⭐️ Study Guide Qs 5,7, & 10
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Trade Deficit
a nation imports more than it exports
Trade Surplus
a nation EXPORTS more than it IMPORTS

Balance of Trade
Exporting, Selling more = Surplus → More Money! 🙂
Importing, Buying more = Deficit → Less Money ☹
“More exports? Yay! 🙂 || More imports? Gotta pay! ☹ “

Mercantilism
The old idea that a country gets richer by selling more to other countries (exports) and buying less from them (imports).
The goal: bring in more gold and silver.
“Sell more, buy less, get rich with gold.”
Exports = 💰 coming in
Imports = 💰 going out
More exports = More treasure 🪙
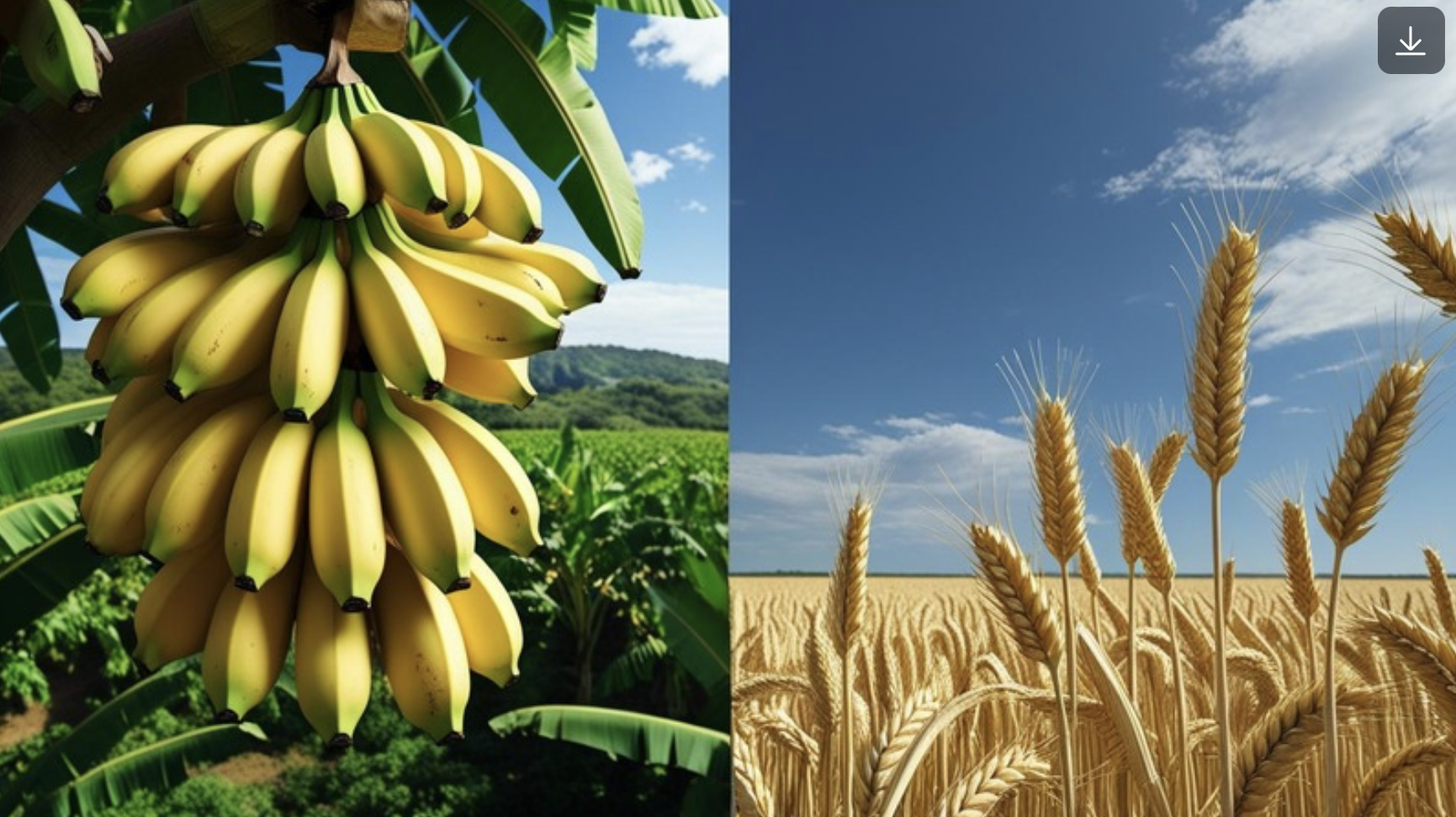

Absolute Advantage
Abundantly producing a specific resource over other countries
🍌 Example: The U.S. and Brazil
The U.S. can produce 100 tons of wheat or 30 tons of bananas in a year.
Brazil can produce 50 tons of wheat or 100 tons of bananas in a year.
📊 Who has the absolute advantage?
The U.S. makes more wheat → it has an absolute advantage in wheat.
Brazil makes more bananas → it has an absolute advantage in bananas.

Comparative Advantage
A country focuses its energy on what they do best. (Manufacturing, services, or agriculture) and trades for what others produce more efficiently.
Product Life Cycles (International Trade Theory)
| Stage | Goal |
| ------------------- | ----------------------------------------- |
| Development 🛠 | Build and test the product (no sales yet) |
| Introduction 🌱 | Create awareness and attract early users |
| Growth 🚀 | Increase sales and market share |
| Maturity 🌳 | Maximize profits and defend market share |
| Decline 🍂 | Cut losses or reinvent the product |
Strategic Trade (International Trade Theory)
Governments can strategically intervene in big industries by providing funding — like Boeing and Airbus
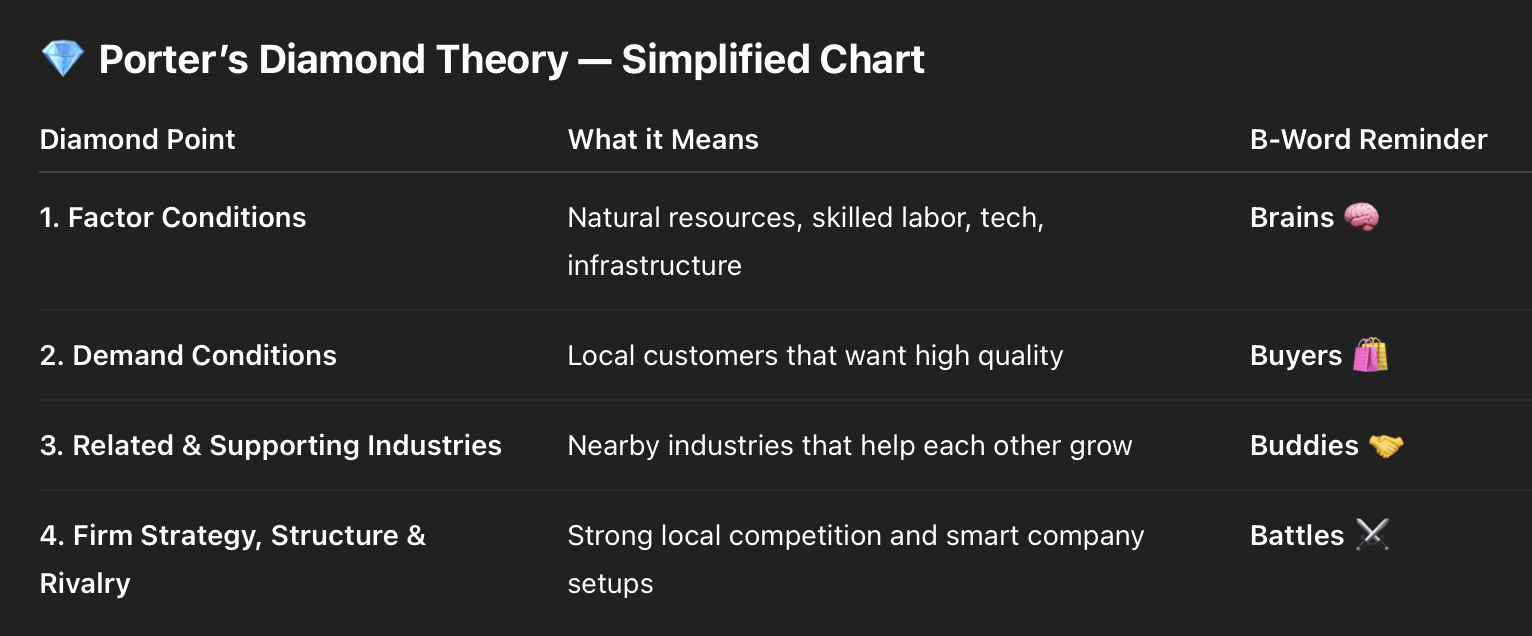
Diamond (International Trade Theory)
Brains, Buyers, Buddies, Battles — build advantage!
Exchange Rate
Exchange rate tells the trade fate—how much of one money you swap for another on any given date.
Exchange rates move like a seesaw — always going up and down depending on what people think and do. Like at Bed Bath and Beyond, prices changed daily
What are the determinants of supply and demand for an exchange
rate market?
| Exchange Rate | | Supply or Demand? | __________________________________________________
| 🔼 Exchange Rate ↑ | 📈 Demand ↑ or 📉 Supply ↓ |
| 🔽 Exchange Rate ↓ | 📉 Demand ↓ or 📈 Supply ↑ |
Purchasing Power Parity
🛒🌍💵 = 🛒🌍💶
“Same stuff, same price, no matter the country.”
What does it mean if a country’s currency depreciates?
Appreciates?
Depreciation – Currency loses value
Appreciation – Currency gains value
Fixed Exchange Rate
High and strict govt intervention
Keeps currency at a fixed value by buying/selling currency reserves constantly
Pegged Exchange Rate
High but Flexible Govt Intervention
Allows currency to fluctuate within a set range; intervenes when it goes outside band
Floating (Clean) Exchange Rate
None or Minimal Govt Intervention
No direct intervention; market forces fully determine exchange rate
Managed (Dirty) Float Exchange Rate
Moderate and Occasional Govt Intervention
Mostly lets market decide but occasionally steps in to prevent excessive fluctuations
Exchange Rate Relationship Chart
| Factor | Effect on Exchange Rate (📈 = up, 📉 = down) |
| ----------------- | --------------------------------------------- |
| 🔼 Interest Rate | 🔼📈 Exchange rate up (currency stronger) |
| 🔽 Interest Rate | 🔽📉 Exchange rate down (currency weaker) |
| 🔼 Inflation Rate | 🔼📉 Exchange rate down (currency weaker) |
| 🔽 Inflation Rate | 🔽📈 Exchange rate up (currency stronger) |
🔼 Interest Rate goes UP
Exchange Rate GOES UP (currency value increases)
🔽 Interest Rate GOES DOWN
Exchange rate down (currency value gets weaker)
🔼 Inflation Rate GOES UP
Exchange rate GOES DOWN (currency gets weaker)
🔽 Inflation Rate GOES DOWN
Exchange Rate GOES UP (currency value is stronger)
Transaction Risk (foreign countries) Example
You agree today to pay 100 euros for a cool gadget.
Today, 1 euro = 1.10 dollars, so you expect to pay $110.
But on payment day, if 1 euro = 1.20 dollars, suddenly you need $120 instead — that extra $10 is the transaction risk!
Currency Hedging
Locking in a price (This occurs in forward transactions)
🟩 Spot Transactions
🟩 Exchange currency right now (within 2 days)
🟦 Forward Transactions |
🟦 Agree today to exchange currency at a fixed price later to avoid surprises
(Currency Hedging)
🟧 Swap Transactions
Buy one currency now and agree to sell it back later at a set price — like a two-step exchange happening at the same time.
If a company seeks to limit foreign exchange rate exposure in the
forward direction, what is the most effective way to do this?
The company should enter a forward contract to fix the exchange rate now for future currency payments or receipts
An example of first mover advantage
Amazon was one of the first to launch a large online marketplace.
Advantages:
Builds strong brand recognition early
Can set the standards and customer expectations
Gains early access to key resources and locations
Disadvantages:
Faces higher risks and costs (uncertain demand)
Has to educate the market
Competitors can learn from their mistakes
Late mover example
Walmart entered the online marketplace after Amazon.
Advantages:
Can learn from the first mover’s mistakes
Can improve on products or services
Usually lower initial costs
Disadvantages:
Harder to build customer loyalty
May face tough competition from established firms
Less control over market standards
Two modes of foreign market entry
Exporting
Federal Direct Investment
What is EXPORTING?
What it is: Selling products made in your home country to customers in another country.
Scale: Usually a smaller-scale, low-risk way to enter a foreign market.
Example: A U.S. coffee company shipping its beans to cafes in Europe.
ONE WAY TO ENTER THE FOREIGN MARKET
What is FDI?
Foreign Direct Investment
What it is: Setting up operations or buying assets inside the foreign country (like factories, offices, or stores).
Scale: A large-scale, higher-risk entry method involving more commitment.
Example: Toyota building a manufacturing plant in the U.S.
ANOTHER WAY TO ENTER THE FOREIGN MARKET