PATIENT ASSESMENT EXAM II
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
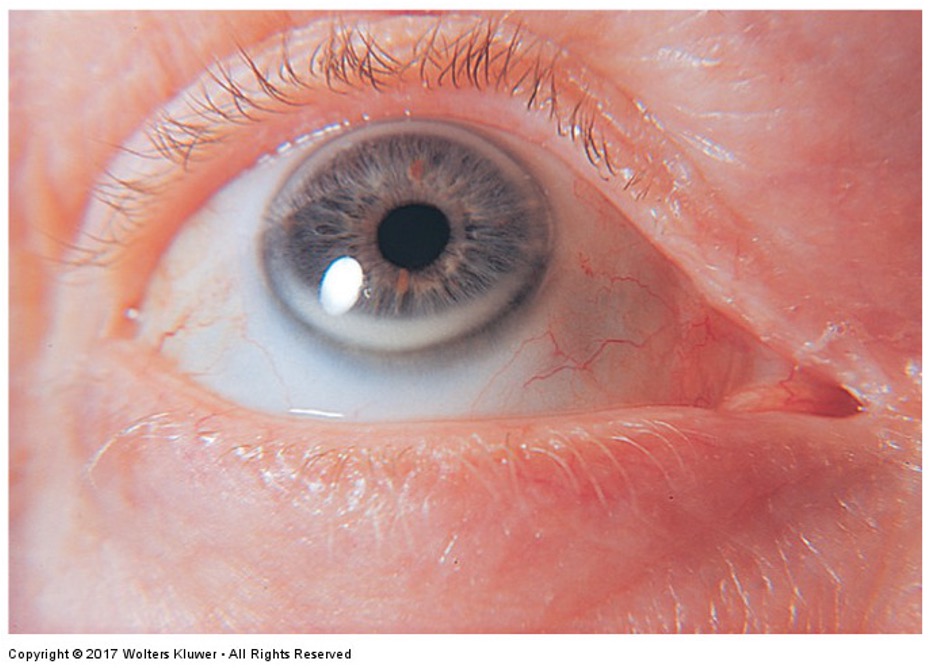
What is this irregular finding called? What levels are high with this associated finding?
Corneal arcus; high cholesterol

What is this irregular finding called? What disease is associated with this finding?
Kayser Fleischer ring; Wilson's disease (copper metabolism disorder)
Miosis
constriction of the pupil, often associated with opioid use or neurological disorders.
mydriasis
dilation of the pupil, often associated with sympathetic stimulation or drug use.
Normal pupil size
3-5 mmin diameter in a resting state.
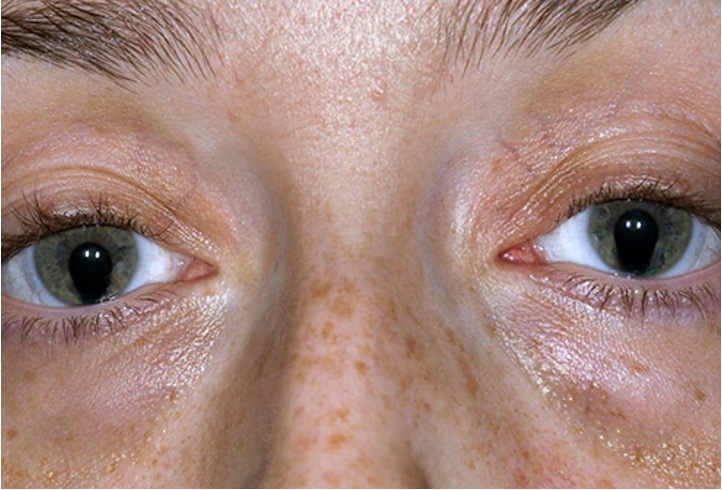
What is this irregular finding called?
Coloboma
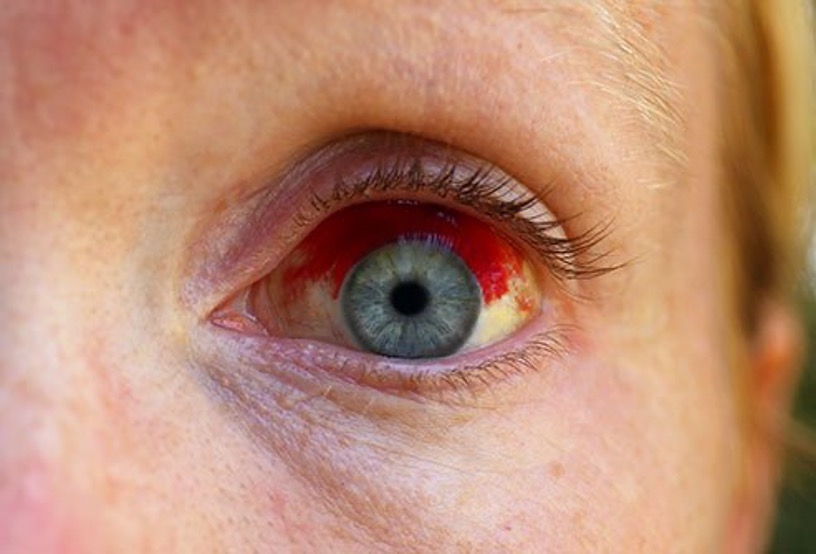
What is this irregular finding called?
Subconjunctival hemorrhage, a condition where bleeding occurs underneath the conjunctiva.
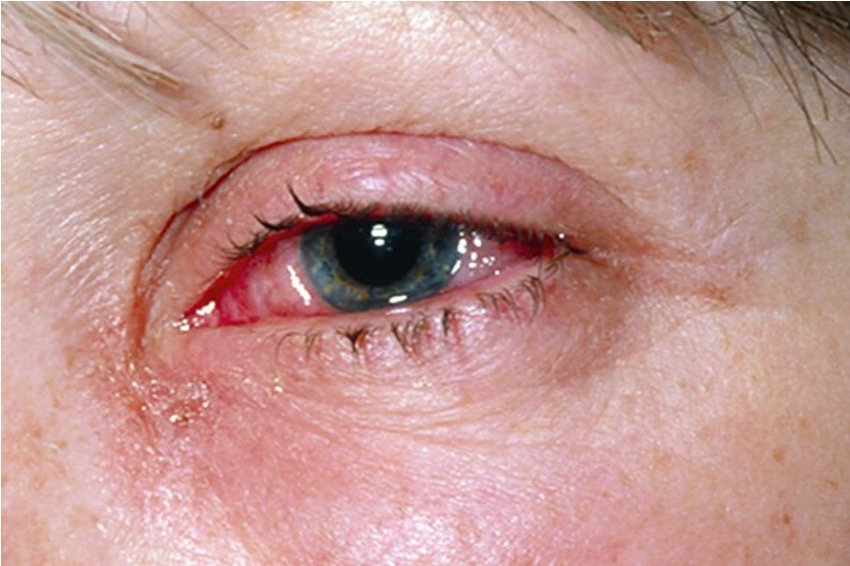
What is this irregular finding called?
Conjunctivitis
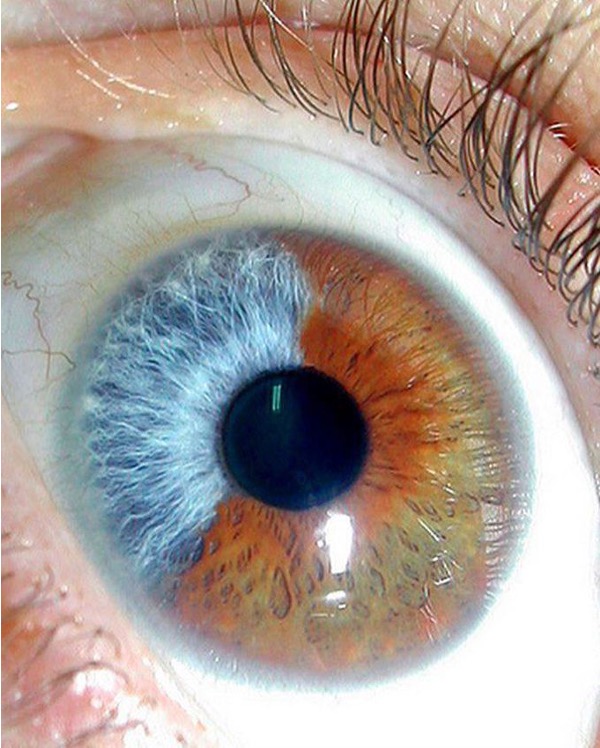
What is this irregular finding called?
Hematochromia iridium
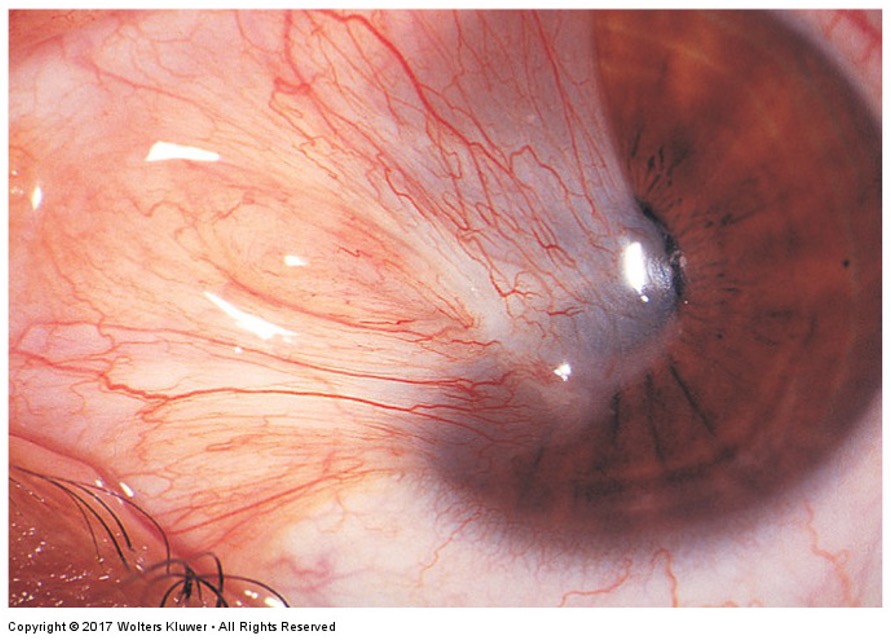
What is this irregular finding called?
Pterygium
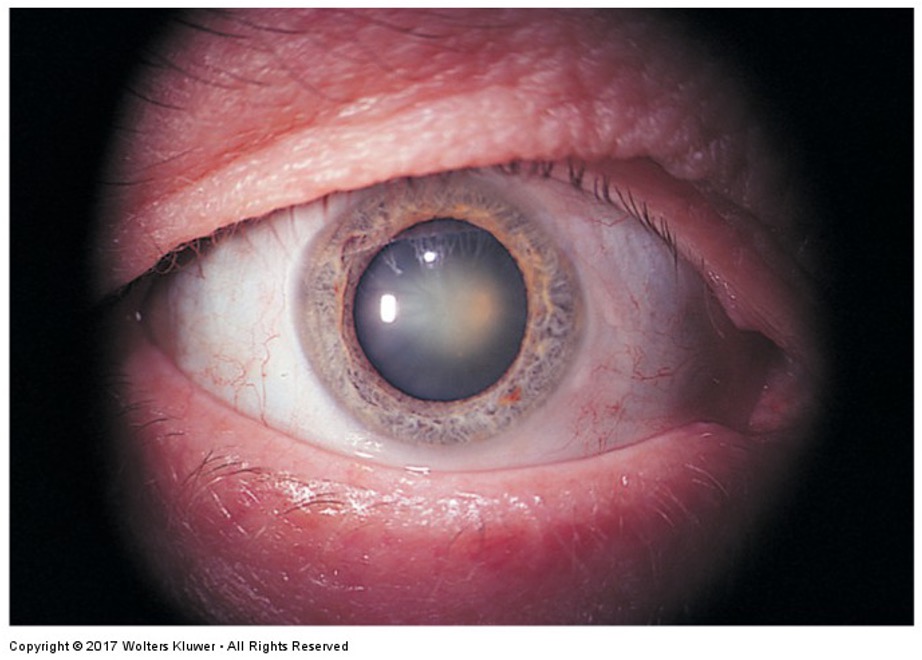
What is this irregular finding called?
Cataracts
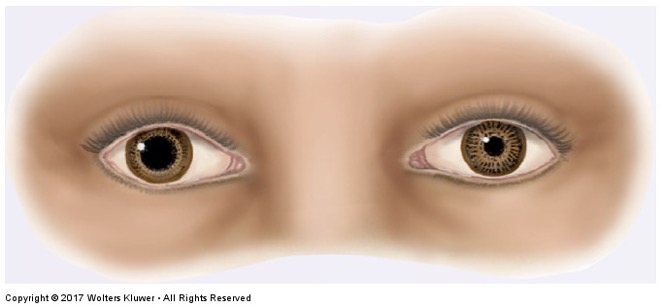
What is this irregular finding called?
Tonic pupil (Adie Pupil) a condition in which affected eye has reduced or os absent reaction to light. The eye constricts very slowly. The affected pupil is the dilated pupil.
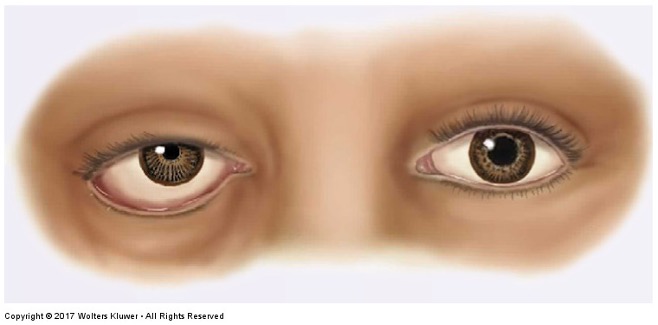
What is this irregular finding called?
Horner’s syndrome, rare condition characterized by drooping eyelid, pupil constriction where aniscoria is greater than 1 mm, and loss of sweating. The pupil dilates very slowly. The affected pupil is the constricted pupil.
What is considered aniscoria?
the condition where there is a noticeable difference in the size of the pupils, typically defined as a difference greater than 0.4 mm.
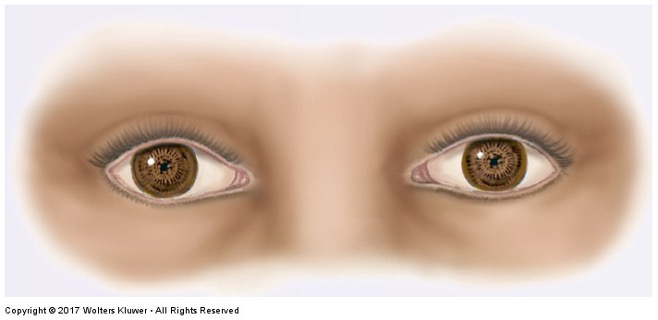
What is this irregular finding called?
Argyll Robertson Pupils
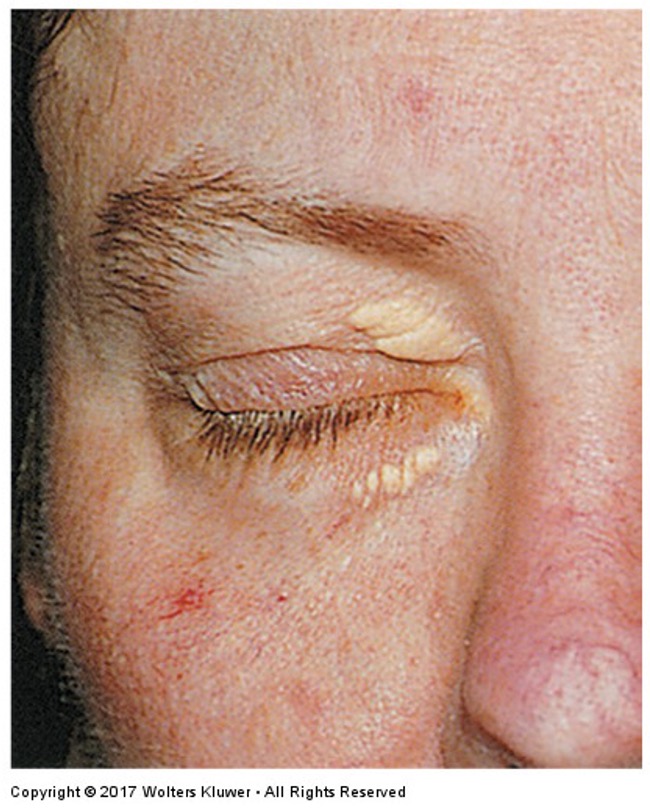
What is this irregular finding called? What needs to be checked based on this finding?
Xanthelasma; check for hyperlipidemia
Is there any pain with a subconjunctival hemorrhage?
No
Afferent pupillary defect
a condition where one pupil constricts less than the other in response to light, indicating potential damage to the optic nerve or severe retina injury.
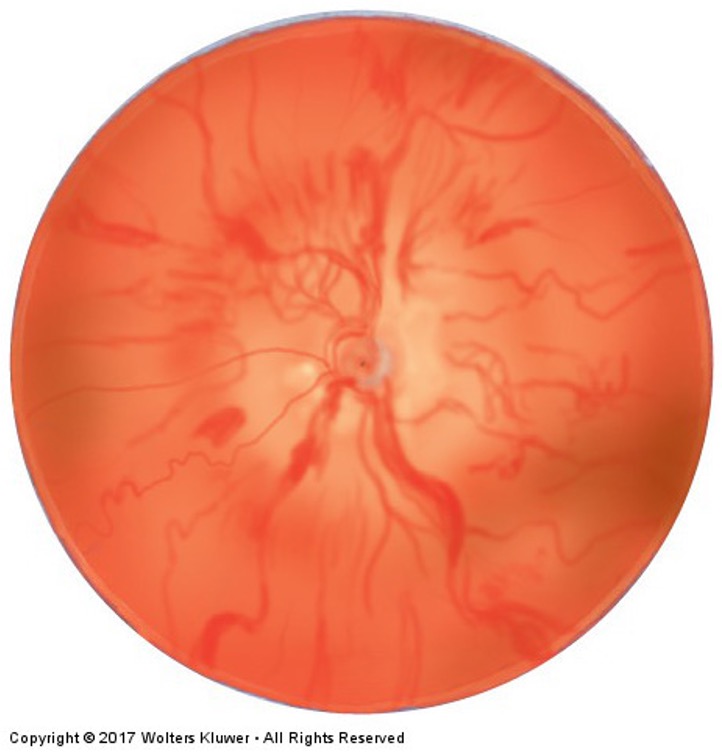
What is this irregular finding called?
Papilledema; blurred margins on all sides, pink/hyperemic, and physiological cup not seen.
What condition is known to cause lid lag?
Graves' disease due to hyperthyroidism
What should the diopter be at to look in the anterior chamber?
+10
In conductive hearing loss, is bone conduction or air conduction greater?
Bone conduction is greater. (BC>AC)
In sensorineural hearing loss, is bone conduction or air conduction greater?
Air conduction is greater. (AC>BC)
In unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, sound is heard where?
Louder in the better ear (weber test shows lateralization to good ear).
In unilateral conductive hearing loss, sound is heard where?
Louder in the affected ear (Weber test shows lateralization to bad ear).
What test is used to detect corneal perforation?
The Seidel test, which identifies leakage of aqueous humor from the eye.
Acute otitis media with purulent effusion is commonly caused by what?
Bacterial infections, often Streptococcus pneumoniae or H. influenzae.
What medications are known to cause permanent hearing loss?
aminoglycosides
What commonly known viral infection can cause sensorineural hearing loss?
Meniere disease
Presbycusis
is age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from the gradual deterioration of the inner ear structures or auditory pathways, making them more likely to miss sibilant consonants
Who are more susceptible to fungal ear infections?
Individuals with compromised immune systems or those with diabetes, as well as people with prolonged exposure to moisture.
Tympanosclerosis
is a condition characterized by the thickening or hardening of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) due to calcium deposits, often resulting from chronic ear inflammation or infection.
What test is used to differentiate conductive and sensoerineural hearing loss?
The Rinne test is used to differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss by comparing air and bone conduction.
What does type C tympanometry indicate?
negative middle ear pressure, common with refracted TM
What does type B tympanometry indicate?
little to no mobility, suggestive of ear effusion or fluid behind the eardrum
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
an inherited disorder characterized by the development of distinctive mucocutaneous pigmentation and gastrointestinal polyps, increasing cancer risk.
Kawasaki disease
a rare childhood illness that causes inflammation in blood vessels, leading to really red lips
Which cranial nerve is responsible for soft palate rising?
CN X
Class I of Mallampati scale
the soft palate, uvula, and fauces are all visible.
Class II of Mallampati scale
the soft palate and uvula is visible but pillars are not visible
Class III of Mallampati scale
soft palate and base of uvula are visible
Class IV of Mallampati scale
only the hard palate is visible.
What happens in CN X paralysis?
there may be uvular deviation toward the unaffected side, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing due to impaired soft palate elevation.
torus palatinus
a bony growth on the hard palate, often asymptomatic and varies in size.
How to distinguish leukoplakia and oral candidiasis?
Leukoplakia presents as white patches that cannot be scraped off, while oral candidiasis appears as white lesions that can be wiped away, often revealing a red, inflamed area underneath.
Black line in gums might suggest what?
lead poisoning
Lesion of CN XII leads to what?
Asymmetric protrusion of the tongue toward the affected side.
Men older than 50 y/o are at higher risk of cancers of the tongue and oral cavity, most commonly what?
squamous cell carcinoma (which can lead to erythroplakia and leukoplakia)
What are the centor criteria for GAS?
includes the presence of fever, tonsillar exudates, absence of cough, and swollen lymph nodes.
Deficiency in what can lead to glossitis?
Vitamin B12
A person with strawberry tongue might indicate what?
scarlet fever
What causes oral hair leukoplakia?
EBV virus