Gluconeogenesis Exam #2
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
process/precursors?
process: make glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors. also maintain blood glucose levels
precursors consist of:
1- pyruvate (glycolysis)
2- glycerol (TAG breakdown → glycerol → DHAP → gluconeogenesis)
3- amino acids (except luecine and lysine (losers))
enter as alpha ketoacids
4- lactate (cori cycle)
lactate → liver → converted to pyruvate → gluconeogenesis
what state?
body locations?
cell location?
activated/inhibited by?
fasting state
body location: liver (+ kidney)
cell location: cytosol
activated: increased ATP/NADH/acetyl coA/amino acids/glucagon/epinephrine/PEPCK
inhibited: decreased ATP (increased AMP)
Pathway (first step)
Opposite of glycolysis
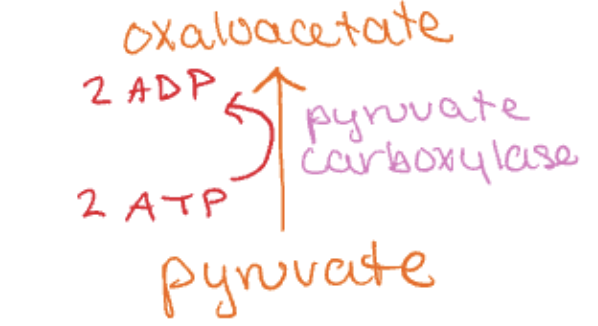
2nd step

3rd step
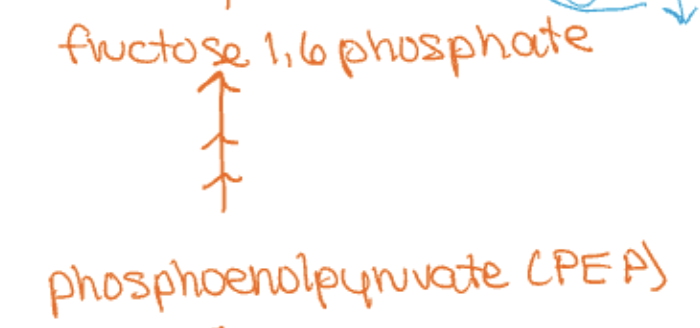
4th step
fructose 1-6 biphosphate is enzyme
activated by decreased F2,B6P (caused from increased PEPCK/glucagon (beta cells))

5th and 6th (final) step
enzyme glucose 6 phosphatase
dephosphorylizes

Von Gierke disease
causes:
side effects:
causes: decrease in glucose 6 phosphatase (enzyme in converting glucose 6 phosphate to glucose)
side effects: hypoglycemia, light headedness, fatigue
lactic acidosis can occur