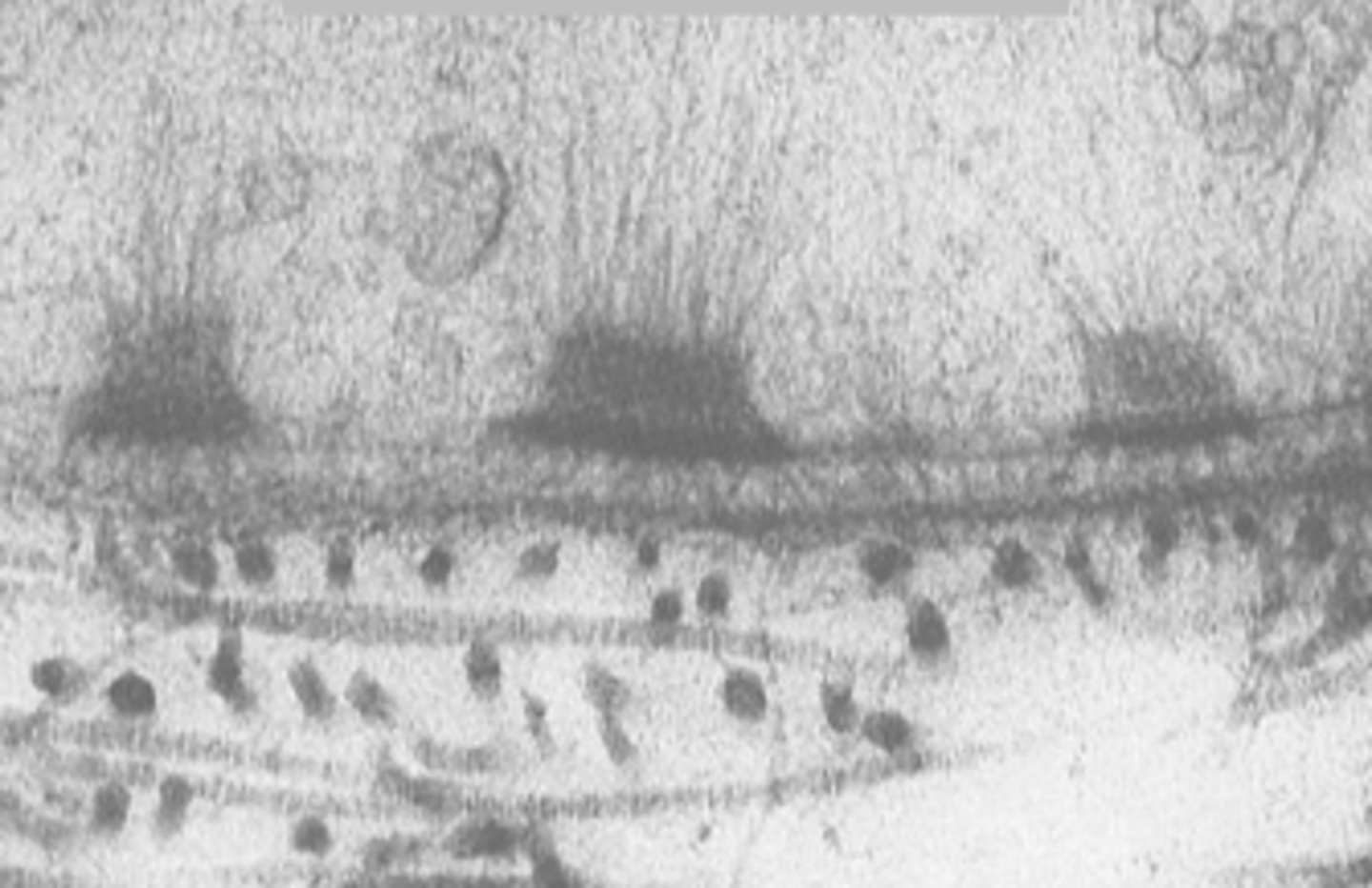
B
What would be the effect of exposing an embryo to laminin-specific neutralizing antibodies?
A. All the processes of cell migration would stop
B. Migration of primordial germ cells would stop
C. Migration of neural crest cells out of the neural plate would stop.
D. Migration of all lymphoid cells would stop.
C
Which of the components we have discussed in this module (list below) could be represented by the hydropathy plot shown below?
A. Glycosaminoglycan
B. Basement membrane
C. Integrin
D. Collagen
E. Matrix Metalloprotease
F. Laminin
G. Fibronectin
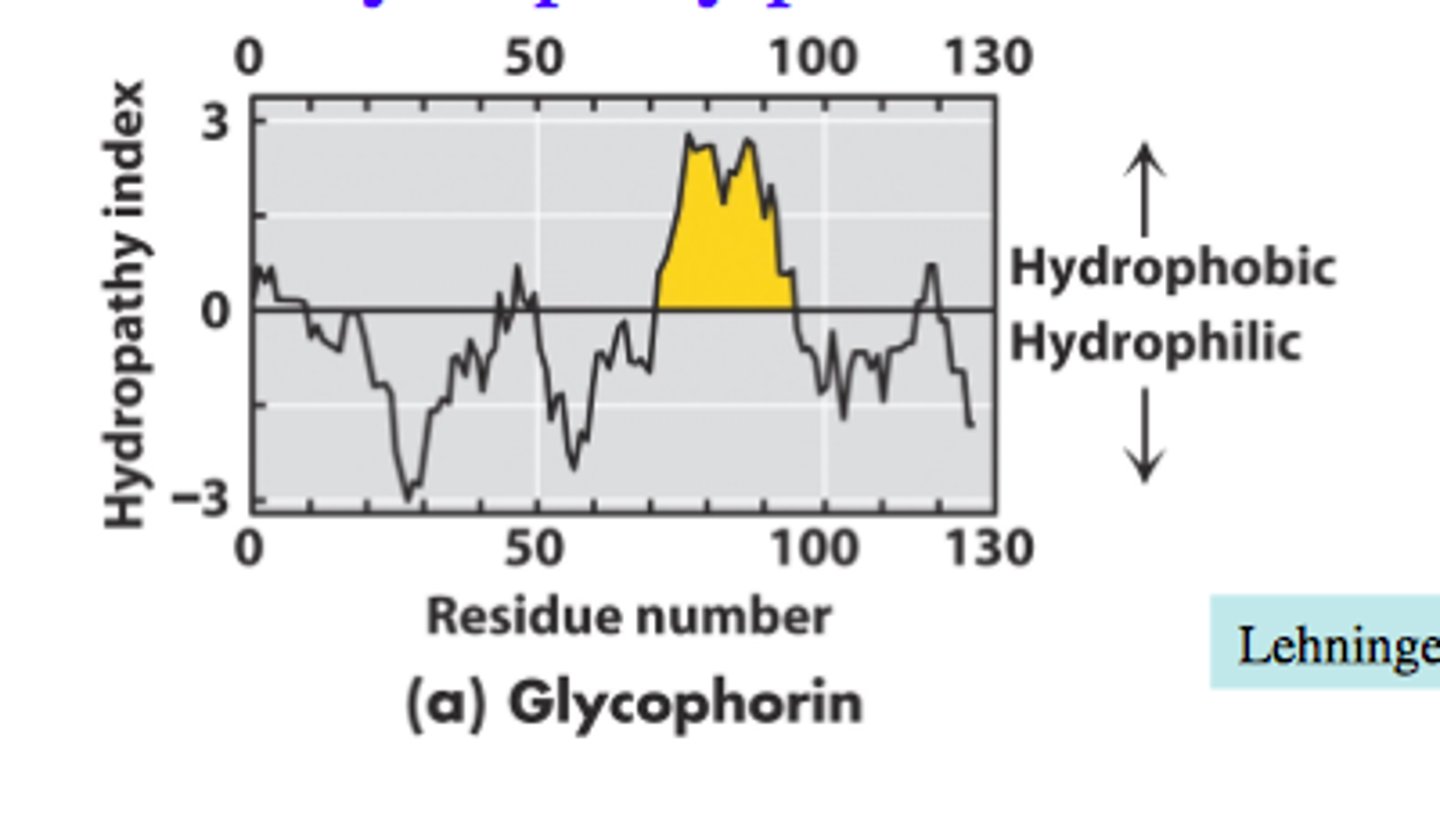
A
The ______ activation of integrins is triggered by a cytoplasmic signal and leads to increased affinity of the integrin extracellular domain for a ligand
A. Inside-out
B. Outside -in
D
Unlike malignant cells, normal cells ____ grow unless they are cultured on a solid substratum. The type of signaling involved in this process is an example of _____
A. Can; Inside-out signaling
B. Can; Outside-in signaling
C. Cannot; Inside-out signaling
D. Cannot; Outside-in signaling
B
In an experiment, you combine the cells, fibronectin, proteoglycan and one of the two following peptides:
1. Experiment A: T-A-R-R-G-G-T-A
2. Experiment B: D-A-V-R-G-D-P-T
In which experiment do you expect cells will attach?
A. Cells in Experiment A will attach
B. Cells in Experiment B will attach
C. Cells in both experiments will attach
D. Cells will not attach in any experiment
A
What are the three major proteins that are involved in cell-cell adhesion/ interactions?
A. Cadherins, Immunoglobulins and Selectins
B. Integrins, Cadherins and Proteoglycans
C. Selectins, Cadherins and Cell plate
D. Intermediate filaments, Laminin and Selectins
E
What biological process occurs by presence of selectins and immunoglobulins as a primary response to infection?
A. Apoptosis
B. Leukocytosis
C. Meiosis
D. Embryogenesis
E. Inflammation
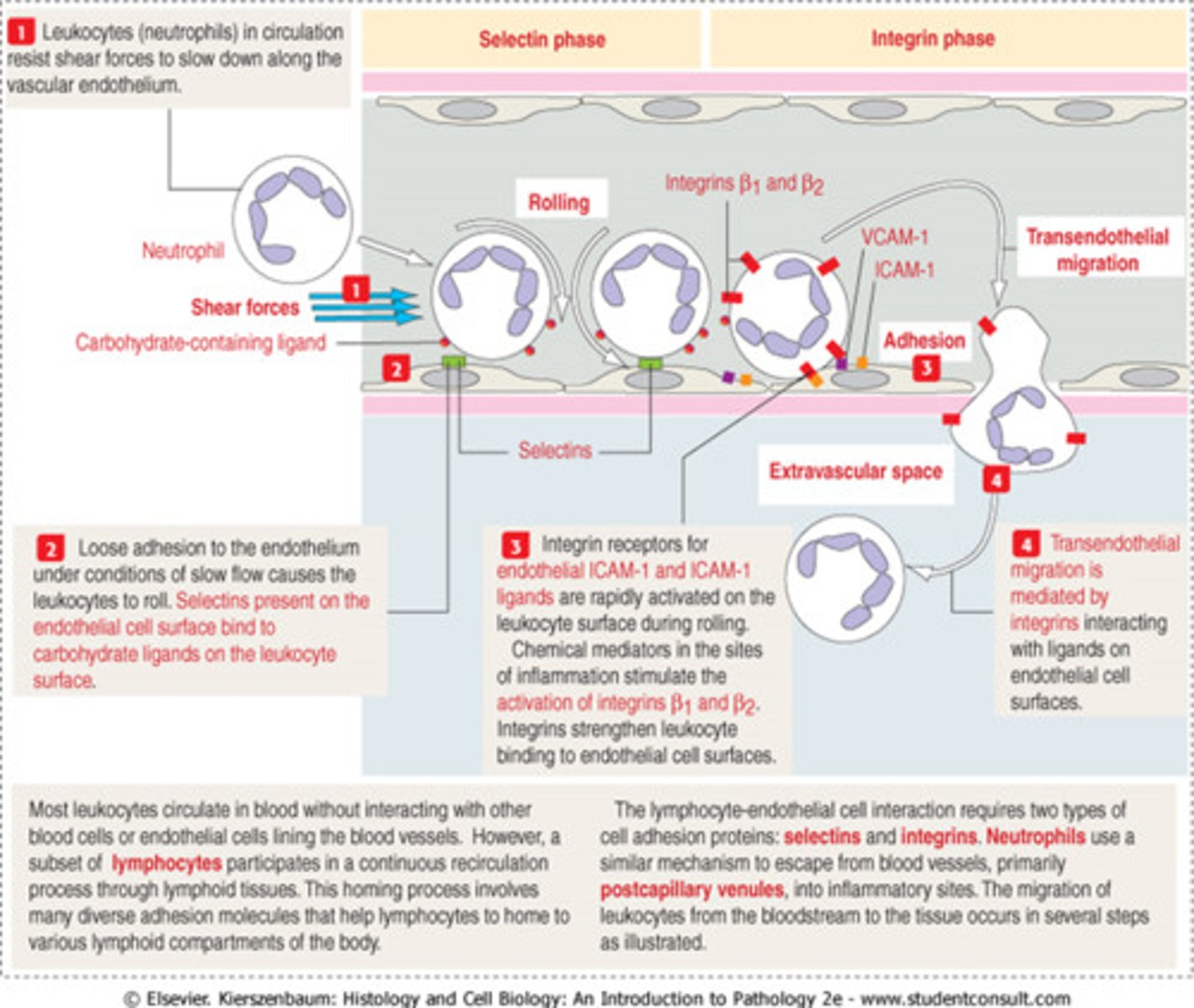
B
According to the assigned reading, the ability to feel "lumps" during a breast exam is associated with
A. Increased activity of metalloproteases in the ECM
B. Altered cross-linking and organization of collagen in the ECM
C. Increased migration of neutrophils to the breast tissue
D. Increased presence of fibrinogen and integrins in the ECM of the tumor cells
D
When cells from different parts of an embryo are dissociated and then intermixed, the cells initially aggregate and then sort out by associating with other cells of the same type. This recognition is mediated by ______
A. Immunoglobulins
B. Integrins
C. Selectins
D. Cadherins
E. Fibronectin
C
The symptoms observed in these blistering diseases are the result of:
A. Abnormal attachment of the actin filaments
B. Loss of cell viability by inactivation of signaling kinases such as FAK
C. Weak attachment of the epidermis to the dermis
B
One of the most important roles of selectins is to_____
A. Mediate adhesive contacts to construct tissues and organs in the embryo
B. Slow down and recruit leukocytes during inflammation
C. Mediate adhesion between non-immune cells during neural development
C
Which of the following phenotypes would you expect to be associated with a malignant cell phenotype?
A. More adhesive than normal cells
B. Lower migration rates
C. Higher expression of matrix metalloproteases (MMP)
D. Higher expression of E-cadherins
E. C and D
Focal Adhesions:
- are temporary
- are mobile
- use actin
Focal Adhesions:
- are (temporary/permanent)
- are (mobile/immobile)
- use (what protein?)
C
The correct order of passage of materials produced in a biosynthetic pathway is:
A. ER, Golgi complex, plasma membrane, secretory vesicle.
B. ER, lysosome, secretory vesicle, plasma membrane.
C. ER, Golgi complex, secretory vesicle, plasma membrane.
D. Nucleus, Golgi complex, ER plasma membrane.
C
A tissue has been briefly labeled with radiolabeled amino acids. It is then transferred to a medium containing unlabeled amino acids. This can be done several times with different tissue samples for varying periods of time. What is the entire procedure called ?
A. Pulse
B. Chase
C. Pulse-Chase
D. GFP-Chase
E. RACE
B
The process of co-translational translocation involves
A. Translocation of fully synthesized proteins into the ER
B. Translocation of proteins to the ER while they are still being synthesized
C. Translocation of ribosomes to the membrane of the Golgi complex
D. Translocation of ribosomes to the plasma membrane
E. Induced transcription of extracellular proteins
A
Membrane-bound ribosomes produce many proteins that are ________, while free ribosomes produce many proteins that are _____
A. Exported from the cell; Used inside the cell
B. Used inside the cell; Exported from the cell
C. Used in the cytoplasm; Destined for the plasma membrane
D. Used in the nucleus; Used in the cytoplasm
E
Membrane-bound ribosomes are bound to the ________, and synthesize proteins that contain a signal sequence in the ______
A. Plasma membrane; Plasma membrane
B. ER membrane; Last amino acid
C. Golgi membrane; C-terminus
D. Plasma membrane; Transmembrane domain
E. ER membrane; N-terminus
B
Which of the following organelles are part of the endomembrane system?
1. Lysosomes
2. Golgi complex
3. Nucleus
4. Plasma Membrane
5. Mitochondria
A. 1, 2 and 3
B. 1, 2 and 4
C. 1, 2, 3 and 4
D. All except the plasma membrane
E. All except the nucleus
B
A scientist wishes to visualize movement of a protein in a living cell. Which procedure would work best?
A. Pulse-chase
B. Fusion of the green fluorescent protein gene to the gene encoding the protein to be tracked through the cell
C. Fusion of the green fluorescent protein gene to a membrane-bound ribosome
D. Pulse-chase using fluorescent antibodies
A
During the "pulse" of a pulse-chase experiment:
A. The cell is incubated with radioactive amino acids, which are incorporated into the proteins
B. The cell is incubated with unlabeled amino acids, and allowed to continue regular cellular activities
C
In a pulse-chase procedure, if the chase is longer, which statement below correctly describes the location of the radioactively labeled proteins in the cell?
A. Closer to the synthesis site
B. Farther from the nucleus
C. Farther from the synthesis site
D. Closer to the nucleus
D
Why are viruses useful in the study of protein movement through the biosynthetic pathway?
A. Viruses can be seen in electron microscopy, specifically colonizing the ER
B. Viruses can deliver radioactive amino acids into the cell, which allows to track protein movement
C. Viruses specifically colonize ER-bound ribosomes, which are secreted via the biosynthetic pathway
D. Viruses force cells to synthesize and secrete large amounts of viral proteins
E
Protein A is synthesized in ER-bound (membrane bound) ribosomes. Protein A could be a ________ protein
A. Golgi complex
B. ER
C. Mitochondria
D. Plasma membrane
E. A, B and D
A
Succinate dehydrogenase is most likely synthesized by
A. Free ribosomes
B. ER-bound ribosomes
False
True or false, eukaryotic cells contain two different types of ribosomes: cytosolic (free) ribosomes are chemically and structurally different from ER-bound ribosomes
C
A stretch of 6-15 hydrophobic amino acids known as ______, is usually located in the _____ of _______
A. Transmembrane domain; C-terminus; Secretory proteins
B. Translocon; C-terminus; cytosolic proteins
C. Signal sequence; N-terminus; Secretory proteins
D. Signal peptide; N-terminus; Mitochondrial proteins
E. Ribozyme; C-terminus; Chloroplastic proteins
A
Synthesis of all proteins starts in free ribosomes. A signal sequence in the N-terminus, signals the ribosome to temporarily halt synthesis of this peptide and relocate to the ER membrane, where synthesis of this protein continues. This process is known as
A. Co-translational translocation
B. Co-transcriptional translocation
C. Collaborative translocation
D. Ribosomal translocation
B
The Signal Recognition Particle (SRP) is an abundant protein that targets specific proteins to the ER. Would this protein itself contain a signal sequence on its N-terminus?
A. Yes, of course it would
B. No, of course it would not
collagen, laminin, and fibronectin
Metrix Metalloproteases (MMPs) consume . . .
collagen + proteoglycans
Cartilage =
Hemidesmosomes:
- are permanent
- are immobile
- use intermediate filaments
Hemidesmosomes:
- are (temporary/permanent)
- are (mobile/immobile)
- use (what protein?)
assosiated with the adhesion of non immune cells
What do Immunoglobulin Superfamily (IgSF) do?
mediate adhesive contacts to constructive tissues
What do cadherins do?
recruit and dirrect leukocytes to sites of inflamation
What do selectins do?
E
The process of co-translational translocation is important for
A. All proteins synthesized in a cell
B. All proteins that start and finalize synthesis in free-ribosomes
C. All proteins synthesized in ER-bound ribosomes
D. All proteins that need to be secreted from a cell
E. C and D
C
A mitochondrial membrane protein, like succinate dehydrogenase, will contain a signal sequence on the N-terminus
A. False, the signal is on the C-terminus
B. True, since it is an integral membrane protein
C. False, since it is mitochondrial bound
D. True, the signal is on the N terminus
E. Both B and D are correct
B
Protein glycosylation is the process by which
A. More amino acids are added to some proteins in the Golgi complex
B. Carbohydrate molecules are added to some proteins
C. Lipid molecules are added to some proteins in the Golgi complex
D. Proteins are properly folded in the ER
E
UGGT and calnexin are proteins involved specifically in the cellular process known as
A. The Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)
B. Protein Ubiquitination
C. The biosynthetic pathway
D. The endomembrane system
E. Quality control
B
Which of the following is/are correct about the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP)?
A. It is a protein that resides within the ER (ER lumen)
B. It is a protein that resides in the cytoplasm
C. It binds to an ER-bound ribosome after it has attached to the ER membrane
D. It temporarily stops synthesis of proteins that contain a signal peptide on the C-terminus
A
Which proteins will be synthesized in ER-bound ribosomes?
A. Proteins that need to end up as part of any compartment of the endomembrane system, including the plasma membrane or the extracellular space
B. Proteins that need to end up in the nucleus, the cytoplasm, the mitochondria or the chloroplast
A
A region of at least 20 hydrophobic amino acids, flanked by positively charged and negatively charged amino acids, would most likely be found in
A. membrane-bound secretory proteins
B. free secretory proteins
C. Both
A
Which of the following proteins would you expect to contain a signal peptide in its amino acid sequence?
A. membrane-bound secretory proteins
B. free secretory proteins
C. Both
B
How are plasma membrane proteins embedded in the membrane?
A. A ribosome travels to the plasma membrane during protein synthesis and a protein complex helps insert the protein directly in the PM
B. A ribosome travels to the ER membrane during protein synthesis and a transloconhelps insert the protein in the ER membrane
D
The process of protein glycosylation involves adding ______. This process starts in the ________
A. More amino acids to carbohydrates; Cytoplasm
B. More amino acids to proteins; ER lumen
C. Carbohydrates to proteins; Cytoplasm
D. Carbohydrates to proteins; ER lumen
D
Which of the following is correct about the process of quality control?
A. It is activated in response to the presence of abundant misfolded proteins
B. Verifies that integral membrane proteins are properly embedded in the membrane.
C. Occurs in the Golgi Complex
D. Ensures that glycoproteins are properly folded
C
When a mannose (carbohydrate) is removed from a glycoprotein during quality control, the protein ____
A. Is recognized by calnexin (a chaperone), which tries to fold it again
B. Is recognized by the conformation-sensing enzyme UGGT
C. Cannot be recycled anymore and is degraded
D. Is now properly folded and can leave the ER
COPII:
moves materials from the ER "forward" to the golgi
COPII:
moves materials from the _____ "(forward/backward)" to the _____
D
You are following a protein that is being transported backwards, from the Golgi complex to the ER. How do you think this protein will reach its final destination?
A. It will arrive in a clathrin-coated vesicle
B. It will arrive in an ER-bound ribosome
C. It will arrive in a free-ribosome
D. It will arrive in a COPI-coated vesicle
E. It will arrive in a COPII-coated vesicle
C
Which of the following proteins will most likely contain a KDEL sequence?
A. A selectin
B. An integrin
C. An enzyme that synthesizes phospholipids
D. A protein of the Krebs cycle
E. A lysosomal enzyme
D
Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in ______ ribosomes and are transported in ____
A. Free; COPI- coated vesicles
B. Free; COPII- coated vesicles
C. ER-bound; COPI- coated vesicles
D. ER-bound; Clathrin-coated vesicles
C
Which of the following proteins will most likely contain a KDEL sequence?
A. A selectin
B. An integrin
C. An enzyme that synthesizes phospholipids
D. A protein of the Krebs cycle
E. A lysosomal enzyme
D
How is the process of quality control different from the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)?
A. Only quality control occurs in the ER
B. Only the UPR occurs in the ER
C. Only quality control involves the use of chaperones
D. Only the UPR is activated in response to accumulation of misfolded proteins
A
Synthesis of proteins ____
A. Always starts in free ribosomes
B. Always starts in ER-bound ribosomes
C. It depends on the presence/absence of a signal sequence on the N-terminus
D. It depends on the presence/absence of a signal sequence on the C-terminus
B
A protein with a signal sequence on the N-terminus
A. Could represent a protein that will be fully synthesized in free-ribosomes
B. Could represent a protein that will be processed by co-translational translocation
C. Could only represent a plasma-membrane protein
C
What is responsible for temporarily halting the process of translation in free-ribosomes, and directing the ribosome-mRNA-synthesizing peptide to the ER membrane?
A. The ribosome receives a signal from the nucleus, indicating it should translocate to the ER
B. The nascent peptide binds to a chaperone that sends it to the ER
C. The recognition of the signal sequence by the signal recognition particle (SRP)
C
If a protein needs to end up in the plasma membrane, it will
A. Become embedded in the membrane after it is glycosylated
B. Become embedded in the membrane after being released by the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR)
C. Become embedded in the ER membrane during translation
D. Become embedded in the membrane by a plasma-membrane bound ribosome
Are
C
The process of quality control takes place in
A. The Cytoplasm
B. The Golgi complex
C. The ER
D. The Nucleus
E. The plasma membrane
D
What kind of proteins could act as "helpers" to alleviate stress caused by misfolded proteins?
A. Chaperones
B. Quality control proteins
C. Clathrin-coat proteins
D. A and B
E. All of the above
D
Which of the following proteins are transported by COPII-coated vesicles?
A. Enzymes involved in glycosylation process in the Golgi complex
B. Proteins involved in the process of quality control
C. Ion channels in the plasma membrane
D. A and C
E. All of the above
D
What happens if some essential ER-proteins escape by accident?
A. The cell will automatically undergo apoptosis
B. The cell will synthesize an entire new ER to recover them
C. The Unfolded Protein Response (UPR) will be activated
D. They can be retrieved, if they have a special signal in the C-terminus
E. They can reach the ER if they have a signal sequence in the N-terminus
True
True or false, an ER-resident protein like disulfide isomerase contains a KDEL signal sequence on the C-terminus and a signal peptide sequence on the N-terminus
E
Lysosomal enzymes carrying a _________ are recognized by specific receptors and transported from the trans Golgi network to the lysosomes in _______ coated vesicles
A. KDEL sequence; COPI
B. Glucose-6-Phosphate; Clathrin
C. RGD sequence: COPII
D. Signal peptide; COPI
E. Mannose-6-phosphate; Clathrin
A
Mannose is a type of _____. If the sorting signal for lysosomal enzymes is the presence of a phosphorylated mannose, that means that most lysosomal enzymes are ___
A. Monosaccharide; Glycosylated
B. Polysaccharide; Synthesized in free ribosomes
C. Lipid; Hydrophobic
D. Amino acid; Hydrolyzed in the Golgi complex
E. Sugar; Very sweet
A & C
Which of the following happen in the Golgi Complex?
A. Proteins are sorted to their final destination
B. More amino acids are added to proteins
C. More sugars are added to glycoproteins
D. Escaped proteins are retrieved if they have an N-terminus signal sequence
B
Assume a plasma membrane glycoprotein has a very specific and distinct arrangement of sugars, some of which need to be phosphorylated. Which of the following best describes this protein?
A. This protein was glycosylated only in the Golgi complex
B. This protein was initially glycosylated in the ER and further modified in the Golgi complex
C. This protein never passed the process of quality control
D. This protein was glycosylated only in the ER
C
Lysosomal enzymes are synthesized in ______ ribosomes and modified in the ______
A. Free; Golgi complex
B. Free; Cytoplasm
C. ER-bound; Golgi complex
D. ER-bound; ER
COPI:
moves materials from the golgi "backward" to the ER
COPI:
moves materials from the _____ "(forward/backward)" to the _____