Chemistry Topic 4
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Enthalpy
Heat content - stored chemical potential energy that can be transferred during a reaction
Total enthalpies of reactants is not equal to products
enthalpy is released or absorbed as heat energy
System
particles involved in a chemical reaction
delta H =
H products - H reactants
-delta H value = exothermic reaction
+delta H value = exothermic reaction
individual atoms will have a _____ amount of stored potential energy than atoms which combine to form molecules
larger
When steam condenses to form water, heat energy is _______ to the surroundings
released
The potential energy of a substance in the solid state is ______ than the potential of the substance in its liquid state
smaller
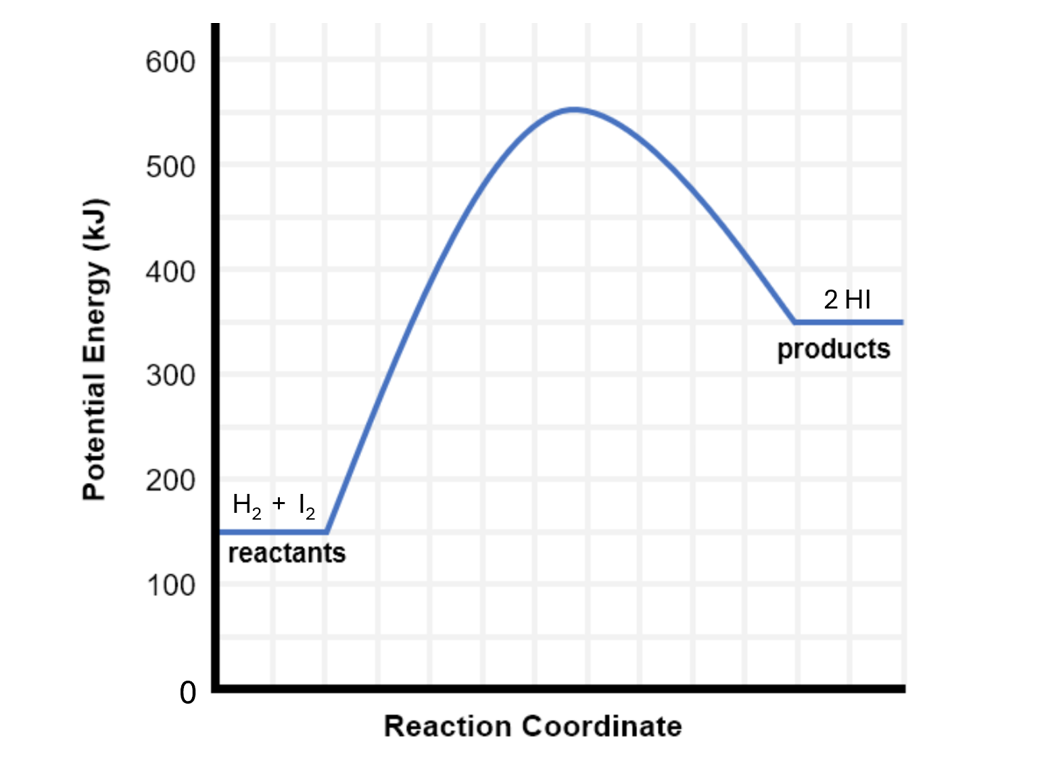
the transition state is
the highest potential energy state for the reacting particles, bond breaking and bond formation are taking place
surface area decrease
Less surface area is exposed therefore there will be a lower frequency of collisions and therefore a lower rate The same proportion of collisions are successful.
Temperature decrease
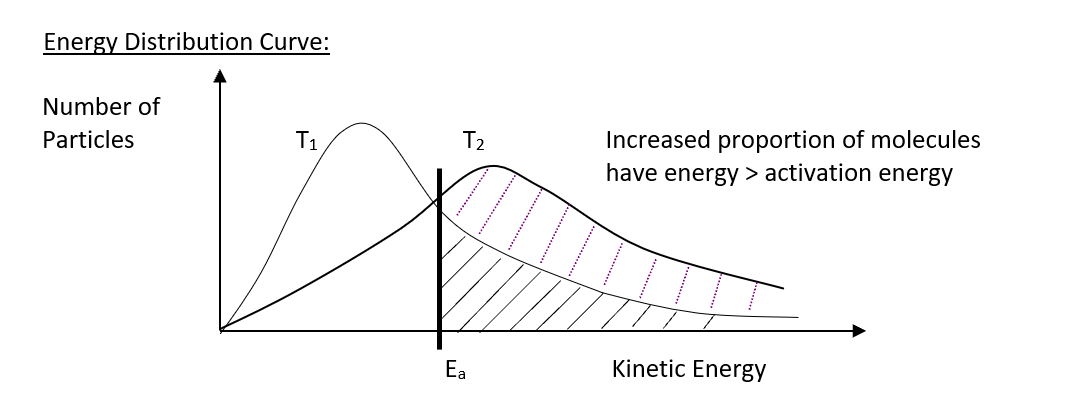
decreases the average kinetic energy of the reactant particles. Particles move more slowly and therefore collide less frequently, but MORE IMPORTANTLY a smaller proportion of particles have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy (Ea) barrier. This greatly reduces the freqency of successful collisions, reducing the rate of reaction lower temperature. graph shows the reduced proportion of particles with sufficient energy to overcome Ea barrier
Catalyst present on rate
The presence of a catalyst provides an alternate pathway (mechanism) for the reaction with a lower activation energy (Ea). This increases the proportion of reactant particles with sufficient energy to collide successfully and therefore increases the frequency of successful collisions and therefore the rate.
energy profile diagram
energy distribution curve
concentration decrease
More reactant particles in a given volume and therefore a greater frequency of collisions (more collisions per unit time) and therefore a faster rate. The same proportion (e.g.1 in a 100) are successful.
Things about catalysts
Reactants and products are same
Heat of reaction, delta H is same with or without catalyst
Catalysed pathway, lower Ea
Catalysts take part in reaction, absorb or an inbetween substance
Catalyst not consumed, re-used
Cheaper to use catalyst, instead of temp
Why gas occupies the complete volume of the flask in which it is contained?
The gas particles are moving in a rapid, random, straight line motion and there are no significant forces between the particles holding them together. Therefore, the particles are free to move until they hit the sides of the container.
temperature is the measure of average kinetic energy and Ek = ½ mv2 which means in gases
at the same temperature, gas particles with a higher mass will have a lower velocity and vice versa
Pressure in gases is directly proportional to the
frequency of collisions, however pressure is dependent on the frequency and force of collisions in a given area.
Increasing the pressure of a gas…
decreases its volume - Boyle’s law
Explain using kinetic theory of gases why when a syringe of gases is compressed, the pressure of the gas increases
Compressing a syringe decreases the volume of the container. This forces the particles closer together and closet to the walls of the container, increasing the frequency of collisions with the walls of the container, thus increasing the pressure.
Use the kinetic theory of gases to explain why the pressure in a car tyre increases when the car is driven long distances.
As the car is driven, the gas inside heats up. As a result, the average kinetic energy of the gas particles increases. The particles therefore collide with the tyre walls with a greater frequency and with a greater force. Because the tyre has constant volume, the pressure increases.
Explain using kinetic theory of gases why an increase in the temperature of a gas filled balloon leads to an increase in the size of the balloon.
Increasing the temperature increases the average kinetic energy of the particles. This results in an increase in the average velocity of the particles. They collide with the sides of the balloon more frequently and with greater force. This forces the balloon to increase in size to maintain atmospheric pressure.
Avogadros Law of gases
States that at constant temperature and pressure, equal volumes of gases contain the same number of molecules.
at STP, the molar volume of all gases is
22.71L
name each variable in PV=nRT
P = pressure, V = volume, n = number of moles, R = ideal gas constant, T = temperature