spinal cord
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
spinal cord
links peripheral body to brain
distributes impulses along peripheral nerves
carries sensory and motor impulses
location: enclosed by vertebrae in the vertebral canal
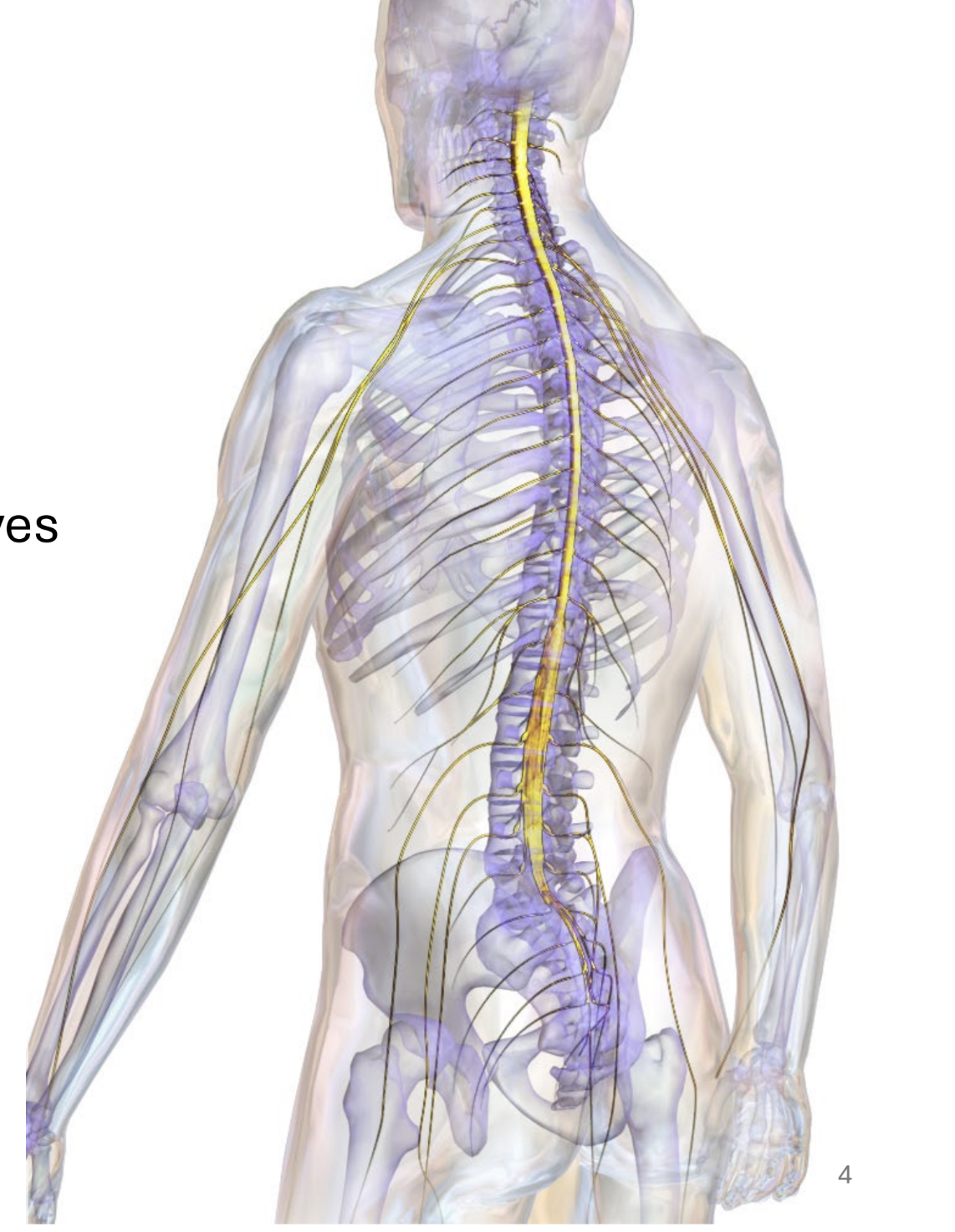
foramen magnum to L1-2
spinal cord begins at _______ ______ where it meets the medulla, and ends at intervertebral disc between regions ____
conus medullaris
tapered, cone-shaped
distal portion of spinal cord
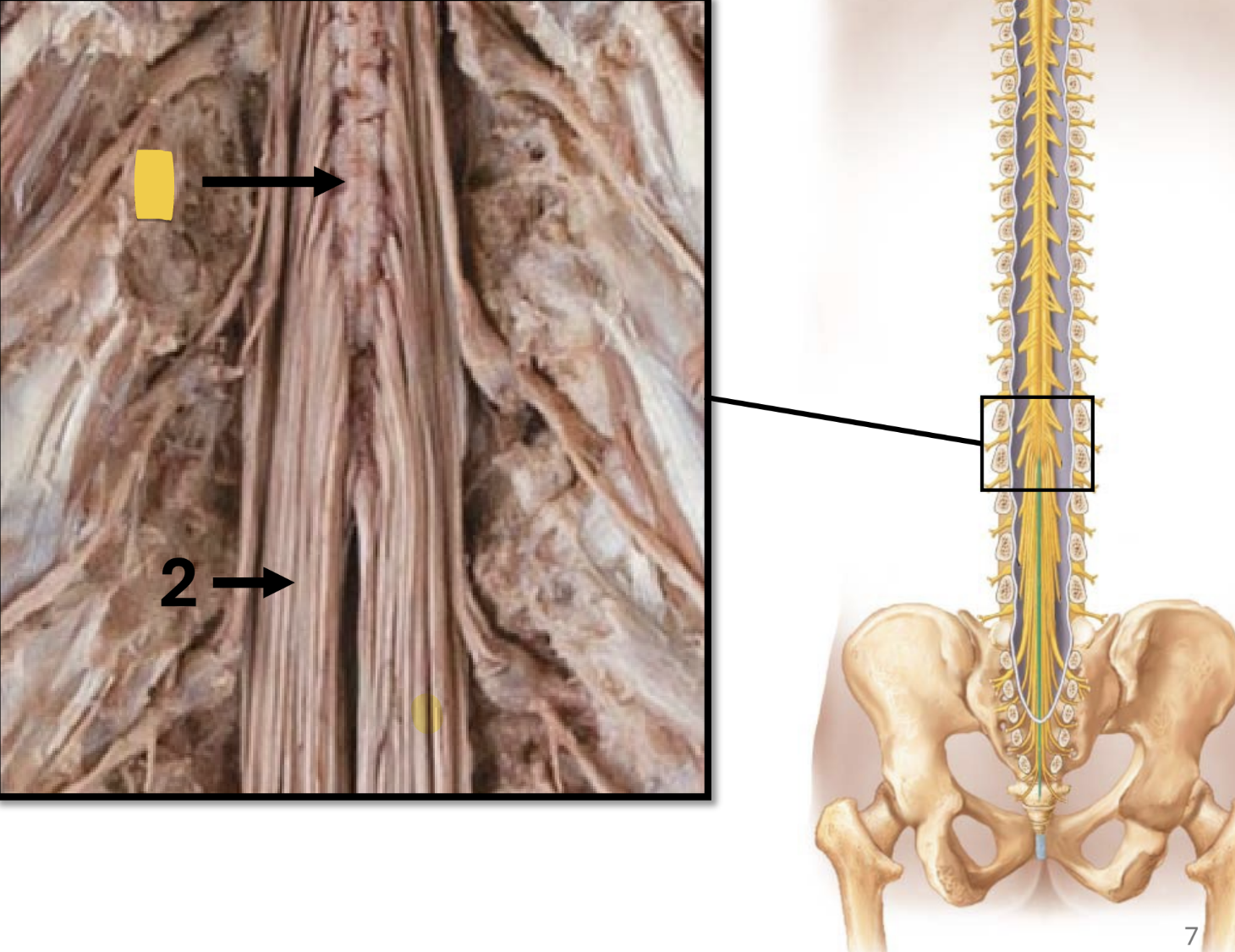
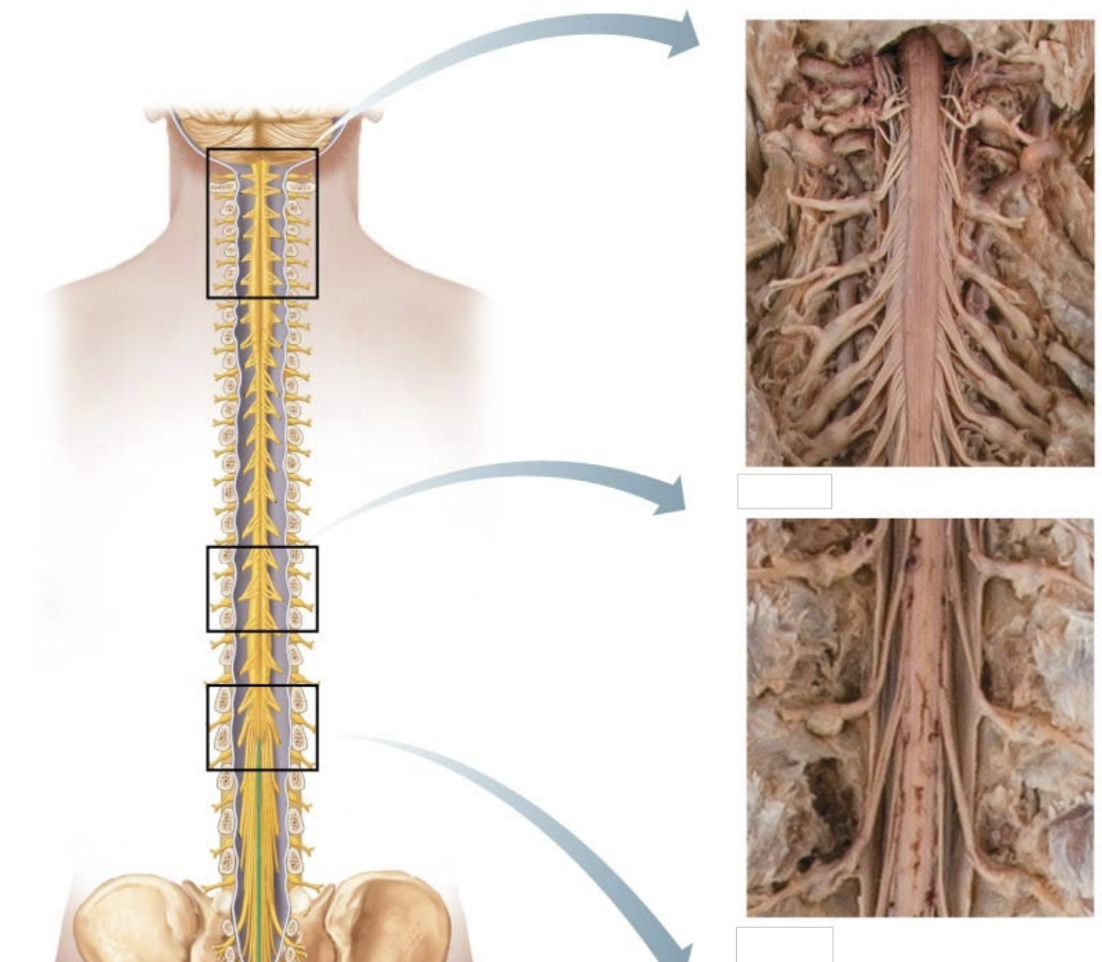
cauda equina
strands of fibers: “horse’s tail”
extends from the distal end of the spinal cord
composed of nerve roots
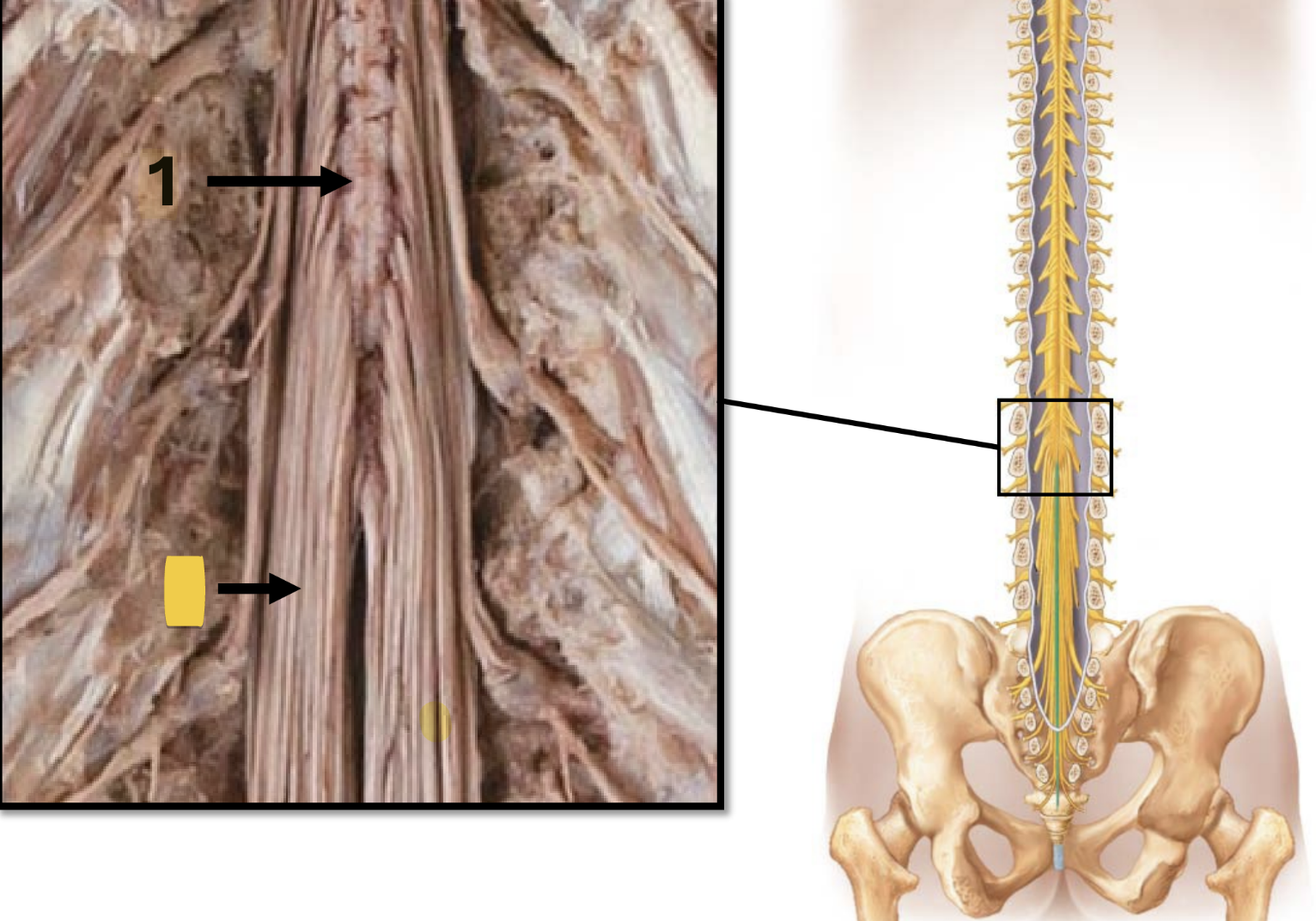
filum terminale
extension of pia mater
long, thin strip of CT
extens inferiorly from conus medullaris
anchors cord to coccyx
cervical and lumbar enlargements
thickened regions of the spinal cord
additional neurons to supply limbs
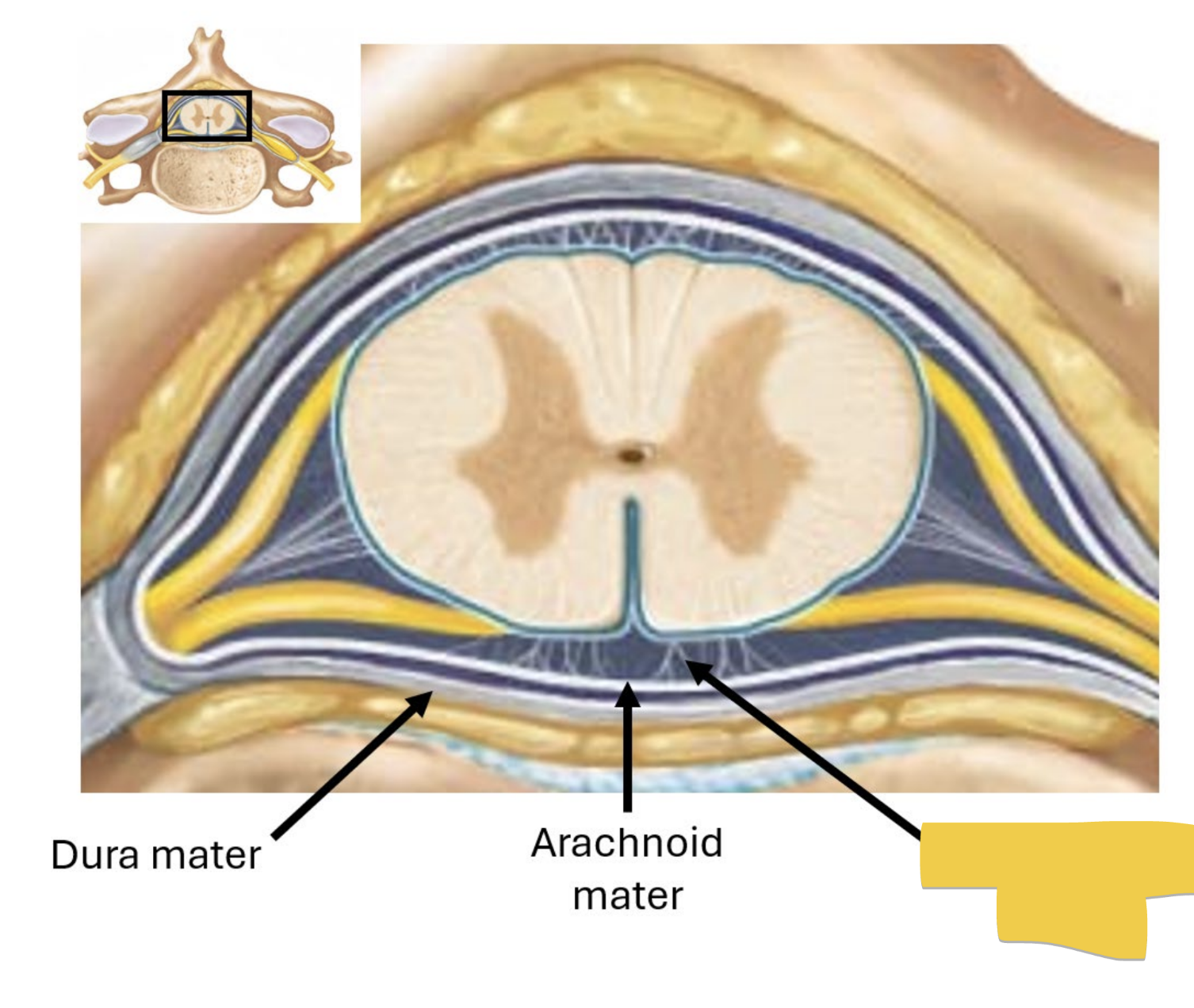
subarachnoid space
located between arachnoid and pia mater
contains cerebrospinal fluid (csf) — ultrafiltrate of plasma produced in ventricles of the brain
characteristics: clear, colorless, odorless
cushions brain
provides nourishment to and carries waste away from CNS
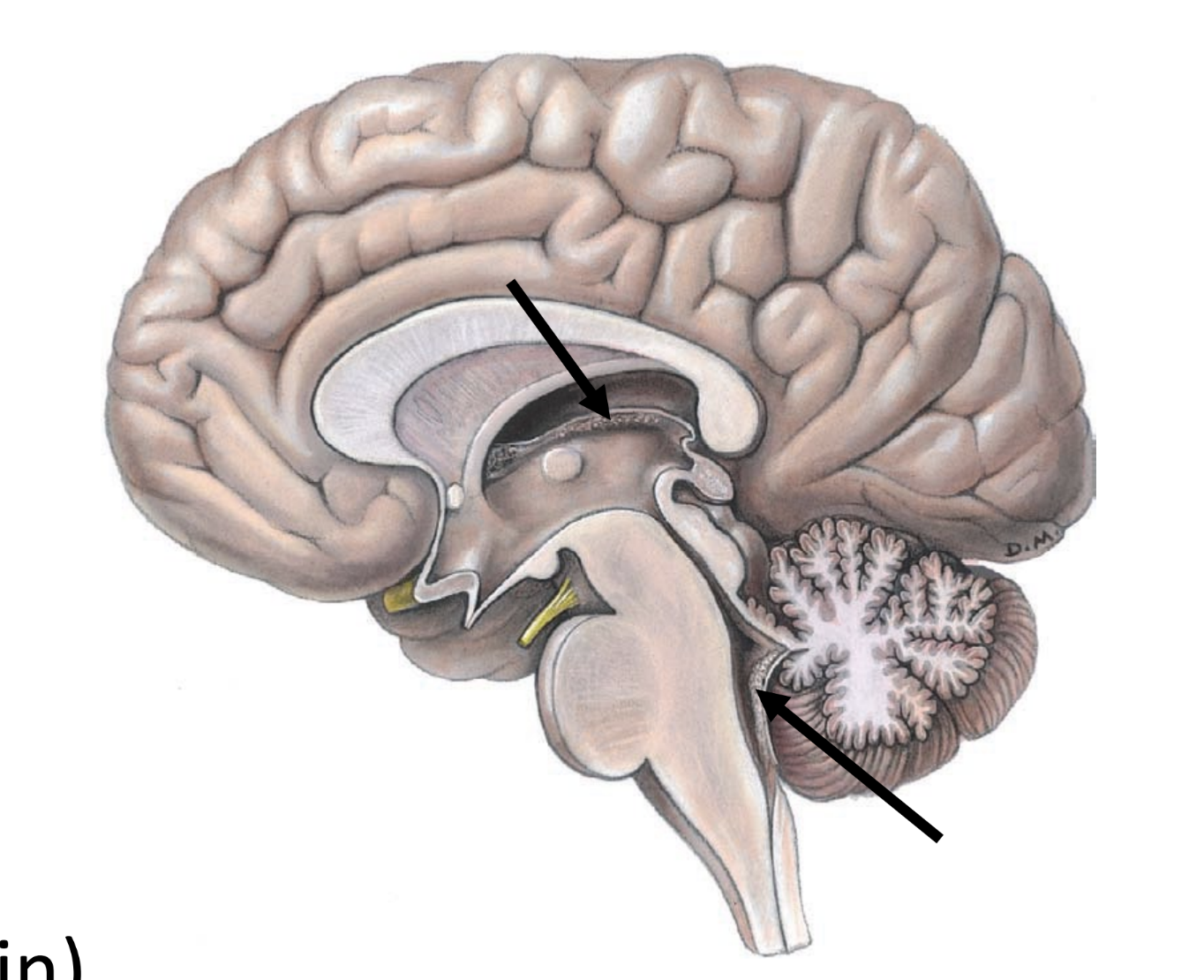
choroid plexuses
clusters of specialized capillaries
produce CSF
located in cerebral ventricles (spaces in brain)
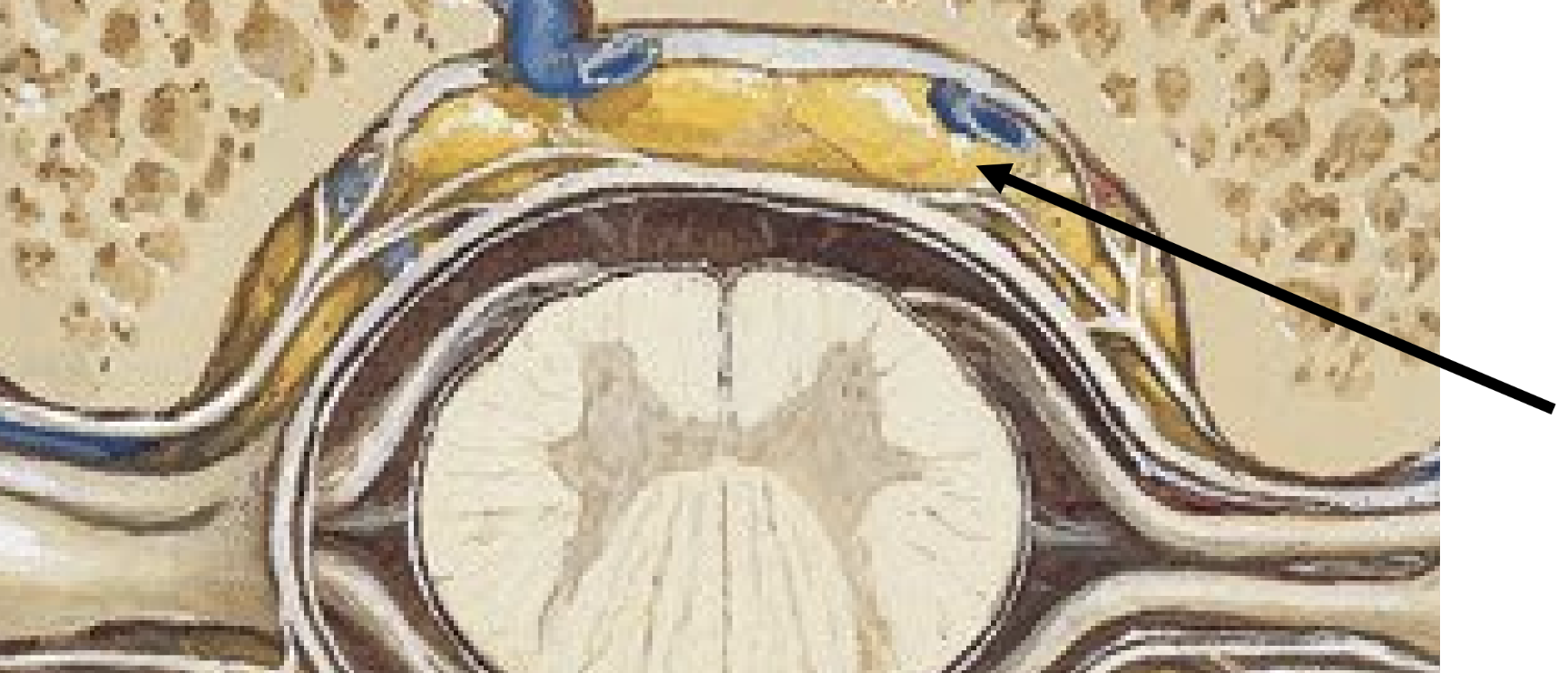
epidural space
located external to dura mater
contains fat & blood vessels which supply the spinal cord
subdural space
deep to dura, between dura and arachnoid
nothing found here normally
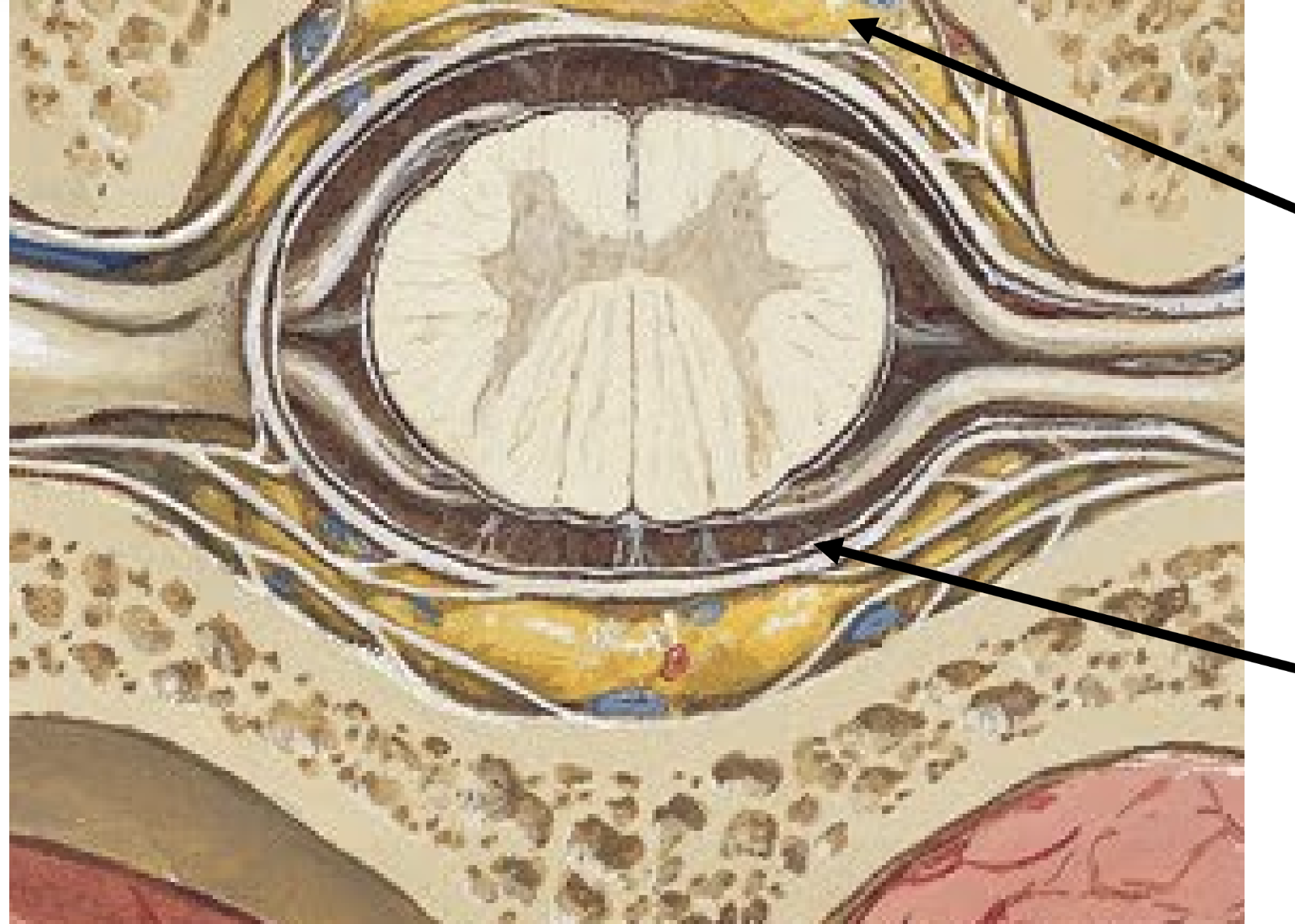
lumbar puncture
collect cerebrospinal fluid from the subarachnoid space for analysis or drainage
order of structures
skin
subcutaneous tissue
muscle
ligaments
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pain management
injection of anesthesia into epidural space
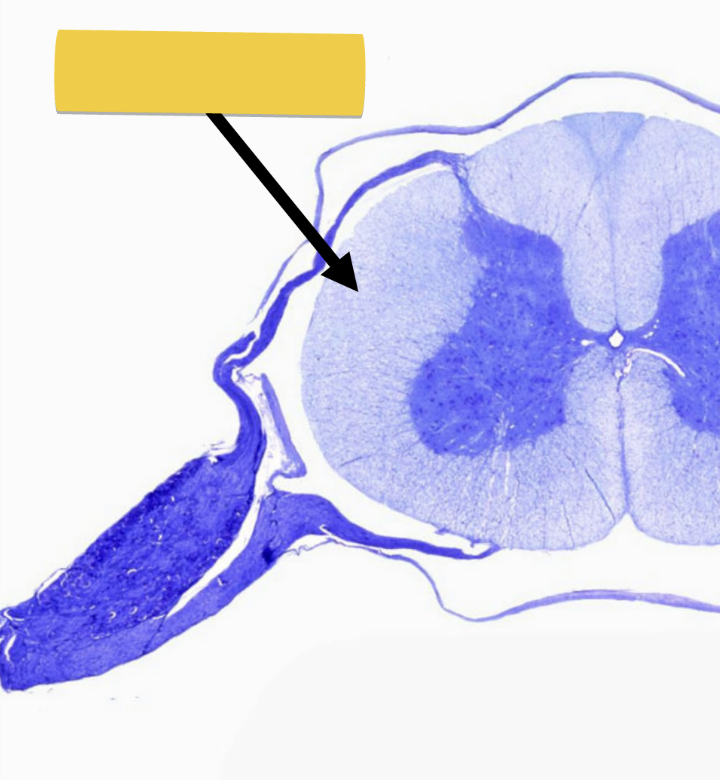
white matter
contains bundles myelinated axons
lipids in myelin sheath → white color
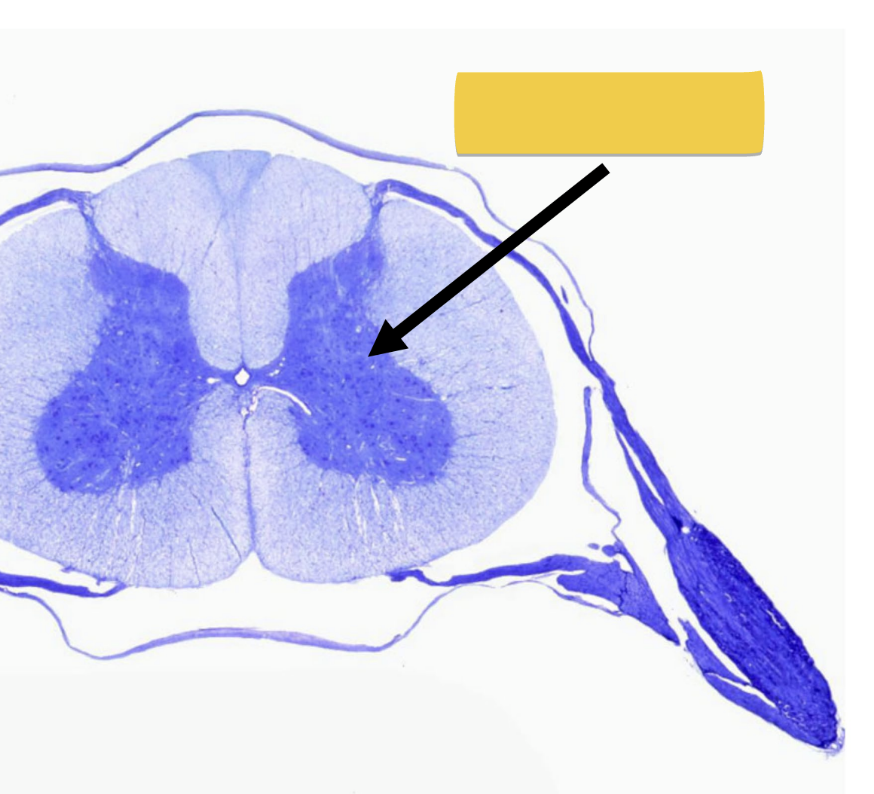
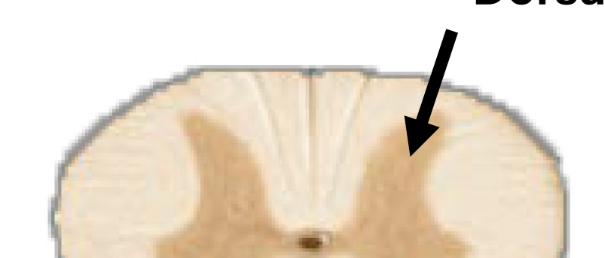
gray matter
contains unmyelinated cell bodies of neurons
forms “butterfly” shaped regions
no myelin → gray color
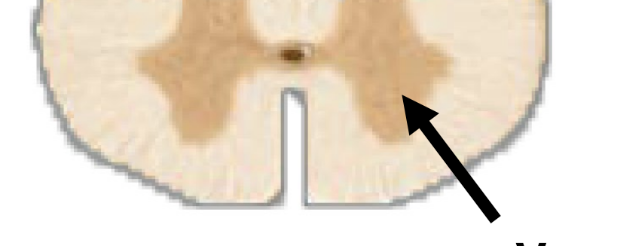
ventral gray horn
cell bodies for motor neurons
dorsal gray horn
cell bodies for sensory neurons
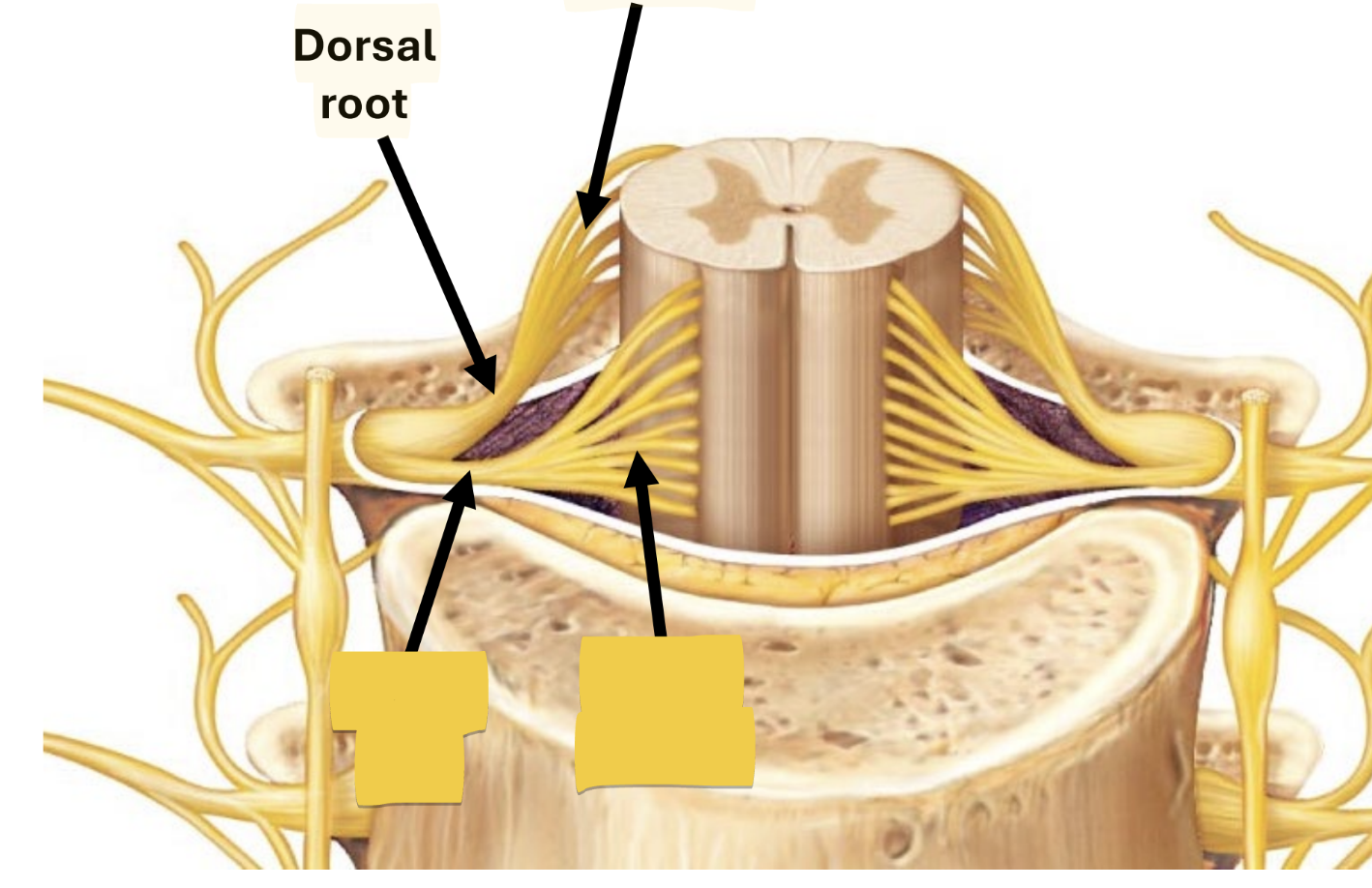
dorsal root/rootlets
enter/exit cord carrying sensory impulses
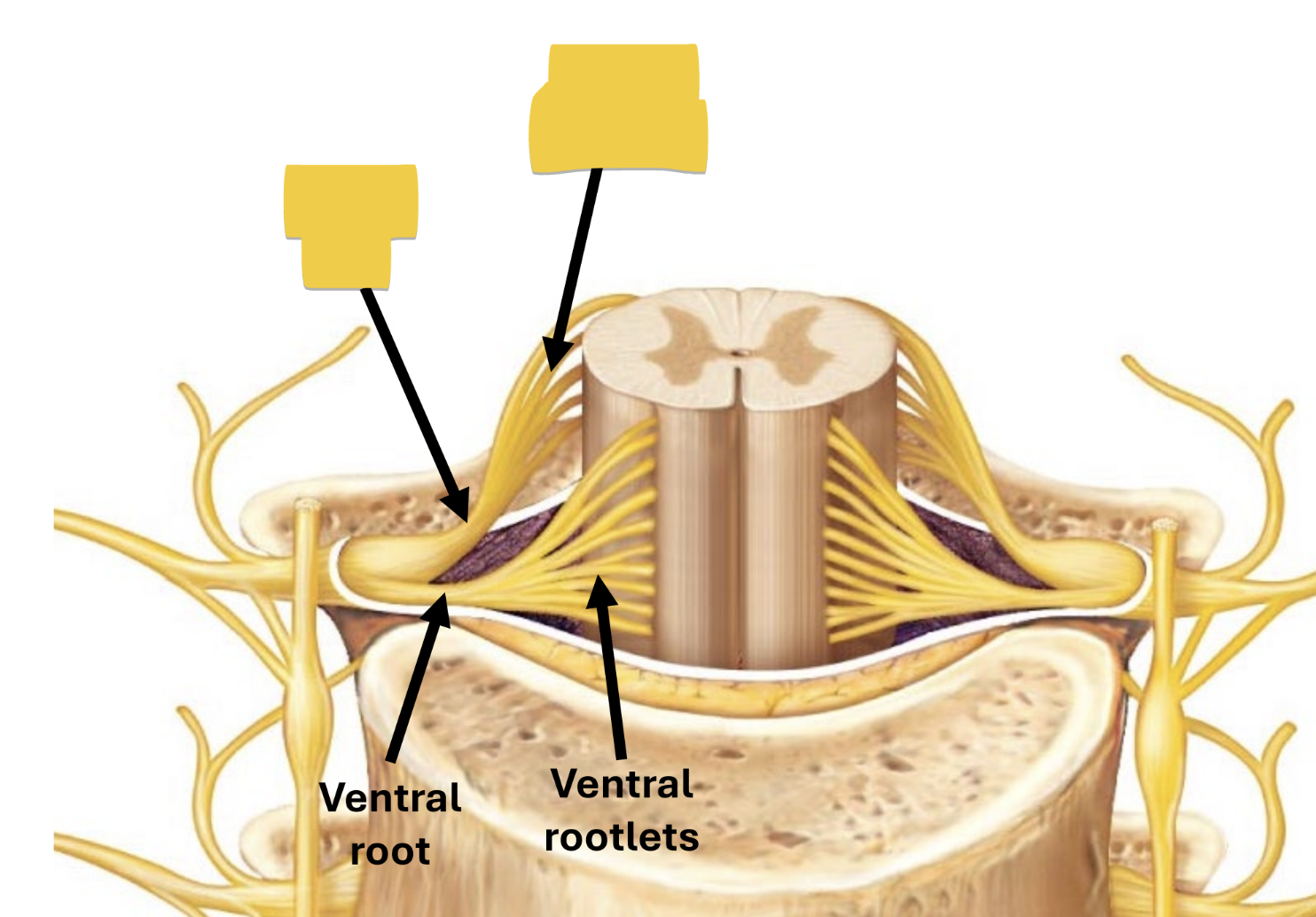
ventral root/rootlets
enter/exit cord carrying motor impulses
dorsal root ganglion
contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
spinal nerve
short segment carrying ALL sensory and motor impulses at certain level of spinal cord
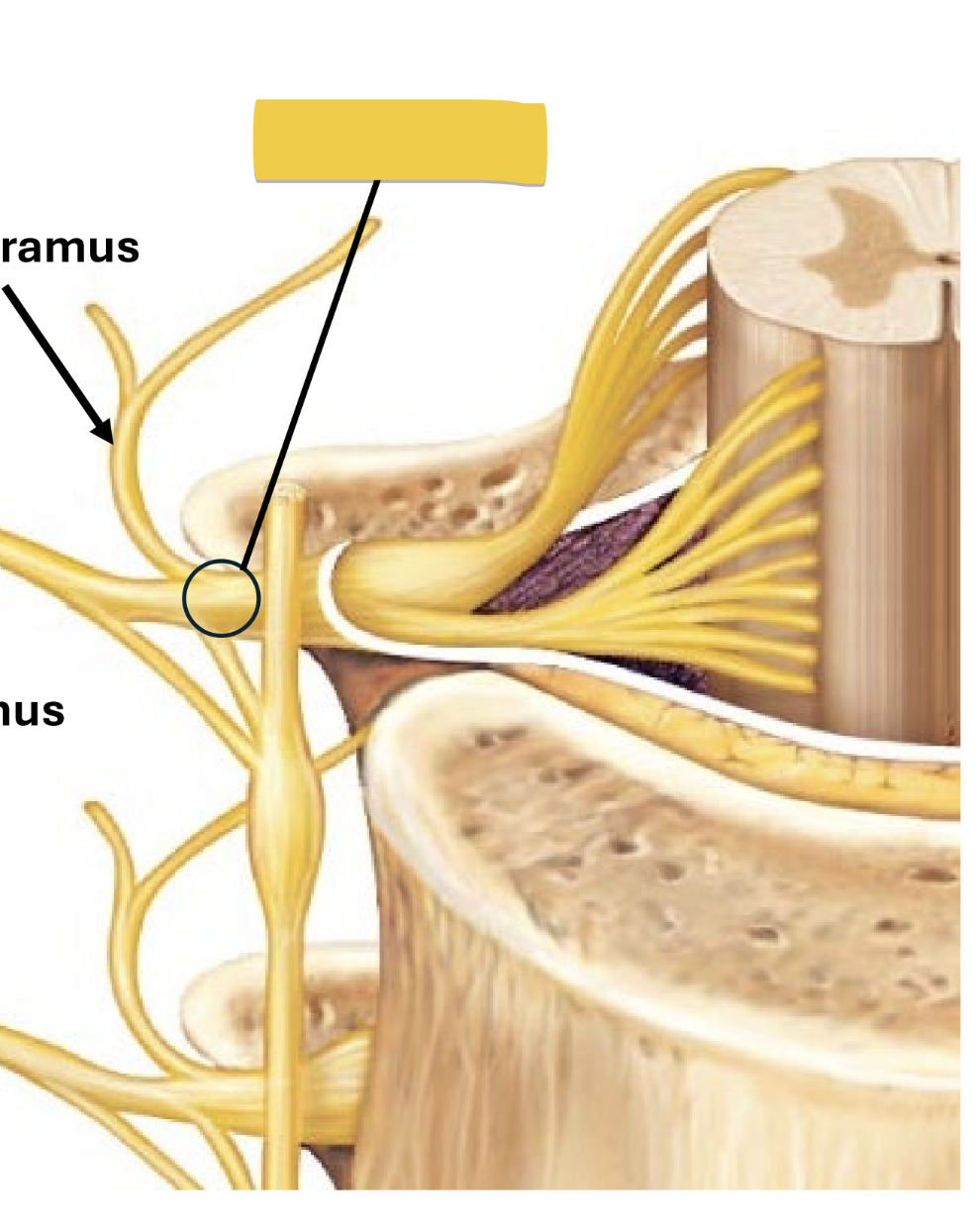
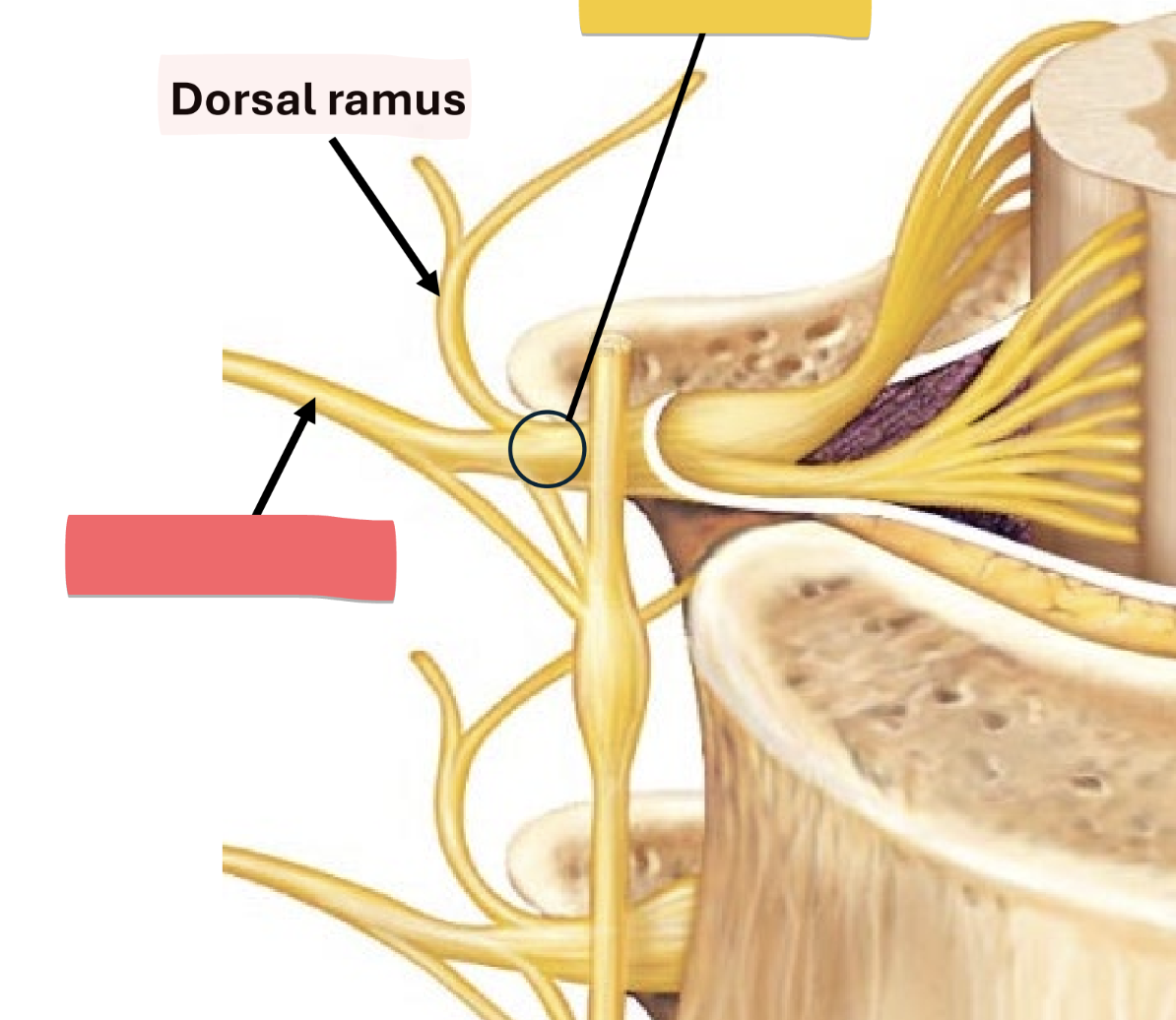
dorsal ramus
nerve of skin & axial muscles of back
carries all sensory and motor impulses
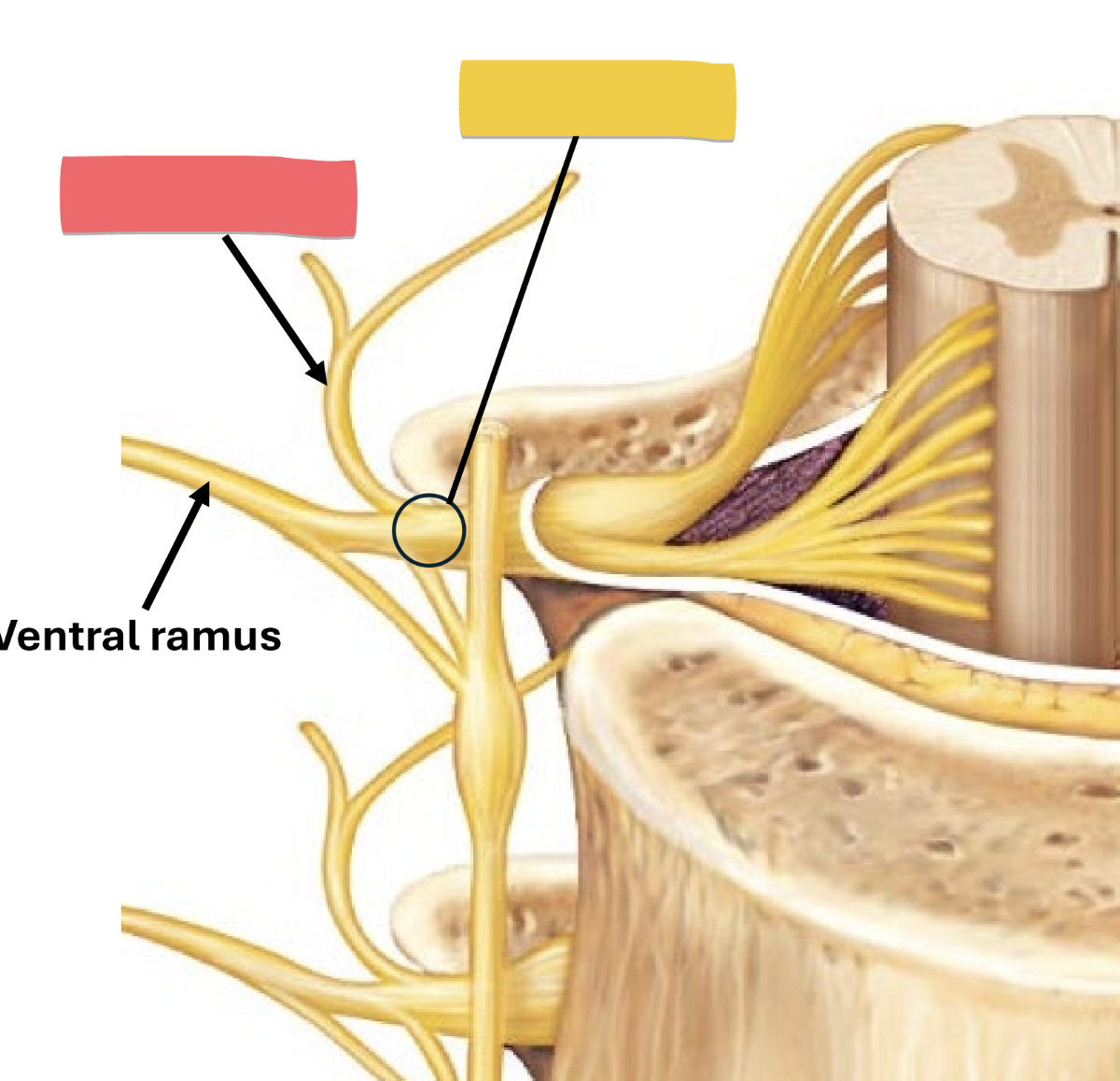
ventral ramus
anterior/lateral body wall and all limbs
carries all sensory and motor impulses
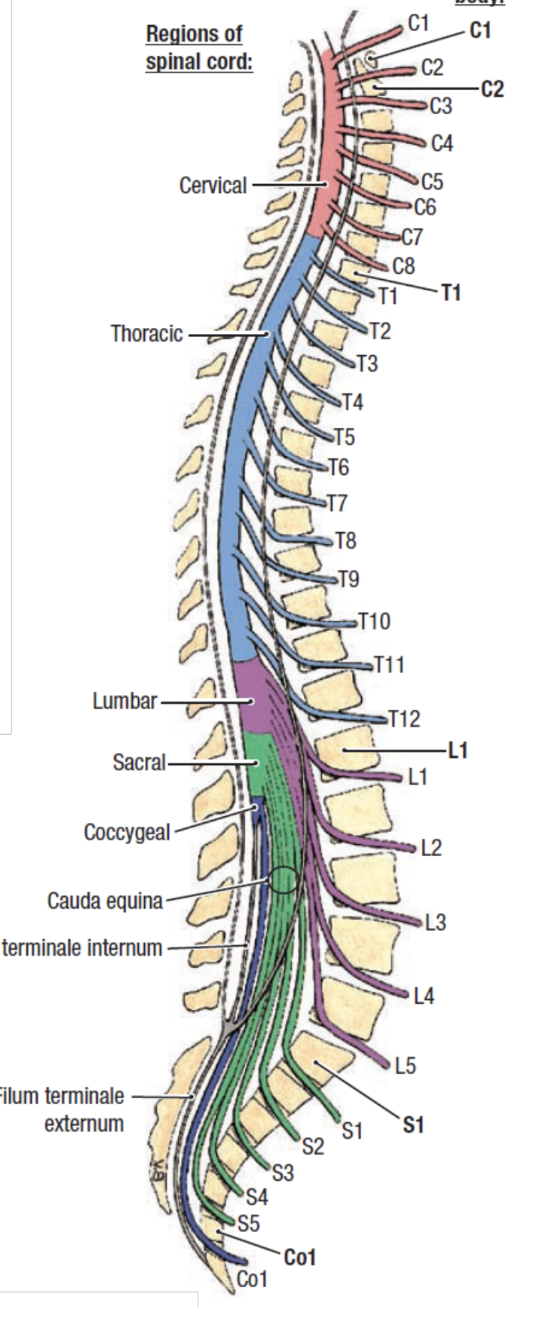
spinal nerves
31 pairs, pass through intervertebral foramina throughout spine
cervical - 8
thoracic - 12
lumbar - 5
sacral - 5
coccygeal - 1
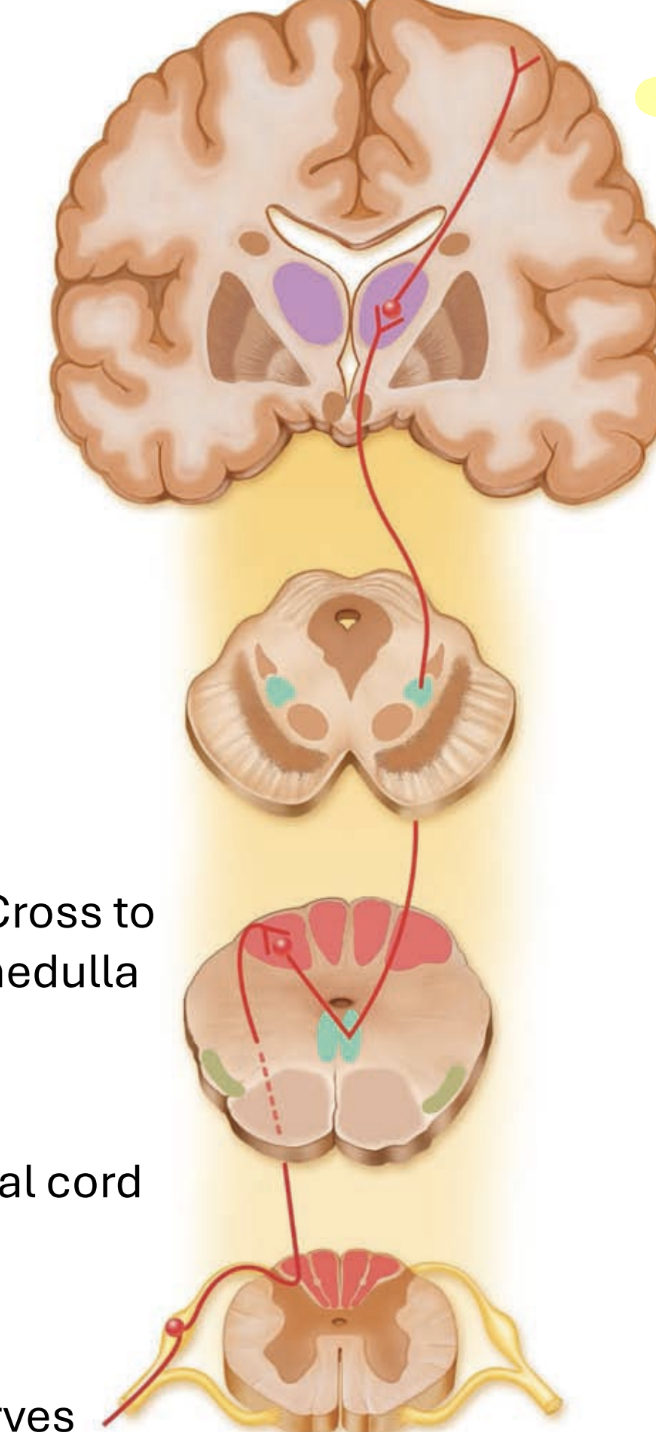
spinocortical tract
origin: sensory nerves
pathway: up spinal cord
decussation: cross opposite side in medulla
destination: brodmann areas 3,1,2 - somatosensory cortex
dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway
fine touch & proprioception
two bundles in dorsal (posterior) spinal cord
fasiculus cuneautus
sensory from upper body
fasiculus gracilis
sensory from lower body
corticospinal tract
origin: brodmann area - 4 motor cortex
decussation: crosses at medulla
travels down to spinal cord
then onto skeletal muscle
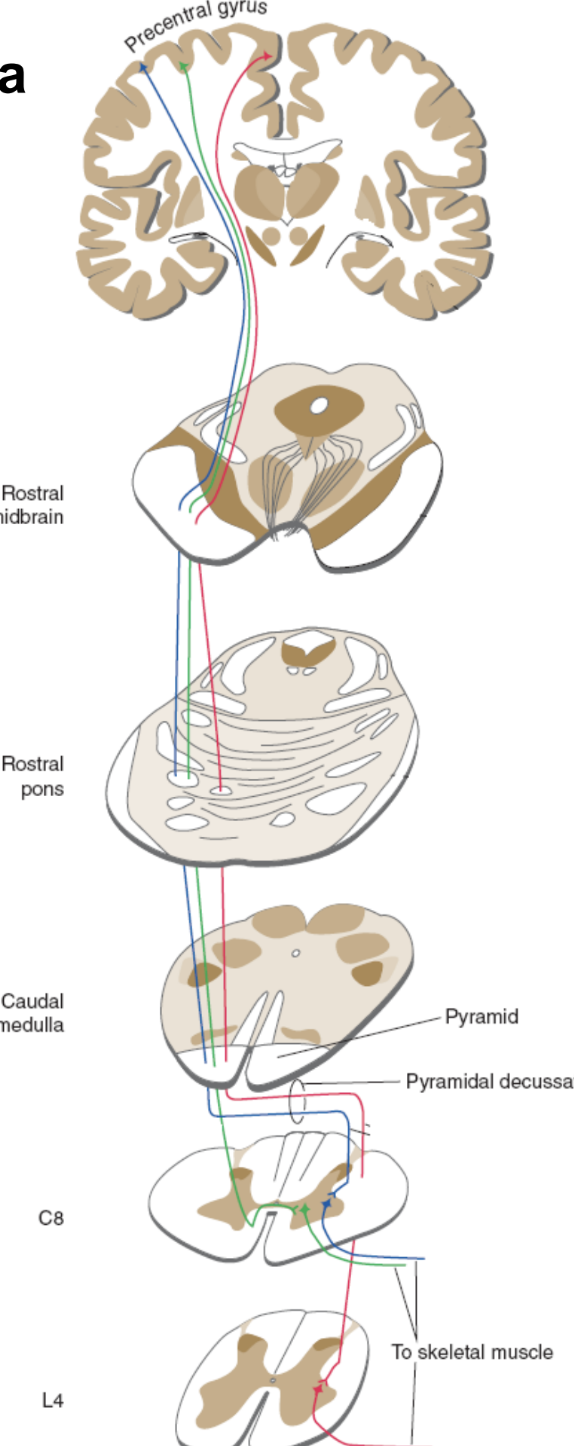
upper motor neuron
starts in brain, ends in spinal cord
cell body located in gray matter of cortex (precentral gyrus)
axon synapses on lower motor neuron in spinal cord
lower motor neuron
aka. peripheral motor nerve
starts in spinal cord and ends in muscle
cell body is in brain stem or ventral gray horn in spinal cord
its axon synapses on skeletal muscle fibers
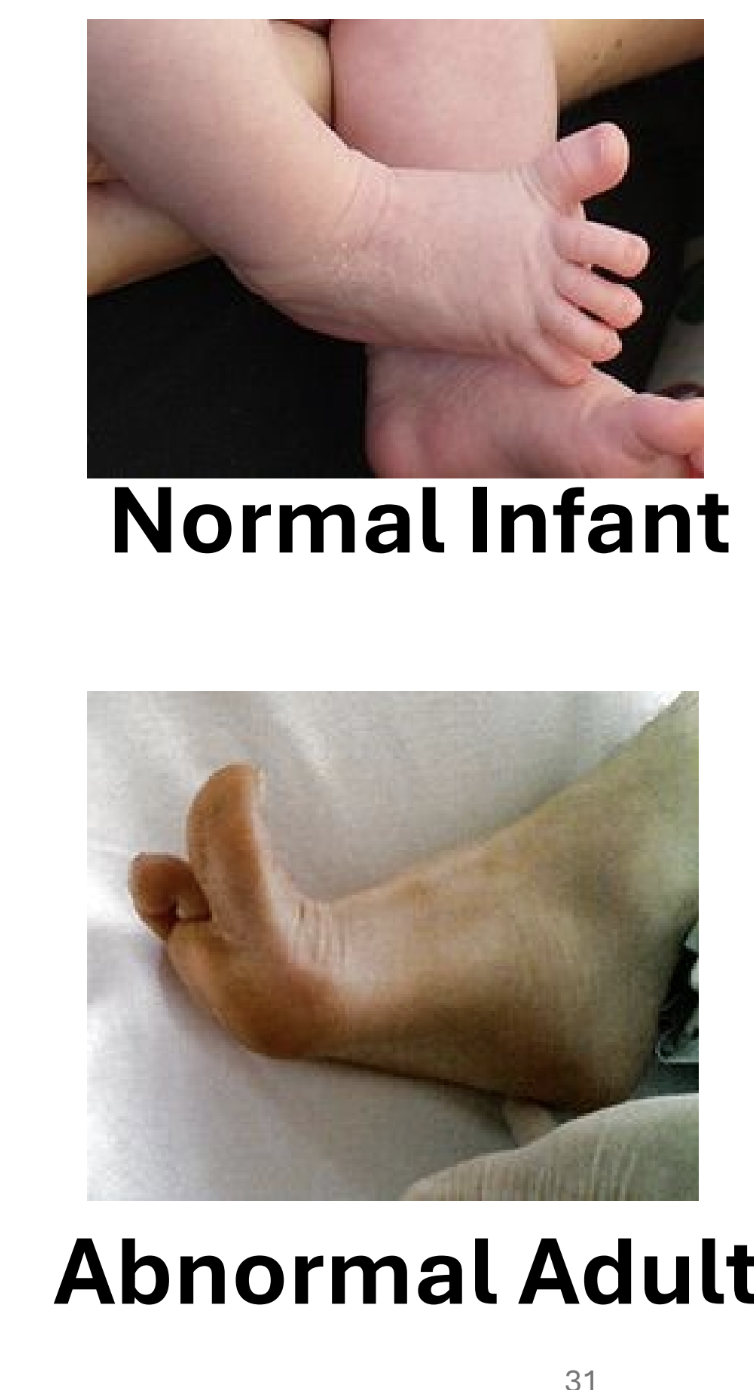
babinski sign
upper motor neuron normally keeps sensory impulse from spreading to other nerve roots
normal stimulation of sole: baby - hallux extension
adults - all toes curl and adduct
damage = impulse distribution not controlled, adult responds like infant
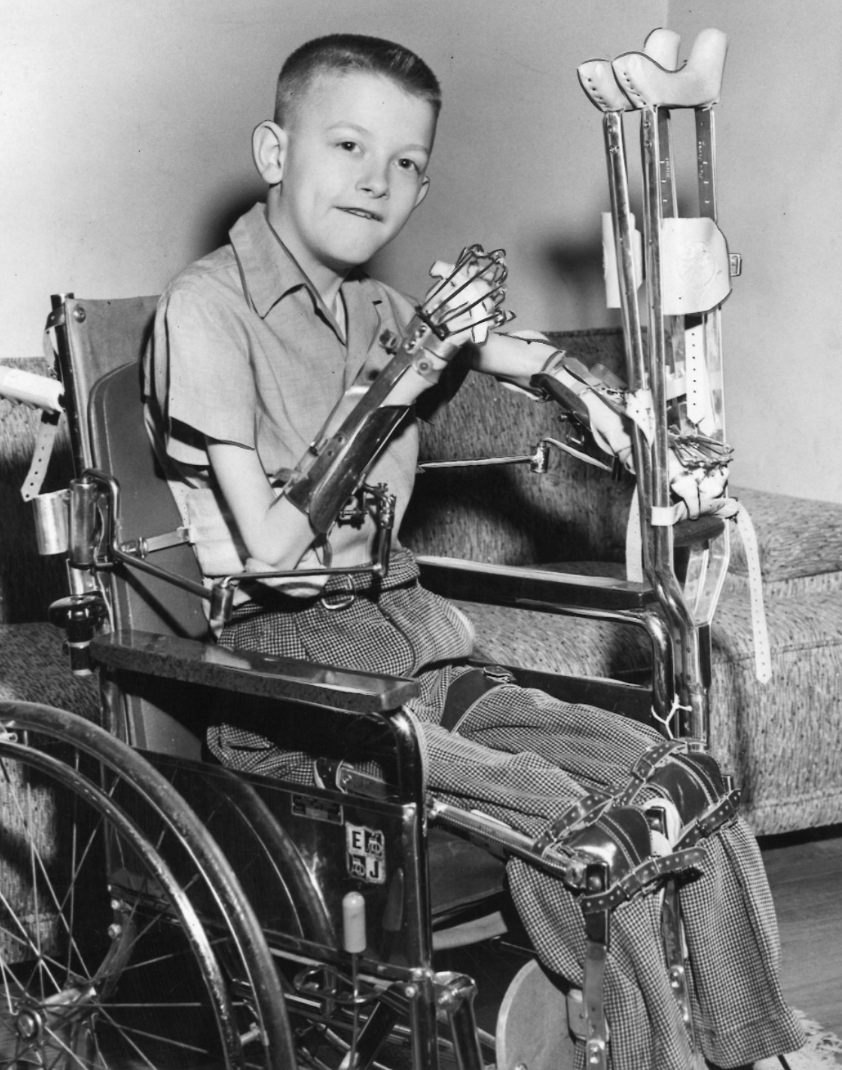
poliomyelitis
viral infection
in extreme cases, motor neurons destroyed
flaccid paralysis
reflexes absent
muscles atrophy
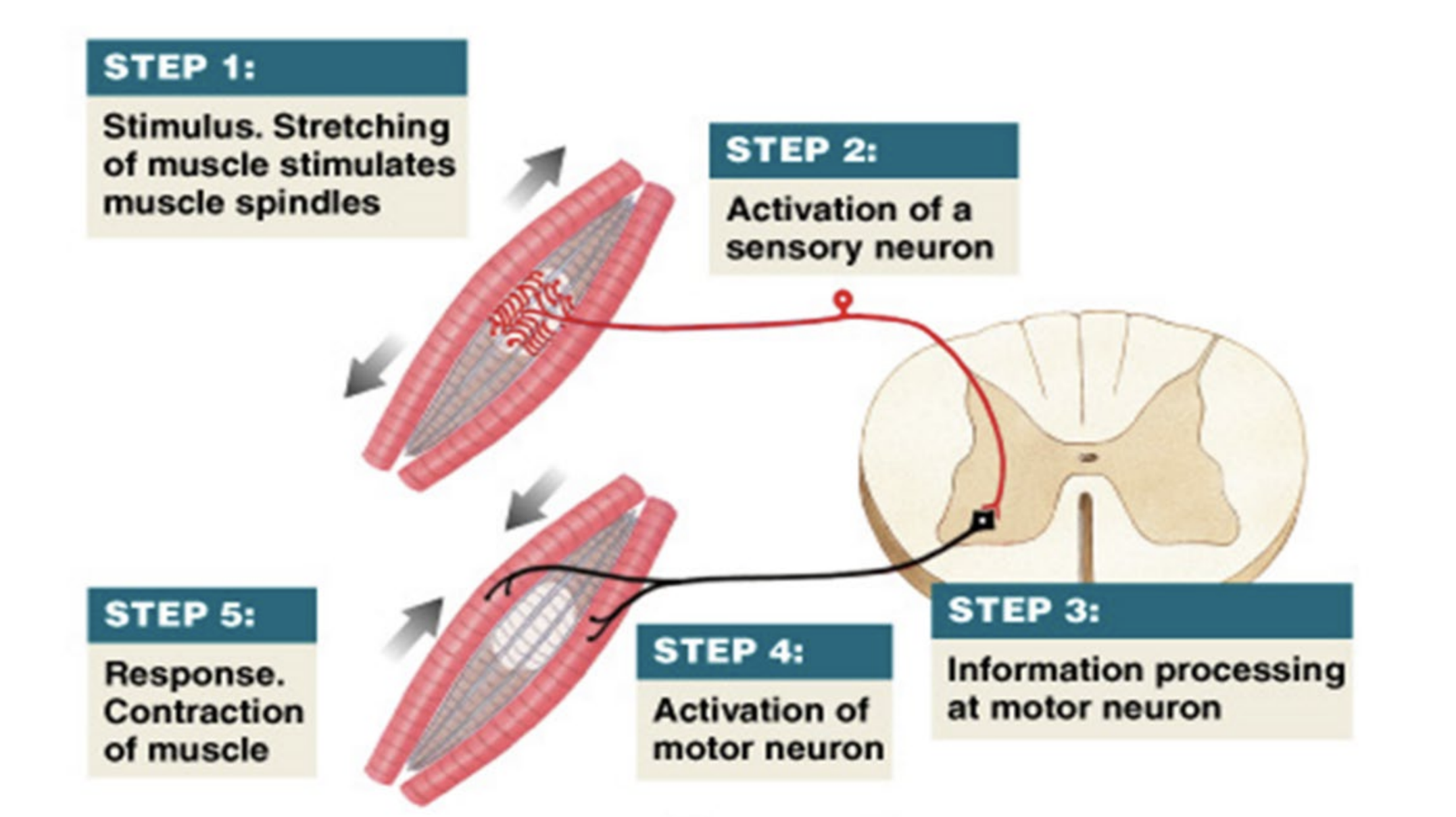
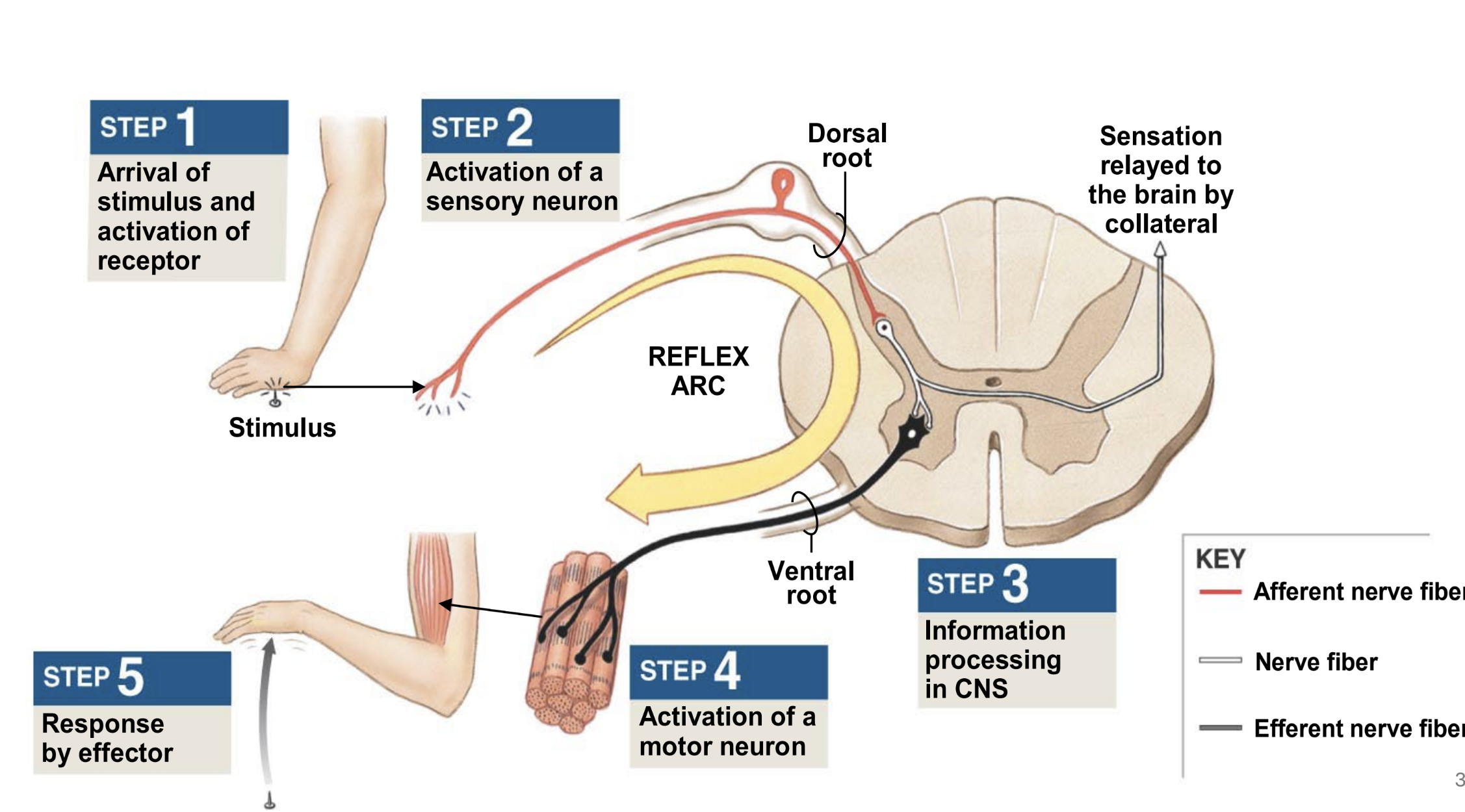
spinal reflexes
rapid, unconscious & automatic response to a stimulus
sensory stimulus triggers a motor response in the spinal cord, NOT from the brain
simple stretch reflex
muscle spindle receptor in muscle tendon responds to stimulus and initiates impulse
sensory neuron in dorsal root ganglion transmits impulse to cns (spinal cord)
motor neuron in ventral gray horn of spinal cord transmits impulse from cns to pns (via spinal nerve)
effector — skeletal muscle responds to motor neuron impulse
polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
pain receptor responds to stimulus and initiates impulse
sensory neuron in dorsal root ganglion transmits impulse to cns (spinal cord)
interneuron links between sensory and motor neurons
motor neuron in ventral gray horn of spinal cord transmits impulse from cns to pns (via spinal nerve)
effector — skeletal muscle responds to motor neuron impulse
absent reflex
lower motor neuron issue
stimulation cannot elicit motor response
exaggerated response
upper motor neuron issue
poor or no inhibition of lower motor neuron