IB 132 L6
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Orientation terms for brain
-superior: dorsal
-rostral: anterior
-caudal: posterior
-ventral: inferior
Central sulcus
separates frontal and parietal lobes (deep divide)
Mylenation
comes with experience - younger people have less white matter
Visible light
400-700 nm
blue=short wavelength
red=long wavelength
Reflected light
we see reflected light
ex: a red object absorbs all other colors and only reflects red
Seeing color
depends on light source, object, and detector (eye)
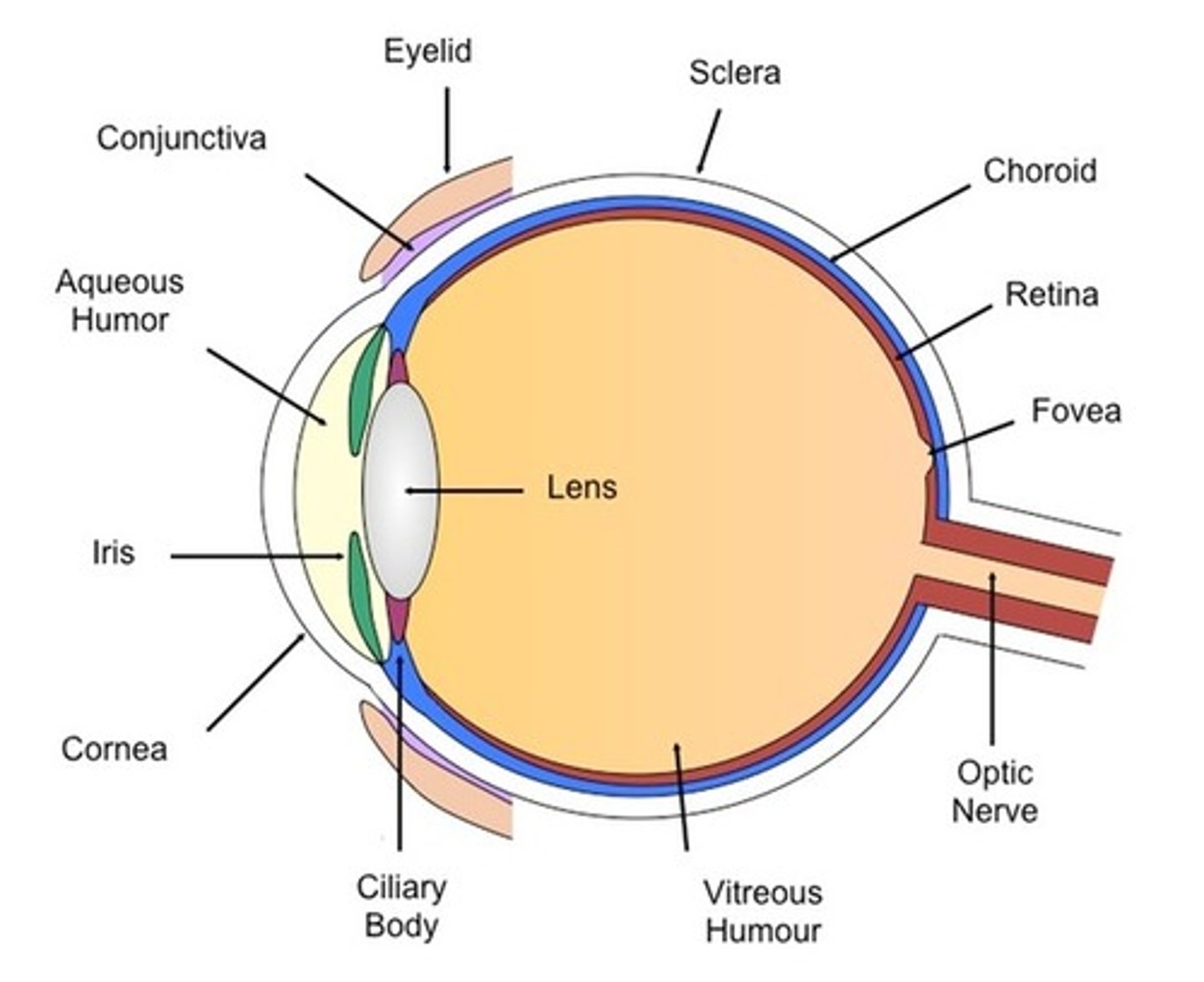
Lens of eye function
-curved shape of the lens bends light
-lens focuses the light on back of eye
-lens attached to muscles that will change its shape (ciliary muscles)
Far object in focus
-relaxed ciliary muscles, tension on zonular fibers, flattened lens
-light rays from distant objects are nearly parallel
Object out of focus
-relaxed ciliary muscles
-light rays from near object diverge
Zonular fibers
connecting the ciliary muscles with the lens of the eye
Near object in focus with accommodation
firing of parasympathetic nerves, contracted ciliary muscles, slackened zonular fibers, rounded lens
Image on back of eye
reversed
Visual field
images on your left end up in the right occipital lobe, vice versa
Optic chiasma
the crossing of the optic nerves from the two eyes at the base of the brain
Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
A synapse in the thalamus, part of the midbrain, that receives input from the retinal ganglion cells and has input and output connections to the visual cortex.
retina -->LGN (synapse 1) --> occipital cortex (synapse 2)
Depth perception
binocular coverage
-binocular zone is where L and R visual fields overlap (accounts for mismatch btwn 2 eyes)
-monocular zone is the portion of the VF associated with only one eye
Rods
-more light sensitive
-dark/light sensing (grayscale)
-many produce one signal
Cones
-color, sharp detail
-fewer per signal
Anatomy of eye
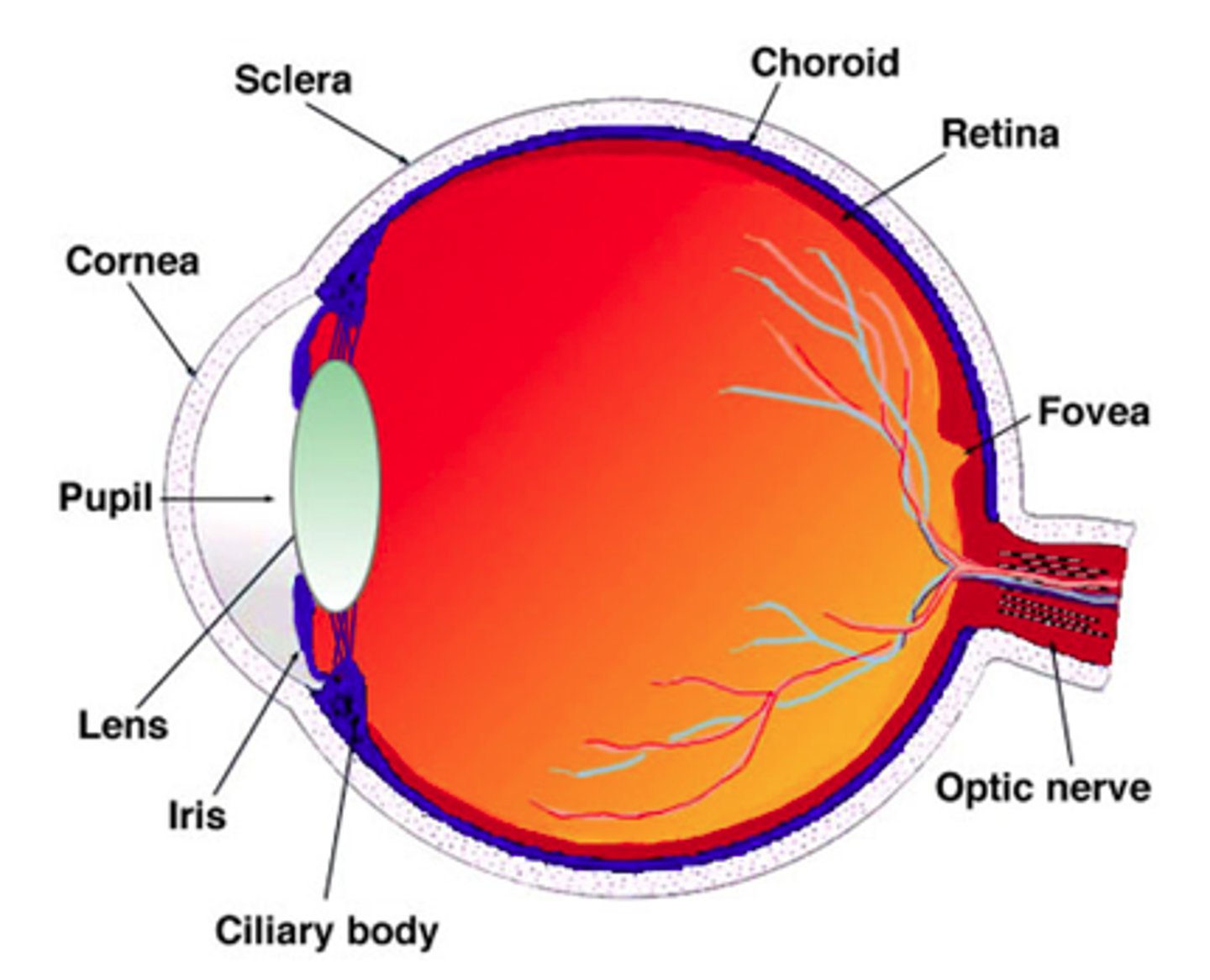
Fovea centralis
area consisting of a small depression in the retina only containing cones and where vision is most acute
-->within the macula
Retinal ganglion cells
retinal neurons whose axons leave the eyeball and form the optic nerve
--> have 2 main kinds of receptive fields
ON center, OFF surround
-light in center --> stimulation of ganglion cell
-light off center --> inhibition of ganglion cell
-light half in center half off --> weak stimulation of ganglion cell
OFF center, ON surround
-light in center --> inhibition of ganglion cell
-light off center --> stimulation of ganglion cell
-light half in center half off --> weak stimulation of ganglion cell
Coding: shape processing in visual cortex area V1
-simple cells: responds to a bar in a certain orientation and position
-complex cell: responds to a bar in a particular orientation regardless of position
-hypercomplex cell: respond when bar ends in their receptive field, good for edge detection
Trichromatic theory
-different photoreceptors sensitive to: red, green, and blue
-can combine these 3 colors of light to produce other colors
Opponent process theory
-2 types of color receptors: R-G and B-Y (and light/dark)
-the idea is if inhibit receptor sees one color (eg. red), if excite get the other (eg. green)
Two problematic mysteries
1. Get after images of the opposite color (eg. red-green, blue-yellow) --> spectrally opposed "opponent process" cells in LGN of the thalamus
2. color-blindness is always R-G or B-Y
Complementary color theory
Pairs that mix to white
3 types of cells that function in color opposition: blue-yellow, red-cyan, green-magenta
Receptor
protein that binds a ligand, initiates action
Sensory receptor
cell (eg. neuron) that initiates a sensory signal (whole cell w receptors on tip)
-->brings sensory info into brain
Receptive field size differences
smallest (most localizable) in lips, fingertips
Stimulus intensity and frequency
The more frequent/harder pressure the stronger the stimulus
-->Intensity is encoded in the frequency of APs arriving at the sensory cortex
Lateral inhibition
the reduction of activity in one neuron by activity in neighboring neurons
-->enhances signal localization
-->common in vision and touch
Lateral inhibition and T + pain
temperature and pain sensing have little to no lateral inhibition
Somatosensation areas of the brain
-frontal lobe association area
-somatosensory cortex
-parietal lobe association area
-occipital lobe association area
-temporal lobe association area
Descending inhibition
Activity descending from higher centers in the brain and brainstem can "screen out" certain types of sensory information by inhibiting neurons in the afferent pathway
-->not ideal to feel everything
Illusions in touch and proprioception
-loss of ability to distinguish finger surfaces
-->plasticity in the brain --> remapping in the somatic map
Illusions in somatosensation: phantom limb
-signals misattributed to missing limb
-substantial reorganization of somatosensory map after limb loss may be related
Illusions in somatosensation: referred pain
-pain from injury or damage in one part of body is interpreted as coming from another source
-opposite the "labeled lines" for small sensory receptive fields
-occurs because multiple primary sensory neurons converge on a single ascending tract
-ex: cardiac ischema in men felt in neck, left shoulder/arm
Neuron pathway to brain
-pain receptor
-dorsal root ganglion
-spinal cord
-sensory pathway to brain