Biology Chapter 8
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is cytology?
study of cells
What are the 3 principles of cell theory?
1. All organisms are made of cells
2. All existing cells are produced by other living cells
3. The cell is the most basic unit of life
unicellular
Made of a single cell
multicellular
Consisting of many cells
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
organ
A collection of tissues that carry out a specialized function of the body
organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
eukaryotic
Cell with a nucleus (surrounded by its own membrane) and other internal organelles.
prokaryotic
No nucleus
what are other names for cell membrane?
plasma membrane and phospholipid bilayer
where is the cell membrane found?
all cells and on the edge of cell
hydrophobic
Water fearing tails
hydrophillic
water loving heads
What structure on the cell membrane allows things to pass through?
Proteins
How does signal transmission across a membrane happen?
a) Receptor protein receives signal molecules
(ligand) that cause a response in the cell
b) Receptor protein and ligand shape must
match to be received
c) If they match the shape changes
what do mitochondria do?
make energy
mitochondira nickname
powerhouse
how many membrane do mitochondria have?
2
What are cristae?
inner membrane of mitochrondria
What do cristae do?
provide vast surface area to maximize energy production
where are cell walls found?
Only in Plants
what do cell walls do?
they filter things
what are cell walls make of?
cellulose
made while cell is developing
primary wall
made while cell is mature it has more cellulose
secondary
what does cytoplasm do and what does it look like?
it holds the organelles and its jelly like
liquid of cytoplasm
cytosol
what are the 3 organellles where DNA is found?
Nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast
how many mitochrondira cfn be found in a cell
numerous to a few, large scale
what do ribosomes do?
make protein and ships then to the golgi apparatus
what are ribosomes made of?
protein and RNA
where are ribosomes found?
free-floating in the cytosol, or bound to the rough ER or the nuclear envelope
what are the two kinds of endoplasmic reticulus
RER - rough - ribosomes
SER - smooth - no ribosomes
function of RER and SER
The RER is responsible for processing and folding proteins.
The SER is responsible for making and processing lipids.
what is the purpose of the golgi apparatus
Packaging - Process, sort,
and deliver proteins and lipids
how does the Golgi apparatus work?
Sacs get pinched off
Packaged into a vesicle
or shipped somewhere else
what is the nickname of lysosomes
garbage men
what do lysosomes do?
membrane packages that break down with digestive enzymes
what is the cytoskeleton?
frame of the cell
What are the cytoskeleton made of and what does each part do?
Microtubules - give shape and act as railroad tracks
Intermediate filaments - add strength
Microfilaments - smallest diameter & help w/cell division
how are cilia and flagella the same?
they both move cells
how are cilia and flagella different?
Cilia- many and short, help move substances across cells
Flagella- few and long, move cells
what are chloroplasts
Membrane-bound organelles where photosynthesis takes place in plants
thylakoids vs grana
grana is stacks of thykaloids
chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplast
stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
what is the purpose of vacuoles and vesicles
to store food and waste
what is turgor pressure
the water pressure inside the vacuole of the plant cell in response to the force of water within the cell
How does turgor pressure work?
Healthy plant cells contain more solutes than the water surrounding them so water is always trying to flow into the cell. Cells will fill until the pressure of the surrounding cell wall will not let any in, which keeps the cell "plump" (turgid). This turgor pressure provides the most support in non woody plant parts.
what are centrioles used for?
produes spindle fibers for cell divison
what is the control center
nucleus
where does DNA replicate?
nucleus
describe the nuclear envelope
Double membrane around nucleus
Nuclear pores - openings in envelope
Holds DNA
Nucleolus - contains RNA and starts to make protein
what is the nucleolus?
contains RNA and starts to make protein
what is homeostatis
Keeping a stable internal environment
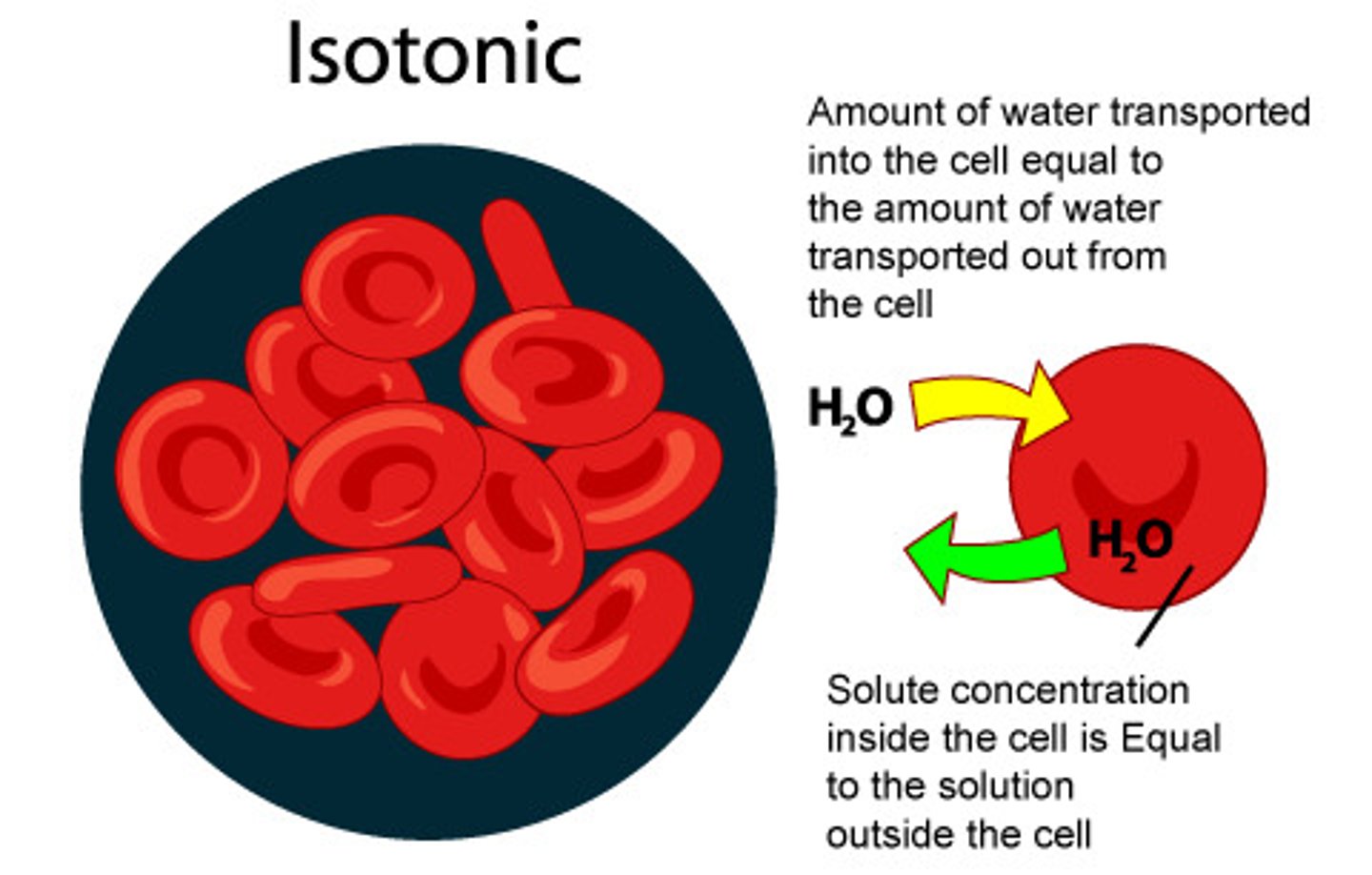
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
hypertonic solutions
solutions that cause cells to shrink or shrivel due to loss of water
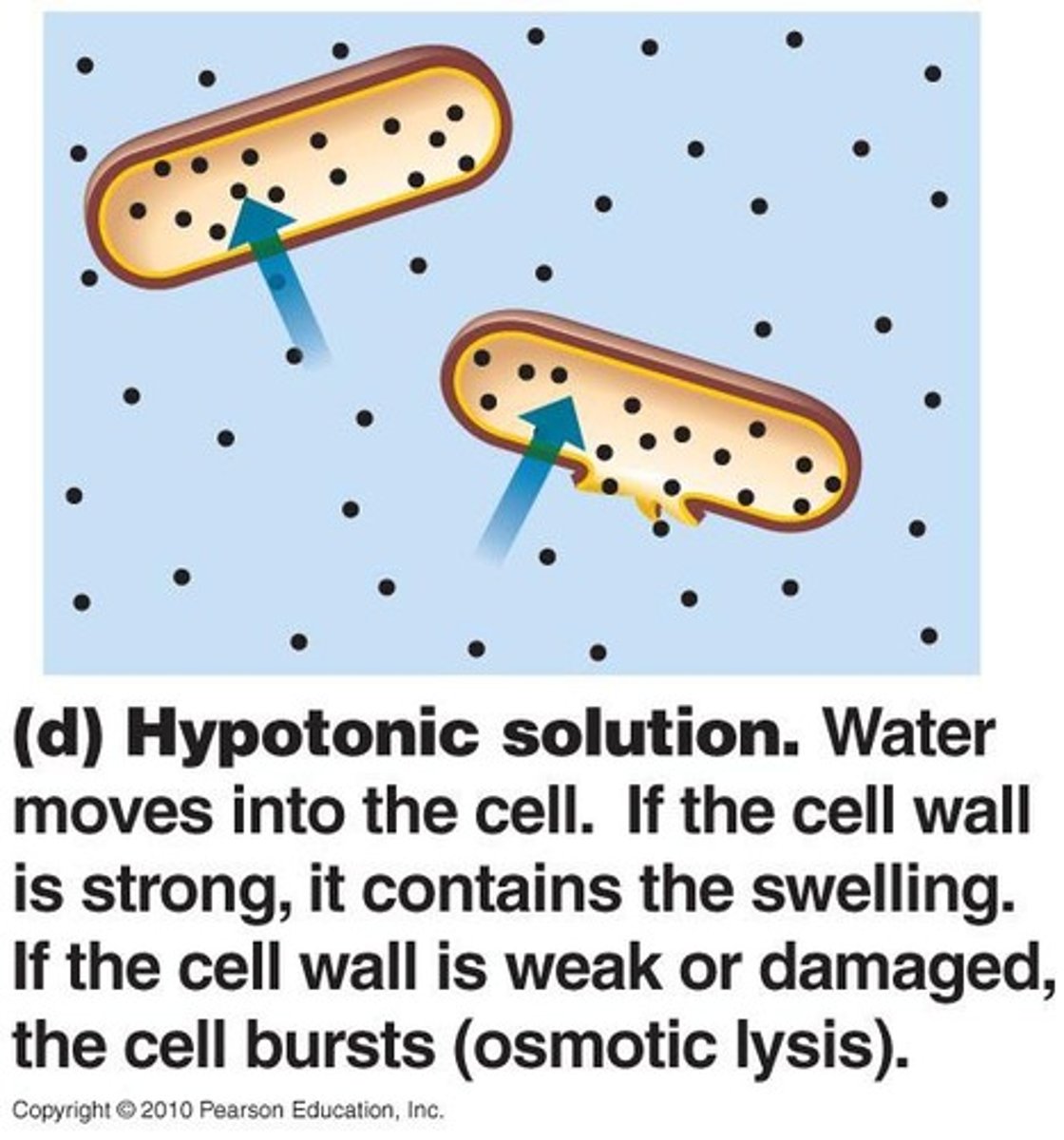
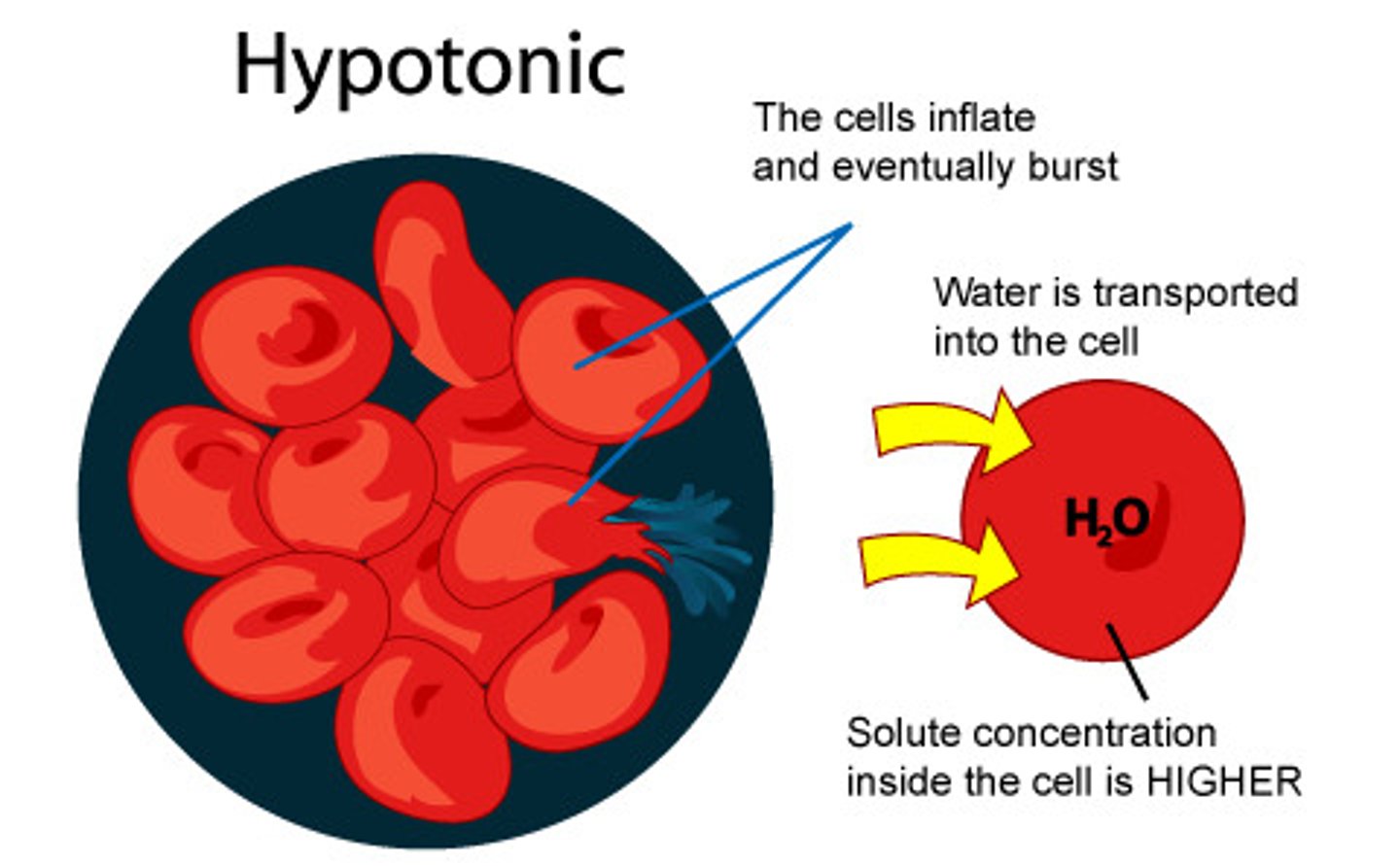
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
what is passive transportation?
Transportation that does not require energy
High → Low Concentration
what are 2 examples of passive transportation?
diffusion and osmosis
What are 3 things that affect the speed of transport?
size, shape and electrical charge
what is active transport?
needs energy
how do carrier proteings fit into active transport?
they physically bind to specific molecules (like ions or glucose), change shape using energy (usually from ATP), and shuttle them against their concentration gradient (low to high),
exocytosis
going out of the cell
endocytosis
going into the cell
phagocytosis
Cell eating
pinocytosis
Cell drinking
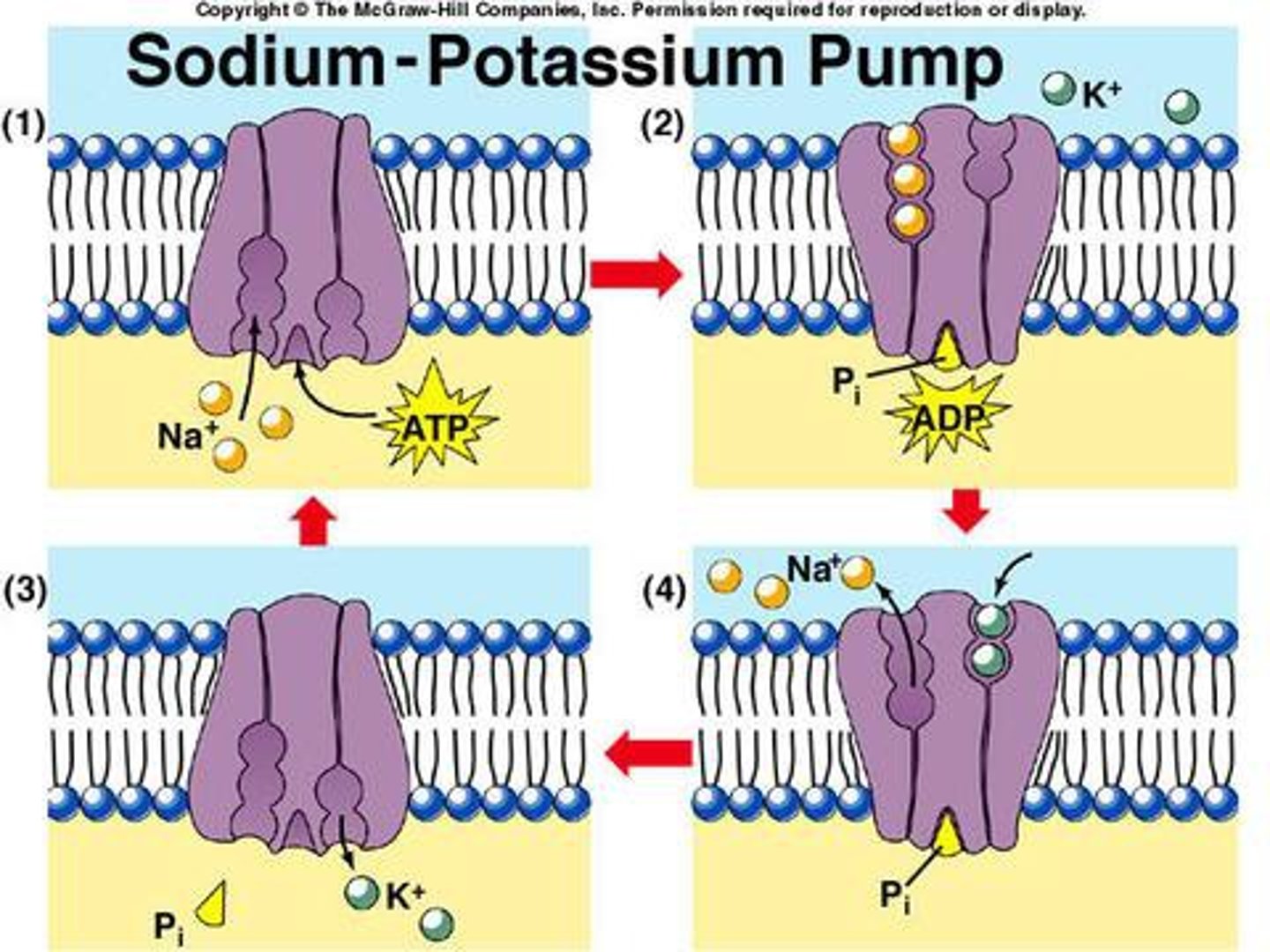
sodium potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell