Interdental Adjunct Aids (CH 27)
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Introduction to oral self care
Toothbrushing alone is ineffective in removing plaque from proximal surfaces and hard to reach places
Plaque re-growth occurs first in the interproximal areas; therefore interdental biofilm control is essential to complete patient’s oral self-care program
Interproximal plaque removal is beneficial for the prevention of gingival and periodontal diseases
Individual assessment is important to determine an appropriate device and/or techniques for supplemental oral self-care
Interdental cleaning devices should be
user friendly
effective with plaque removal
no negative effects on soft and hard tissue
When preventive treatment plan is made for a patient, assessment is made of
oral condition
problem areas
overall prognosis
Addition of floss or interdental brushed used with toothbrushing may reduce gingivitis and dental biofilm (true/false)
true
Daily interdental cleaning is needed for dental biofilm removal and to reduce ____ inflammation
gingival
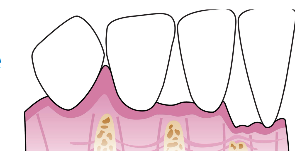
Interdental gingival fills the
interproximal space and under contact of adjacent teeth
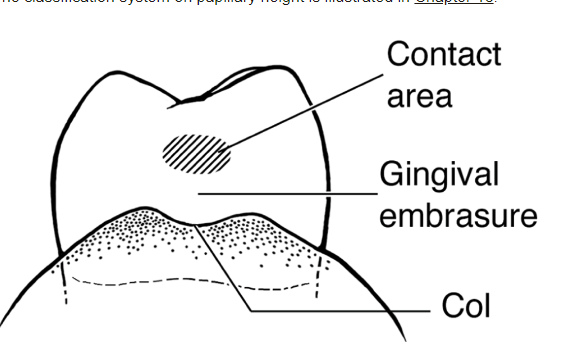
Gingival embrasure Class II
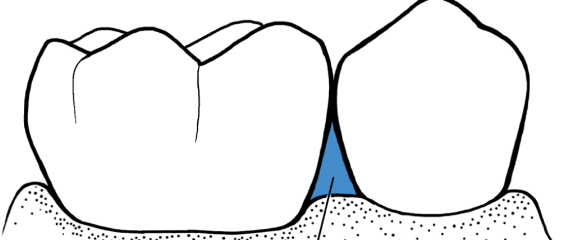
Info about interdental area (col)
Posterior- two papillae connected by a col, a depressed concave area that follows the shape of the apical border of the contact area
Anterior-single triangular papilla; small col under contact area
Epithelium-not keratinized therefore less resistant to infection, becomes deeper during inflammation from inflammatory cells and edema
Col not accessible for regular brushing, so microbes may be harbored there which can lead to periodontal disease since it affects nearby tissues
Incidence of gingivitis is greatest in interdental tissues
Proximal tooth surfaces
bacterial infection=loss of attachment=reduced papilla heigh=exposed proximal tooth surfaces
Root concavities, grooves, furcation areas provide protection and accumulation; also malocclusion or irregularities in tooth position
Increased root surface and complexity of roots makes bacterial removal harder
Planning interdental care
1) Patient assessment:
- history of personal oral care (what’s used, frequency and time spend, preferences, compliance)
- dental and gingival anatomy (teeth position and variation, embrasure shape, clinical attachment level and PD condition, prostheses, areas where brush can’t reach)
-extend and location of biofilm (scores, disclosing agent, evidence)
-personal factors (disabilities, oral health literacy of biofilm and removal)
2) Evidence-based clinical decision making
-determine PD health status, embrasure size, general health
Type I Embrasure recommendations
dental floss for healthy tissues and high compliance
If there’s low compliance and/or gingival inflammation, other interdental devices should be considered besides floss (true/false)
true
Patients with closed embrasures who lack motivation and/or dexterity can use
easy flossers/floss holder
rubber interdental cleaners/soft picks
oral irrigation
small interdental brushes
Type II and III Embrasure recommendations
interdental brushes (most effective for open embrasure spaces and PD maintenance patients)
Which interproximal cleaning device is the most effective for open embrasure spaces and PD maintenance patients?
interdental brushes
Dental hygiene care plan
Objectives: use motivational interviewing to select right aids, determine if there’s barriers and low compliance, educate about aids, patient must accept responsibility for daily personal care and work as a partner with the oral health team
Initial care plan:
-assess oral health behavior for individualized care plan
-first pick simplest procedures based on patient’s current knowledge, preferences, oral habits
-twice daily is the minimum
-keep daily oral self care at a realistic level with respect to the time patient is able or willing to spend
Selection of interdental aids considerations
user friendly, effective in biofilm removal, cause no damage to soft + hard tissues
oral self care abilities, embrasure size, disease status, risk for future recurrence
while flossing is usually recommended for healthy/normal contour gingiva, it’s technique need instruction and reinforcement due to it being a hard skill for most patients; other aids may be more effective with higher patient compliance
more oral care for patients working to control of arrest disease
interdental brushes when gingival inflammation is present
special consideration for those with gingival recession or AL, furcation, concave
ongoing risk assessment crucial for stable periodontitis patients due to higher risk of recurrence
Recommending effective supplemental aids, consider the following
evidence based practices
patient’s need
patient’s desire
professional judgement and clinical expertise
continual involvement of patient
Frequency of oral self care
individual factors
removal of interproximal plaque at least once everyday is advisable for the prevention of dental caries
removal of interproximal plaque at least ___ everyday is advisable for the prevention of dental caries
once
Self care adjunctive aids examples

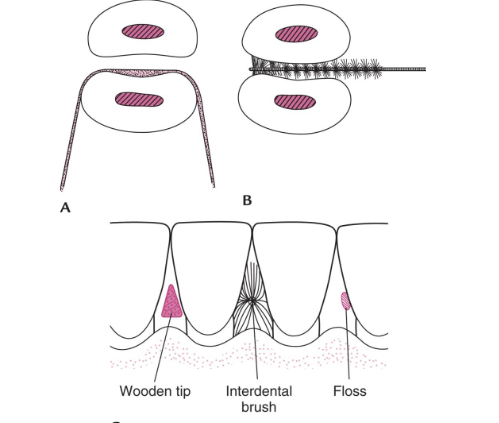
Embrasure spaces
Dental floss objective
• Remove plaque and debris
• Prevent formation of calculus
• Aid in identification of interproximal calculus deposits or overhanging restorations
• Arrest or prevent interproximal carious lesions
• Reduce gingival bleeding and inflammation
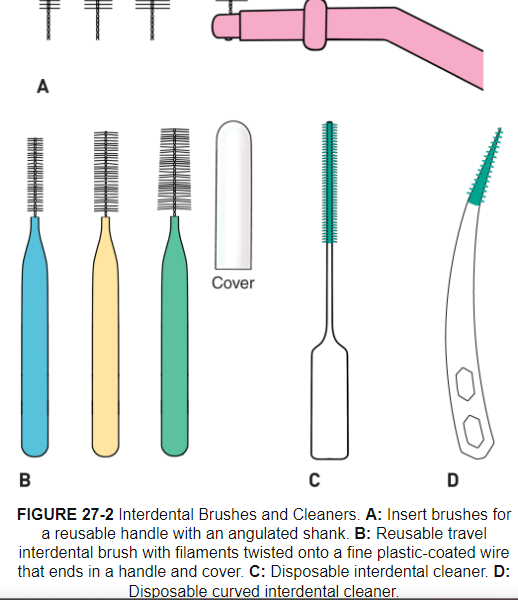
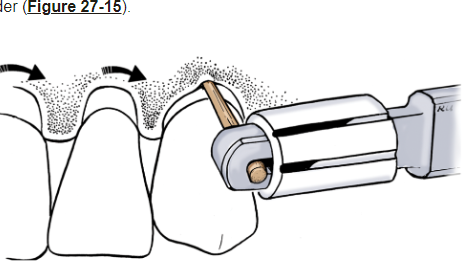
Interdental brushes (Wilkins)
Types: Small insert brushes with reusable handle, travel interdental brush. and rubber interdental cleaners
Rubber interdental cleaners-no wire, effective in biofilm removal and reduce bleeding, popular due to ease of use and may be more comfortable during insertion, may not removal as much biofilm due to bristles
When to use: 1st choice for interproximal cleaning, easier to use and preferred by patients, consider embrasure size to pick the right size, more effective in biofilm removal than floss do to it filling the embrasure
Good for: tooth surface close to open embrasures, orthodontics, fixed prostheses, dental implants, splints, space maintainers, concave proximal surfaces when dental floss and other aids can’t reach, exposed IV furcation areas, patients with open embrasures and moderate to severe AL, patients with periodontitis with larger interdental spaces with recession or root exposure, for application of chemotherapeutic agents (fluoride, gel, mouth rinse, antimicrobial, desensitizing)
Procedure: apply pressure against proximal root surface to removal biofilm (mesial and distal)
Care: clean brush during use via running water, clean thoroughly after use and dry in open air, discard before filaments get worn
Dental floss and tape
consider that high quality flossing is hard to achieve and unsupervised flossing doesn’t result in substantial reduction in inflammation compared to other aids
small reduction in bleeding in low compliance patients and poor technique
determine if high quality flossing is possible
contact no possible when placed over concave surface; consider other aids

Types of dental floss
Materials: silk (past), nylon, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Waxed floss: smooth=helps sliding through contact area, minimize trauma, strength and durability to minimize breakage
Unwaxed floss: thinner=helpful for tight contact areas, careful to avoid injury, become frayed (irregular tooth surfaces, rough restoration, calculus) and decrease patient motivation
PTFE: resist breakage or shredding from calculus, restoration, irregular tooth surface; reduces force needed to pass floss through contact=improve compliance and reduce injury + trauma
Enhancements: color and flavor, therapeutic, expand when in contact with moisture
Tufted dental floss-thicker (super floss); abutments, under pontic of a fixed partial denture, implant, orthodontic
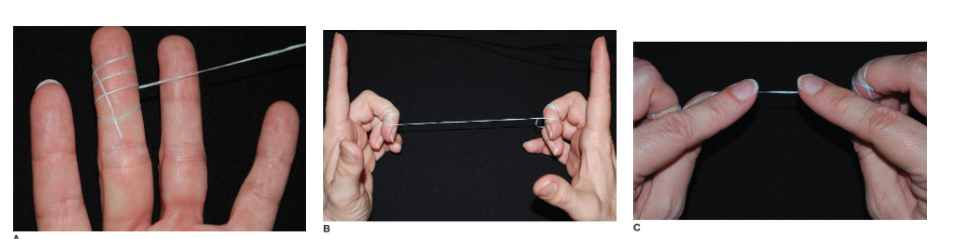
Two methods of flossing are
Spool method
Circle loop method
Note) may be helpful to floss before brushing to help dislodge debris and biofilm
Spool method
floss wrapped around middle fingers
floss pulled tight, leaving thumbs and index fingers free
index fingers placed ¾ to 1 apart
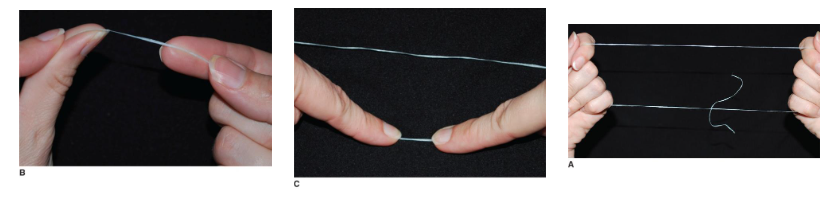
Circle loop Method
all fingers except the thumbs are placed within the loop for easy use
for the mandibular teeth, the floss is guided with the two index fingers
for the maxillary teeth the floss is guided with the two thumbs or one thumb and one index finger
advantage: improved compliance and easier to handle, less waste, increased floss hygiene and biofilm removal
Negative effects of improper dental flossing
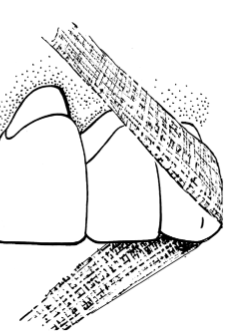
gingival cleft (floss cuts) created from not using the C-shape method of flossing; straight line cuts beginning at the gingival margin and may result if repeatedly injured
Causes: piece of floss that’s too long between fingers when held for insertion, or snapping floss forcefully, not curving the floss enough and cutting into gingival margin
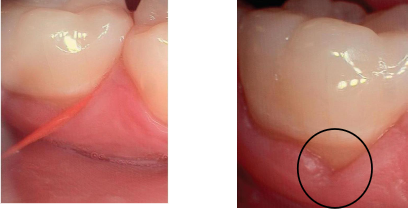
Effects of dental flossing: questions to consider
When should the spool method be recommended? The circle/loop method? Circle loop for increased compliance, easier handling, less waste, increase floss hygiene and biofilm removal
Once the floss is inserted between the teeth, what kind of motion should be performed? Gently back and forth or sawing motion; curve floss for mesial and distal aspect. Slide floss up and down.
What kind of damage can be done to the tissues if practiced incorrectly? Cleft
How far can dental floss reach subgingivally?
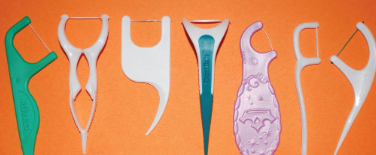
Dental floss holder
May be more effective in establishing a regular flossing habit in non-flossers than finger-manipulated flossing; When can it be recommended?
A variety of floss-holder designs are available; some are pre-threaded, one-time use and others aren’t
Helpful for people with a disability or for parent/caregiver
Should not displace the tissue during proper use
Two handle flossing system (Gumchucks) increases control and dexterity (helpful for young children to make the C shape)
Dental floss holder (reused)
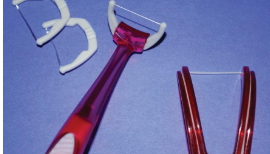
Dental floss holder (one time)
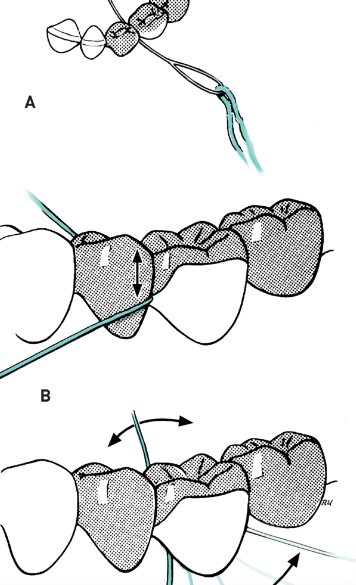
Dental floss threader
• A plastic loop into which a length of floss is inserted
• Used to carry floss interproximally:
• Through embrasure areas under contact points too tight for floss insertion
• Under pontics and fixed prostheses
• Around orthodontic appliances or under fixed partial dentures
• Between splinted teeth
Mesial and distal abutments, under pontic of a fixed partial denture, implant, orthodontic arch wire, other fixed prosthesis

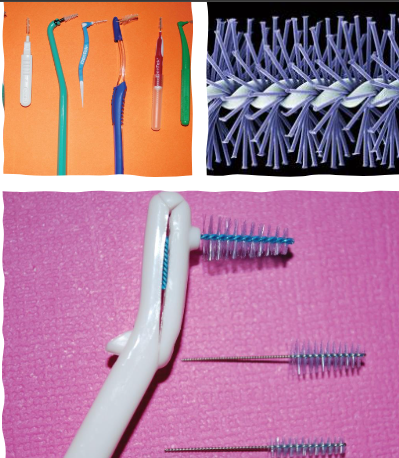
Interdental aids
Automated/Power Flosser:
End-Tuft Brush
Interdental brush (Proxybrush)
Toothpick/toothpick holder
Wooden/plastic triangular stick
rubber tip stimulator
tongue cleaner/scraper
oral irrigators (waterpik and sonicare air-floss)
Automated/power floss
for patients with limited ability to floss and those who don’t clean interproximal regularly
battery operated or air flosser (bursts of air and water droplets)
higher patient acceptance regarding comfort compared to floss

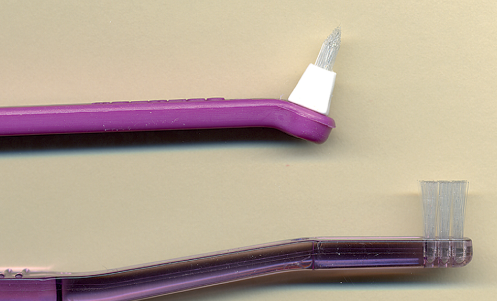
End-tuft brush
Type III embrasure spaces
orthodontic appliances and open interproximal areas
hard to reach areas (lingual surfaces of mandibular anteriors)
flat or tapered
handle straight or contra-angled
use a sulcular brushing stroke

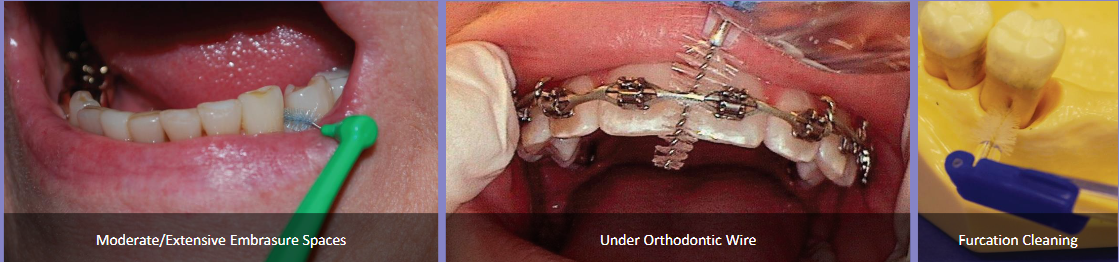
Interdental brush/Proxybrush
Type II & III embrasure spaces
Class IV furcations
Orthodontic appliances
Small diastemas
Fixed prostheses
Dental Implants
Toothpick/toothpick holder
• Round toothpicks
• High risk for gingival trauma
Can be used for periodontitis patients (at and under margin, interdental, furcation and concaves) and orthodontic patients (remove biofilm at gingival margin above bands)
Rubber tip stimulator (interdental tip)
• Primarily for gingival massage/gingival stimulation of blood flow
Can be used to shape interproximal area during healing after surgery
Cleaning debris form indertendal area
Biofilm removal at and below gingival margin
• Contraindicated for healthy gingiva
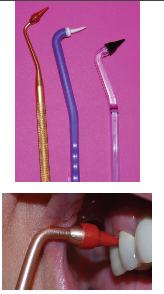
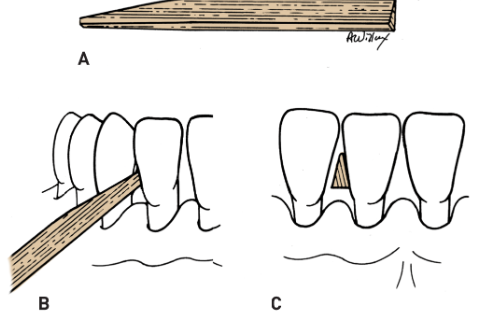
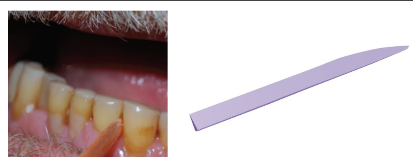
Wooden/plastic triangular stick
• Less potential for trauma
• Embrasure II & III
Proximal tooth surface where surfaces are exposed and interdental gingiva is missing, space must be enough or trauma can happen
Advantage: easy, transported easily, used more frequently than dental floss, reduce bleeding and inflammation but don’t remove biofilm as much as floss
Limitations: only for patients who follow instructions, can’t access root concavities and irregularities in proximal areas to properly removal biofilm, hard in posterior areas and from lingual aspects
Procedure:
fulcrum-hand on cheek or chin, or finger on gingiva
Prep-soften wood via saliva
Patient instructions: insert with tip pointed slightly up (occlusal surfaces) , move via burnishing stroke with moderate pressure and at least 4 strokes, discard as soon as splaying is seen
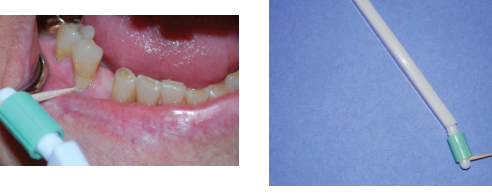
Rubber tip stimulator can be use on healthy gingiva (true/false)
false
Tongue cleaner/scraper
halitosis
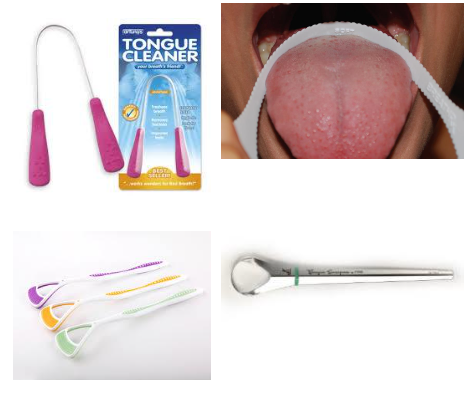
Halitosis causes
• Tongue coating
• Periodontal Disease
• Peri-implant Disease
• Deep carious lesions
• Impacted food/debris
• Decreased salivary flow
• Unclean dentures
• Putrefaction: a combination of protein hydrolysis by the bacteria and catabolism of basic amino acids =malodor producing VSC’s
Oral irrigators (Waterpik)
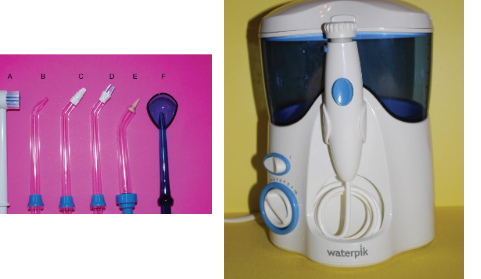
Oral irrigators Wilkins
also called water flosser
lower bleeding and gingivitis indices
recommended over floss for implant and orthodontic treatment
reduce bacteria and inflammatory mediators
water flosser remove supragingival interproximal biofilm and reduce inflammation, but more research
more research on subgingival irrigation in managing PD disease (not appear to reduce visible biofilm, but may have positive effects on gingival health over brushing alone, may reduce counts of PD pathogens)
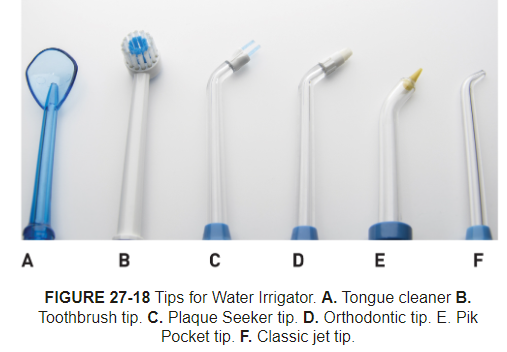
Tips: tongue cleaner, toothbrush tip, filament tip for heard to each areas and around dental implants or bridges, orthodontic tip for biofilm removal, subgingival tip, standard jet tip delivers steady flow of irrigant
Procedure: fill reservoir with water, choose tip, direct toward interdental area until almost touching tooth, hold tip at 90 degrees to long axis of tooth for supragingival irrigation, lean over sink to minimize splatter, turn unit on using low power and increase water pressure if desired, systemic approach, empty reservoir to prevent bacterial growth
Results: inconsistent evidence on improving parameters of PD health, but improve gingival health especially in orthodontics
Oral irrigators (Sonicare air-floss)
Non-traditional interdental aids
Used when previously mentioned products are not readily available:
• Knitting Yarn
• Pipe Cleaner
• Gauze Strip-proximal surfaces of widely spaced teeth, teeth next to edentulous areas, abutment teeth of a fixed partial denture

Review
How many supplemental aids should we recommend in addition to brushing?
What oral hygiene aids would you recommend for:
•Under a 3-unit bridge?
•Patient with strong gag reflex?
•Under an orthodontic wire?
•Between teeth with moderate embrasures?
•Hard to reach areas?
•Someone with lack of motivation to floss?
Documentation
all interdental aid recommendations and demonstrations with the patient
