ENT
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
45 y/o pt presents with a 2 week history of nasal congestion, purulent nasal discharge, and facial pain. He reports that the symptoms initially started as a cold but have worsened. He also reports a decreased sense of smell and mild fever. PE reveals tenderness over the maxillary sinuses and purulent drainage in the nasal cavity. What is the most likely Dx?
acute bacterial sinusitis
35 y/o male with a Hx of asthma presents with nasal congestion, anosmia, and a sensation of fullness in his face. He reports no fever or purulent discharge. On exam, multiple pale edematous masses are seen in both nasal cavities. What is the most likely Dx?
nasal polyps
42 y/o female presents with a Hx of recurrent sinus infections that have not responded well to antibiotic therapy. She also has a Hx of asthma and aspirin sensitivity. Which of the following is the most likely Dx?
Samter’s triad
Which classification of rhino-sinusitis has symptoms that last less than four weeks?
Acute
Which classification of rhino-sinusitis has symptoms that last 4 to 12 weeks?
Subacute
Which classification of rhino-sinusitis has symptoms that last more than 12 weeks?
Chronic
Which classification of rhino-sinusitis occurs more than 4 times a year with complete resolution in between episodes?
recurrent acute
Which sinus is most commonly affected by acute (rhino) sinusitis?
maxillary
What type of infection makes up the vast majority of acute rhino-sinusitis?
viral
What are the most common types of bacteria associated with ABRS?
Streptococcus pneumonia
haemophilus influenza
moraxella catarrhalis
A fever is typically indicative of which type of acute rhino-sinusitis?
bacterial
What is the most diagnostic way to diagnose acute rhino-sinusitis?
CT scan
Patients whose symptoms fail to improve within 10 days are more likely to have which type of rhino-sinusitis?
acute bacterial
What is the best way to manage AVRS?
supportive care
What is the best way to manage ABRS?
antibiotics
Antihistamines help with rhino-sinusitis due to their ___ effect
drying
Which type of medication thin secretions to promote mucous drainage?
mucolytics
What are the symptoms of the ABRS triad?
HA
facial pain/pressure
fever
In addition to fever, which symptom usually indicates ABRS?
purulent rhinorrhea
Which form of ARS does a double sickening pattern indicate?
ABRS
Diagnostic criteria indicative of ABRS:
persistent, fever, purulent discharge, double-sickening pattern
How can you confirm the diagnosis of ABRS?
nasal culture
In the case of ABRS, antibiotics should be prescribed for how many days for adults? for kids?
5-7; 7-10
What type of antibiotics are usually prescribed for ABRS?
first line
When would you send an urgent or ER referral for ABRS?
suspected extension of disease outside the sinuses
List indications that ABRS has spread outside of the sinuses:
vision changes, periorbital edema/ erythema, abscess, mental status changes
Symptoms must persist for ____ to diagnose chronic sinusitis
3 months
For chronic sinusitis, antibiotics should be prescribed for ___
3-6 weeks
What are the symptoms of Samter’s Triad?
severe bronchial asthma
nasal polyps
aspirin sensitivity
Is Samter’s Triad viral or bacterial?
neither
Samter’s Triad presents as __
chronic rhino-sinusitis
Define atopy:
bodies immune response (eczema, asthma, polyps)
Pts with nasal polyps and asthma are advised to avoid use of __ and __
ASA or NSAIDS and alcohol
Hay fever is another name for __
allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is associated with …
asthma and eczema
What clinical findings are indicative of allergic rhinitis?
stringy mucous, pale/boggy inflamed turbinates, rhinorrhea, eye irritation
The classical allergic salute is indicative of…
rhinitis
The common cold is another name for
viral rhinitis
Rhinitis lack __ differentiating it from rhino-sinusitis
sinus sensitivity
Which form of rhinitis best fits the following description: non-allergic, chronic, common in elderly
vasomotor
Which form of rhinitis is caused by medicine?
medicamentosa
What is indicated by pale, edematous masses often covered with mucosa?
nasal polyps
What is the medical term for nose bleed?
epistaxis
Which form of epistaxis is more serious?
posterior
Where is the most common site of anterior epistaxis? is this anterior or posterior?
Kiesselbach plexus; anterior
First method to stop epistaxis:
direct pressure and lean forward x15 minutes
Most common site of posterior epistaxis:
sphenopalatine artery
Posterior epistaxis requires close observation due to the __ which can cause severe complications and death
naso-cardiac reflex
Vestibulitis is caused by?
Staph aureus
What type of infection is rhinocerebral mucormycosis?
opportunistic
Rhinocerebral mucormycosis is caused by?
saprophytic fungi
Black necrotic tissue, cranial neuropathies, and facial pain in immunocompromised pts indicates
rhinocerebral mucormycosis
What should you look for in a nasal fracture?
septal hematoma
Untreated septal hematomas can lead to what?
saddle-nose deformity
Symptoms of a Type 1 Le Forte fracture:
swelling of upper lip, buccal bruising, loosening of teeth, malocclusion
Symptoms of a Type 2 Le Forte fracture:
deformity/swelling of mid face, widening of intercanthal space, mobility of upper jaw/nose, epistaxis, malocclusion, periorbital edema
Symptoms of a Type 3 Le Forte fracture:
lengthening/flattening of face, orbital hooding, enopthalmos, masotoid bruising, ear drainage
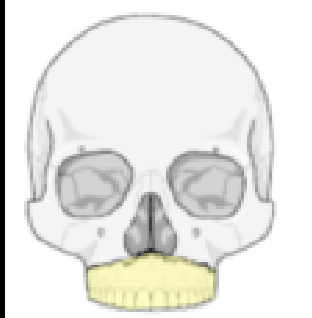
What type of Le Forte fracture is this
1
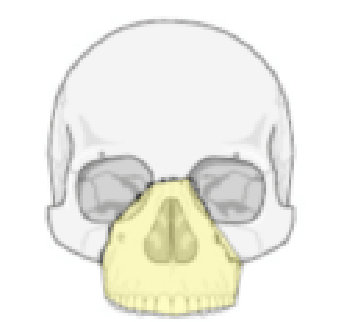
What type of Le Forte fracture is this
2
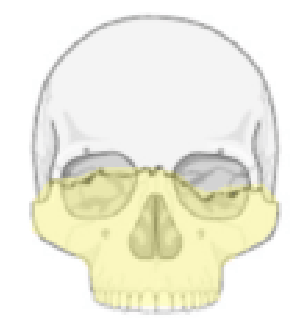
What type of Le Forte fracture is this
3
What is rare and usually asymptomatic until late in clinical course?
malignant nasopharyngeal and paranasal sinus tumors
Where is squamous cell carcinoma most common?
maxillary and ethmoid sinuses
What is the etiology of inverted papilloma?
HPV
What appear as cauliflower-like growths in or around the middle meatus?
inverted papilloma
What is another name for Wegener’s?
granulomatosis with polyangiitis
What is involved in the Wegener’s Triad?
necrotizing granulomas of upper/lower airways
glomerulonephritis
disseminated vasculitis