Chapter 24 - Transition Elements
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
d-block elements
their highest energy/outer shell electron occupy the d-sub shell/d-orbitals
transition element
a d-block element that can form an ion with an incomplete/partially filled d-sub shell
-from Ti to Cu
EXCEPTIONS of transition elements
Sc = can only ion form Sc3+ which contains an empty d-sub shell
Zn = can only form Zn2+ which contains a completely filled d-sub shell
properties of transition elements 1)
form compounds where it has variable oxidation states
-a species containing a transition metal in its highest oxidation state is a strong oxidising agent
properties of transition elements 2)
form coloured compounds
-colour depends on oxidation state of metal which is caused by partially filled d-orbitals
properties of transition elements 3)
elements + compounds act as catalysts
-provide a surface which reaction can take place on
-change oxidation states to form intermediates for lower activation energy pathways
examples = Fe in Haber Process, Ni in hydrogenation of alkenes
complex ion
a transition metal ion bonded to one or more ligands by coordinate bonds
ligand
a molecule or ion that can donate a pair of electrons to the transition metal ion to form a coordinate bond
coordinate bond
a bond in which one of the atoms provides both electrons for the covalent bond (dative covalent bond)
coordination number
the number of coordinate bonds formed between a central metal ion and its ligands
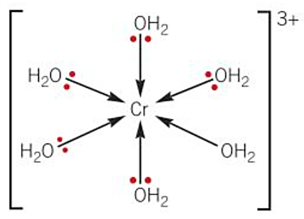
writing complex ions formulae
-square brackets [ ] used to write all parts of complex ion
-round brackets ( ) used to contain ligands that are molecular OR if there is more than 1 type of ligand present
-overall charge written outside of square brackets
-anions or cations that neutralise the charge of ion are not included
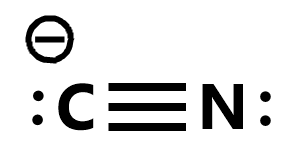
monodentate ligand
donates 1 pair of electrons to central metal ion to form 1 coordinate bond
examples = Cl-, H2O, NH3, CN-
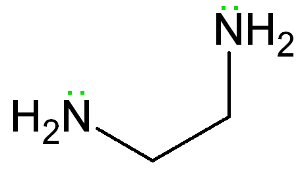
bidentate ligand
donates 2 pairs of electrons to central metal ion to form 2 coordinate bonds
example = ethane-1,2-diamine (en)
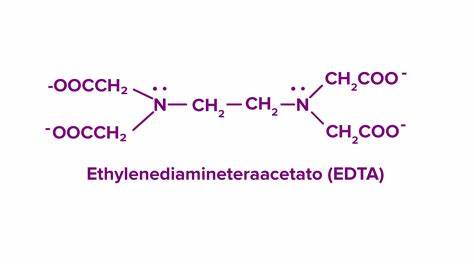
multidentate ligand
donates 3 or more pairs of electrons to central metal ion to form 3 or more coordinate bonds
example = EDTA
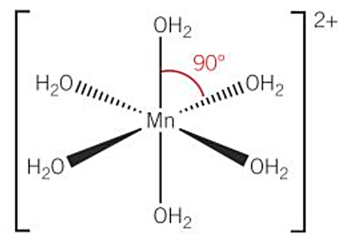
shapes of complex ions -octahedral (DRAW [Mn(H2O)6]2+)
-6 coordinate bonds - coordination number = 6
-4 of the ligands are on the same plane (dashed + wedged)
-1 ligand is above the plane and 1 is below the plane (straight)
-bond angle = 90
-the oxygen atom in H2O ligand must be coordinated to central metal ion as oxygen supplies pair of electrons
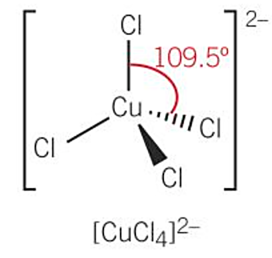
shapes of complex ions -tetrahedral (DRAW [CuCl4]2-)
-4 coordinate bonds - coordination number = 4
-complex ions containing chloride ions tend to be tetrahedral
-bond angle = 109.5
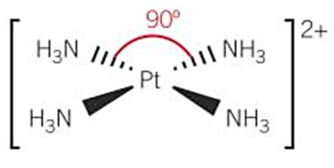
shapes of complex ions -square planar (DRAW [Pt(NH3)4]2+)
-4 coordinate bonds - coordination number = 4
-complex ions containing Pt, Pd, Au and Ni
bond angle = 90
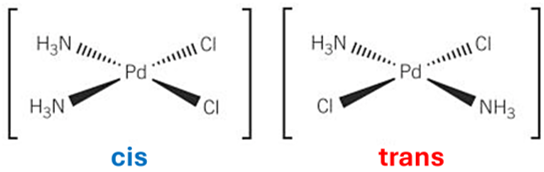
stereoisomers
compounds that have the same structural and molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms in space
cis-trans isomerism (diagram= square planar)
-occurs in square planar + octahedral complexes
-cis or Z = 2 ligands of the same type are adjacent and on the same side of the metal ion - are 90 degrees apart
-trans or E = 2 ligands of the same type are on opposite sides - are 180 degrees apart
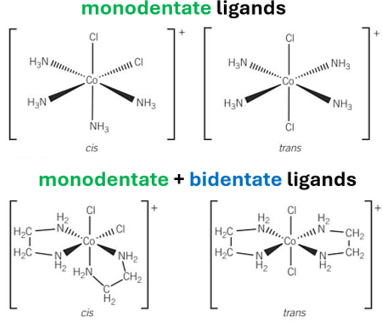
cis-trans isomerism in OCTAHEDRALS -DRAW
-monodentate ligands
-mixture of monodentate + bidentate ligands
optical isomerism
molecules that are non-superimposable images of each other (mirror images that will not look the same when laid on top of another)
-exists in octahedral complexes with multidentate ligands
CONDITIONS for optical isomerism
1) complex with 3 molecules/ions of a bidentate ligand
2) complex with 2 molecules/ions of a bidentate ligand AND 2 molecules/ions of a monodentate ligand
3) complex with 1 hexadentate ligand
uses of cis-platin
-used as an anti-cancer drug
-binds to the DNA of fast growing cells and prevents cell division, reducing growth of cells and can lead to apoptosis
haemoglobin
-has 4 haem groups with Fe2+ in centre
-in 1 haem = 6 coordinate bonds with central Fe2+ ion - 4 with nitrogen atoms, 1 with globin and 1 with oxygen
-shape = octahedral
-temporary ligand = oxygen
haemoglobin + carbon monoxide
-carbon monoxide coordinately bonds with the Fe2+ and forms stronger bonds than oxygen
-so if oxyhaemoglobin already formed, carbon monoxide can replace oxygen and form carboxyhaemoglobin = ligand substitution
-stops oxygen from bonding to haemoglobin so cannot be transported around the body