Econ 201 Final
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Production Function
The maximum amount of output that a firm can produce with a given quantity of inputs and for a given state of technology
Law of Diminishing Returns
If we vary 1 of the inputs, keeping all other inputs as well as the technological level constant, then, at least after some point, successive additional units of the variable input will add less and less to the Total output
Short Run
A period of time in which only the variable inputs, such as labor and materials, could be adjusted
Can distinguish between fixed and variable costs
Long Run
A period of time in which all inputs, including fixed factors, such as capital, could be adjusted
All costs are variable
Assuming that firms produce efficiently
Total Cost [TC]
Represent the total amount of $ spent, in all the inputs required for a business firm in order to produce a given level of output
Assuming that firms produce efficiently
Fixed Costs [FC]
Costs that the firm has to pay even if it doe snot produce anything
Do not depend on the level of output produced
Assuming that firms produce efficiently
Variable Costs [VC]
Costs that vary and are directly related to output
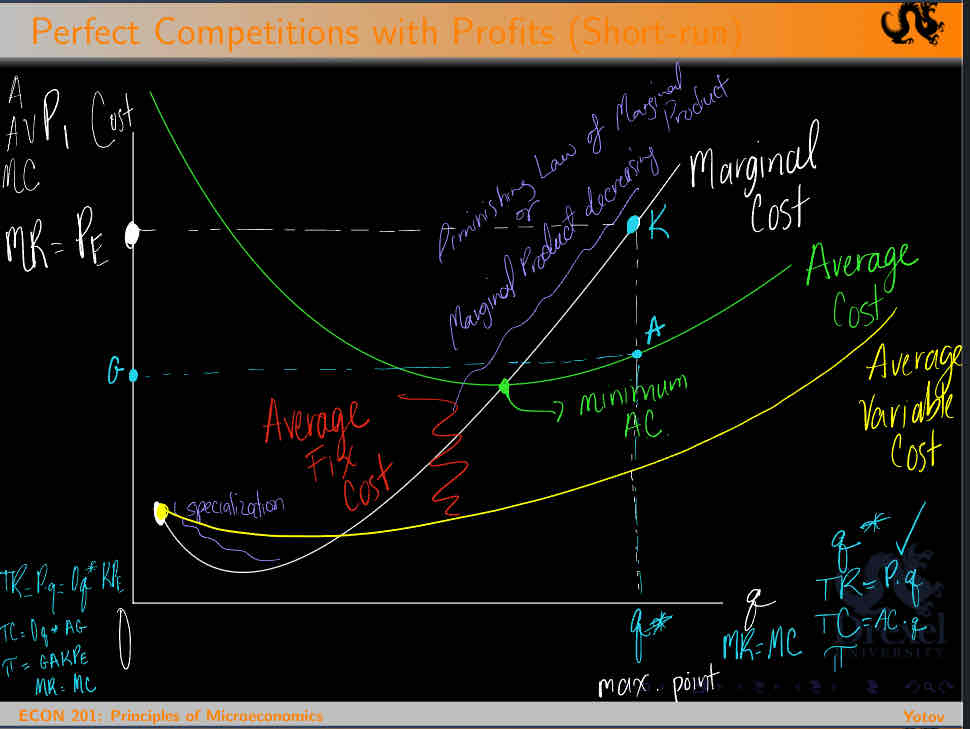
Marginal Cost — MC
Economists definition
The additional expenditure that a firm has to incur in order to produce 1 more unit of output
Average Cost — AC
The ratio between the Total Cost and the quantity produced
AC= TC/Q
Average Fixed Cost — AFC
The ratio between fixed costs and quantity of output produced
AFC = FC/Q
Average Variable Cost
The ratio between variable costs and quantity of output produced
AVC = VC/Q
Perfect Competition
A market setting involving large number of profit maximizing firms that sell a homogeneous product
Cannot individually affect the market price
Free entry and exit are assumed
Perfectly Competitive Firm
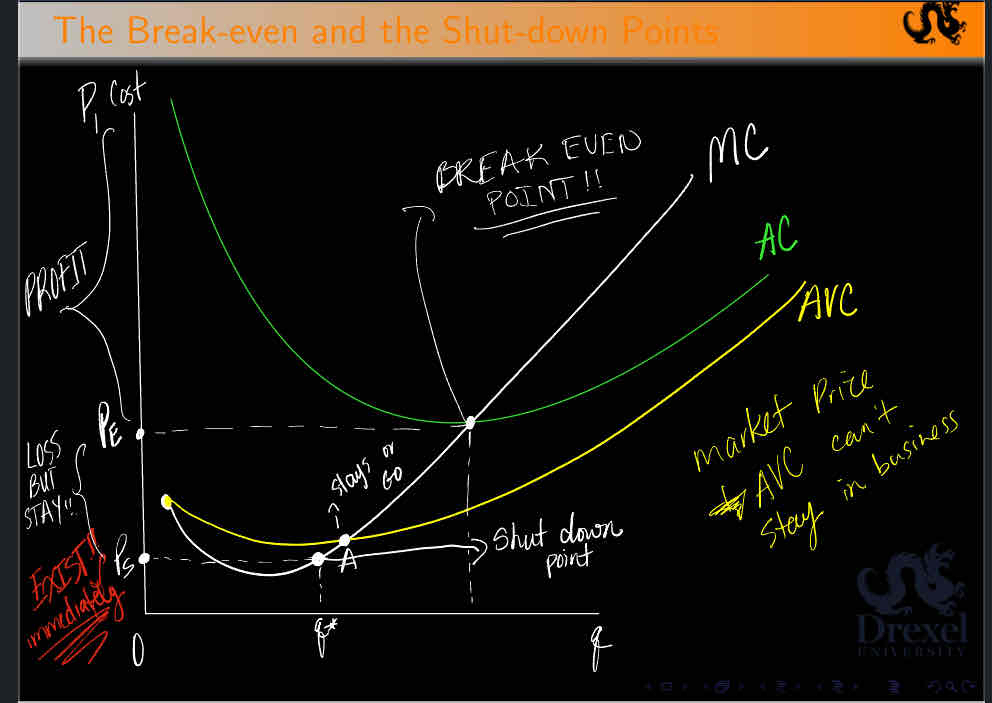
Will maximize its profit when it produce at the level where Marginal Cost = Market Price
MC = P = MR
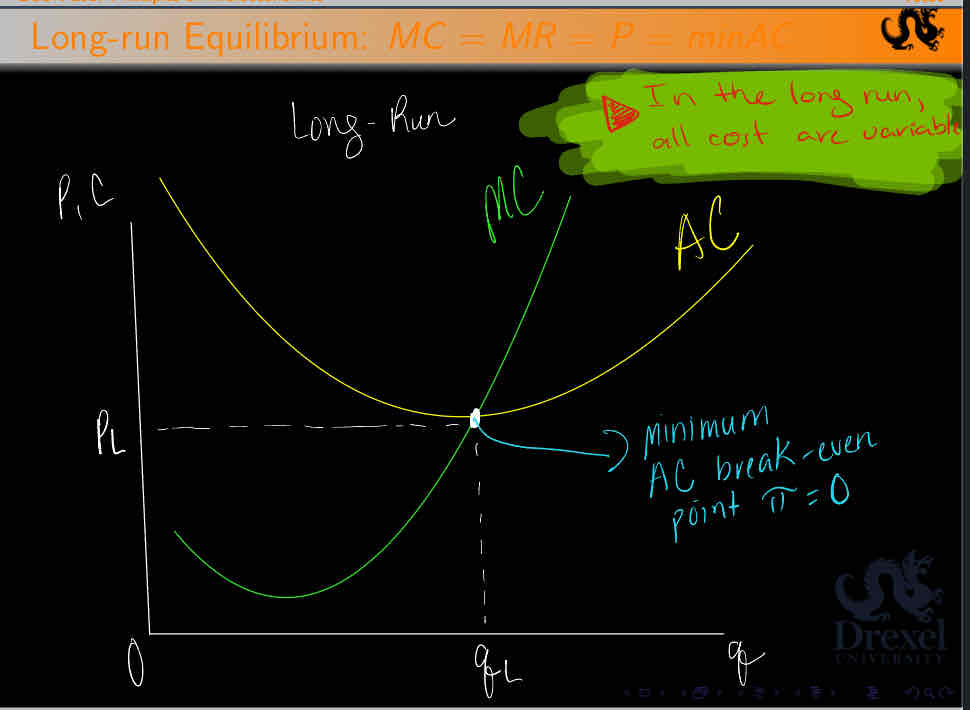
Perfect Competition in the long run
The economic profit realized by each of the large number of identical firms operating in a perfectly competitive market setting w/ free entry and exit will be zero.
The market price will be equal to both the marginal cost and the long - run-minimum-average-cost
MR = P = MC = min AC
Imperfect Competition
Prevails in an industry where individual sellers have some control over the price of their output
Monopoly
Exists when a single firm is the sole producer of a product for which there are no close substitutes
Entry in the industry is blocked
Monopolistic Competition
market structure
A market structure in which a relatively large number of sellers offer similar but not identical products
Entry is easy
Large # of small firms
Differentiated products —> ability to affect price
Entry and exit are easy
Oligopoly
Exists where a few large firms producing a homogeneous or differentiated product dominate a market
These producers are interdependent in their profit-maximizing decisions
Hard to enter their industry
Cartel
A group of producers that creates a formula written agreement specifying how much each member will produce and charge
Marginal Cost decreases at the early stages of production because Marginal Product is increasing
True
False
True
When production reaches a certain point, Marginal Cost will start increasing because of the Law of Diminishing Returns
True
False
True
Marginal Cost increases at the early stages of production because of Specialization.
True
False
False
MC decrease first then increase
When output approaches zero, Average Cost approaches infinity because of fixed costs
True
False
True
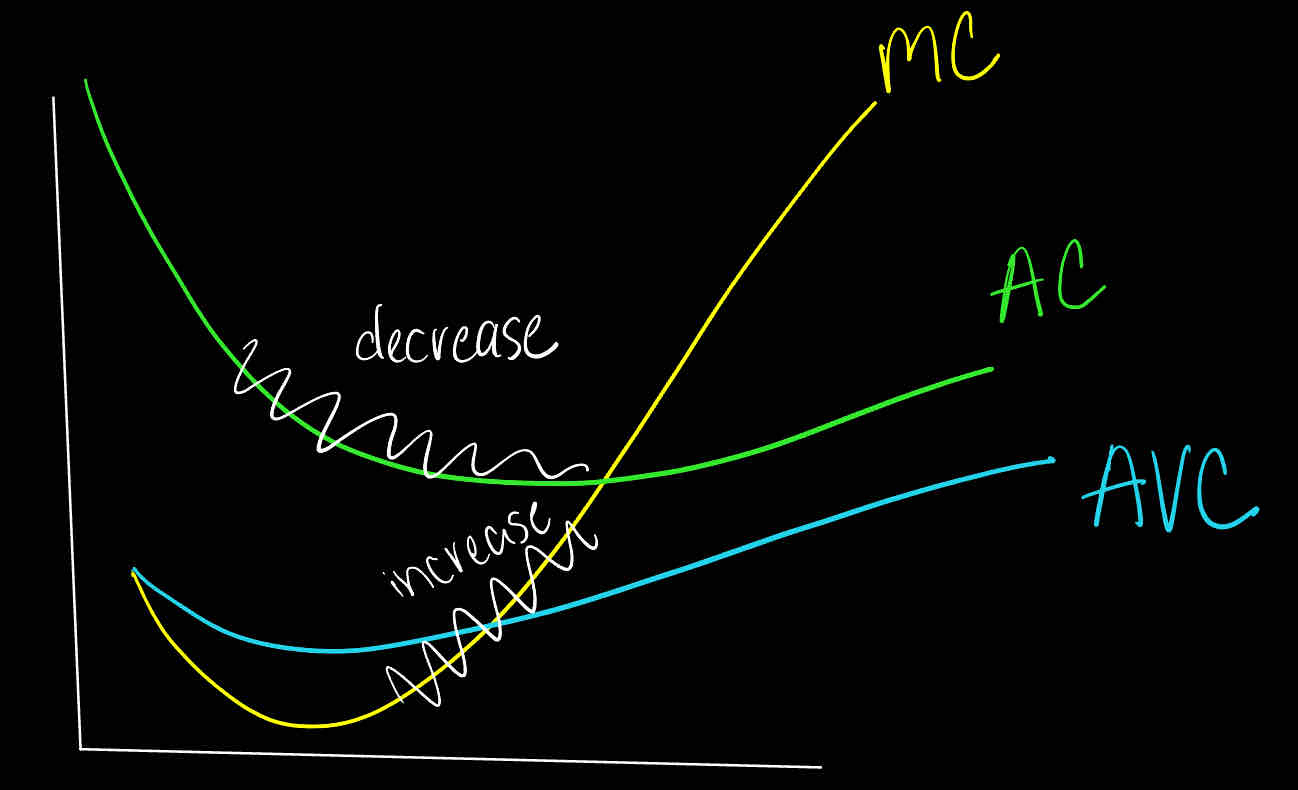
Increasing marginal cost implies increasing average cost
True
False
False
increasing MC means that AC can still have the possibility to be in the decreasing stage
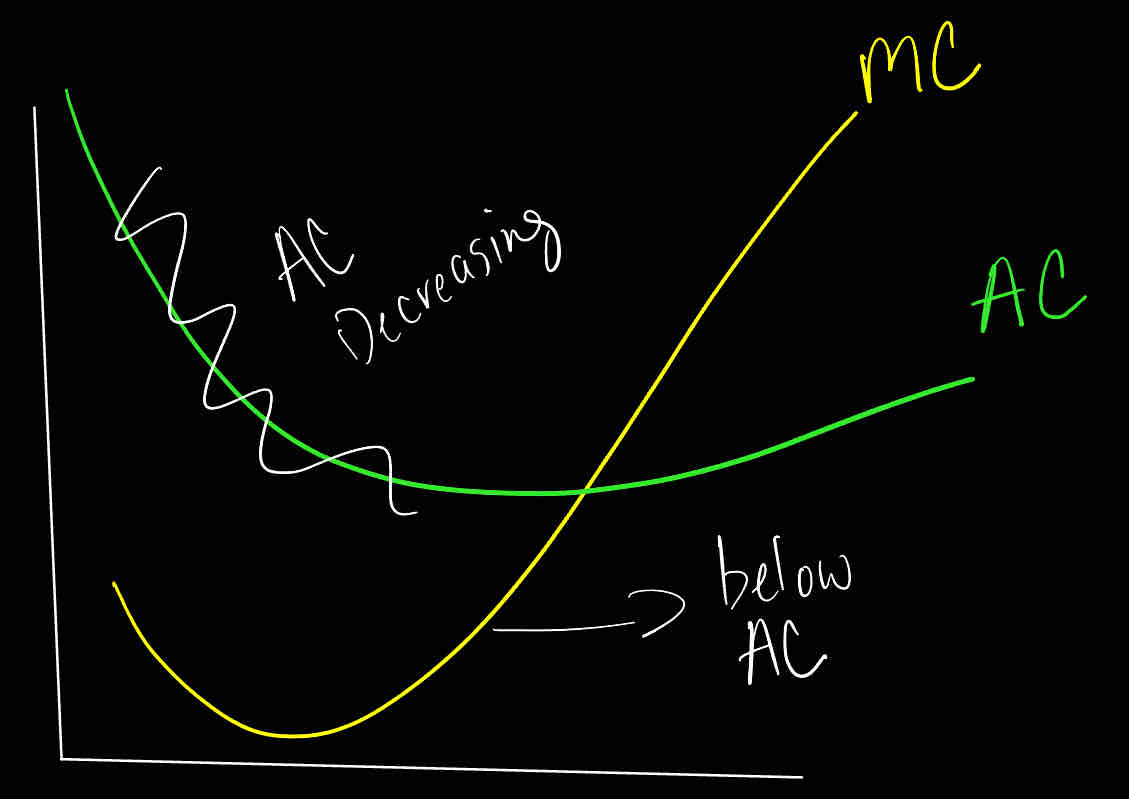
Marginal Cost below Average Cost implies decreasing Average Cost
True
False
True
The supply curve for the perfectly competitive firm is the segment of its Marginal Curve that is above the shut down point
True
False
True
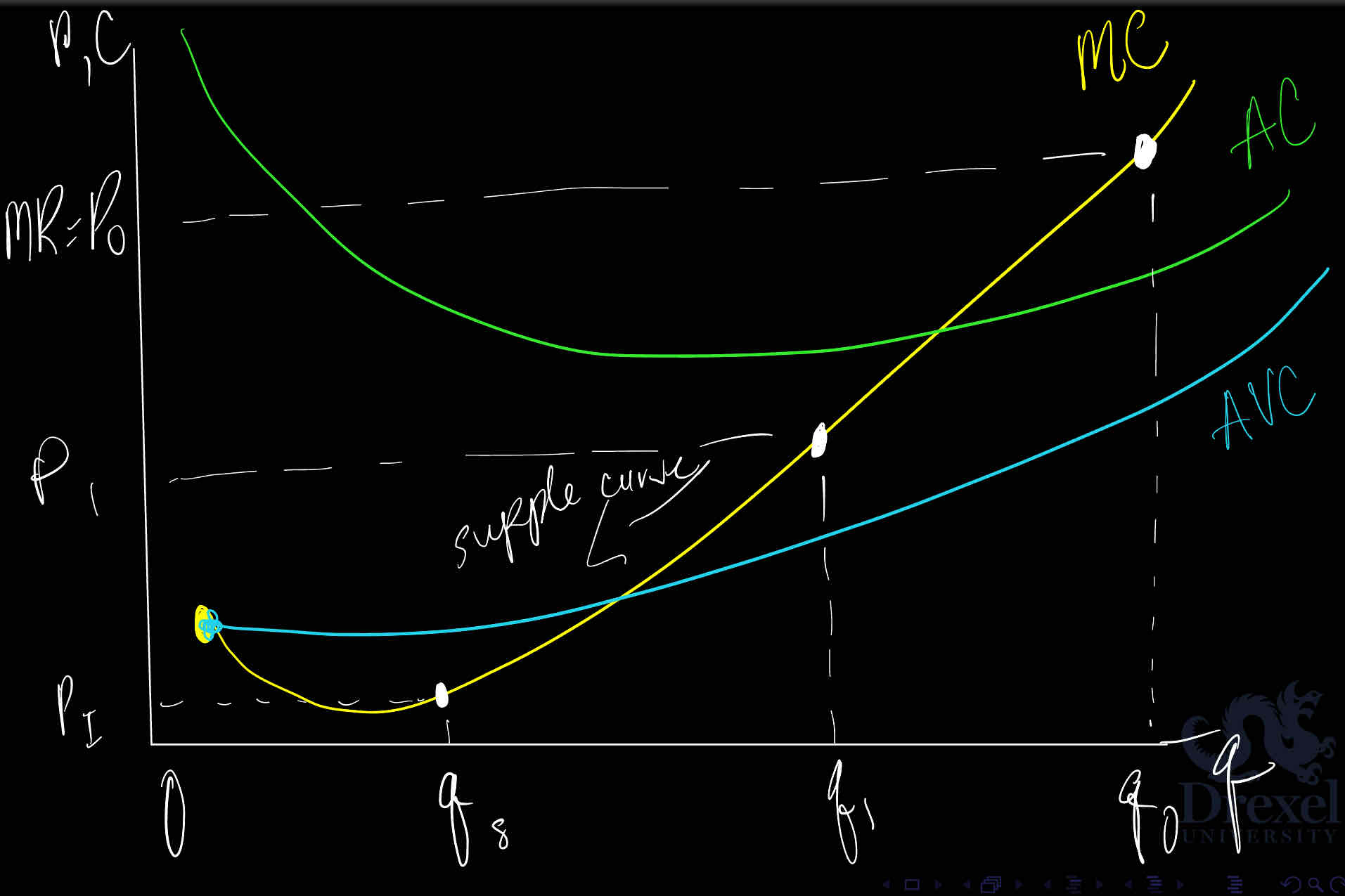
Perfect competitive firms will make zero profits in the long run because of free/easy entry and exit in the perfectly competitive industry
True
False
True
If perfectly competitive firms make profits in the short run, then new firms will enter this industry, and there will be zero economic profits in the long run
True
False
True
If perfectly competitive firms make profits in the short run, then new firms will enter this industry, and there will be positive economic profits in the long run
True
False
False
The marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is always equal to the market price
True
False
True
MR = P = MC
In order to maximize profits, a perfectly competitive form should produce where its marginal cost is equal to its marginal revenue
True
False
True
Which of the following is NOT a distinct feature of monopolistic competition:
Downward-slopping demand ⭐️
Differentiated products
No substitutes
Easy entry & exit
Many firms
No substitutes
Zero economic profit for a firm in the long-run indicates that firm could be:
Monopoly
Perfectly competitive
Small
Large
All of the above
All of the above
You know that for a monopolist MR=$7 and MC=$14 when the output produced by the firm is 12. Which of the following is true if the firm is a profit-maximizer?
The firm is making the right production decision
The firm should produce less than 12
The firm should produce more than 12
There is no sufficient information to decide whether to produce more or less
The firm should leave the industry since MR<MC
The firm should produce less than 12
If prices fall in a perfectly competitive industry, then the firms in that industry will in the short run:
Produce more and increase in number
Reduce production or shut down
Keep output at the same level but make losses
Produce more and decrease in number
Both A and B
Reduce production or shut down
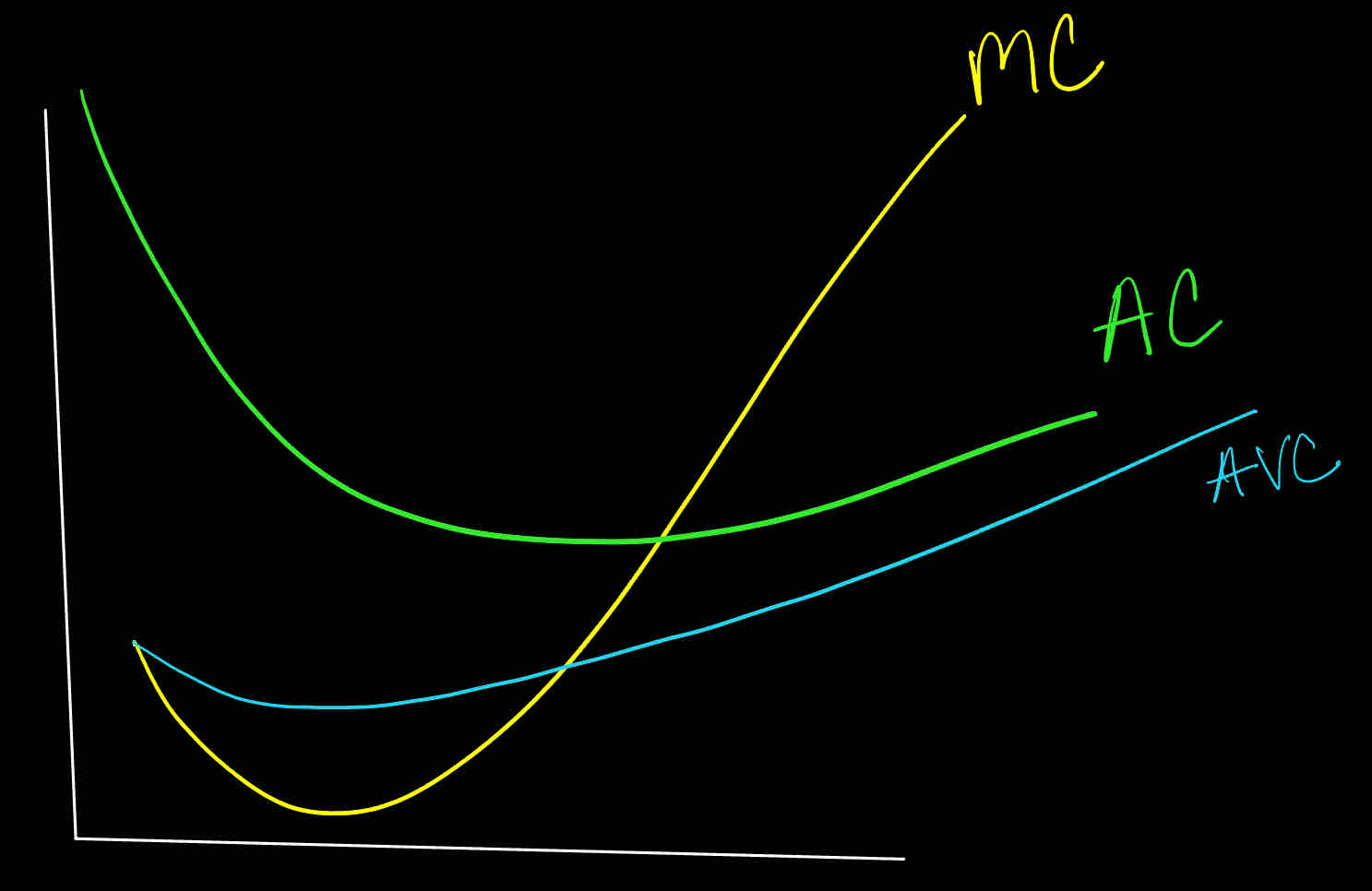
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
AC bellow MC implies rising AC
My below AC implies falling AC
MC rising implies AC rising
AC falling implies MC below AC
AFC is always falling with output
MC rising implies AC rising
True or False
A monopolist will produce when the price of her product is equal to her marginal cost
P = MR = MC
False
True or False
A perfectly competitive will produce when the price of her product is equal to her marginal cost
True
True or False
Marginal Cost decrease at the early stages of production because of Specialization
True
True or False
Free entry into a monopolistic ally competitive industry shifts each firm’s downward sloping demand curve far enough to eliminate all profits in the long run
True
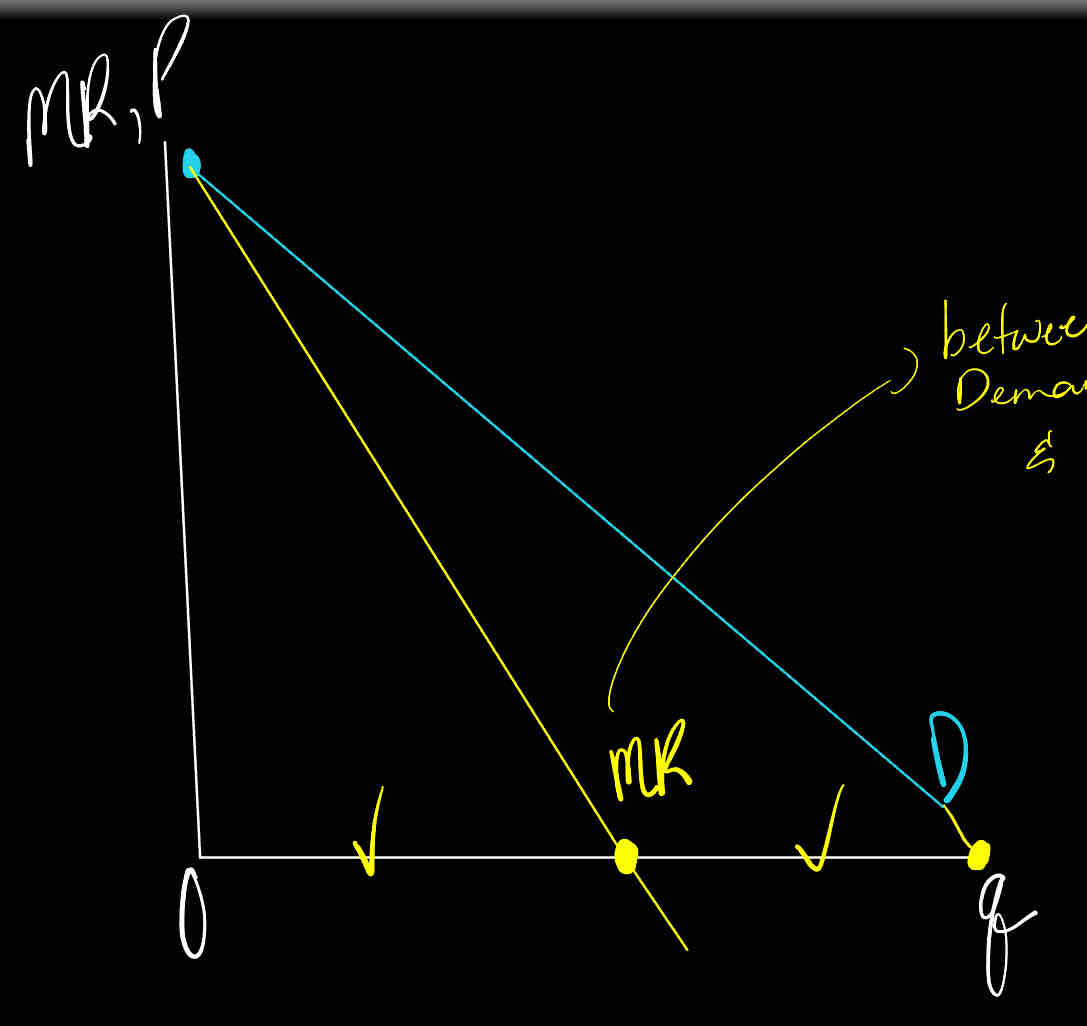
True or False
For the first unit sold, and only for the first unit sold, the marginal revenue for an imperfectly competitive firm is equal to its price
True
True or False
The biggest disadvantage of corporation is that they do not alway pay profits to their shareholders
False
True or False
The biggest disadvantage of corporations is that they have 3 taxations
True
True or False
If marginal cost is increasing, then average cost must be increasing too
False
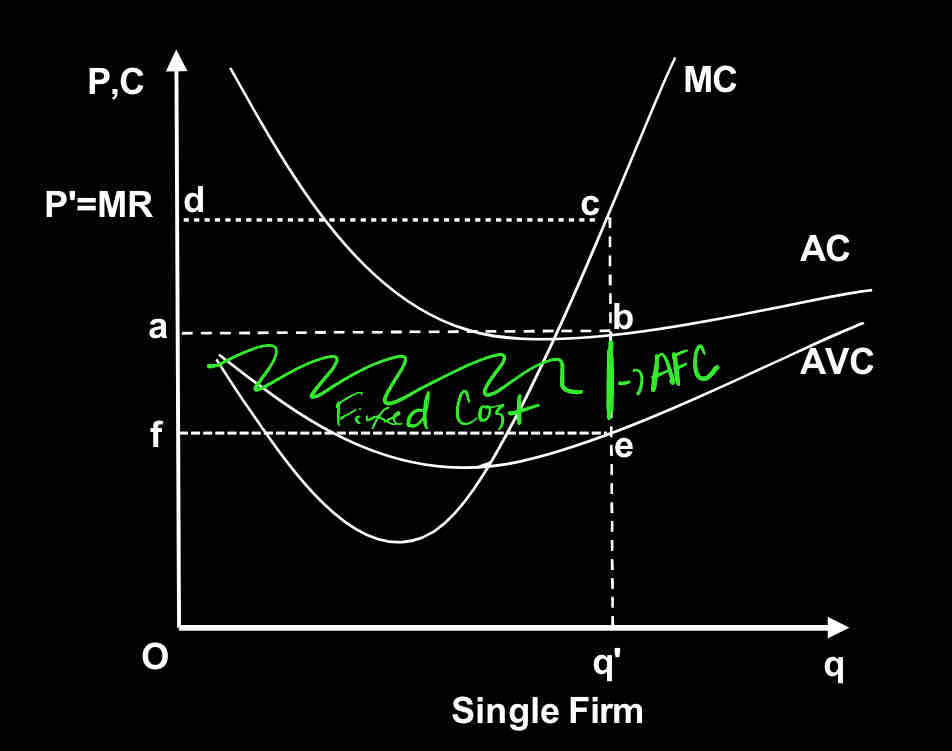
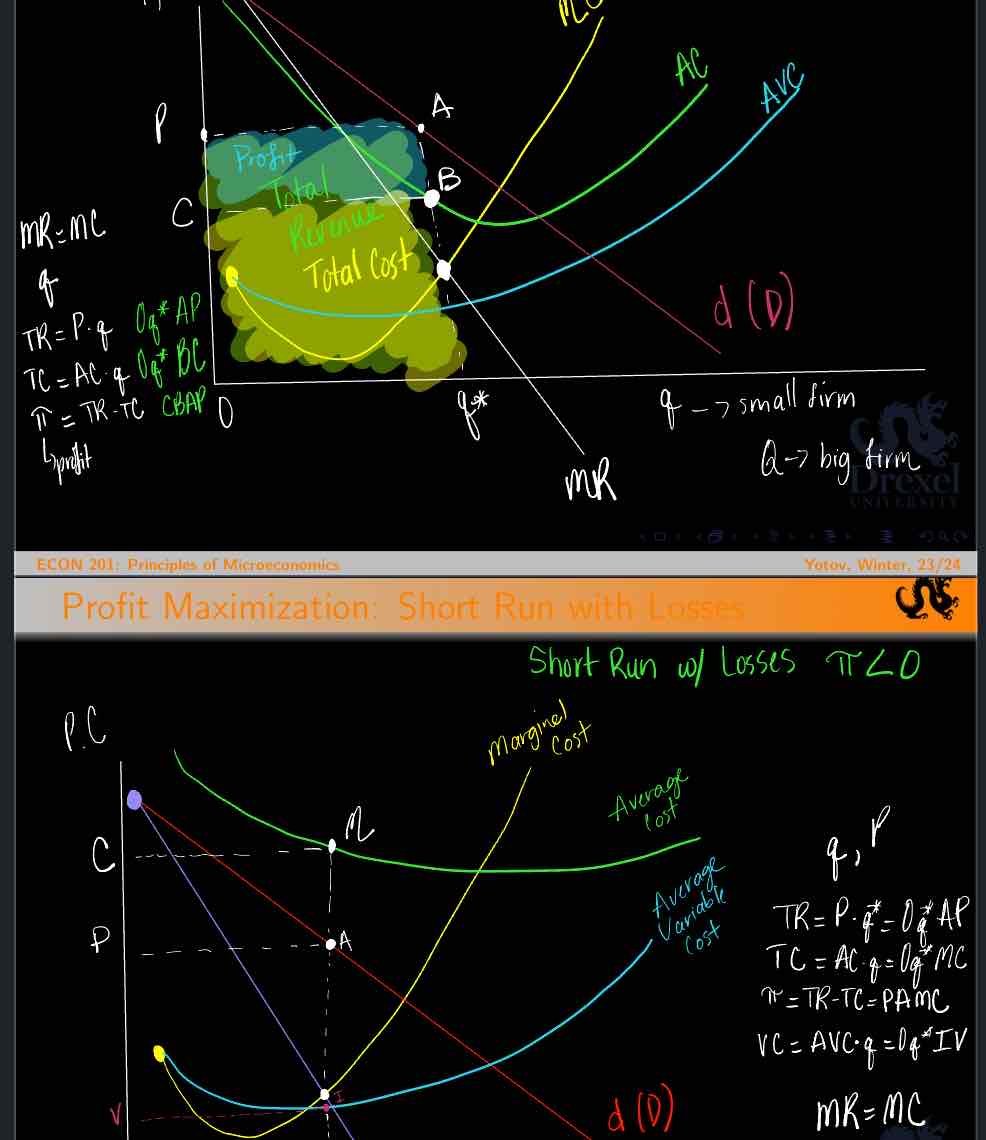
Use the graph:
The figure represents profit-maximization in:
Perfect competition
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Perfect competition
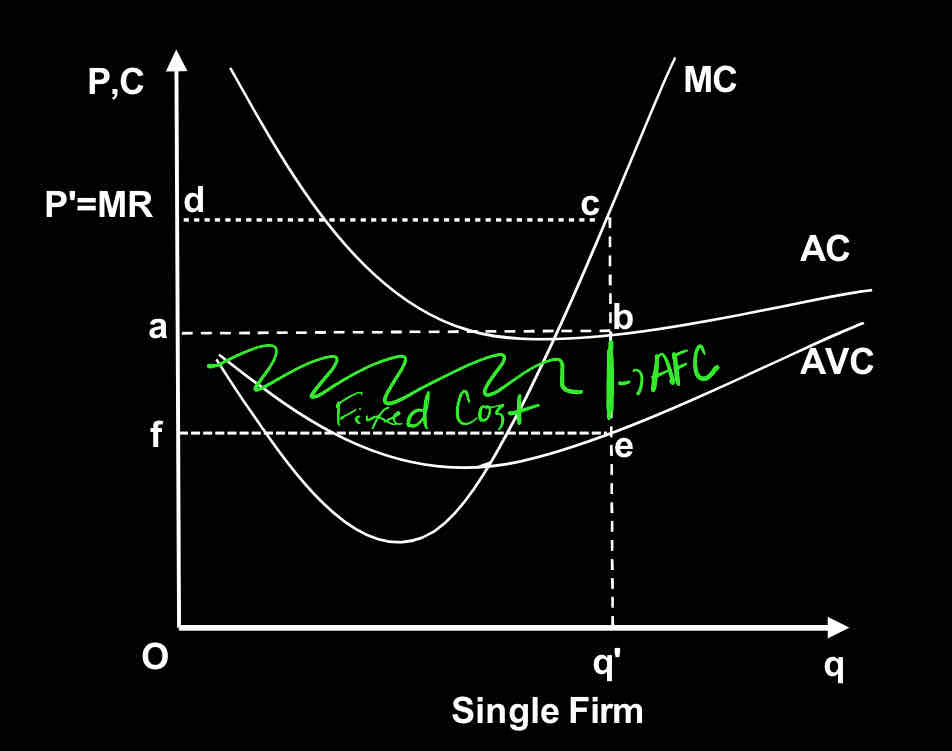
Use the graph:
Total profit / loss (choose one) for the firm is represented by the area:
feba
Oa
Oq’ba
eb
abcd
abcd
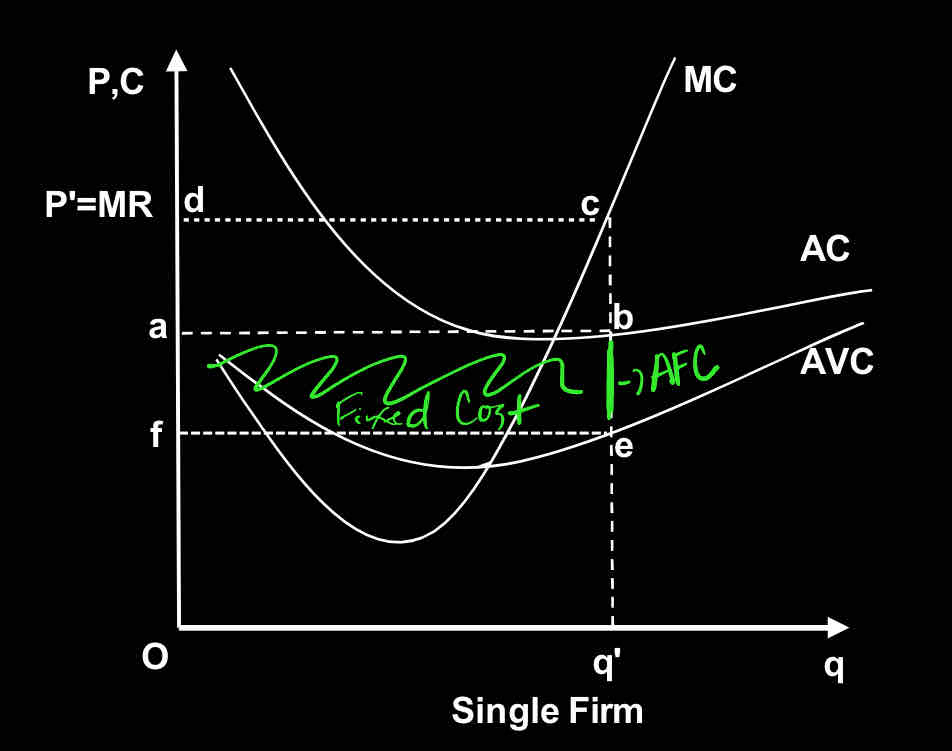
Use the graph:
Segment ‘be’ represent
Average cost
Average fixed costs
Average variable costs
Fixed cost
Variable cost
Average fixed costs
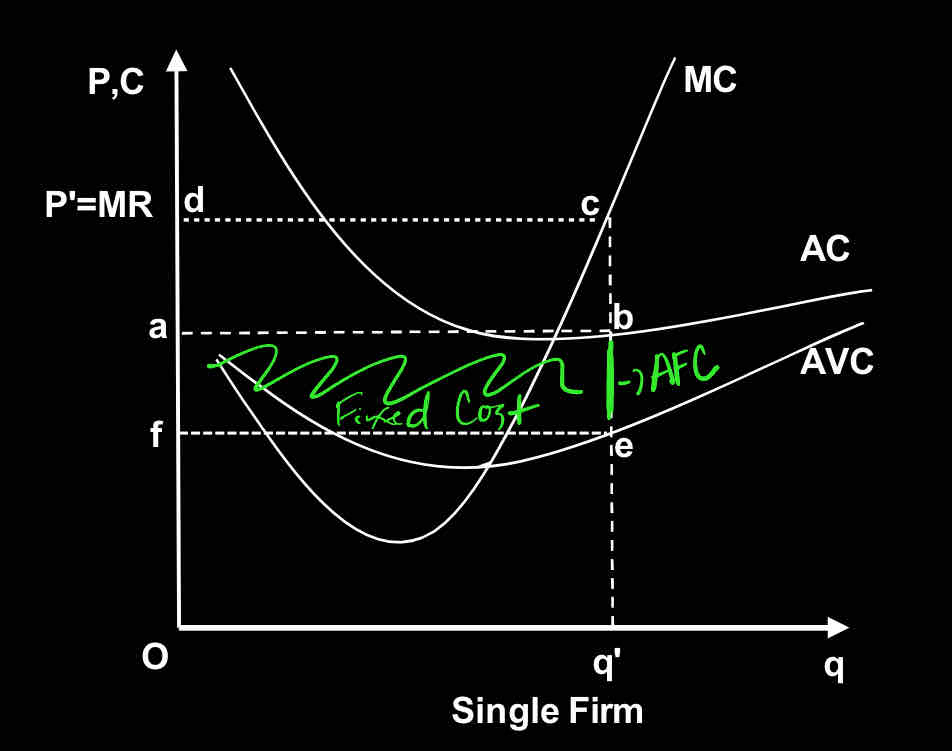
Use the graph:
Area ‘feba’ represents:
Average cost
Average fixed costs
Average variable costs
Fixed cost
Variable cost
Fixed cost
Individual proprietorships
small
Many 80-85%
Unlimited liability
Partnerships
small
Not popular = not too many 5-10%
Unlimited liability
Corporations
forms of business organizations chartered as a ‘legal person’ by 1 of the 50 states or abroad and owned by shareholders who have contributed money, time, ideas, or other resources in exchange for stocks
Large
Small number
Limited liability
Advantages
Size
Scale
Innovation
Disadvantages
Triple taxation
Corporate
State
Dividend
Π [pie] represent
Profit
Fixed Costs — FC
Sunk or overhead costs
Costs that the firm has to pay even is it does not produce anything
Do not depend on the level of output
Variable Costs — VC
costs that are vary with and are directly related to output
Such as : materials and enegry
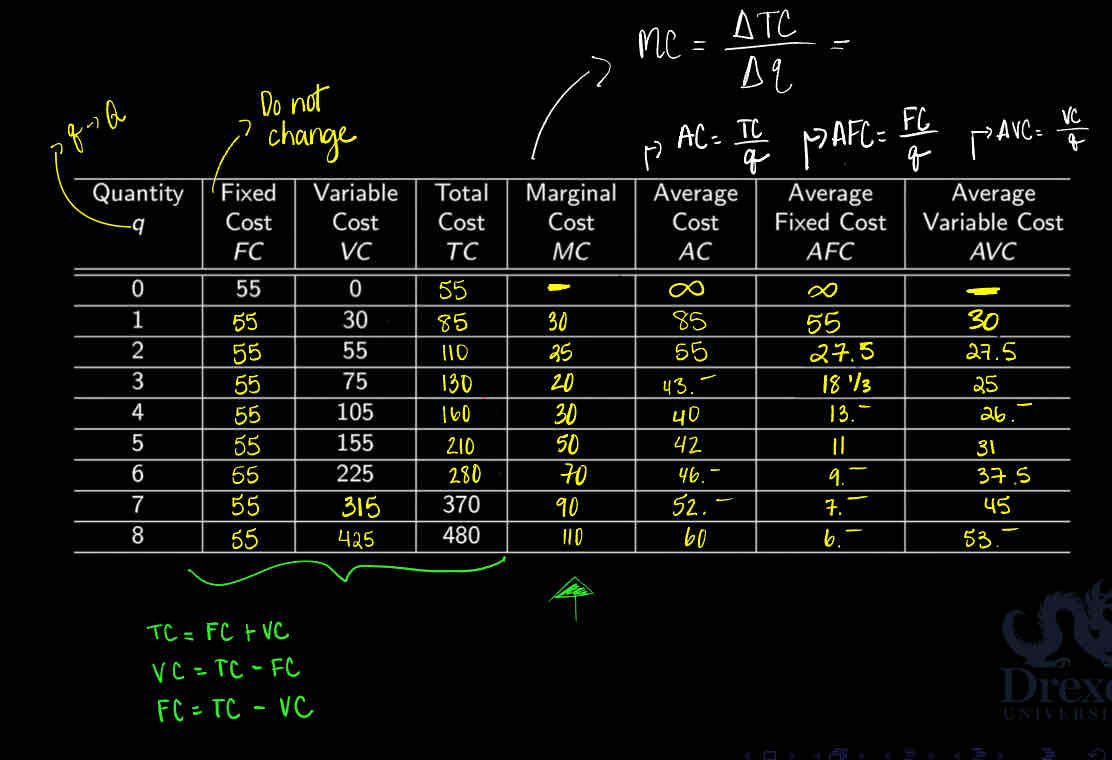
Use the table:
Does fixed cost stay the same?
Yes
Total Cost = _______ + _______
Fixed costs + variable costs
Variable cost = _________ - ________
Total cost - fixed cost
Fixed cost = _______ - _______
Total cost - variable cost
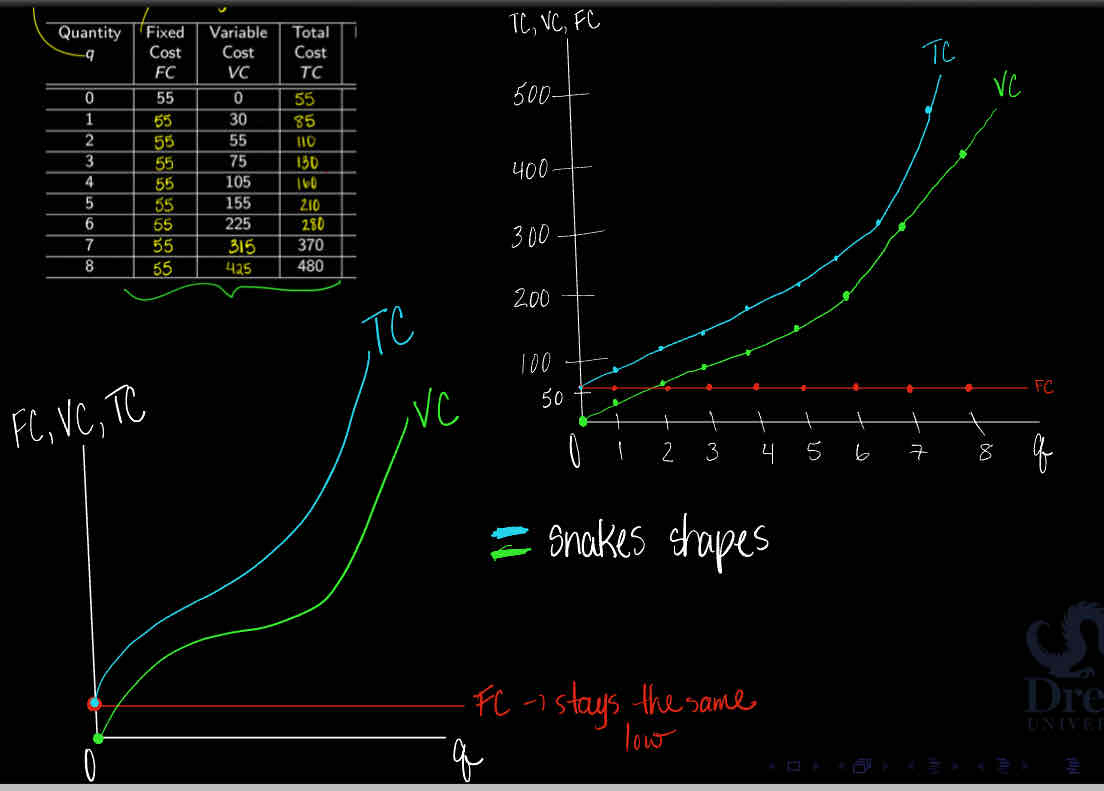
What is the relationship between FC, VC, TC?
Look at the graph
TC and VC are like snake shapes ; will ø intersect due to fixe cost
Fix cost stays the same ; low
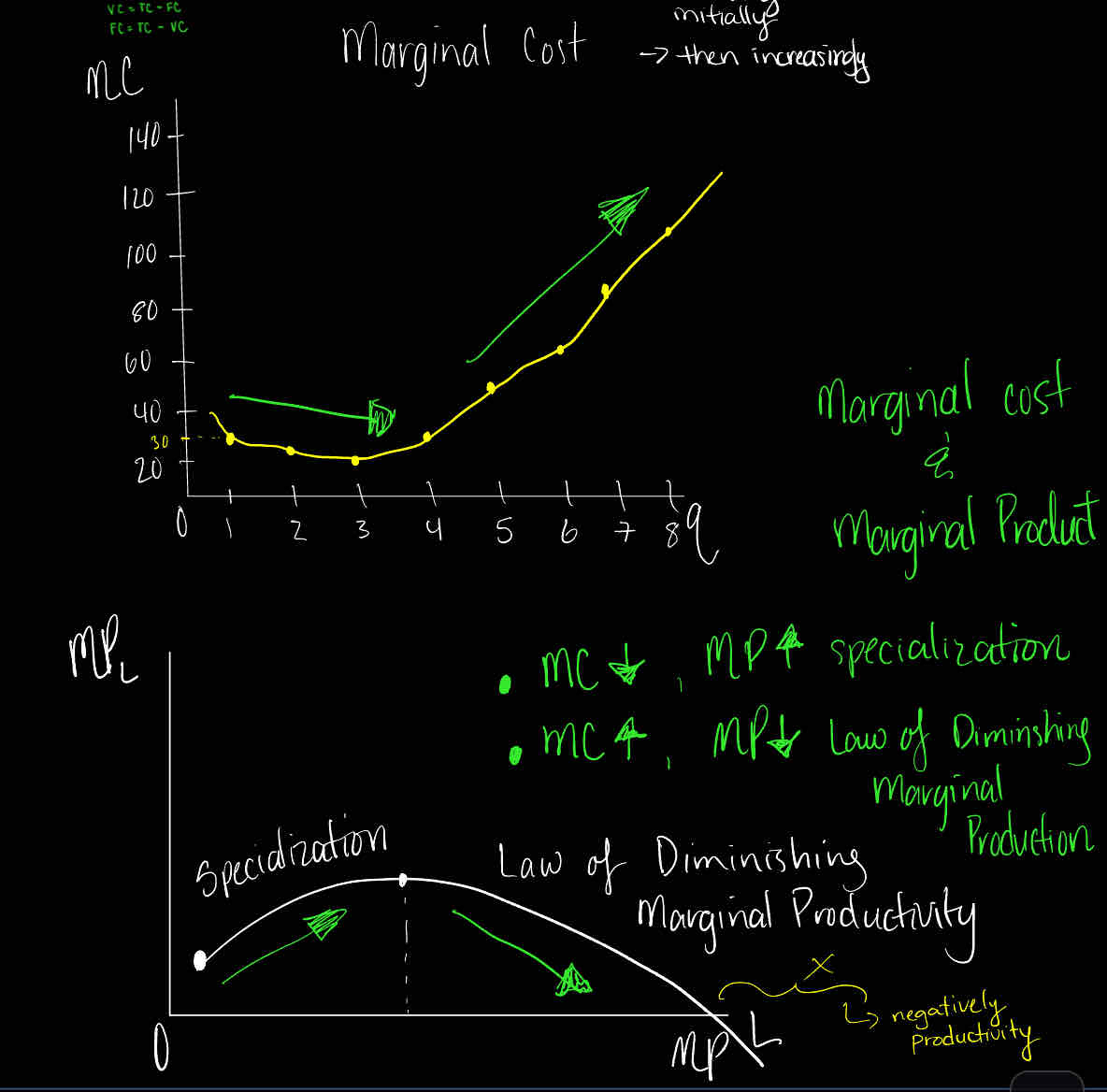
What is the relationship between Marginal Cost and Marginal Product?
Look at the graph:
MC down , MP up = specialization
MC up , MP down = Law of Diminishing Marginal Production
Forms of imperfect competition:
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly
Perfect Competition characteristics
Large number of profit-maximizing producers
Homogeneous product
Each firm is a price taker
Free entry and exit = easy
Perfect Competition with Profits
Short run
Look at graph
Perfect Competition Long Run
Look at graph
MC and AC
When new firm enters in an imperfect competition the demand for the existing firm(s) decrease and becomes more elastic
True or False
True
Imperf
For imperfect competition,
with profits = demand curve is above the minimum AC
With losses = demand curve is below the minimum AC
Look at the graph
Oligopoly characteristic
Differentiated and Homogeneous products
Internal growths vs. Mergers
Barriers to entry
Price-makers
Relatively stable price
Perfect Competition Break-Even and Shut dow points
Look at the graph