Unit 7 Ag Revolutions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Agriculture
The production of food, fiber and fuel from tending plants and livestock for the purpose of human use. (i.e. Farming)
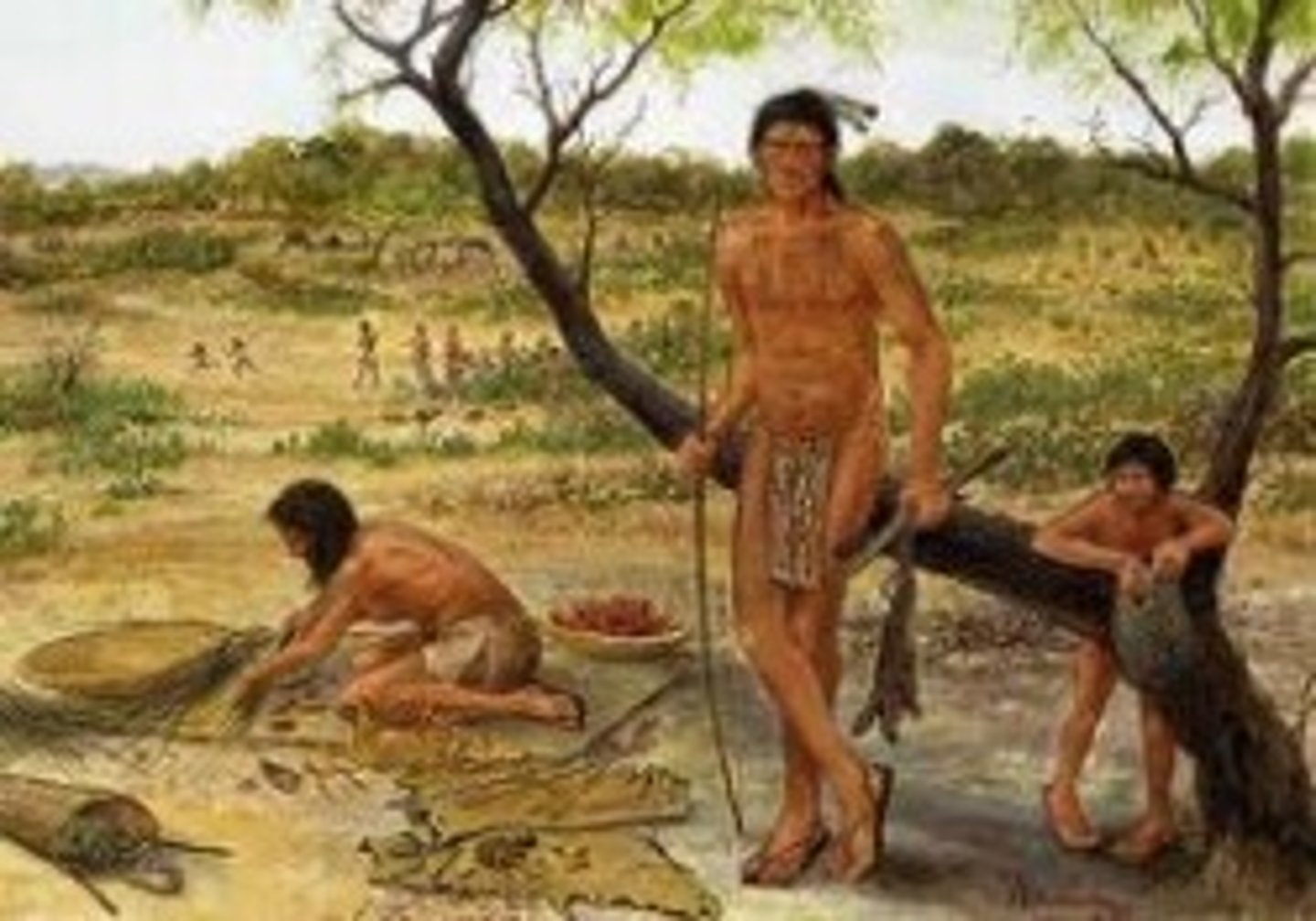
Hunting, Gathering, Fishing
This was the first way humans obtained food. Modern forms of this are still used.

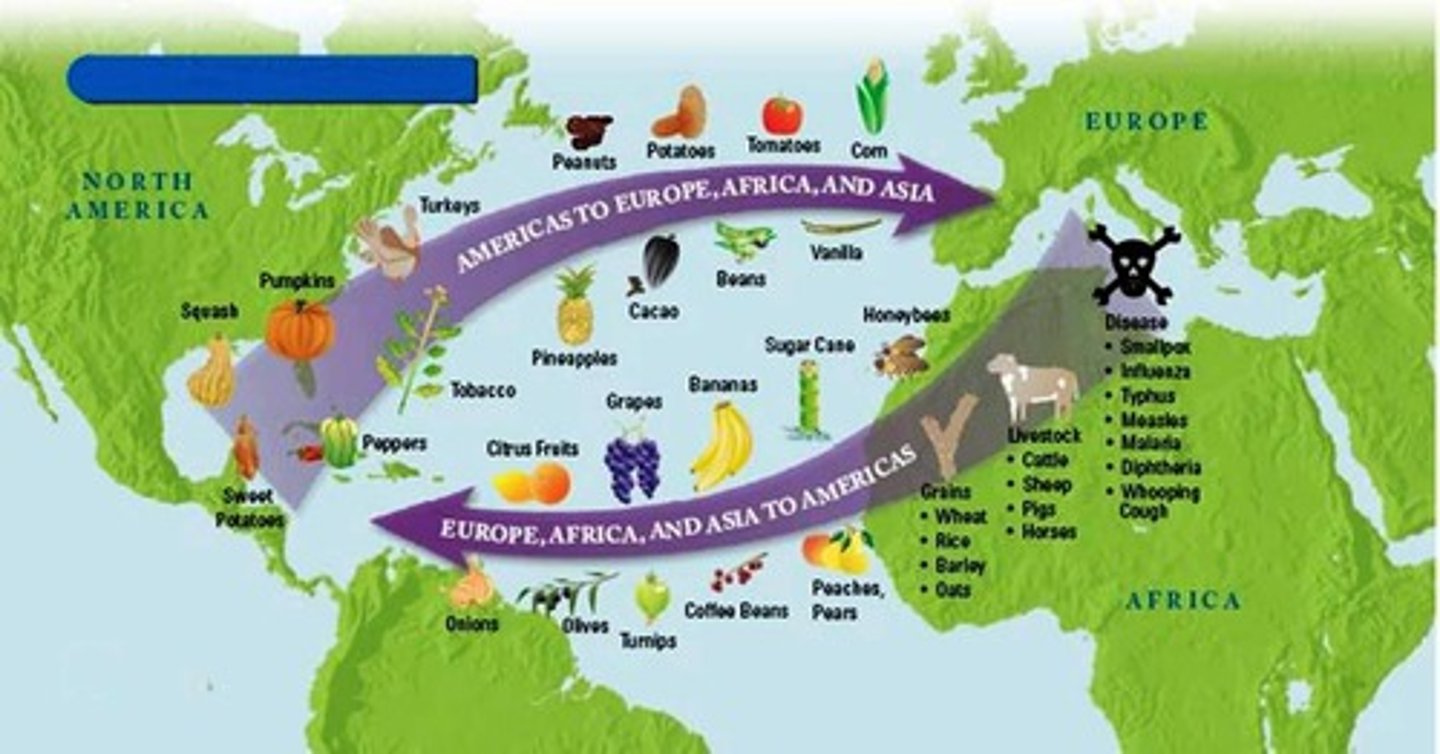
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas (the "New World") and the rest of the world following Columbus' voyages.
Domestication
Selective growing or breeding of plants and animals to make them more useful to humans.
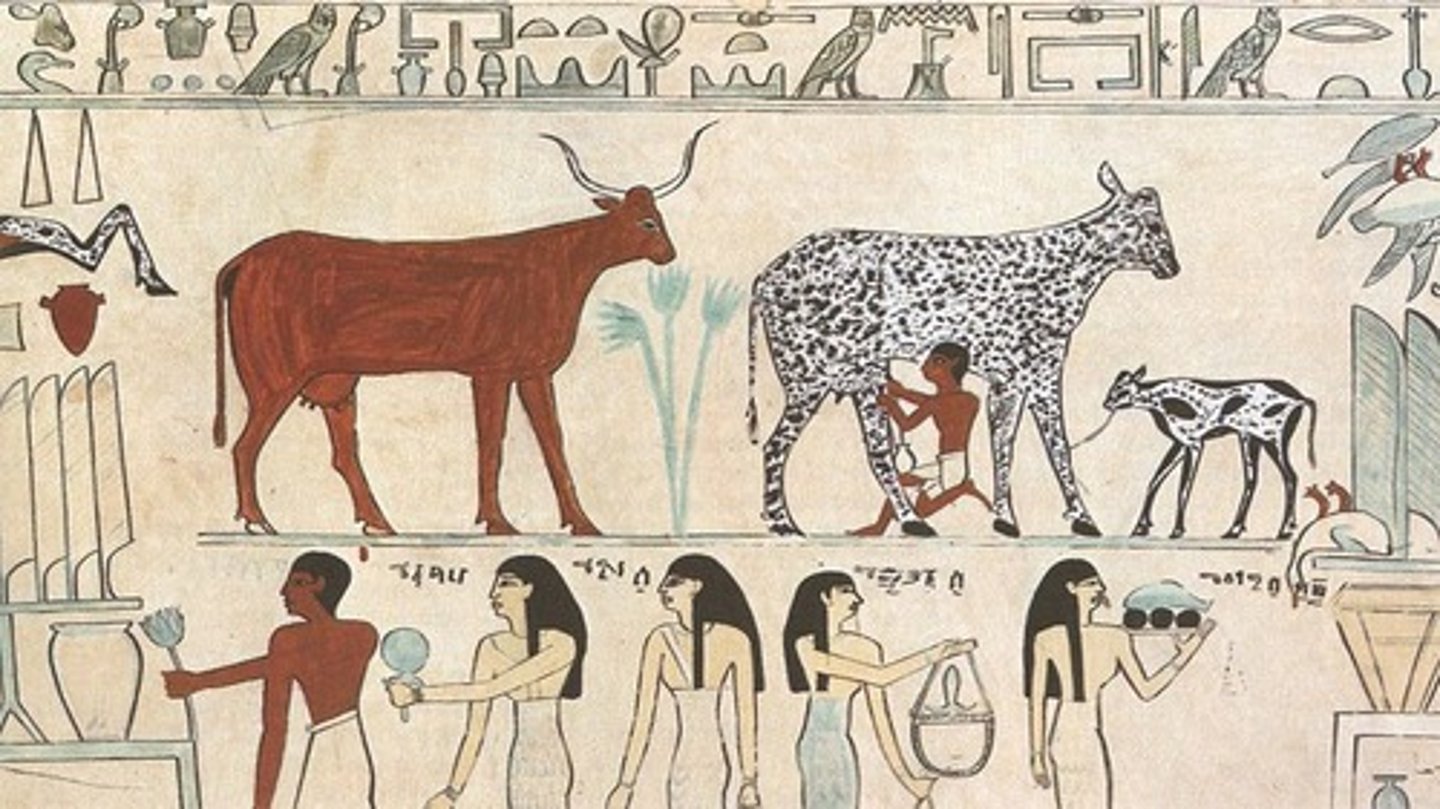

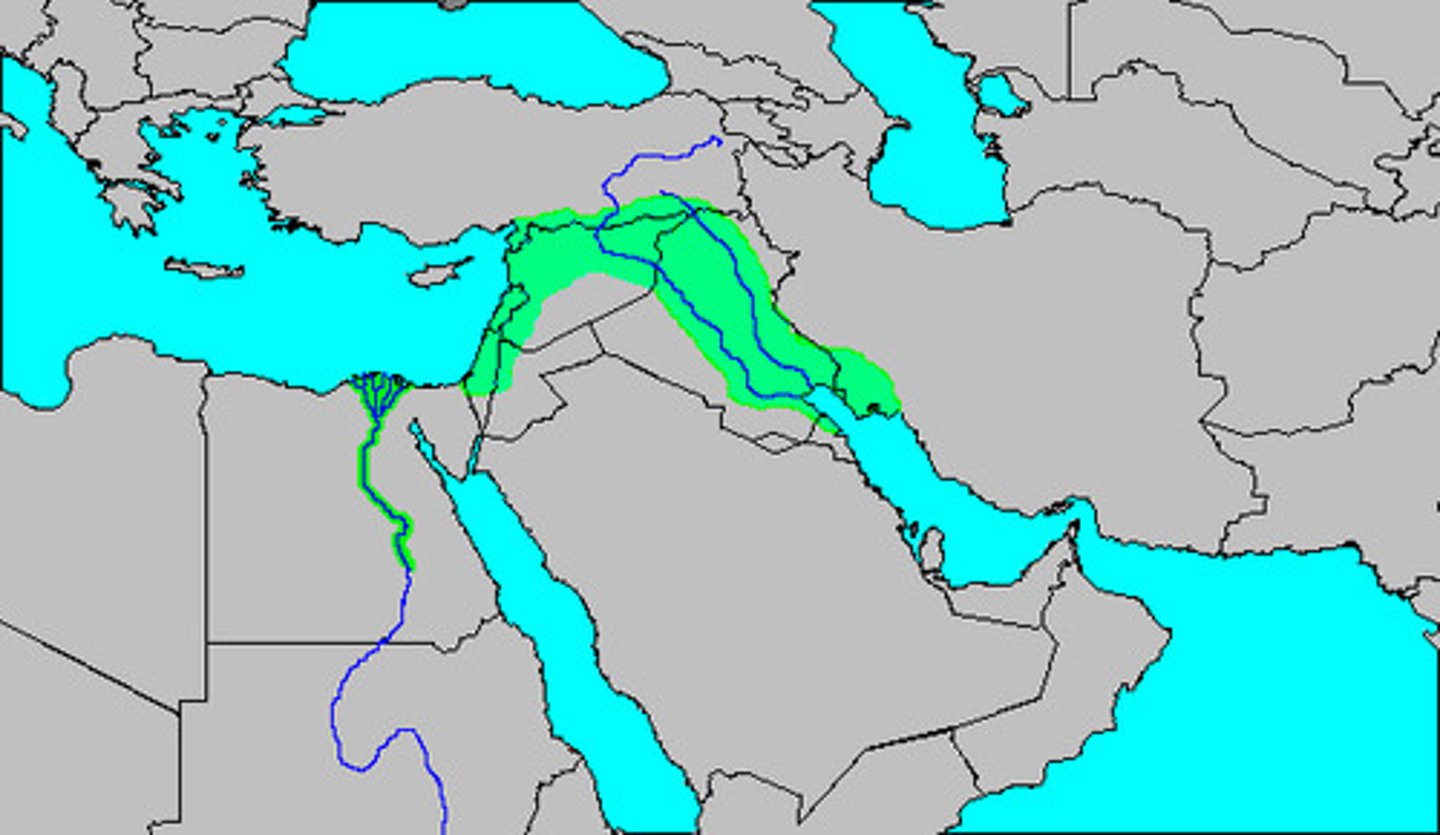
Fertile crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East (Southwest Asia) stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
GMOs (genetically modified organisms)
Plants and animals that have been genetically modified (using processes like gene splicing) to contain genes they would not normally have or could get through traditional breeding programs.
Green Revolution
An agricultural revolution that increased production through improved seeds, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation; helped to support rising populations.
Large scale commercial agricultural operation (factory farms)
large farming for profit such as agribusiness and plantation farming
Subsistence
farming in which only enough food to feed one's family is produced
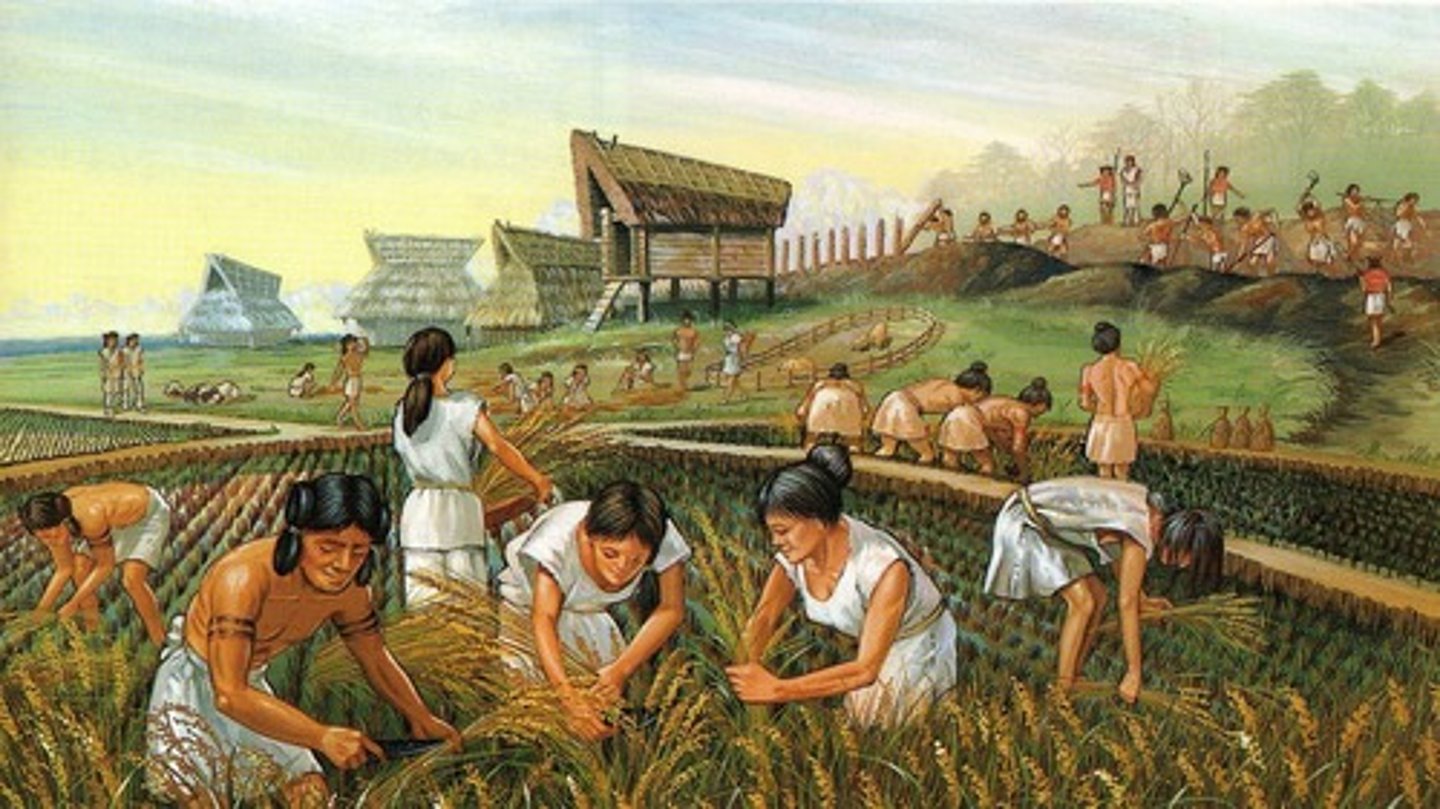
First Agricultural Revolution
The domestication of plants and animals and the resulting start of sedentary societies (also called the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution)

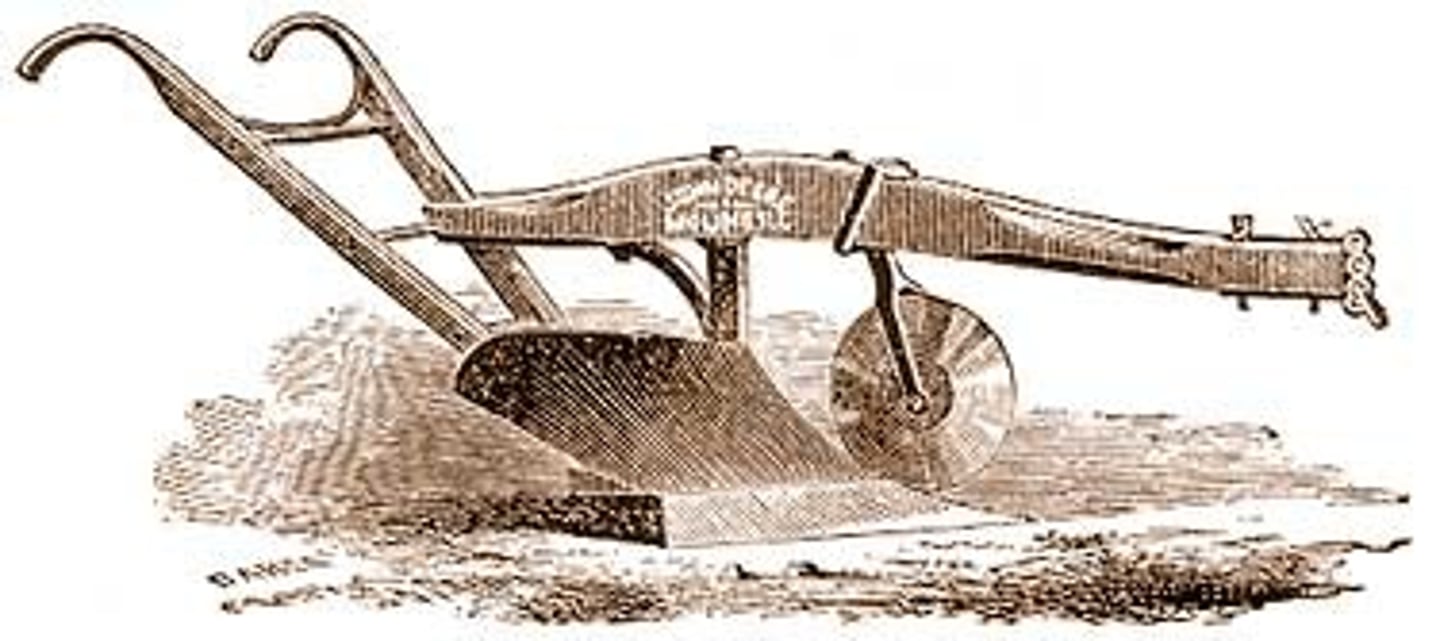
Second Agricultural Revolution
Tools and equipment were modified, methods of soil preparation, fertilization, crop care, harvesting, and food storage improved the productivity of agriculture. Colonialism/Imperialism brings New World crops to Europe. The Industrial Revolution could not have occurred without this and probably vise versa.

"Third Agricultural Revolution"
A fundamental change in agriculture associated with technological innovations and scientific farming techniques developed in the 20th century including extensive mechanization, heavy reliance on irrigation and chemical applications, and biotechnology. This revolution encompasses both the Green Revolution and Large Scale Commercial Agriculture.