Endomembrane System and Protein Trafficking in Cells
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Endomembrane system
Dynamic system of cytoplasmic membranes in cells.
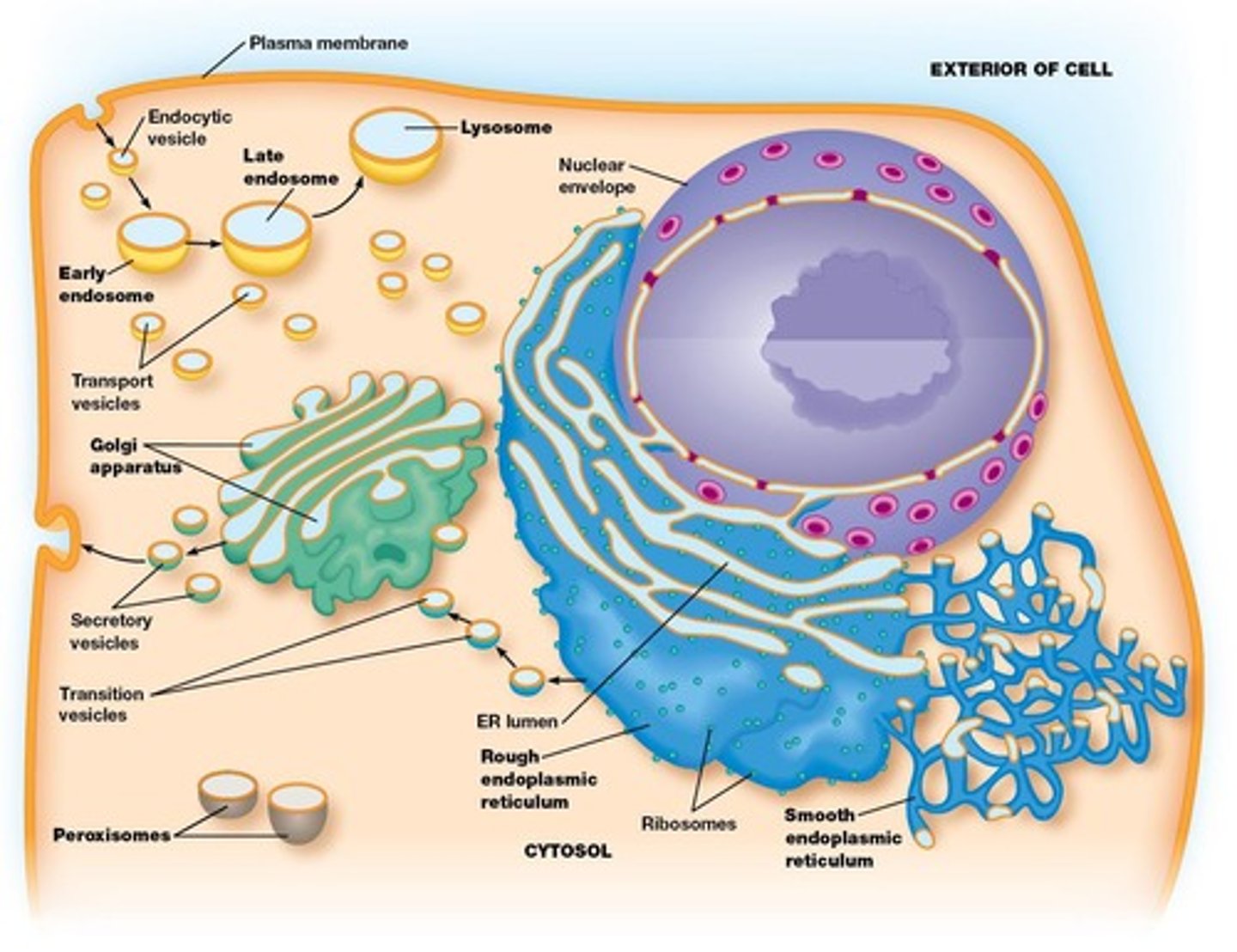
Protein trafficking
Movement of proteins and lipids between organelles.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
50-90% of cell membrane; includes rough and smooth ER.
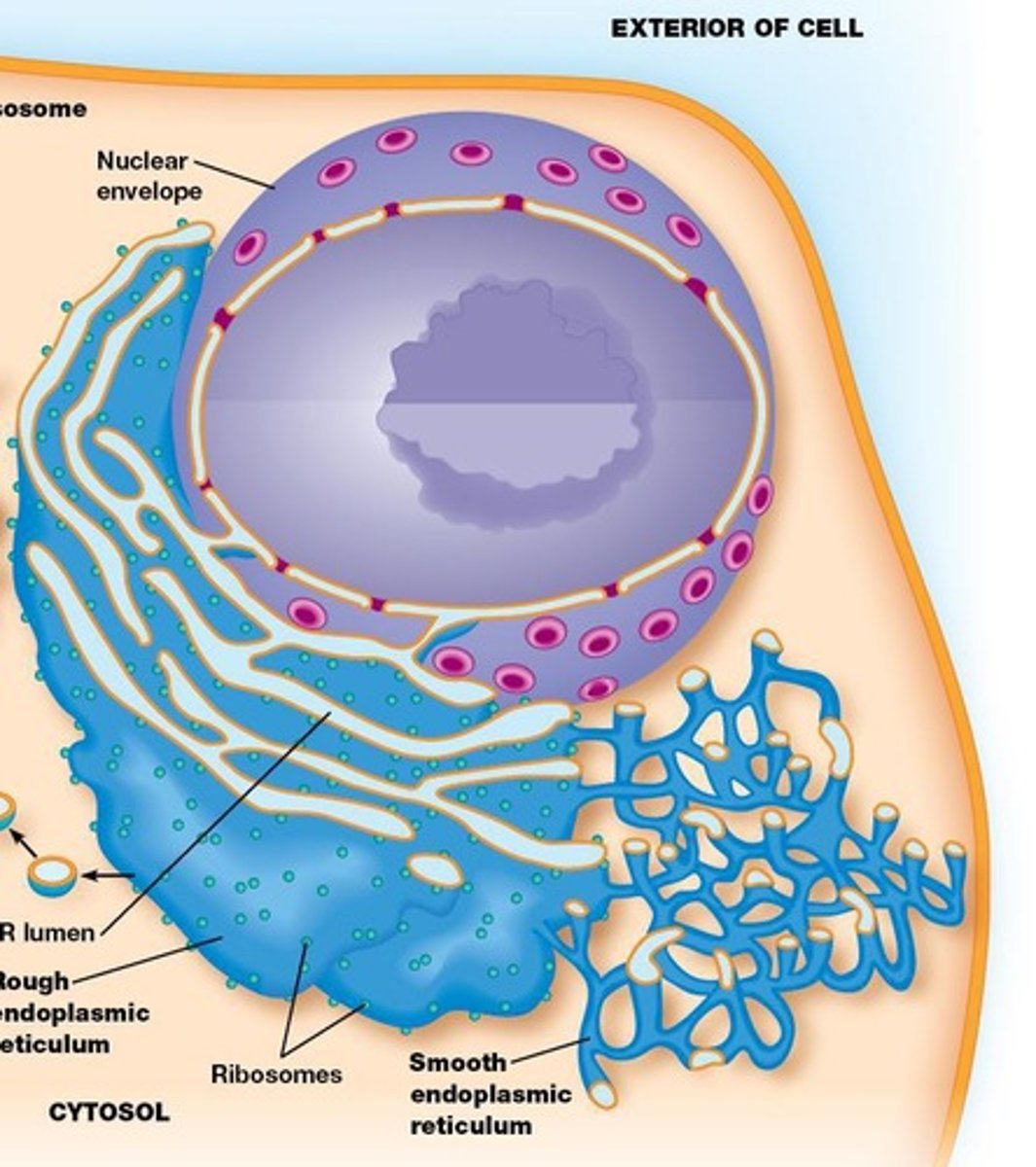
Rough ER
Synthesizes membrane, secretory proteins, and glycoproteins.
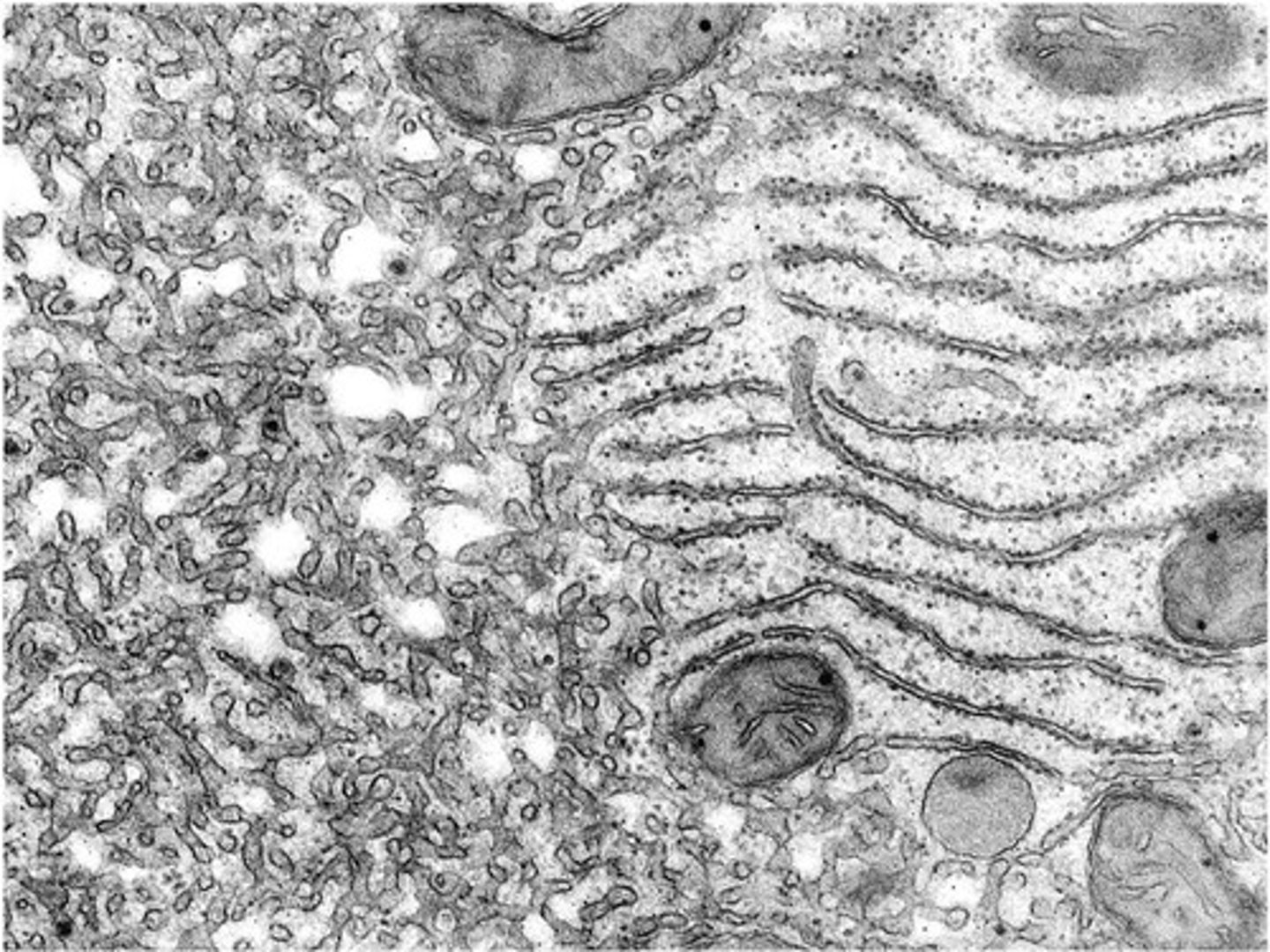
Smooth ER
Synthesizes steroids, membrane lipids, and detoxifies drugs.
Glycosylation
Modification of proteins by adding sugar chains.
BiP (binding protein)
Chaperone preventing aggregation of nonpolar regions.
Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI)
Chaperone reforming disulfide bonds for correct folding.
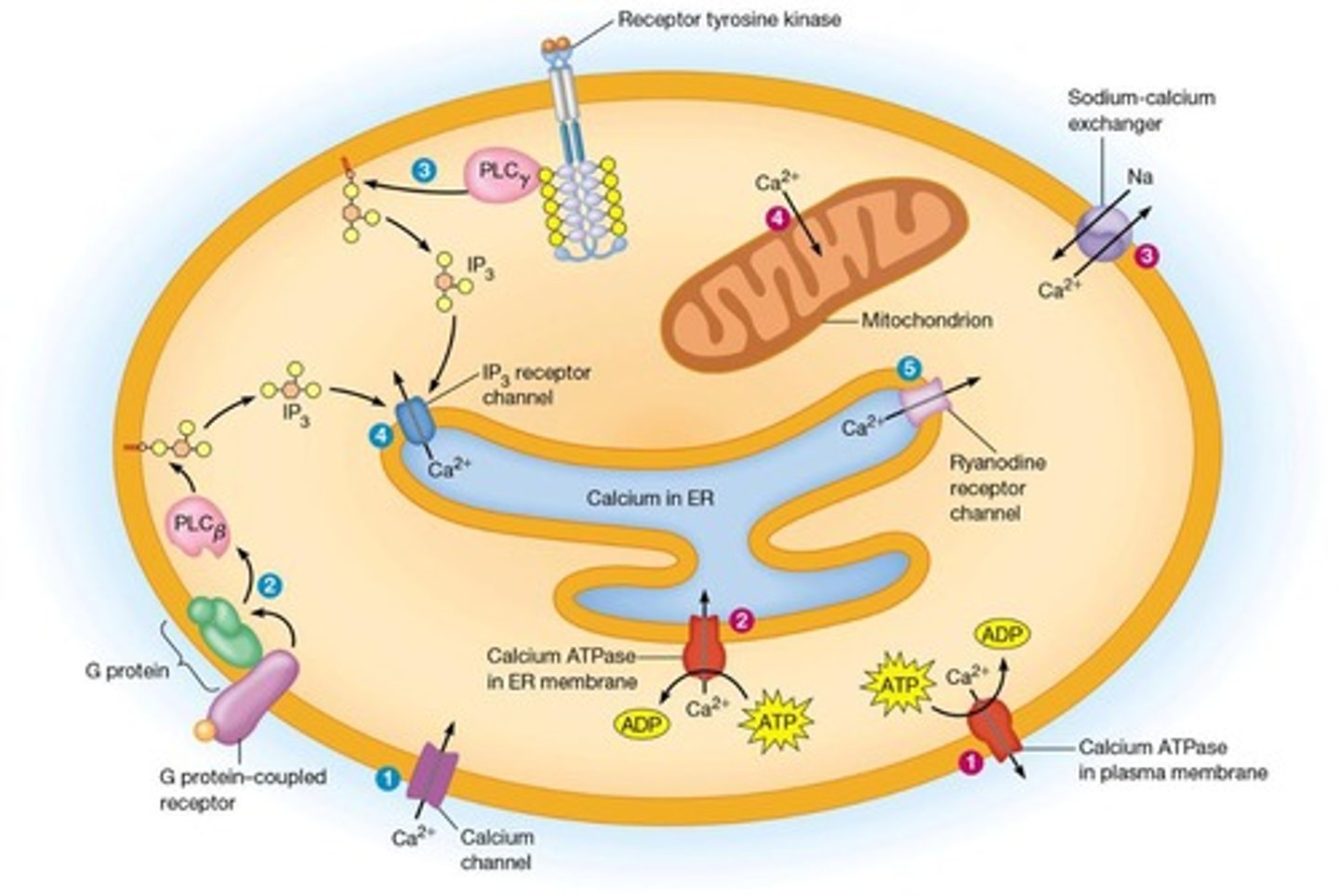
Calcium ATPase
Moves calcium against its gradient in smooth ER.
Cis-Golgi network (CGN)
Interface between ER and Golgi apparatus.
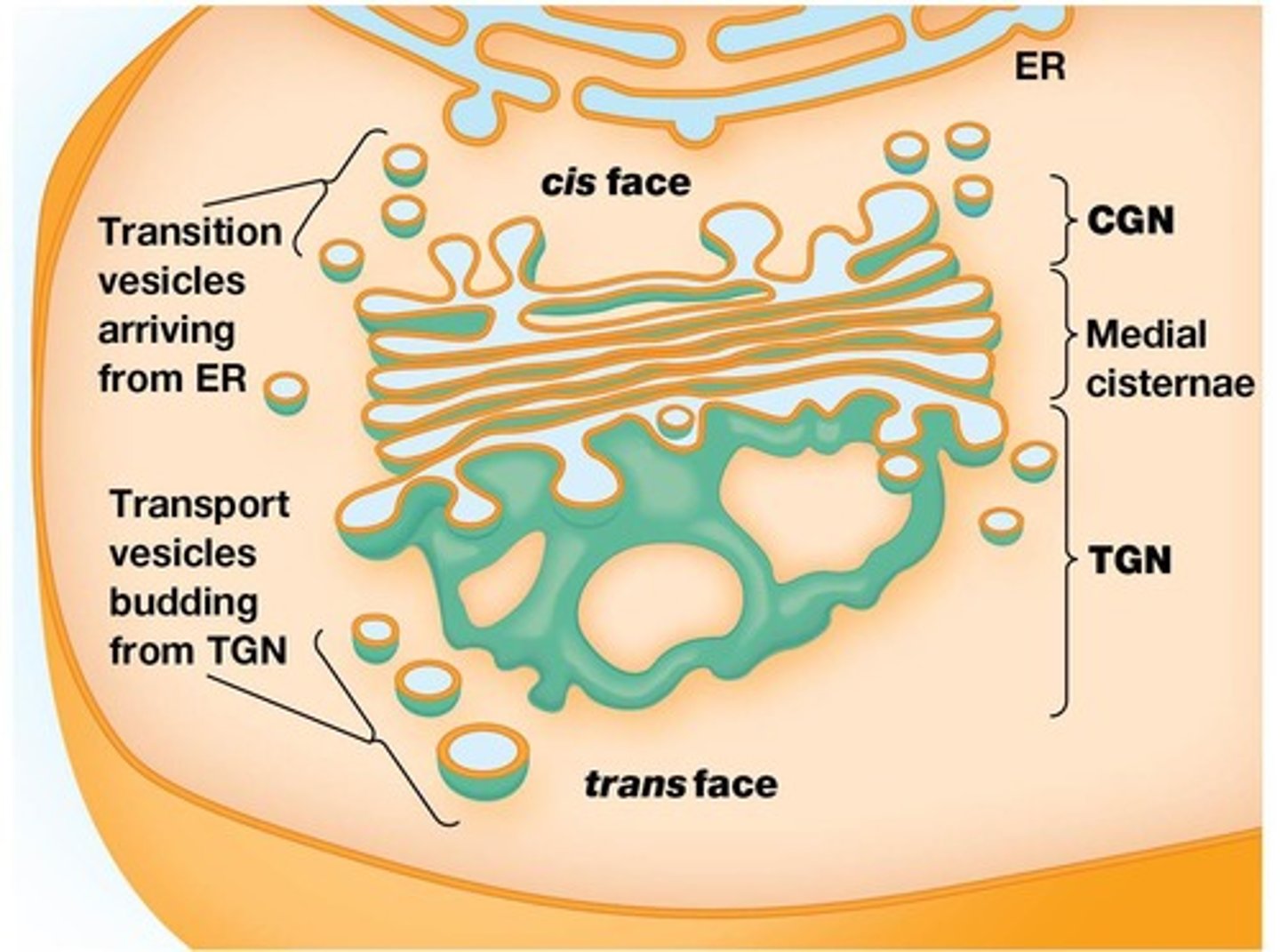
Trans-Golgi network (TGN)
Interface between Golgi stack and plasma membrane.
Anterograde movement
Transport toward the plasma membrane.
Retrograde movement
Transport back toward the ER.
Signal sequence
Short peptide indicating protein's cellular destination.
Posttranslational import
Protein enters organelles after translation completion.
Cotranslational import
Protein enters organelles during translation process.
Nuclear localization signal (NLS)
Sequence directing proteins to the nucleus.
Mitochondrial transit sequence
Sequence guiding proteins into mitochondria.
Integral membrane proteins
Proteins embedded in cellular membranes.
Type 1 transmembrane protein
C-terminus located in cytosol.
Type 2 transmembrane protein
C-terminus located in ER lumen.
Retrieval tags
Signals for returning proteins to ER or Golgi.
Mannose-6-phosphate
Tag for lysosomal enzyme targeting.
I-cell disease
Genetic disorder causing lysosomal enzyme deficiency.
Chaperone proteins
Assist in proper protein folding.
Secretory proteins
Proteins destined for secretion outside the cell.
Lysosomal enzymes
Hydrolases required for breaking down cellular waste.
Polypeptide folding
Process of protein achieving functional three-dimensional structure.
Calcium storage
Smooth ER stores high concentrations of Ca2+.
Drug tolerance
Increased enzyme production in response to drugs.
Quality control
Mechanism ensuring proper protein folding and function.
Vesicular transport
Movement of materials in membrane-bound vesicles.
Cisternae maturation model
Model explaining Golgi protein maturation during transport.
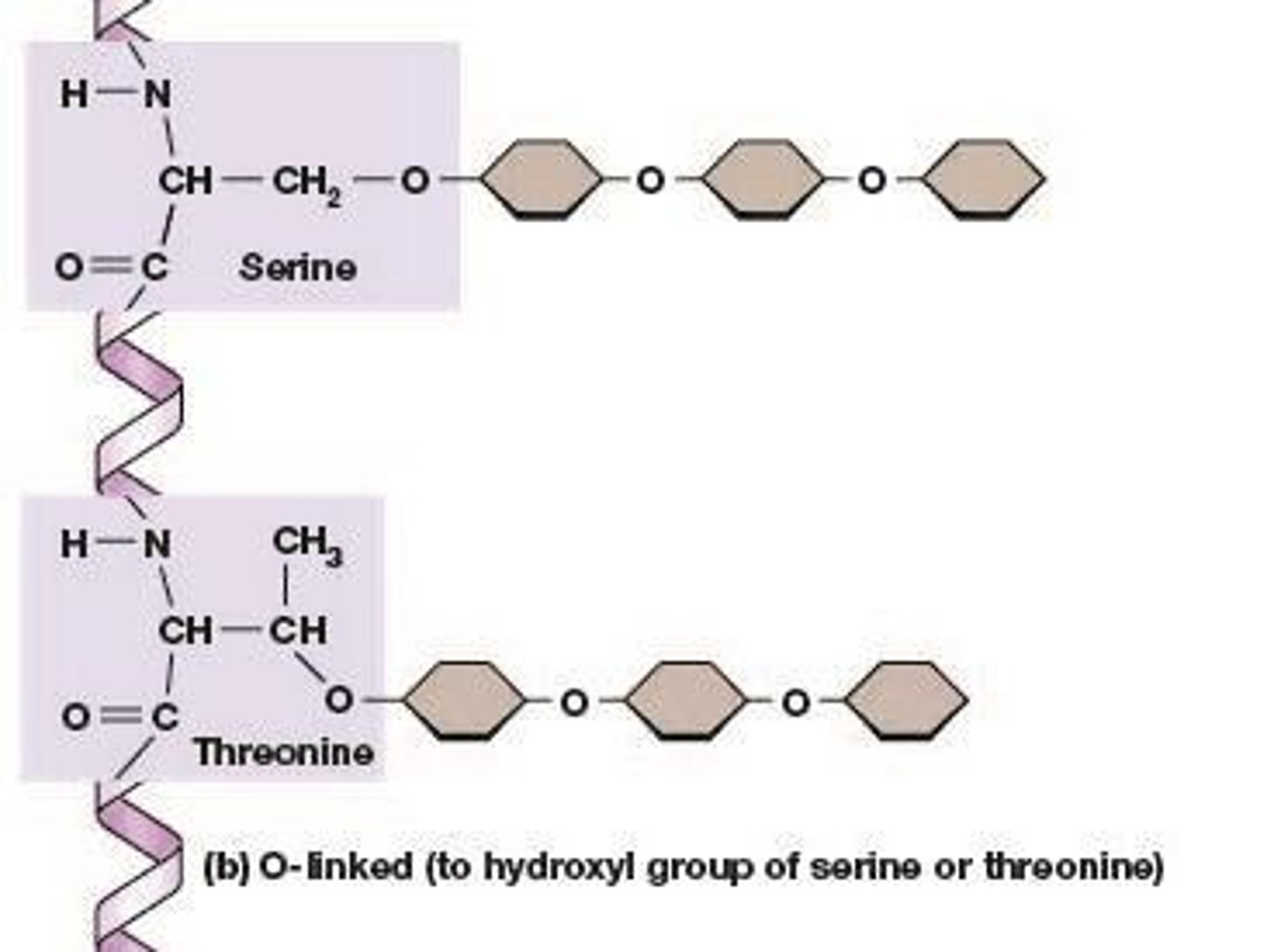
O-linked glycosylation
Glycosylation involving attachment to serine or threonine.
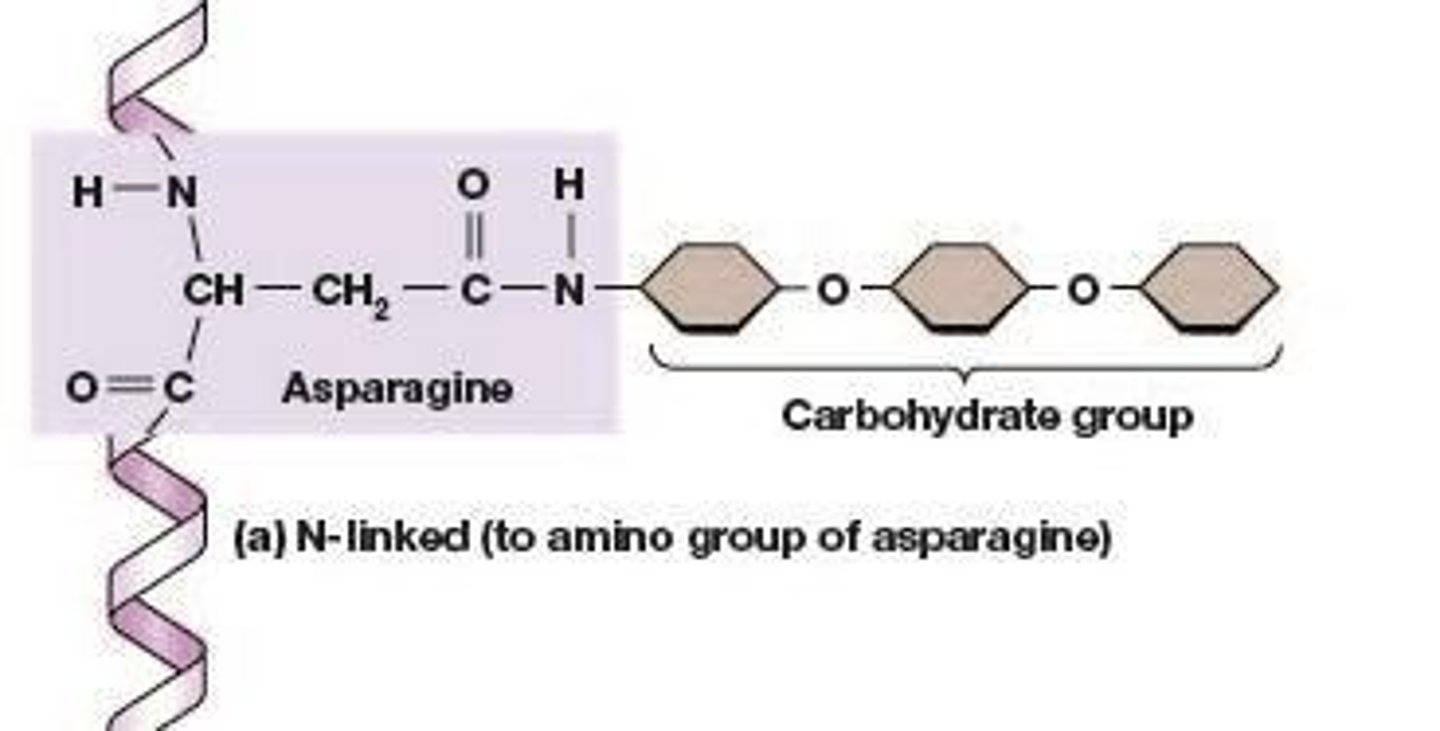
N-linked glycosylation
Glycosylation involving attachment to asparagine.
Free ribosomes
Ribosomes synthesizing proteins in cytosol.
Ribosomes anchored to rough ER
Ribosomes synthesizing secretory and membrane proteins.
Transport vesicle
Vesicle carrying proteins to their destination.
Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
Structure facilitating transport between nucleus and cytoplasm.
Signal recognition particle (SRP)
Binds ER signal sequence during translation.
Start/stop transfer sequence
Control regions of polypeptide in membrane.
Phosphotransferase enzyme
Enzyme phosphorylating mannose on lysosomal enzymes.
Enzyme replacement therapy
Treatment involving direct introduction of functional enzymes.
Substrate reduction therapy
Reducing substrate production to prevent toxic buildup.
HeLa cells
Human cell line used for biological research.
Electrical impulse in muscle cells
Triggers calcium release from the ER.
Polypeptide
Chain of amino acids forming proteins.
Lysosome
Organelle containing enzymes for digestion.
Extracellular secretion
Release of substances outside the cell.