Ionic bonding: Elements compounds and mixtures: Chemistry: (9:1)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Formation of metal ions
Atoms lose outer electrons
Metals
Elements that form positive ions
Formation of non-metal ions
Atoms gain electrons
Charge on non-metal ions
Negative
Group 1 ions charge
+1
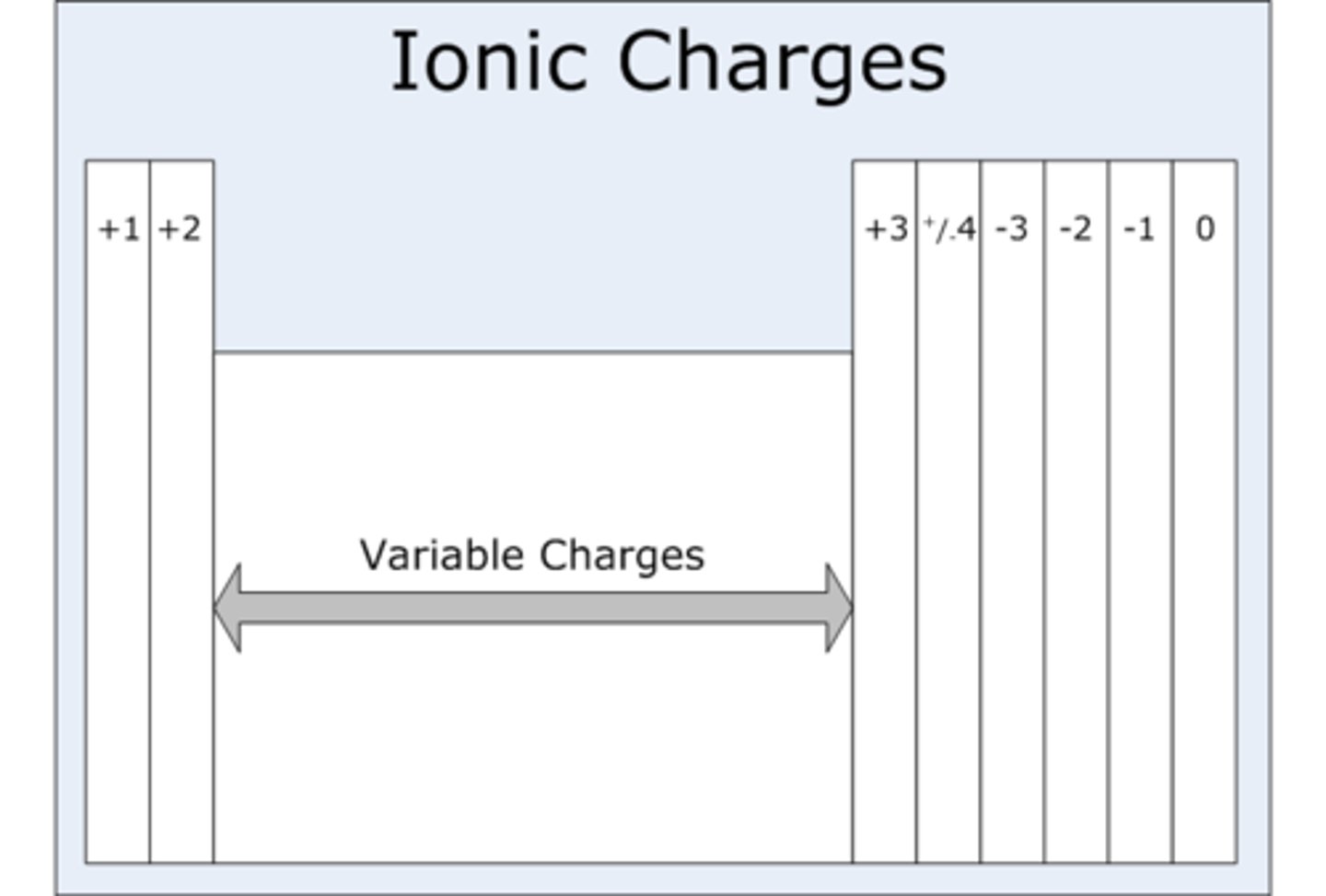
Group 2 ions charge
+2
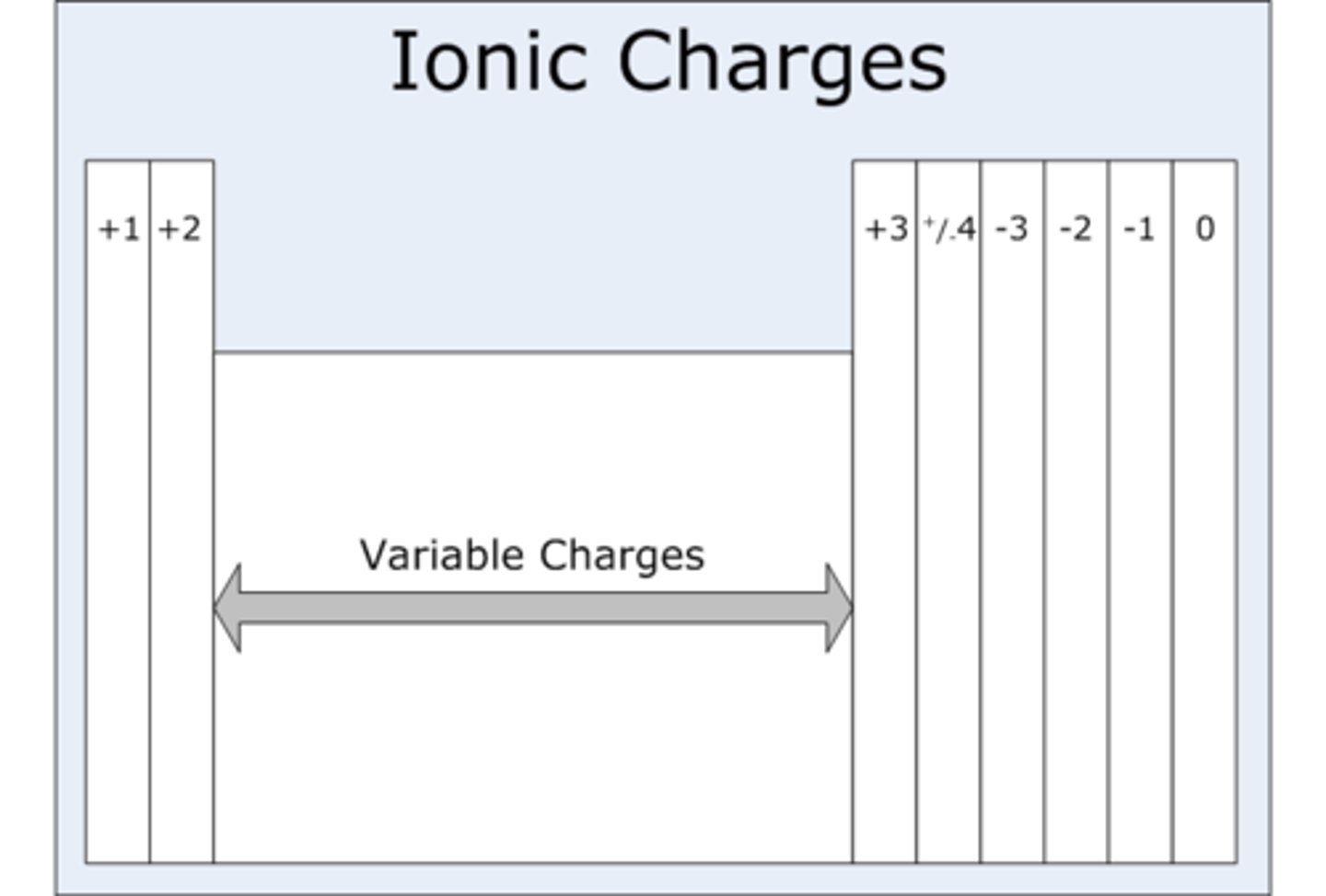
Group 6 (IUPAC group 16) ions charge
-2
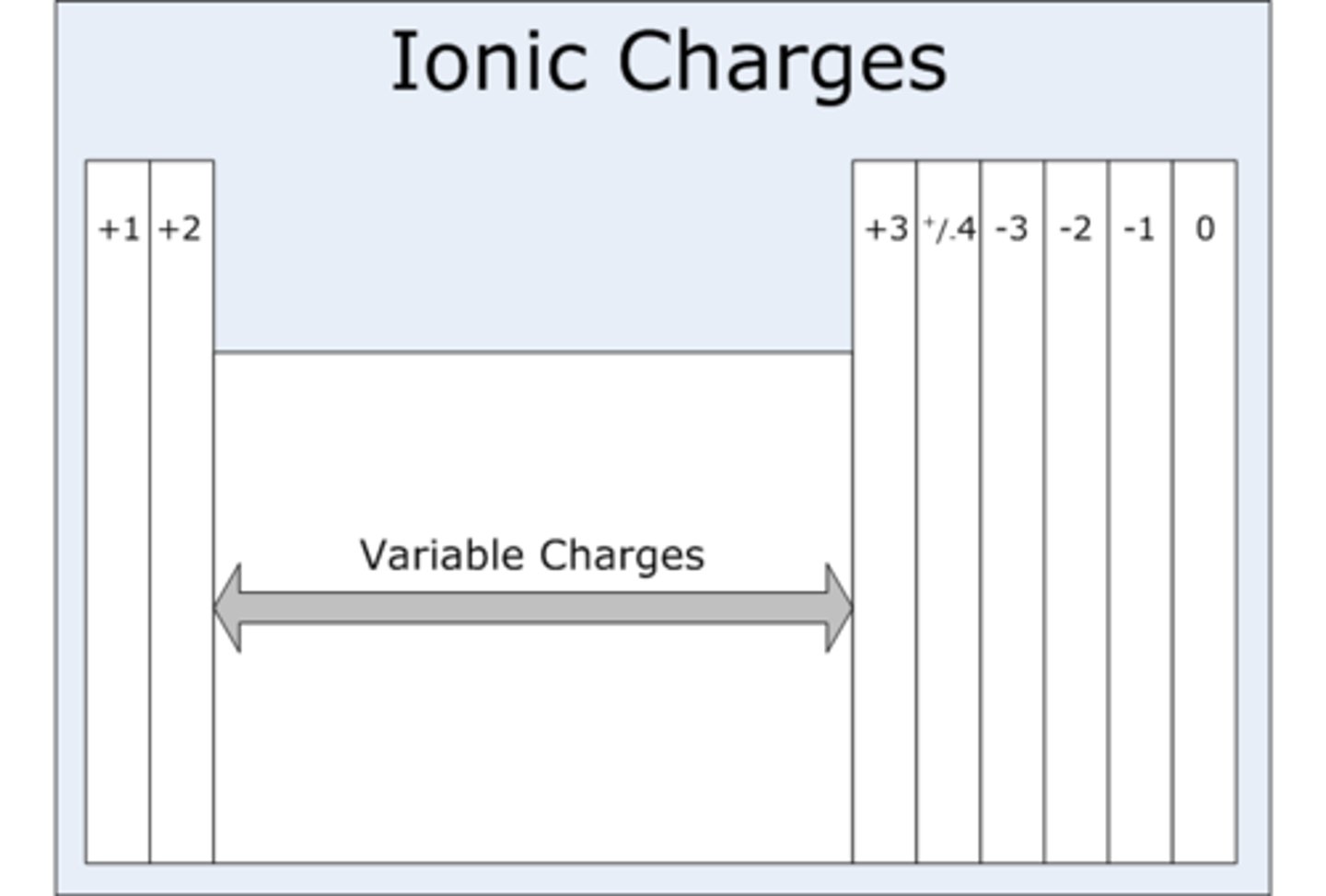
Group 7 (IUPAC group 17) ions charge
-1
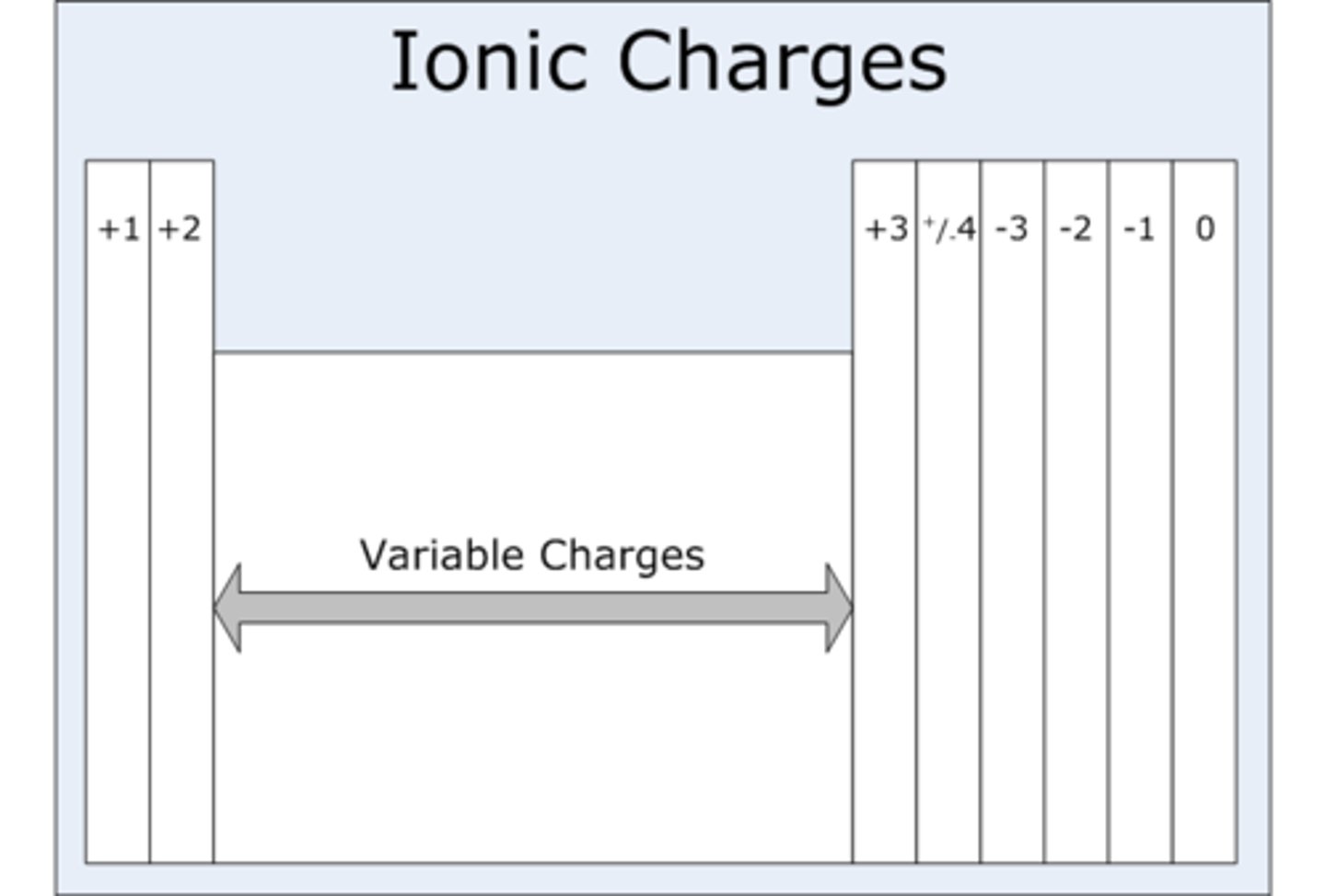
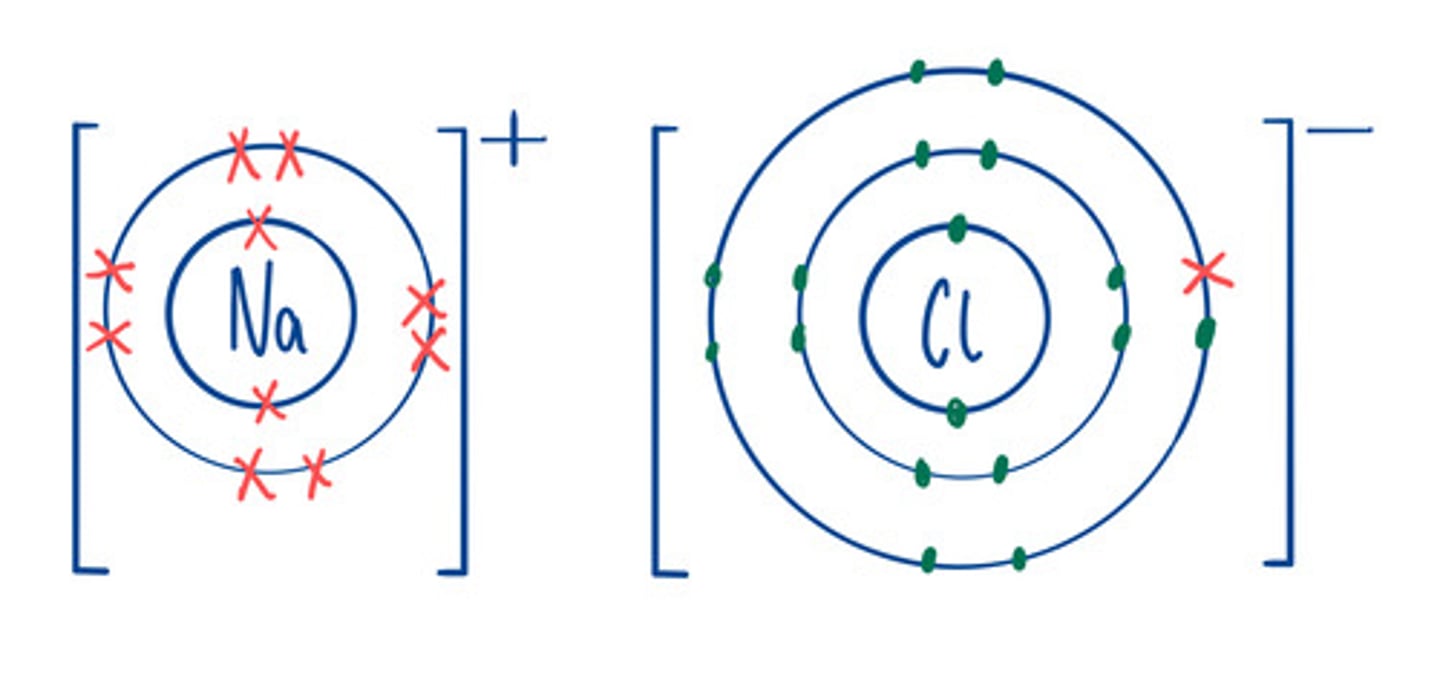
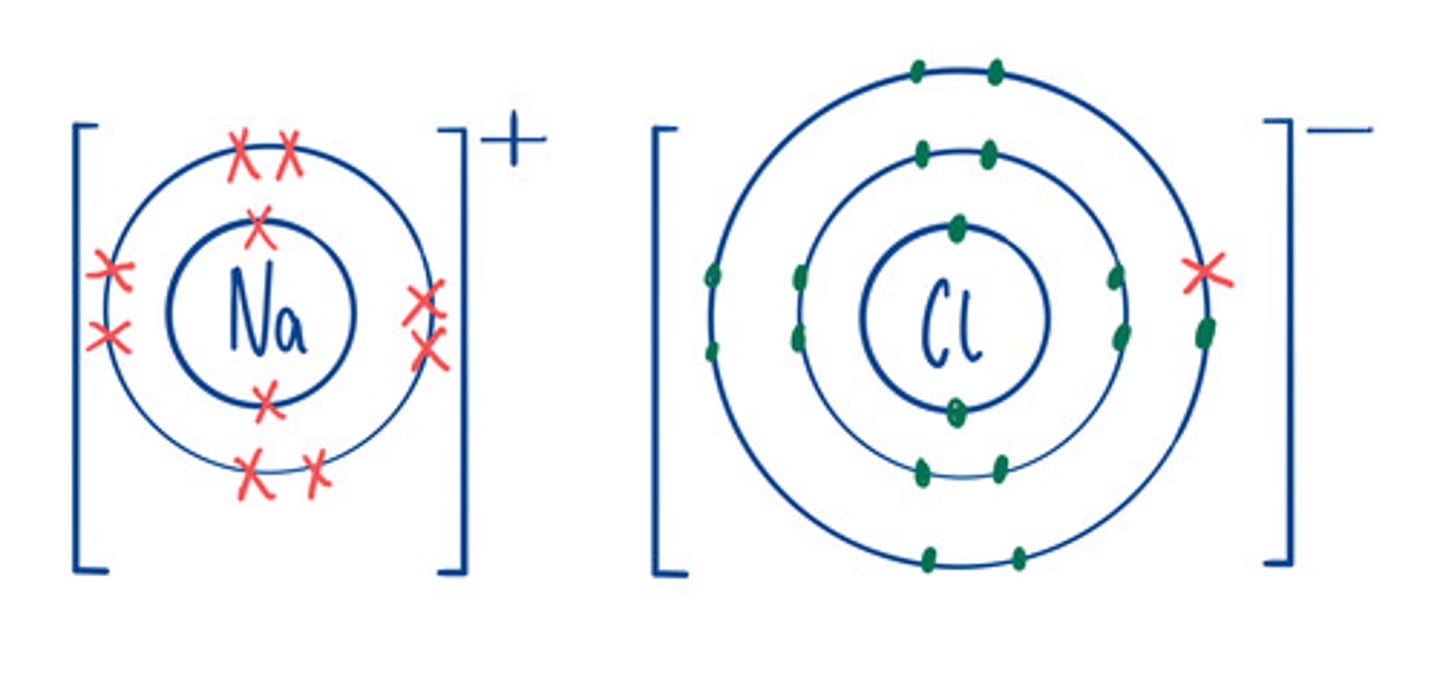
Electron structure of ions
Same as the nearest noble gas
Giant structure
A huge 3D network of atoms or ions
lattice
Regular arrangement of particles.
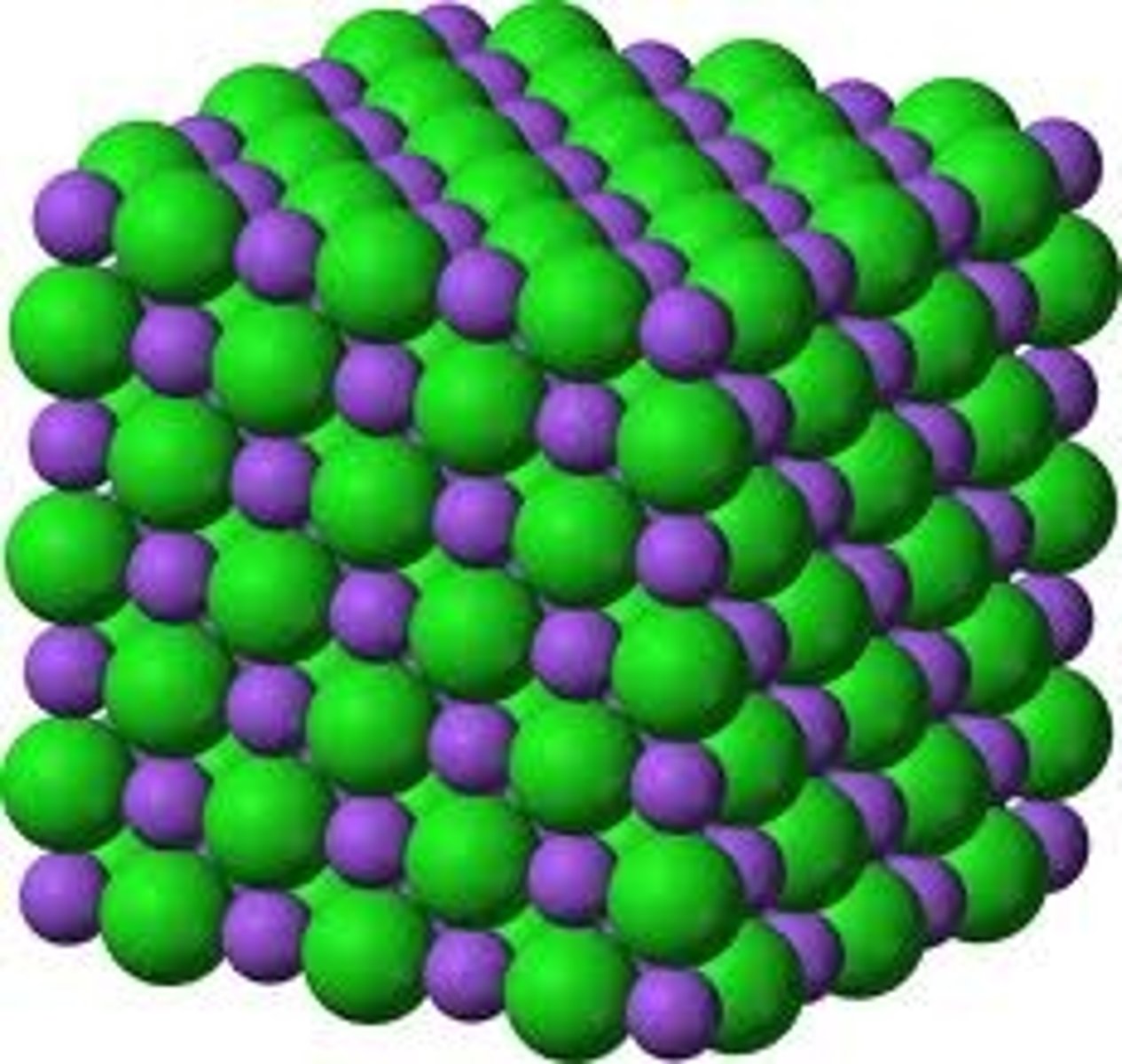
Giant ionic lattice
A huge, 3D, regular structure of oppositely charged ions, held together by electrostatic forces.
Examples of Ionic compounds
NaCl, MgO
Limitations of dot and cross diagram
Looks like the compound only contains a few ions
Limitations of a dot and stick diagram
Looks like each ion is only attracted to a few other ions
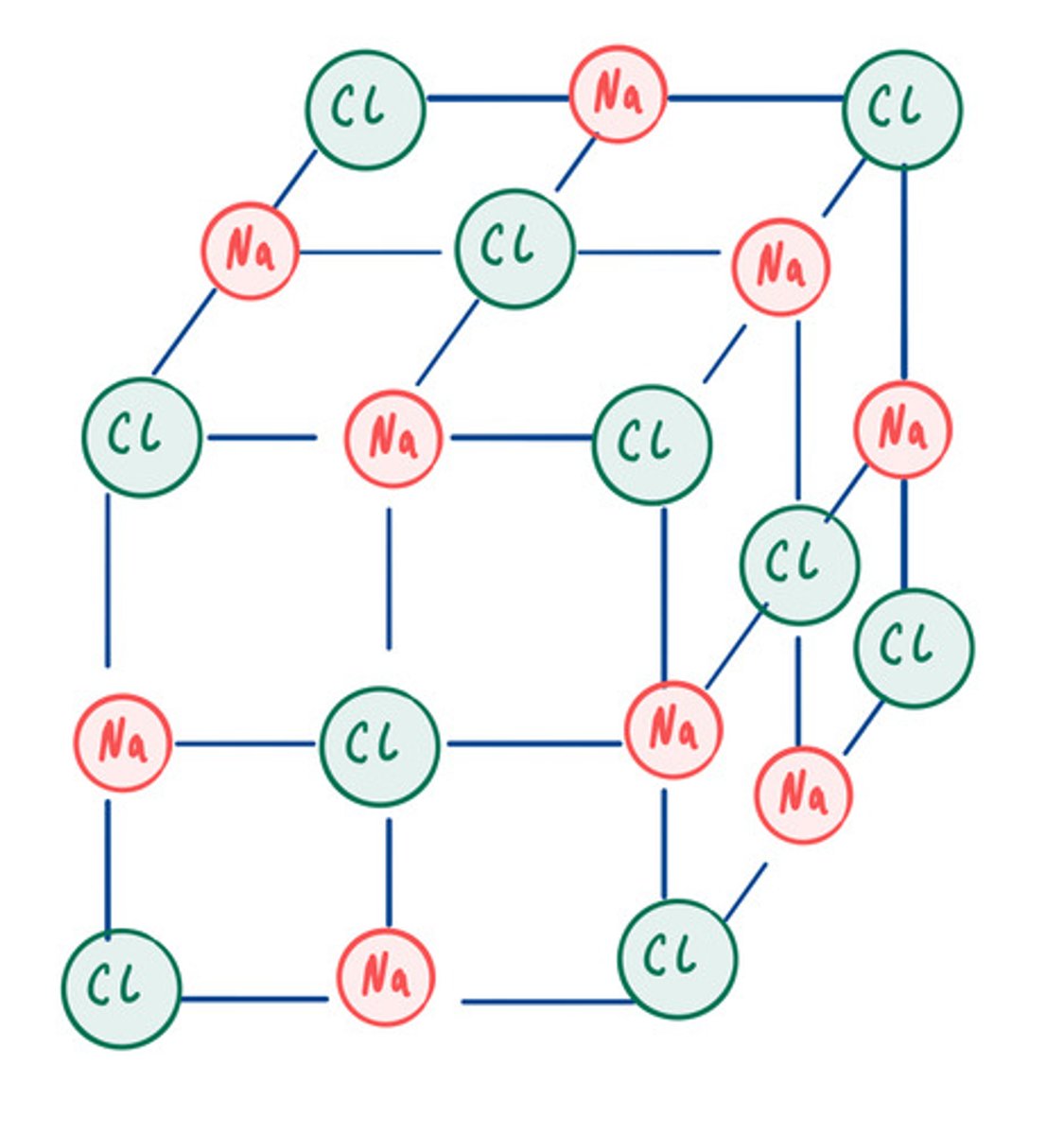
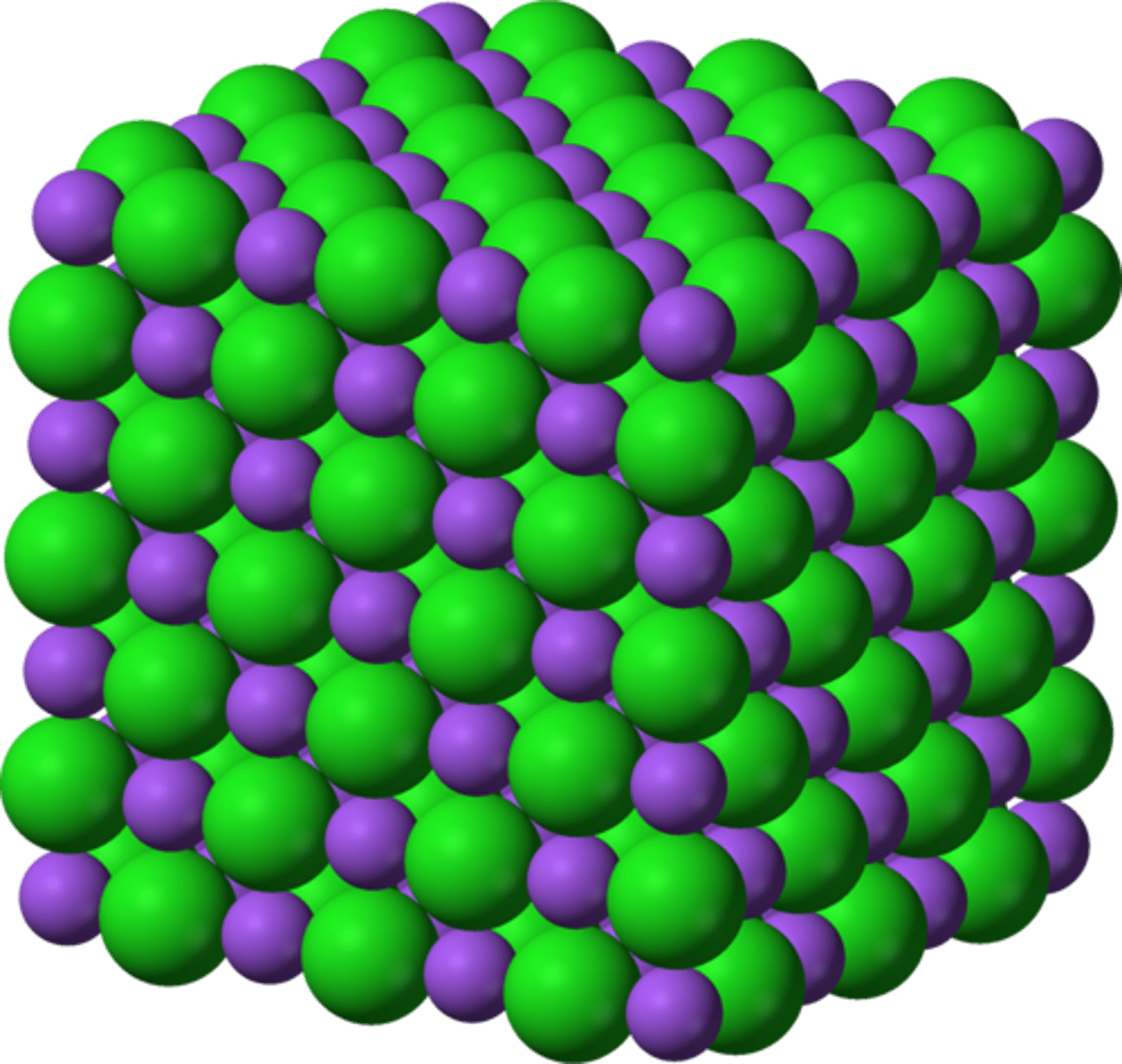
Limitations of a 3D diagram
Looks like it only contains a few ions

Melting and boiling points of ionic substances
high
Reason for melting and boiling points of ionic substances
Strong electrostatic forces between opposite ions need lots of energy to break
Movement of ions in a solid
Ions vibrate around fixed positions
Molten
Made liquid by heat

Movement of ions when molten
Ions can move past each other
Movement of ions in solution
Ions break apart and move freely
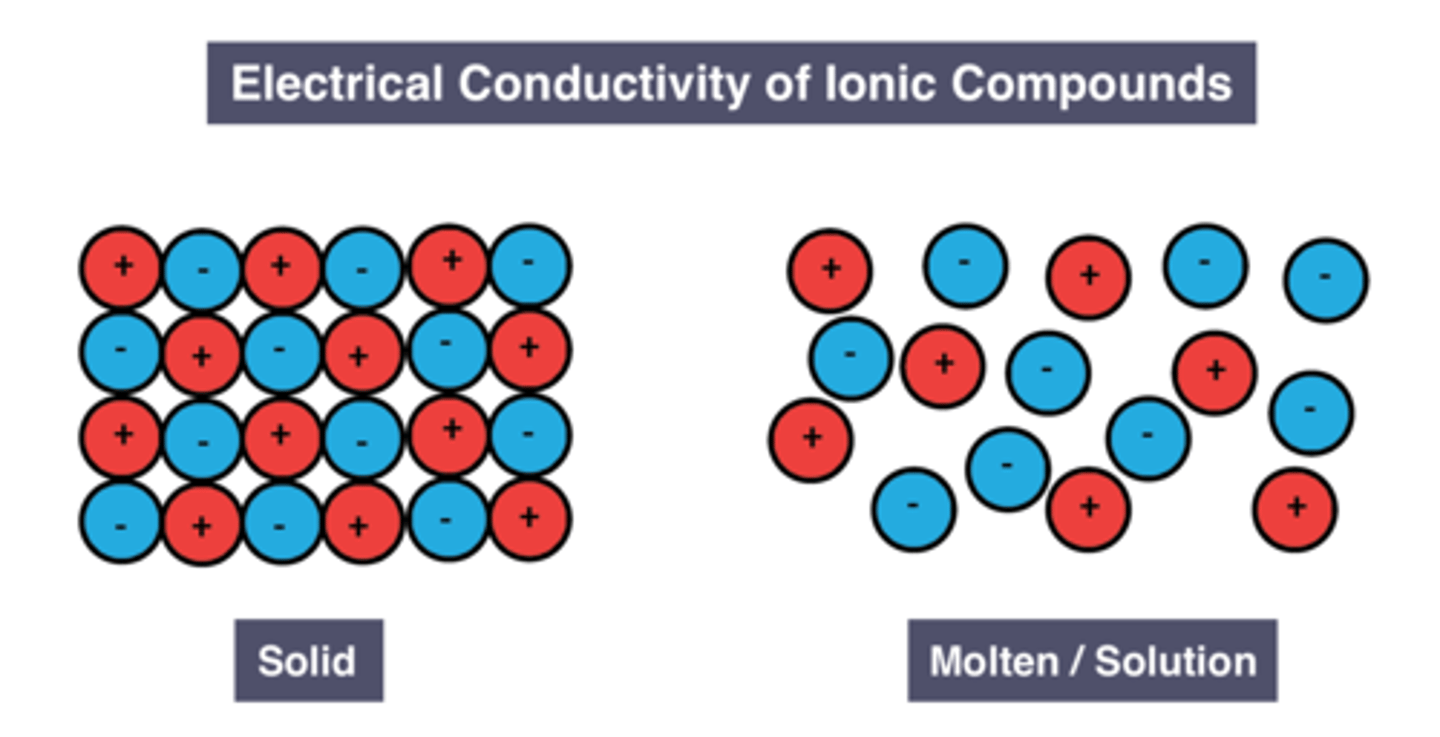
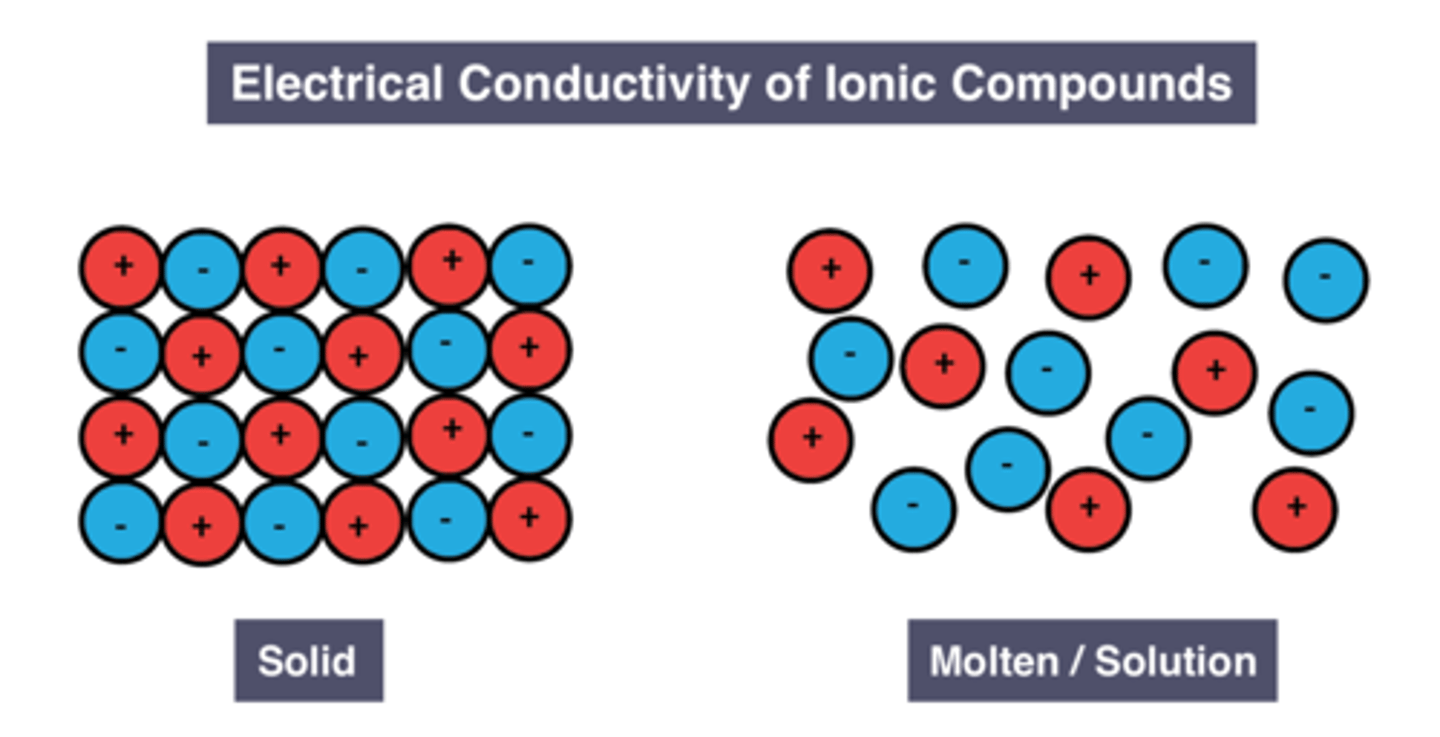
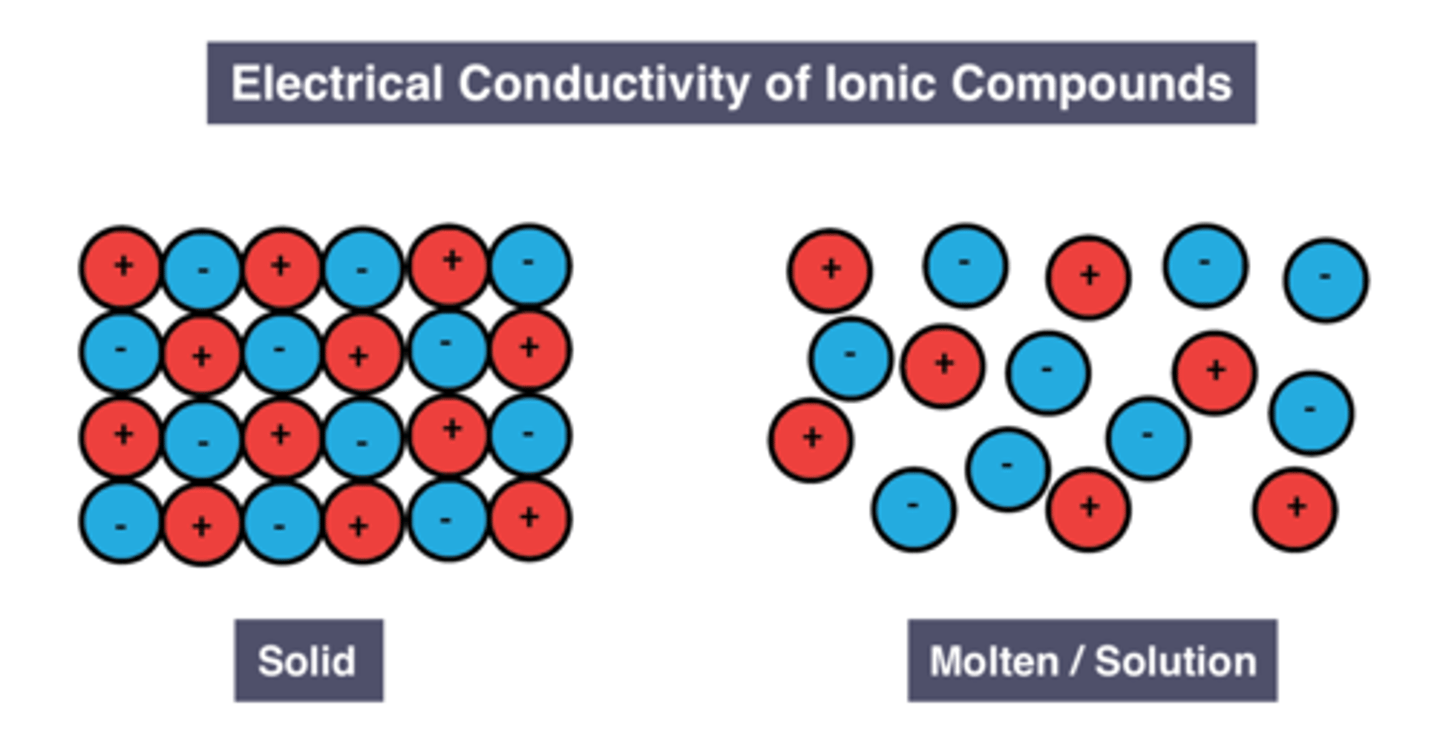
Conductivity of solid ionic compounds
don't conduct
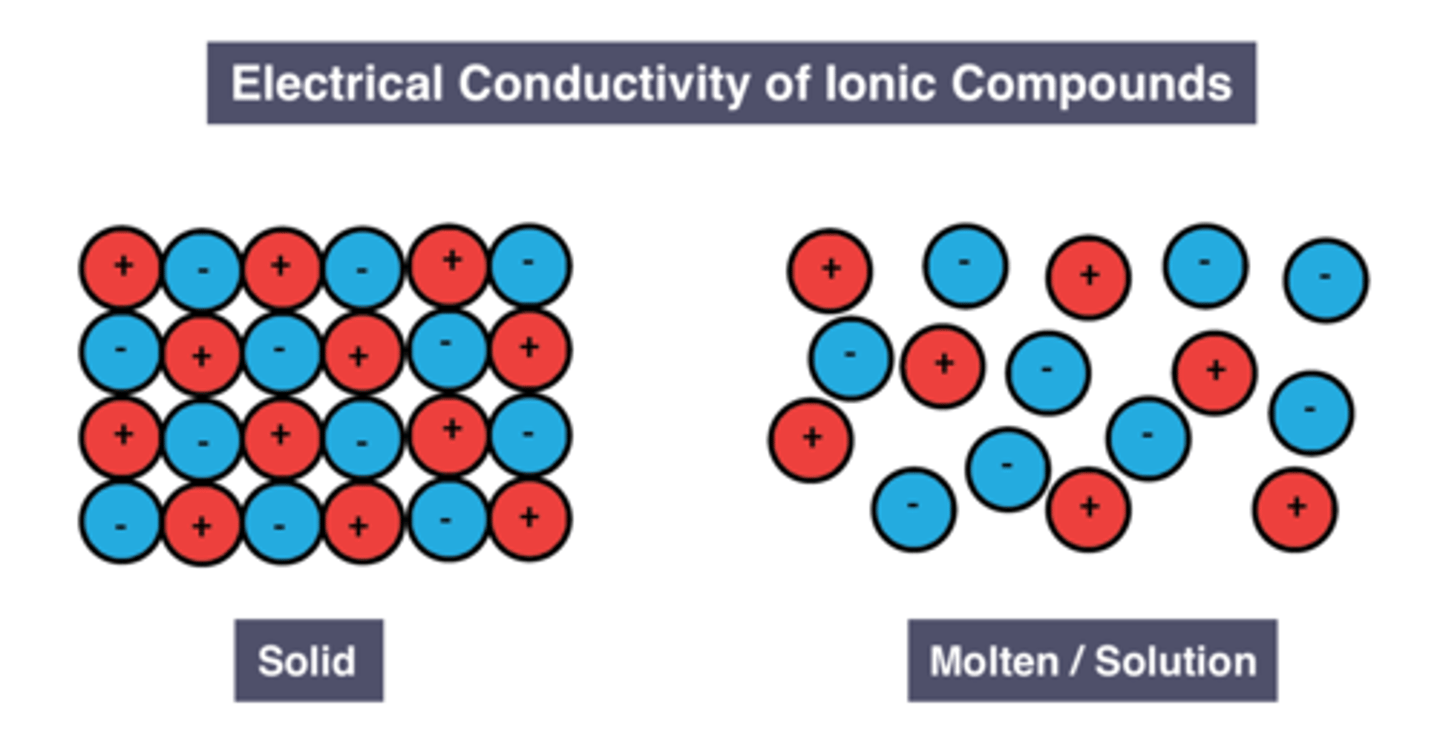
Reason for conductivity of solid ionic compounds
Ions are fixed in place
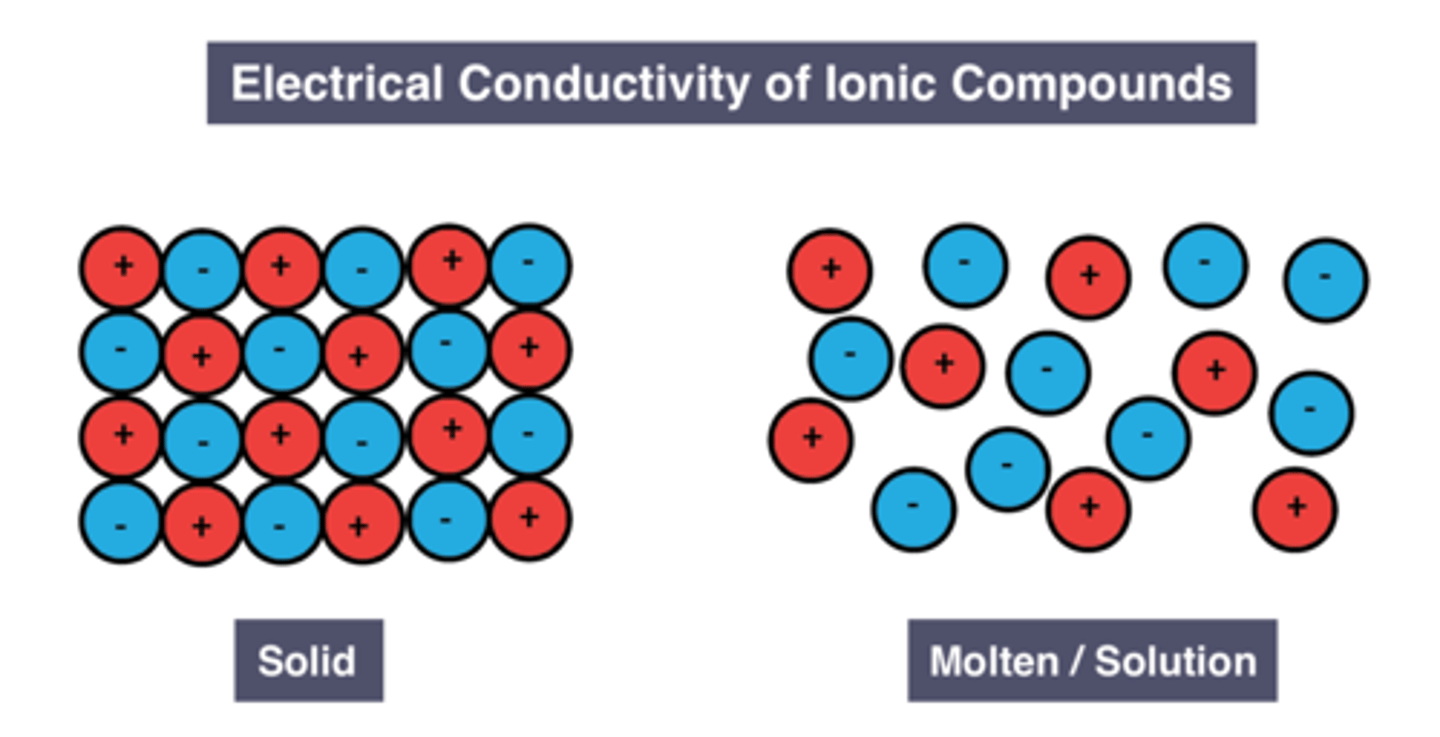
Conductivity of molten/dissolved ionic compounds
good conductors
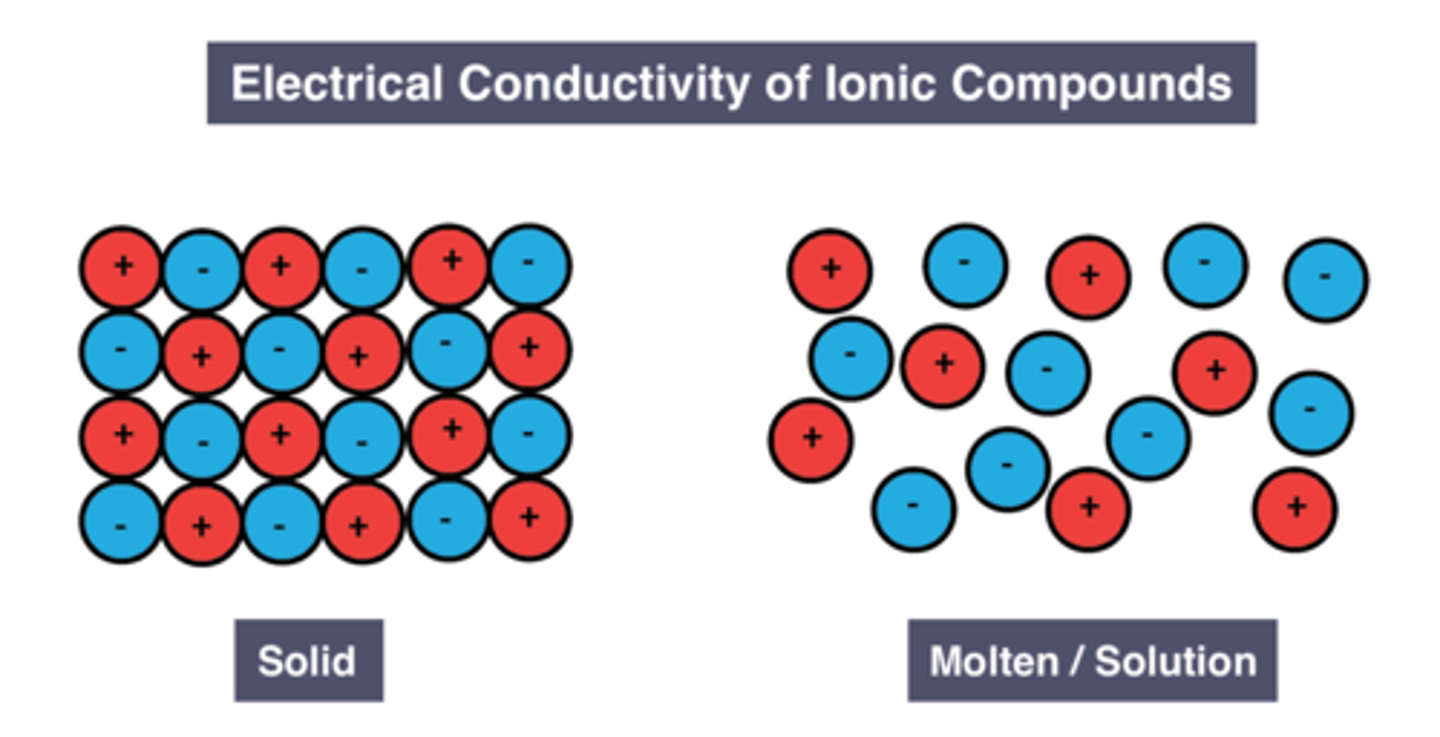
Reason for conductivity of liquid/dissolved ionic compounds
Ions are free to move and carry charge
Electrostatic force of attraction
The attractive force between oppositely charged particles.