Blood pressure, heart, thermoregulation
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What is the cardiovascular system
A closed system of the heart and blood vessels.
What is the function of the cardiovascular system
Transport of nutrients and other materials, via the blood, to and from various parts of the body.
what needs to happen in order for the cardiovascular system to function
The blood must be continuously circulated
What is blood
Blood is a fluid connective tissue
What 3 layers are visible in blood after centrifugation
Plasma
Leucocytes
Erythrocytes
What layer of blood is not visible after centrifugation
Platelets
What total blood volume is made up by plasma
30-60% of total blood volume
What does plasma consist of
water, dissolved organic and inorganic nutrients
dissolved O2, waste products of metabolism
Hormones
Proteins (important for blood clotting)
pH buffers
What is the function of leucocytes
Defend body against infection and disease
Function of erythrocytes
They are red blood cells, transport oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is Haematocrit
Volume of blood that is composed of red blood cells (40-65%)
How many haemoglobin molecules are found in the blood
~250 million haemoglobin molecules
How many subunits do haemoglobin consist of
4
What does each subunit of haemoglobin contain
Each protein subunit contains one heme molecule that binds one O2 molecule
How many O2 molecules can each haemoglobin bind
4
Function of capillaries
Capillaries are the site of gas and nutrient exchange
Role of platelets
Play a crucial role in the formation of blood clots
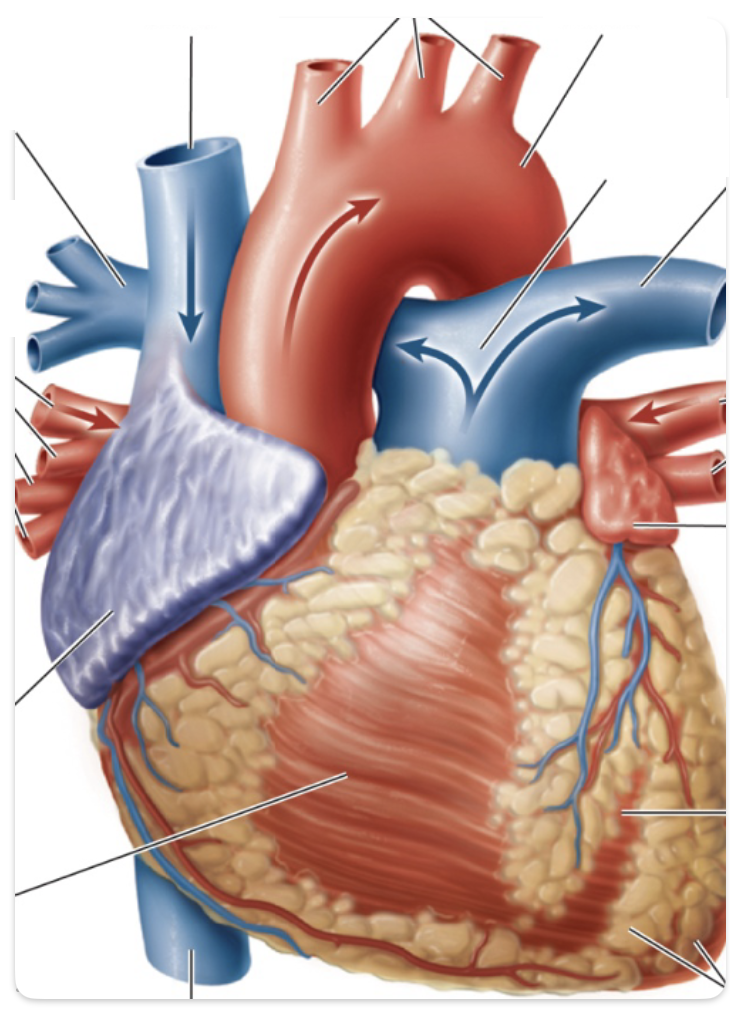
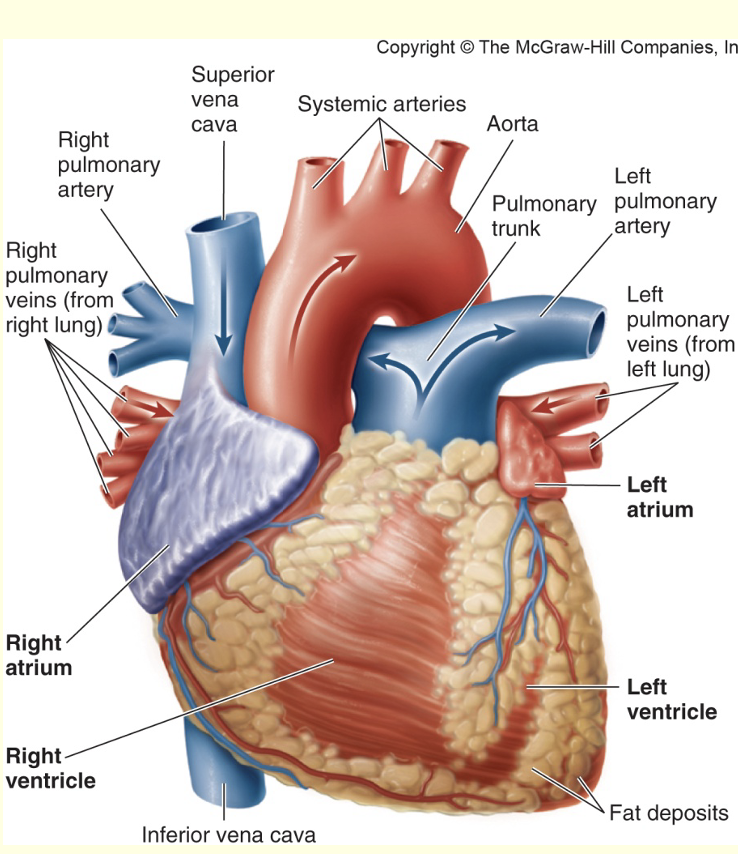
label the heart
superior vena cava
systematic arteries
aorta
pulmonary trunk
left pulmonary artery
left pulmonary veins (from left lung)
left atrium
left ventricle
fat deposits
inferior vena cava
right ventricle
right atrium
right pulmonary veins (from right lung)
right pulmonary artery
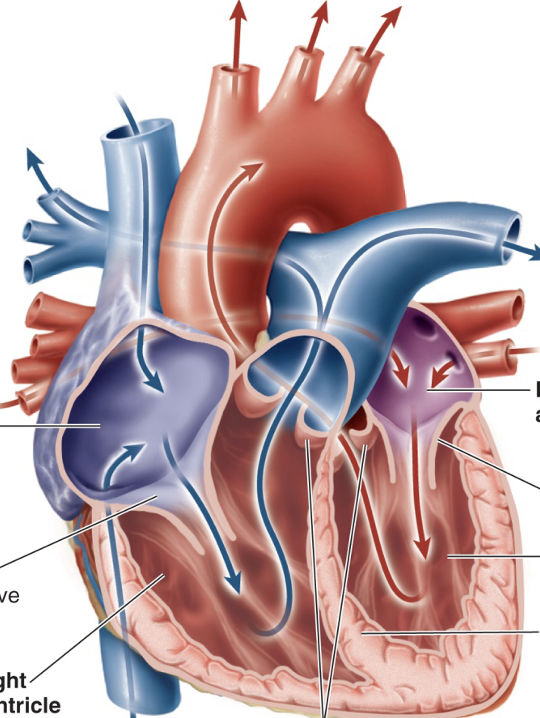
Label the interior of heart
left atrium
left AV valve
left ventricle
septum
semilunar valve
right ventricle ]right AV valve
right atrium
![<ul><li><p>left atrium </p></li><li><p>left AV valve </p></li><li><p>left ventricle </p></li><li><p>septum </p></li><li><p>semilunar valve </p></li><li><p>right ventricle ]right AV valve </p></li><li><p>right atrium</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9674359d-475e-4ec8-8cc5-54c8a72c85dc.png)
What is the size of a single cardiac muscle cell
20µm
Function of electrocardiogram
record the electrical activity of the heart
Name the 2 types of circulations
Pulmonary circuit
systemic circuit
Describe the distribution of blood at rest
Some organs (kidney, liver, gastrointestinal tract) receive blood in excess of their metabolic needs
What organ can least tolerate disrupted blood supply
The brain
What causes irreparable damage to the brain
Irreparable damage to brain if blood supply is disrupted >4 mins
Formula for blood pressure

What is a pressure gradient
Pressure gradient is the difference in pressure between the beginning and end of vessel
In what direction does blood flow
Blood flows from area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
What is the main driving force for blood flow through a vessel?
When heart contracts, it exerts pressure on the blood, which is main driving force for flow through a vessel.
What occurs as result of resistance in the vessel
The pressure drops as blood flows
What is resistance
Measure of hindrance or opposition to blood flow through a vessel, caused by friction between the blood in the vessel wall.
What happens if resistance to flow increases
If resistance to flow increases, it is difficult for blood to pass through a vessel, therefore, flow rate decreases
What are the main determinants of resistance
viscosity of blood
length of blood vessel
radius of the blood vessel
What does a slight change in radius of the vessel do to the blood flow?
Produces significant change in blood flow
What does the vascular tree consist of
arteries
arterioles
capillaries
venules
veins
Function of arteries
Carry blood away from heart to tissues. Serve as rapid-transit passageways for blood from heart to organs.
What are arterioles
Smaller branches of arteries
What are capillaries
Smaller branches of arterioles
Smallest of vessels across which all exchanges are made with surrounding cells
What are venules
Formed when capillaries rejoin
Return blood to heart
Features of large vein
few layers of smooth muscle and connective tissue
few elastin layers
wide lumen
endothelium
features of venule
connective tissue
endothelium
Differences between fenestrated and continuous capillary
Both have endothelial cells, only fenestrated capillaries have pores
Features of large artery
many layers of smooth muscle and connective tissue
several elastin layers
lumen
endothelium
features of arteriole
smooth muscle fibres
lumen
endothelium
What effect does the structure of arteries have on their resistance to blood flow and pressure
Due to their large radius, arteries offer little resistance to blood flow.
Act as pressure reservoir to provide driving force for blood when heart is relaxing
What do arterial connective tissues contain
collagen fibres (provide tensile strength)
elastin fibres ( provide elasticity to arterial walls)
Name the two invasive measurement of blood pressure
systolic pressure
diastolic pressure
What is systolic pressure
Peak pressure when blood is ejected
What is diastolic pressure
Minimum pressure when blood is draining off into vessels downstream.
What is a normal measurement of blood pressure
120/70 mmHg (systolic / diastolic )
What is a high measurement of blood pressure
>140/>90mmHg
What percentage of the UK population have a high blood pressure
~40% of the UK population
What are factors affecting blood pressure
peripheral vascular resistance - diameter of blood vessels ( an inc in pressure gradient and resistance)
cardiac output
blood volume
vessel elasticity
Function of arterioles
Controllers of blood pressure and tissue blood flow. Major resistance vessels.
What do arterioles convert
Convert the pulsatile systolic to diastolic pressure swings in the arteries into the non-fluctuating pressure present in the capillaries.
Why can the radius of the arteriole be adjusted
Radius of the arteriole can be adjusted to:
distribute cardiac output among systemic organs, depending on body momentary needs
help regulate arterial blood pressure
What is arteriole vasoconstriction caused by
↑ myogenic activity
↑ oxygen
↓ carbon dioxide and other metabolites
↑ endothelin
↑ sympathetic stimulation Vasopressin, angiotensin II
Cold
What is arteriole vasodilation caused by
↓ myogenic activity
↓ oxygen
↑ carbon dioxide and other metabolites
↑ Nitric oxide
↓sympathetic stimulation Vasopressin, angiotensin II
Heat
What is the internal core temperature
37℃
subject to precise regulation
What makes up our internal core temperature?
Abdominal and thoracic organs, central nervous system, skeletal muscles.
Why is it important to maintain an internal core temperature?
Tissues function best at relatively constant temperature.
What makes up our outer shell
Consists of skin and subcutaneous fat
What temperature is the skin
Skin temperature varies between 20℃ and 40℃ without damage
What effect does an increase in core temperature have on reactions
speeds up cellular chemical reactions
Is overheating or cooling more serious, why
overheating more serious than cooling, can cause:
nerve malfunction, irreversible protein denaturation
internal body temperature 41℃ causes convulsions, 43℃ upper limit compatible with life
What effect does a decrease in core temperature have on reactions
Slows down cellular reactions
What does a prolonged fall in body temperature cause
Pronounced, prolonged fall in body temperature slows metabolism to fatal level.
How does the skin regulate heat exchange on a cold day?
warm blood enters arteries
vessels dilate to allow blood to bypass the colder surface vessels
vessels constrict to reduce heat loss
blood leaves veins retaining most of its heat
How does the skin regulate heat exchange on a hot day?
warm blood enters from arteries
vessels constrict to shunt the blood to skin surface
heat is lost due to dilated vessels
blood leaves veins having lost some of its heat
Name the mechanisms of heat transfer
radiation
conduction
convection
evaporation
What is the role of the hypothalamus in regulation of temperature
Hypothalamus acts as thermostat that speeds u heat loss or heat production as needed
How is the hypothalamus activated for temperature regulation
Activated in 2 ways:
Thermal receptors in skin provide input to central command
Direct stimulation of hypothalamus through changes in blood temperature perfusing this area