Week 4 - Recognizing Traumatic Skeletal Abnormalities & Arthritis
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Fractures appears as a ___________________ at the highly reflective bone-soft tissue interface
Discontinuity
What is a complete fracture?
broken all the way through
What is an incomplete fracture?
Part of the cortex is fractured
What are the two types of incomplete fractures?
- Greenstick Fracture
- Buckle Fracture
What is a greenstick fracture?
An incomplete fracture where only one part of the cortex is fractured that is MC in children
What is a buckle fracture?
Compression of the cortex leading to the bulging of the cortex
What is dislocation?
Bones are no longer in apposition
What is Subluxation?
partial dislocation
An 80 year old woman arrives at the ER w/ severe right shoulder pain and immobility. On P/E, he right arm is abducted and external rotated. Most likely Dx?
Shoulder dislocation
What is the cause of shoulder dislocation?
Fall on an outstretched arm
What is the different between Anterior vs. Posterior Shoulder dislocation?
Anterior - Presents w/ abducted and external rotated arm and "squaring off" of shoulder (90% of Shoulder dislocations
Posterior - Common w/ seizures and arm present as adducted and internally rotated
What is Hill-Sachs deformity?
A dent in the humeral head common in Anterior shoulder dislocation
What is a Bankart lesion?
Fracture of anterior inferior glenoid common in Anterior shoulder dislocation
What is the lightbulb sign?
Loss of normal half-moon overlapping present in posterior shoulder dislocation
What is rim sign?
Increase space b/w humeral head and anterior glenoid rim present in posterior shoulder dislocation
What is congenital/development dysplasia?
Abnormal positioning of the femoral head in the acetabulum presenting with asymmetric skin folds and limited hip abduction with + Barlow's/ortolani maneuver
What is posterior hip dislocation?
- An injury that occurs when force is applied to a flexed, adducted hip
- Account for 90% of sports-related hip dislocation
What is anterior hip dislocation?
Presents as a reported force/blow to an extended, externally rotated leg
What are avulsion fractures?
a piece of your bone is pulled off by a tendon or ligament
What are the common sites of avulsion fractures?
- ASIS - from sartorius
- AIIS - from rectus femoris
- Ischial tuberosity - from hamstring
- Lesser trochanter - from ilopsoas
35 y.o. Triathletes presents with pain that improves at rest. On P/E, there is pain upon palpation o the second and third metatarsal bone of the right foot - most likely dx?
Stress Fracture
What are the causes of stress fractures?
- Fracture of 3rd metatarsal common in military
- Fracture of shaft of 2nd and 3rd metatarsal also called March fracture
How is stress fracture evaluated?
- Bone scan/MRI (if needed)
What is the cause of a Nightstick fracture?
Isolated fracture of the ulna (transverse and mid-diaphysis, usually from direct blow)
Signs and symptoms:
laceration of the volar forearm,
decreased active and passive ROM
30 year old man sustained a left forearm injury as a result of falling from a 15-foot ladder. lacteration over the volar forearm. pain and swelling of affectd arm with decreased active and passive ROM Most likely dx?
Nightstick fracture
What is a Monteggia fracture?
Fracture caused by Fall on an Outstretched Hand (FOOSH) or a direct blow to the ulna presenting with proximal ulnar shaft fracture and radial head dislocation
due to direct blow to the ulna ir FOOSH
includes both proximal ulnar shaft and the radial head dislocaiton
can include the radial nerve
10 year old presents with a blunt injury to his right arm that is swollen and tender around his elbow on PE. Most likely Dx?
Monteggia Fracture (Proximal ulnar shaft Fracture)
What is a Galeazzi fracture?
Distal radial shaft fracture with dislocation of the ulnar-radial joint caused by FOOSH/falling on a pronated forearm
23 y.o. Male landed on his pronated outstretched left arm and presents with tenderness to palpation with a notable deformity characterized by radial wrist angulation. Distal ulna is palpable. Most likely dx?
Galeazzi Fracture
What is a Colles fracture?
fracture of the distal radius with dorsal displacement caused by FOOSH and presents with "dinner fork" deformity
73 y.o. Female tripped and experienced immediate pain and swelling over the right wrist and presents with dinner fork deformity of the wrist. Most likely dx?
Colles Fracture
What is a Smith's fracture?
fracture of the distal radius with volar displacement (aka reverse Colles fracture)
What is Boxer's Fracture?
Fracture at the neck of the 5th +/- 4th metacarpal
What is a Jones' Fracture?
Transverse fracture of 5th metatarsal caused by planar flexion of foot and inversion of ankle
What is Jefferson Fracture?
Fracture of C1 involving both anterior and posterior arches
How does Jefferson fracture present on X-Ray?
Bi-lateral, lateral offset of lateral masses of C1-C2 on AP open mouth view
How is Jefferson Fracture confirmed?
CT
What is Hangman's Fracture?
Fracture of posterior elements of C2 that is best seen on lateral X-Ray view
What is Burst Fractures?
Comminuted compression fracture of vertebral body associated with neurologic deficit
Are rib fractures detectable on initial exam?
No; it's not uncommon for them to be undetected
2 fractures in each or 3 or more contiguous ribs results in _________
Flair chest
What is the Salter-Harrison Classification?
Type I - Epiphyseal plate fracture
Type II - Epiphyseal plate and metaphysis (**corner sign)
Type III - Epiphyseal plate and epiphysis fracture
Type IV - Epipheseal plate, epiphysis and metaphysis fracture
Type V - Crush injury of Epiphyseal plate
What are the main sites of pathological fractures?
- Ribs
- Spine
- Proximal appendicular skeleton
What causes pathological fracture?
Metastatis
Osteoporosis
How long does the bone remodeling process take after a fracture?
8-12 weeks
What is seen on the xray with Internal endosteal healing
Indistinctness of fracture line (black)
What is External Periosteal Healing?
External Callus formation leading to bridging of fracture site (white)
What is the imaging of choice for arthritis?
X-Rays
Hypertrophic Arthritis (A)
Erosive/Inflammatory Arthritis (B)
Infectious arthritis (C)
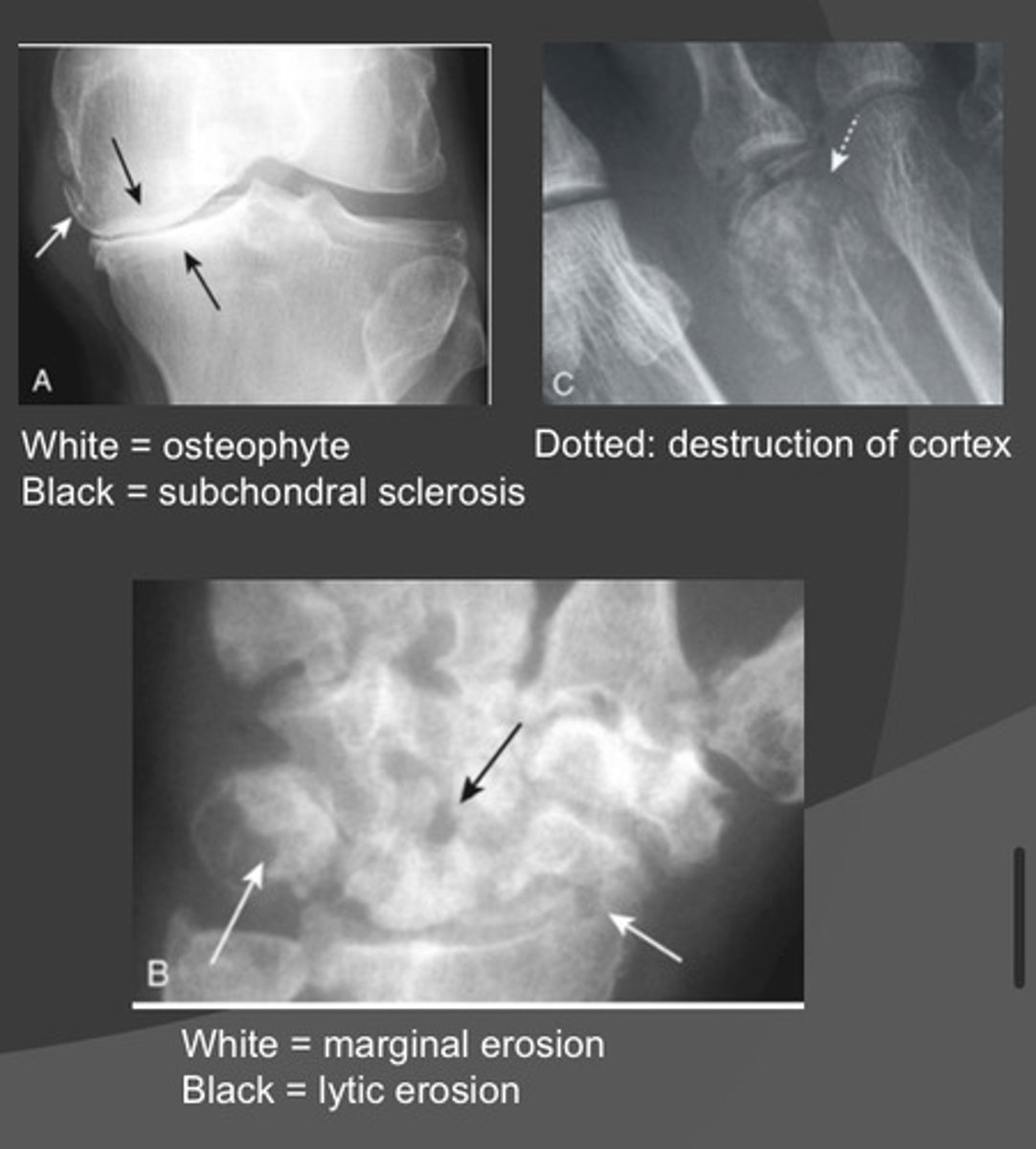
What are the various AKA's for primary Osteoarthritis?
- DJD
- Spondylosis
What is Charcot arthropathy?
Develops from a disturbance in sensation that leads to multiple micro fractures, bone resorption, and bone fragmentation
X-Ray findings of Charcot Arthropathy?
- Fragmentation
- Bone resorption
What is CPPD?
- calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (AKA pyrophosphate arthropathy) that commonly presents in the triangular fibrocartilage of wrist and meniscus
X-Ray findings of CPPD (4 potential findings)
-Chondrocalcinosis
- Hook shaped bone excrescences
- Calcificiation of triangular fibrocartilage
- Scapholunate dissociation
What is Erosive Arthritis?
A type of primary OA that presents with erosive joint changes, typically at the sites of PIP, DIP and/or 1st carpal-metacarpal
X-Ray findings of Erosive Osteoarthritis (1 finding)
Gull-wing deformity
What is Rhematoid Arthritis?
Inflammatory joint disease and pannus formation presenting at MCP, PIP and carpals
Common X-Ray findings of RA (4 findings)
- Ulnar deviation
- Subluxation MCP
- Increased atlantodental interval (ADI)
- Fusion of C/S facet joints
What is Gout?
Inflammatory arthritis with deposition of uric acid
X-Ray findings of Gout
- Rat bites deformities
- Olecranon bursitis
What is psoriatic arthritis?
joint pain and stiffness associated with psoriasis that presents at DIP joints
X-Ray findings of psoriatic arthritis
- Pencil-in-cup deformity
-Juxta-articulate erosion in DIP
What is infectious arthritis?
- AKA septic arthritis
- Usually monoarticular w/ soft-tissue swelling and osteopenia caused by Staph, Gonococcal and Mycobacterium
X-Ray findings of Infectious Arthritis
- Destruction of articular cartilage
- Rapid Destruction