Monopoly
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
monopoly
a single firm in the market is the sole producer of a product for no substitutes
give different types of monopolies
near monopolies
pure monopolies
geographical monopolies
give the characteristics of a monopoly
single seller
unique product
price maker
blocked entry
single seller
the single firm is the sole producer of the product where the industry and firm is synonymous
unique product
there are no close substitutes
price maker
monopolist control the total quantity supplied and will use their power whenever it is advantages to them
price-maker makes the demand curve…
downward sloping
types of blocked entry
economies of scale, legal barriers, ownership of essential resources
what allows for greater economies for scale and why
technology because firm’s average costs decrease as output increases
why does the ‘L’ shaped LRAC cost curve continue to fall and not reach MES
it allows for monopolists to be protected from competition
what happens when monopolists are protected from competition
new firms cannot compete with the same low cost and will be forced out of business by monopolist
why does a natural monopoly occur
this happens if the market demand curve intersects the long-run ATC curve at any point where ATCs are still declining
what are the assumptions of monopolist
patents, economies of scale or resource ownership secure the monopolist’s status
no governmental regulation
firm is a single-price monopolist
legal barriers
patents and licensing
ownership or control of essential resources
a monopolist may own or controls a resource that is essential to production
does MR = AR = D
no
when can the firm sell more units
if it reduces its prices
MR =…
change in TR/change in Q
what is MR greater than
price except for the first unit of output
what happens when MR falls
quantity rises and eventual turns <0
what happens when TR rises at a decreasing rate
it will eventually fall when MR < 0
what happens when MR = 0
demand unit is elastic
MR has the same…
vertical intercept as the AR curve and a horizontal intercept half that of the AR curve
where do monopolists produce
in the elastic region of the demand curve
how is a monopolist a price maker
will never choose a price-quantity combo where price reduction causes TR to decrease
will choose price at elastic region
how do you find output and price determination
TR - TC
MR=MC*
why is there no supply curve
because there is no unique relationship between P and Q
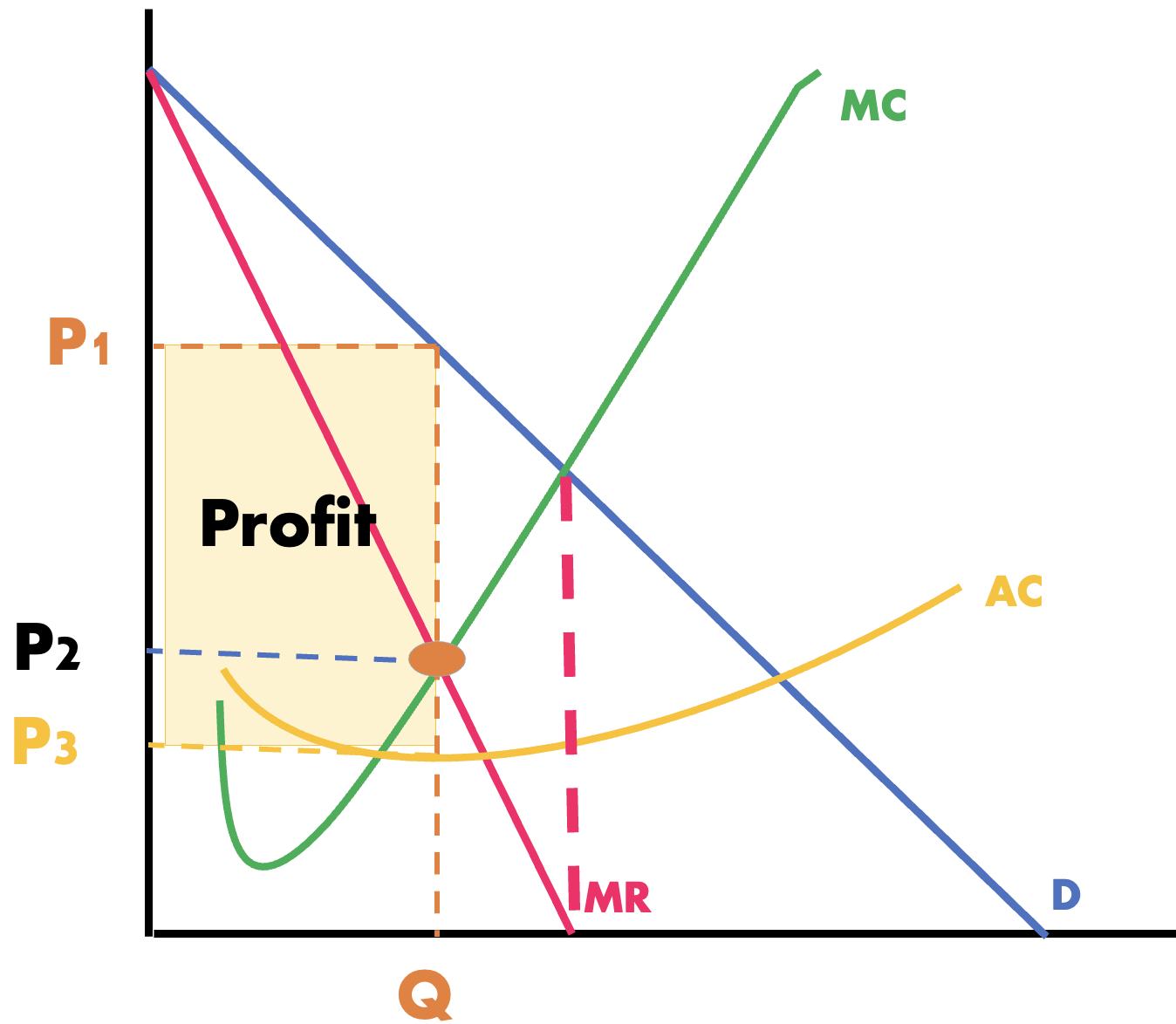

what is this firm making
economic profit
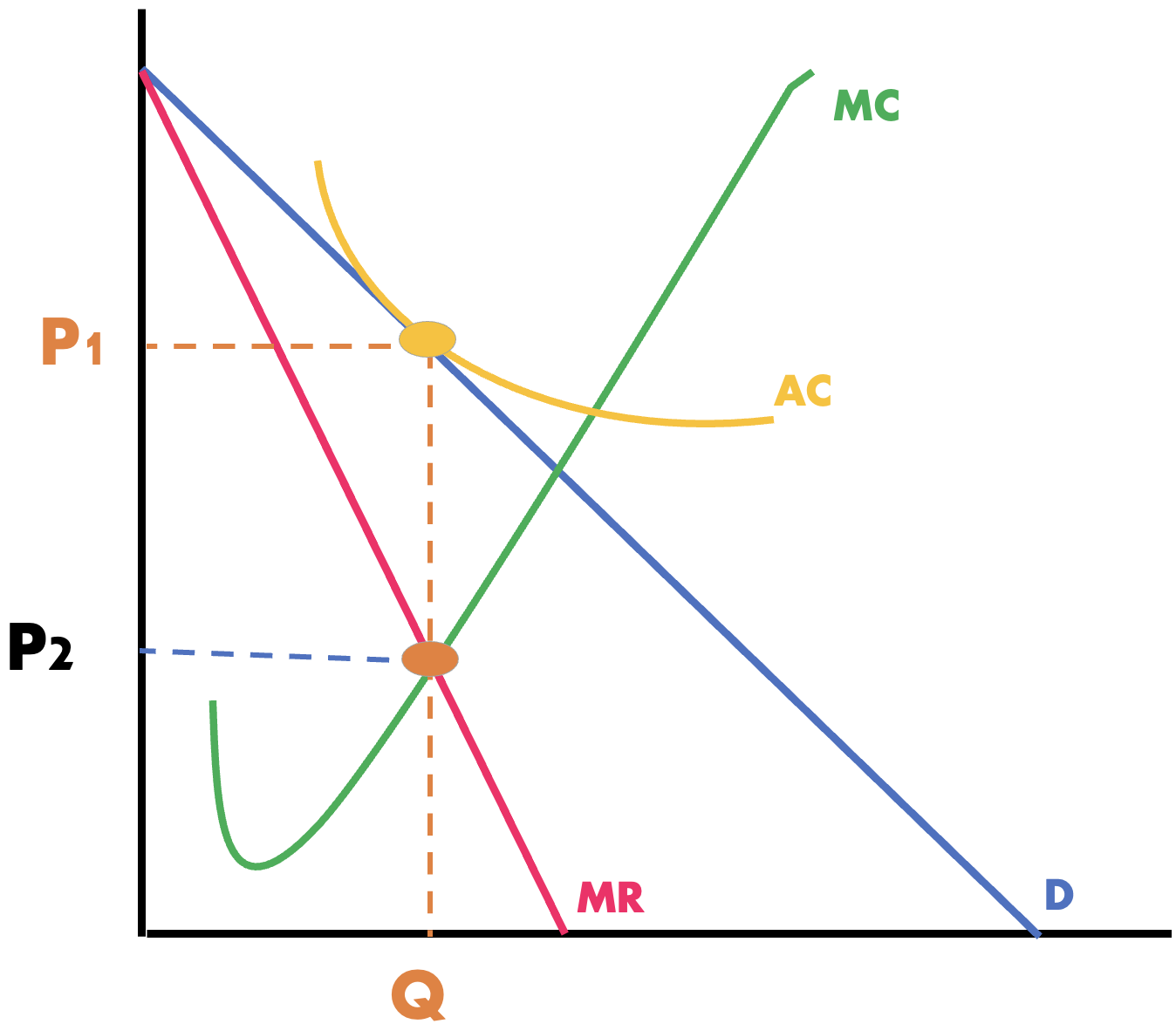
what is this firm making
normal profit
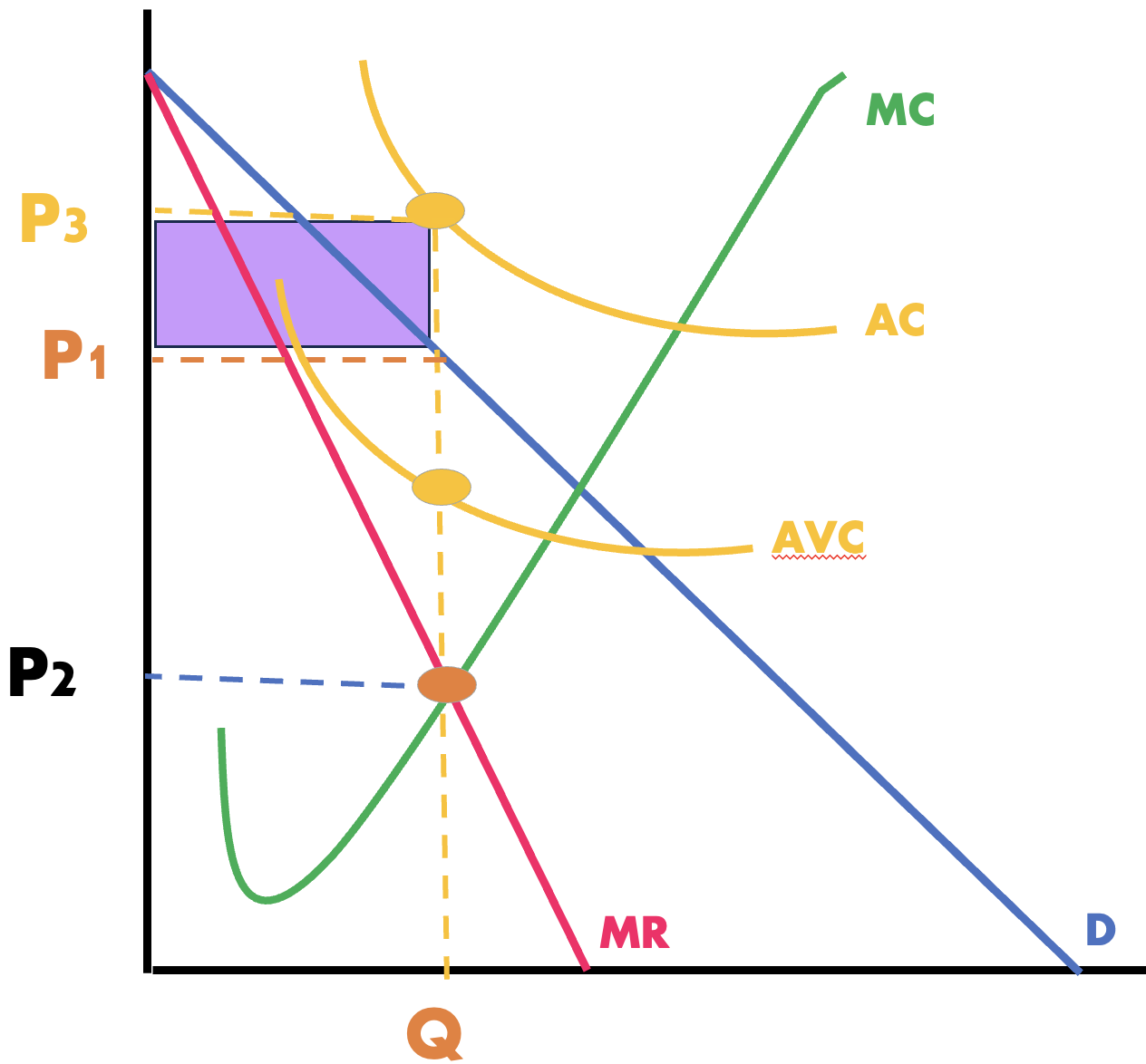
what is this firm making
economic losses
price discrimination
pricing strategy in which a seller prices the same product differently across markets based on what each market’s buyers are willing to pay
give the conditions in price discrimination
monopoly power
market segregation
no resales
are price differences justified by cost differences
no
give examples where you will find price discrimination
airline charges
movies, gym, hotel reservation
coupons
is a monopolist either allocative or productive efficient
no
in the short run, when will firms produce
where P>AVC
in the long run, when will firms produce
where P>ATC
natural monopoly
the economies of scale mean that big firms have lower costs at small firms
consumer surplus
the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay and actually pays (small)
producer surplus
the difference between what the producer is willing to sell it for and what it actually sells it for (big)
what does a monopoly give rise to
dead weight loss
deadweight loss
a loss to society of quantity that is no longer being produced
how does a monopoly regulate itself
social optimum price
fair return price
dilemma of regulation
where do you find social optimum price
P=MC
where do you find fair return price
AC=AR