Chapter 2: Mendelian Genetics and Monohybrid Crosses
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Characters
Observable traits controlled by genes. (color, shape, length, position, etc)
Traits
Different forms of a character.
Monohybrid Cross
Cross studying one character's contrasting traits.
Punnett Square
Diagram predicting offspring genotypes from crosses.
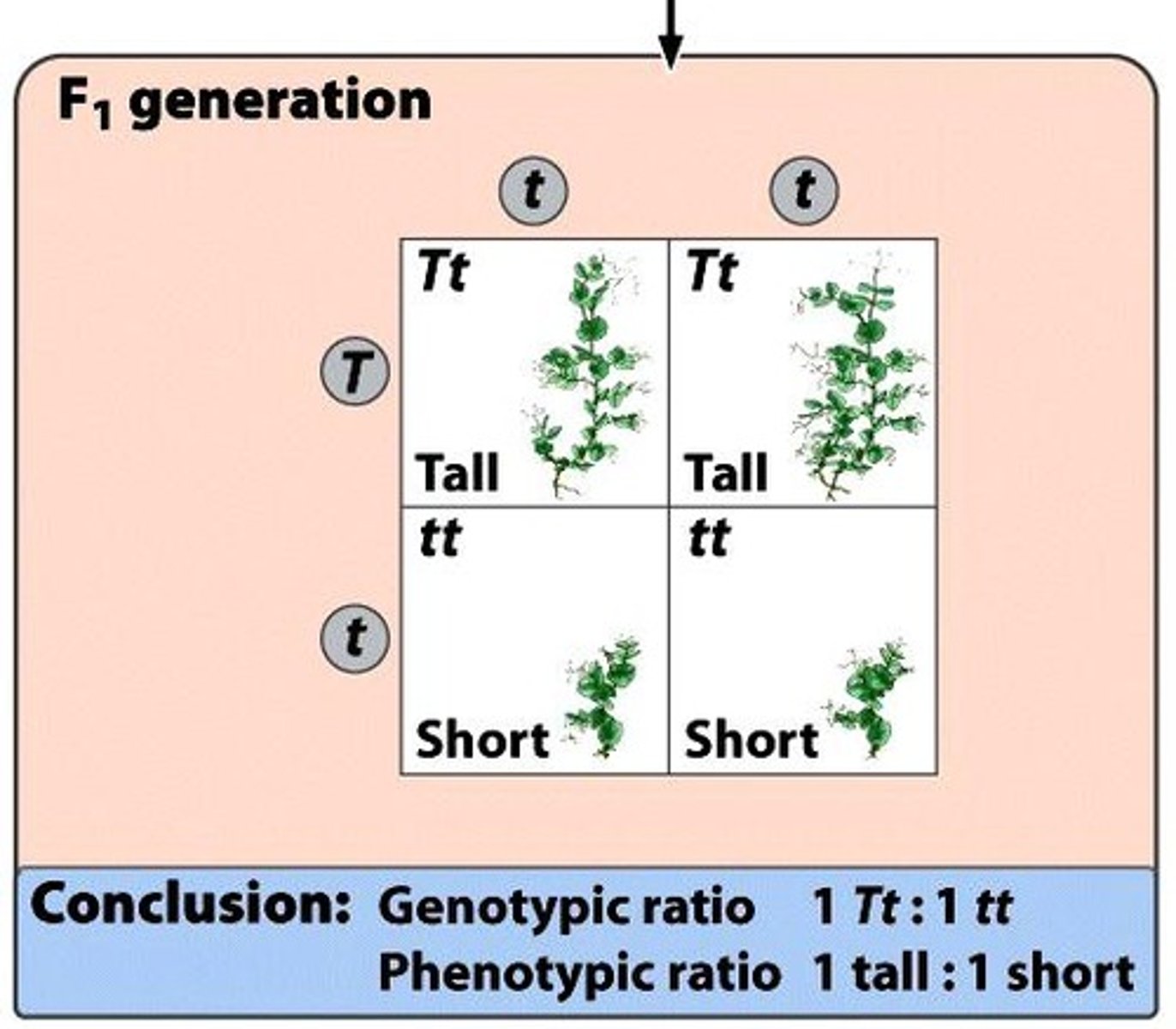
Test Cross
Cross to determine genotype of dominant phenotype.
1:1
Dihybrid Cross
Cross studying two independent characters simultaneously. Most often when both parents are heterozygous for both characteristics.
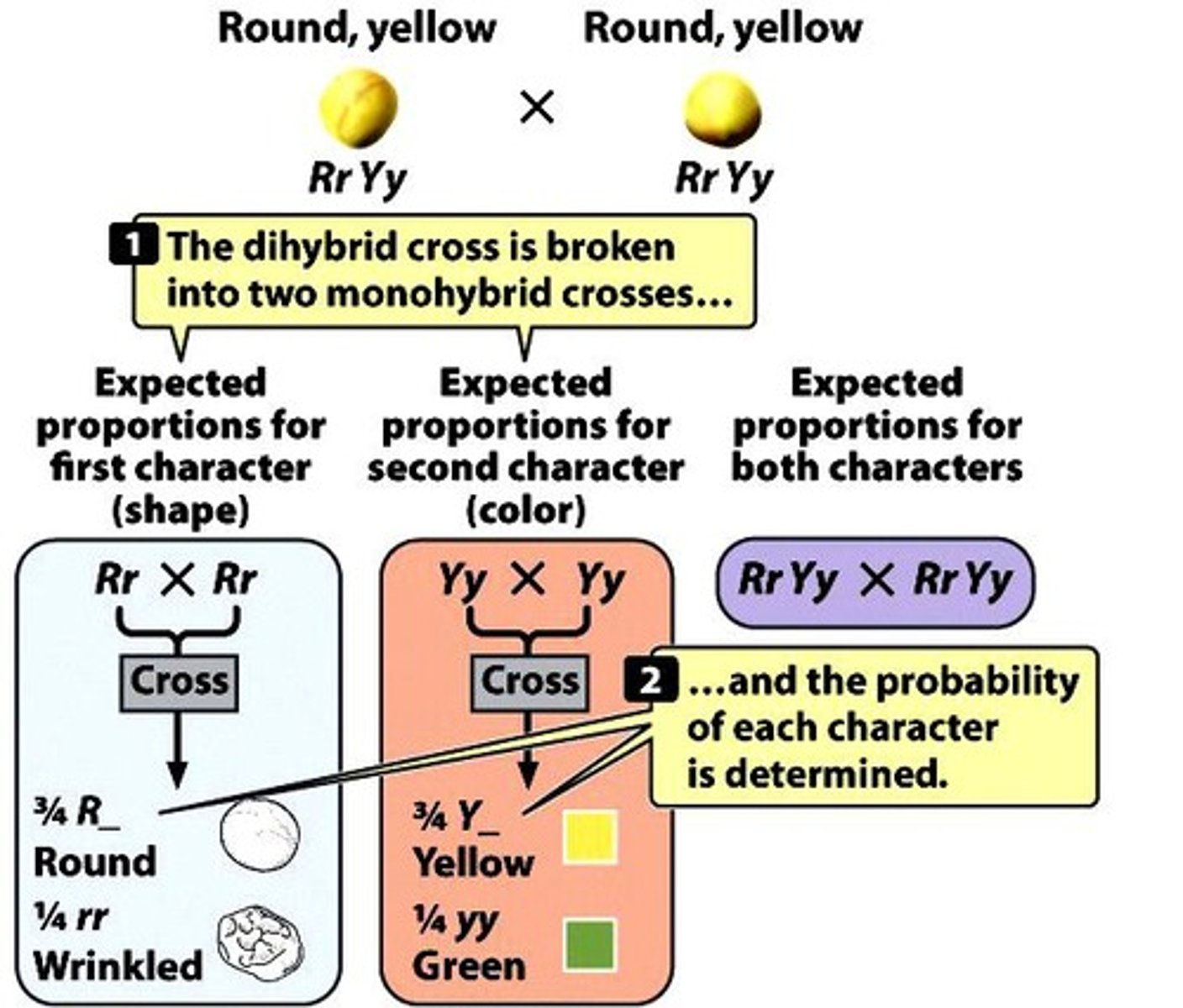
Independent Assortment
Genes segregate independently during gamete formation. Characters controlled by loci on separate chromosomes, and the events that occur in metaphase and anaphase of meiosis I
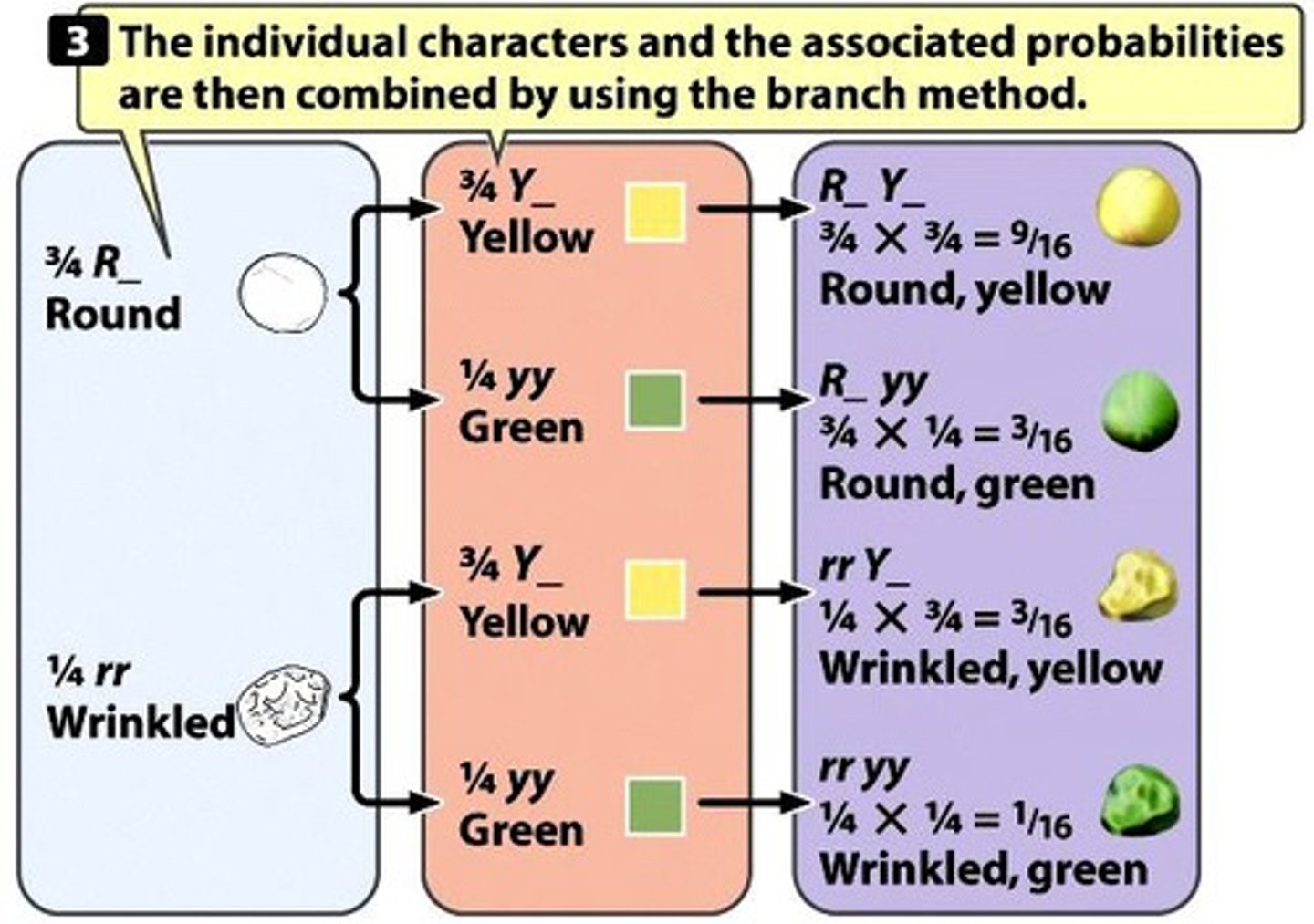
Branch Diagram
Visual tool for calculating phenotypic ratios from a dyhybird cross.
Trihybrid Cross
Cross studying three characters simultaneously.
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half chromosomes.
Gregor Mendel
Father of genetics, studied pea plant inheritance.
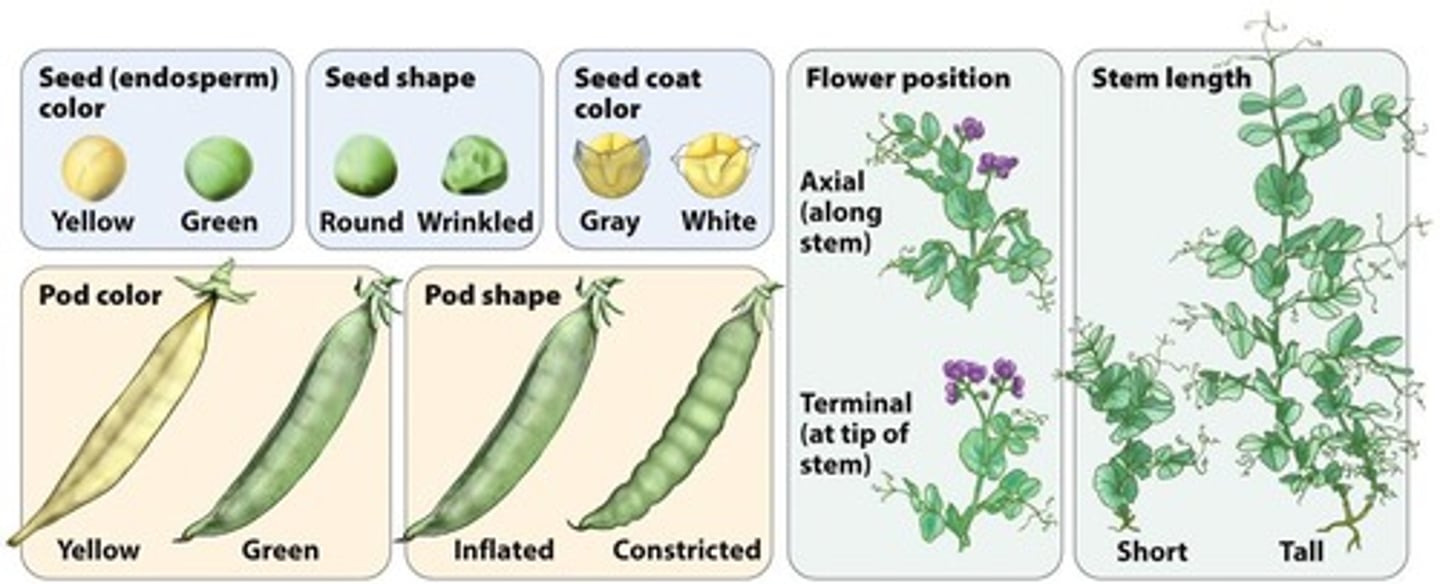
Unit Factors
Genes that determine traits, exist in pairs.
Dominant Trait
Trait expressed when at least one allele is present.
Recessive Trait
Trait expressed only when two alleles are present.
Homozygous
Individual with two identical alleles for a gene.
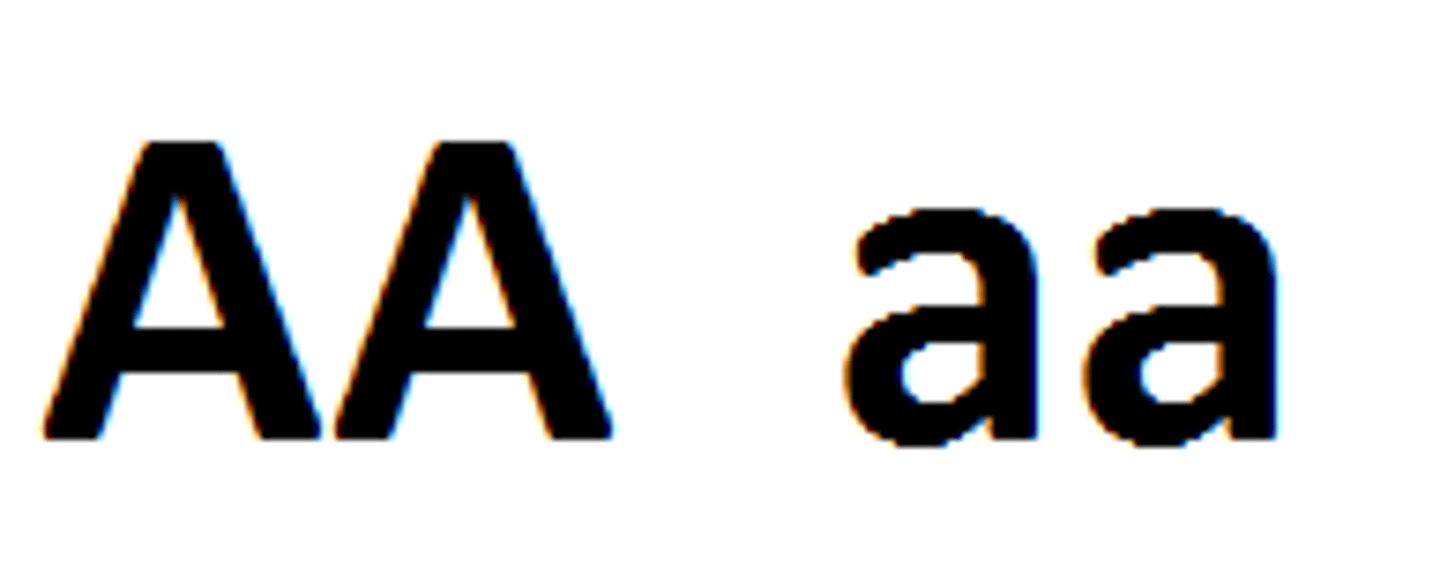
Heterozygous
Individual with two different alleles for a gene.

Phenotype
Physical expression of an organism's genotype.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an individual.
Alleles
Different versions of a gene.
Locus
Specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
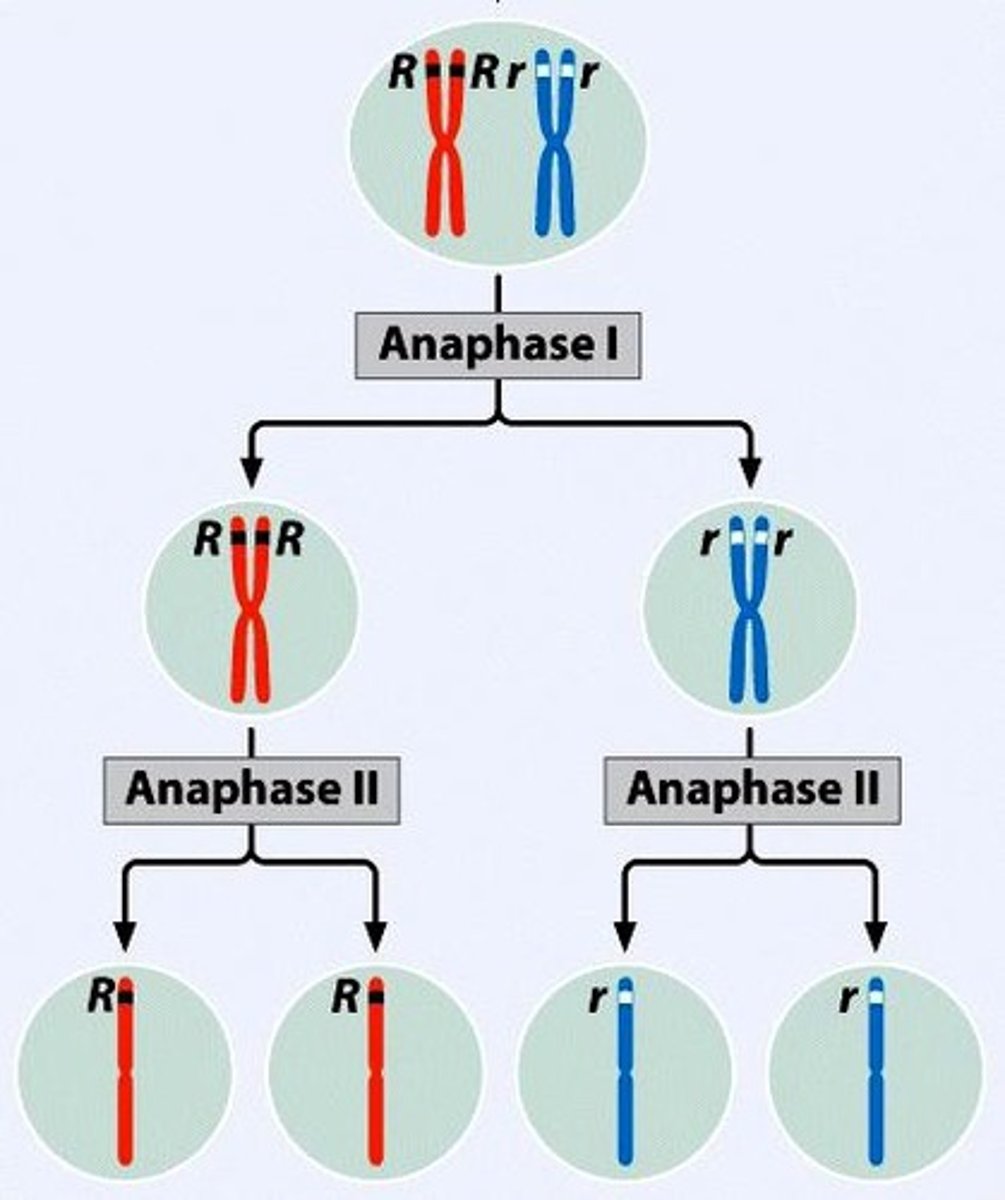
Segregation
Separation of alleles during gamete formation to each receive equal likelihood.
Mendelian Ratios
Expected ratios of phenotypes from genetic crosses.
Mendelian phenotypic ratio for the test-cross will be 1:1
F1 Generation
First filial generation from parental cross.
F2 Generation
Second filial generation from F1 self-cross.
Mendel's Postulates
Fundamental principles of inheritance proposed by Mendel.
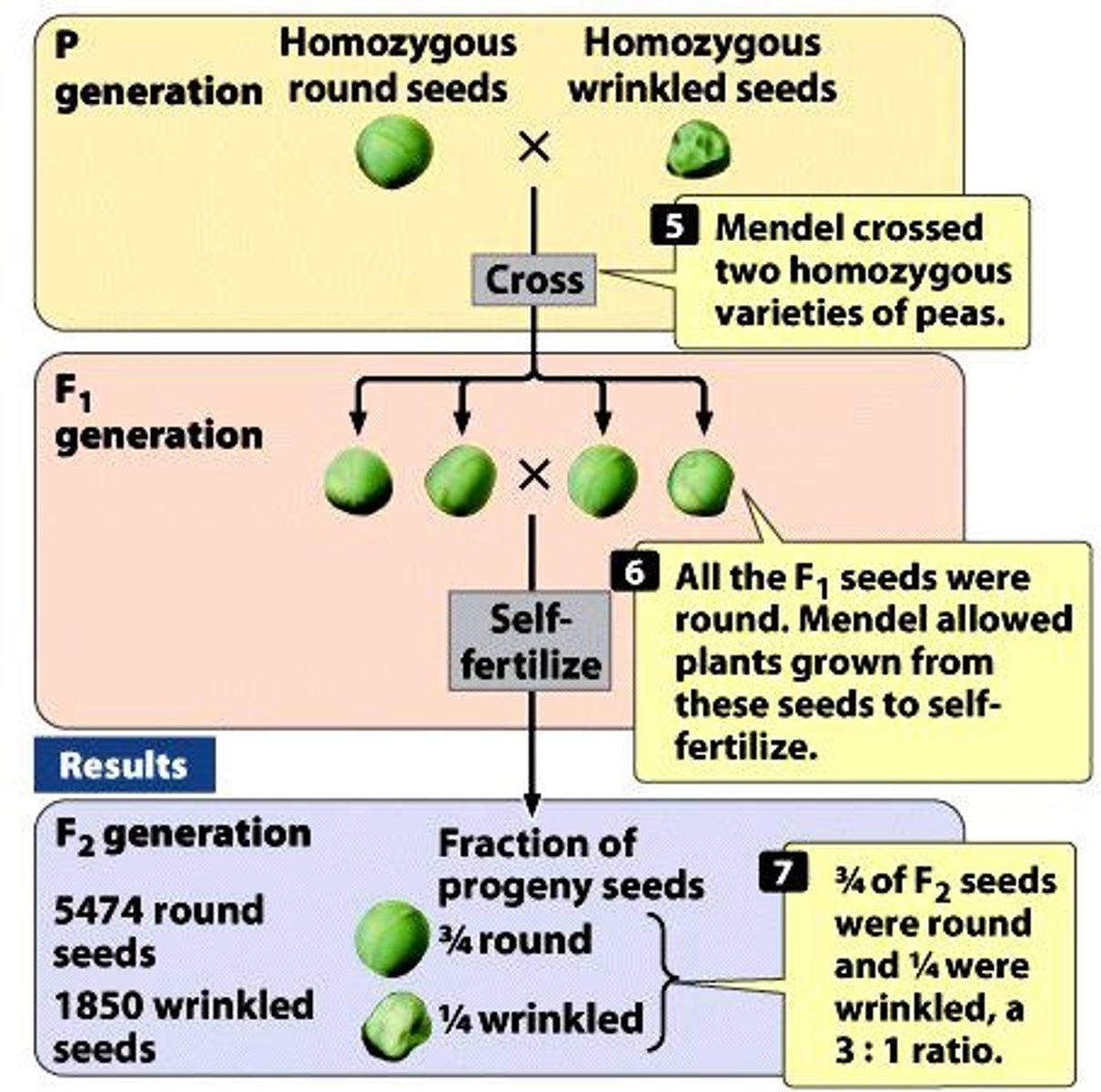
Chromosomal Theory of Heredity
Genes are located on chromosomes, inherited in pairs.
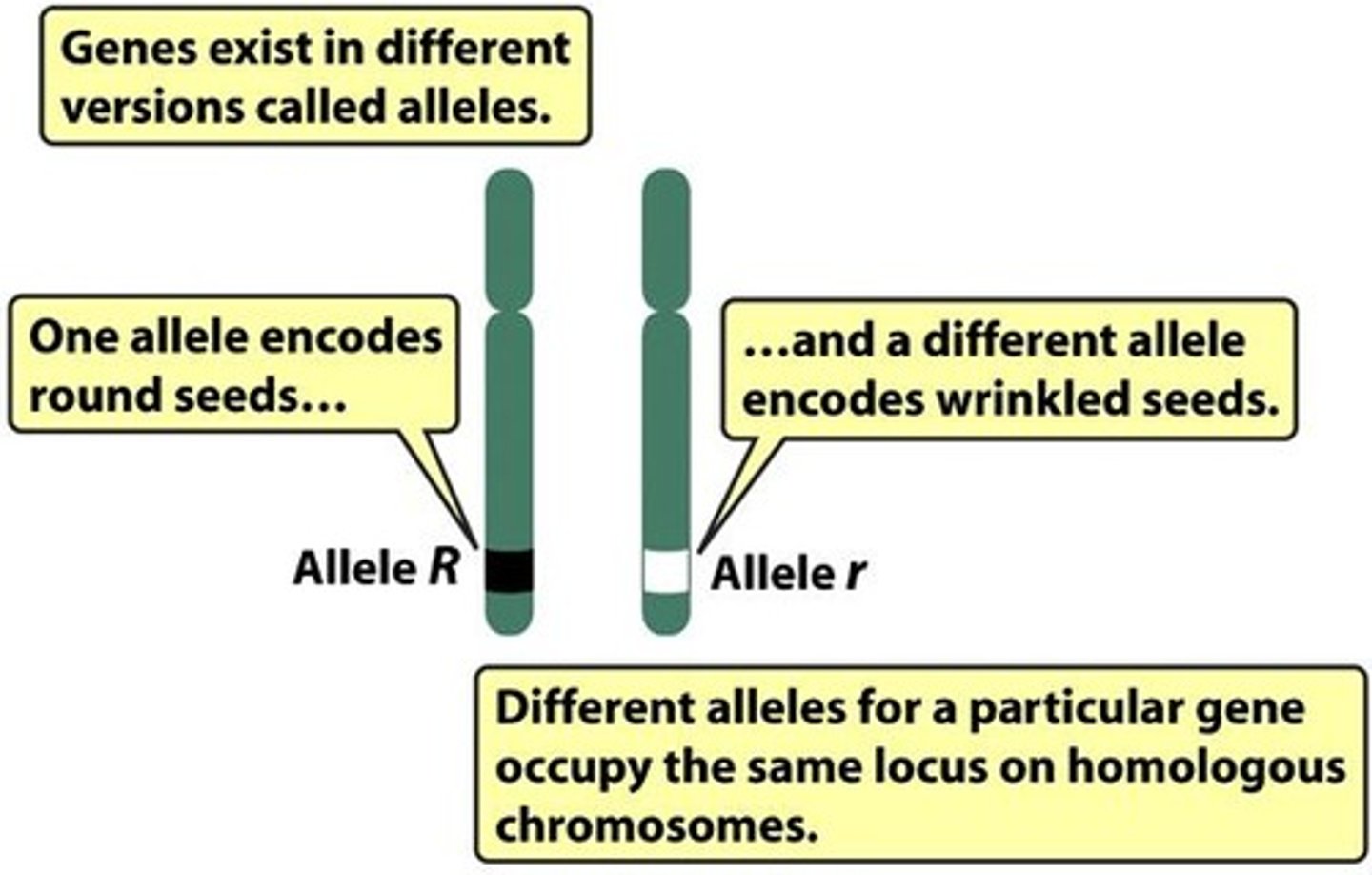
Gametes
Reproductive cells that carry alleles.
Cross-Fertilization
Mating between different individuals to combine traits.
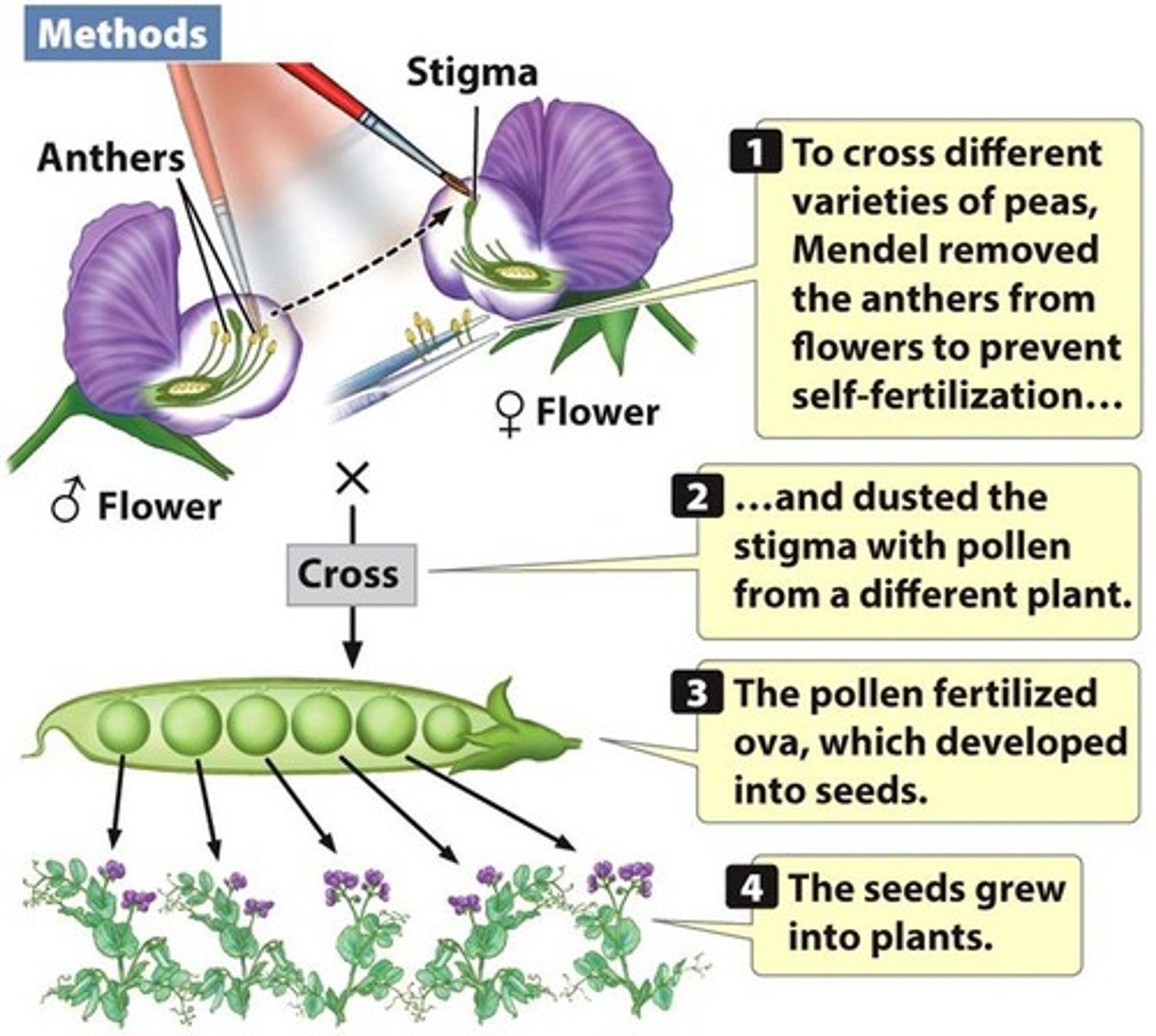
Polymorphic
Genes with multiple alleles in a population.
true-breeding
term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate (garden pea plants)
polymorphic
genes and loci with multiple versions
Mendel's law of segregation
unit factors (alleles) are segregated when the paired homologous chromosomes are separated during anaphase 1 of meiosis
product rule
two independent events occur simultaneously, the combined probability of the two outcomes is equal to the product of their individual probabilities of occurrence