55. Pathology of pregnancy I (implantation disorders, gestosis, trophoblastic tumours)
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Implantation disorders?
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Spontaneous abortion
- Placenta praevia
- Placental abruption
Ectopic pregnancy?
Implantation of the fertilized egg in any site other than the uterine wall
- Occur in 1% of all pregnancies -> 90% of these occur in the fallopian tube
What other places can ectopic pregnancy occur?
- Abdomen
- Ovary
What increases the risk for ectopic pregnancy?
If there is scarring of the fallopian tubes
-> Will decrease the speed at which the egg is moved through the tube -> increasing the risk that it will implant there
When can scarring of the fallopian tube occur?
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Endometriosis
Aka. these are risk factors for tubal ectopic pregnancy
Foetus survival in ectopic pregnancies?
These pregnancies rarely allows fetus to survive
- They will eventually rupture -> therefore: they must be recognized and treated
Rupture of an ectopic pregnancy?
- Sudden intense abdominal pain
- Acute abdomen
Potentially hypovolemic shock & death
Spontaneous abortion?
Loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation
- Occurs in 10% of pregnancies
Causes of spontaneous abortion?
- Chromosomal abnormalities (most common)
Hypercoagulability
- Antiphospholipid syndrome (SLE)
Trauma
Toxins
Antiphospholipid syndrome?
- Venous or arterial thrombosis
- Persistent & unexplained thrombocytopenia
- Recurrent fetal loss
Where does the placenta normally implant itself?
Normally: placenta implants in the upper part of the uterine cavity -> far away from the cervical os
Placenta praevia?
When placenta implants close to the cervical os, even obstructing the cervical os.
- Is dangerous, as fetus will compress the placenta when delivered vaginally
= Will deprive the fetus of blood during delivery
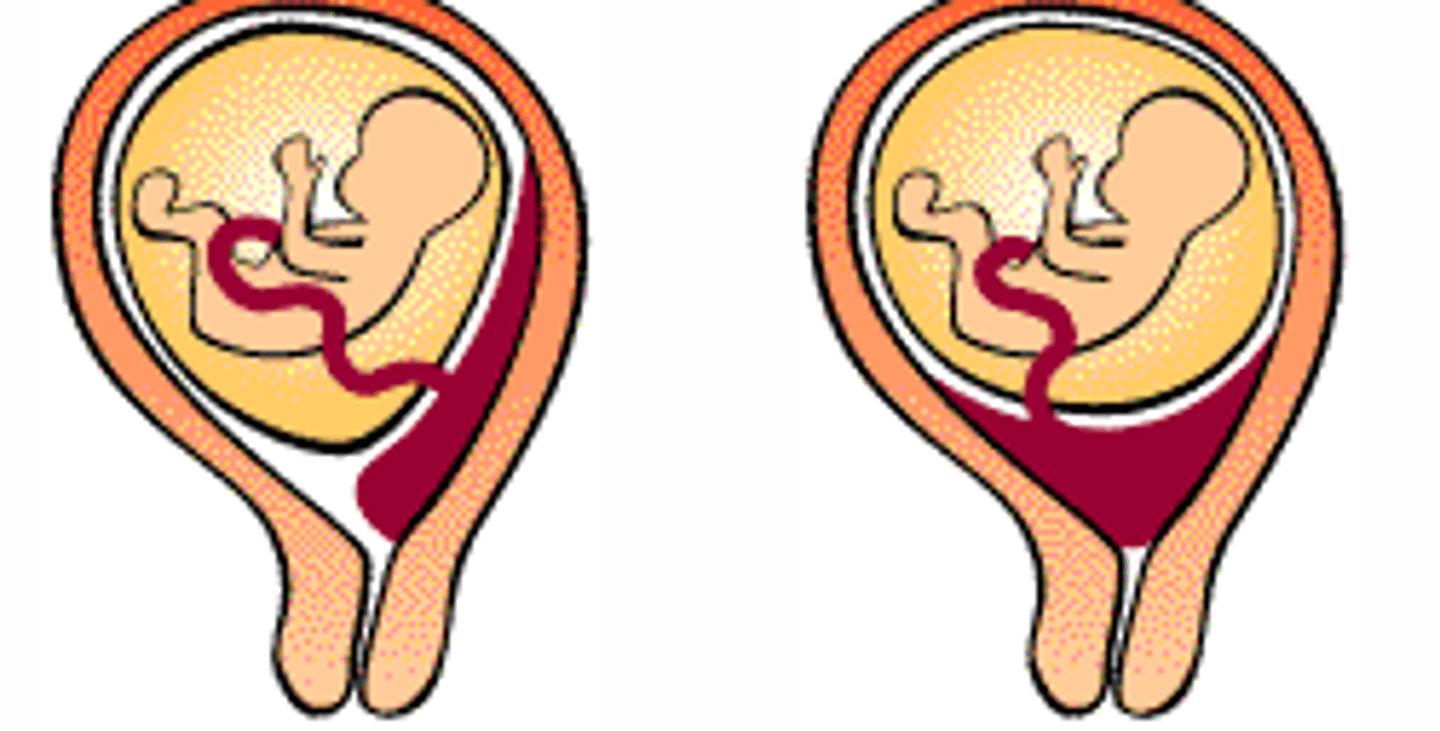
How to prevent dangerous delivery with placenta praevia?
C-section should be performed, instead of vaginal delivery
Risk factors placenta previa?
Increased material age
Prior uterine surgery
Multiple gestation
Multiparous
Placental abruption?
Premature separation of the placenta from the uterine wall after 20 weeks' gestation and before the fetus is delivered
- Causes bleeding & often stillbirth
Gestosis?
Toxaemia of pregnancy
- Mother develops hypertension during pregnancy
Two most important conditions:
- Preeclampsia
- Eclampsia
Preeclampsia?
Development of
- Hypertension
- Proteinuria
- Edema
of the mother during third trimester
Multiple organs are involved & damaged
- Kidney, liver & lungs
Eclampsia?
Most severe form of preeclampsia, where seizures and coma occur
- Occur in 5-10% of pregnancies
- Etiology is poorly understood
Risk factors gestosis?
- Nulliparity
- Age > 35
- African-American race
Pathogenesis - gestosis?
There are no toxins involved, despite the name
- Triggering event is unknown, but:
= All cases are characterized by abnormal development of the spiral arteries in the placenta
- They cannot deliver as much to the placenta - causing placental hypoperfusion
What are the consequences of the hypoxic placenta?
Damages the fetus
Also, somehow increases the level of pro-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic molecules in the mother's circulation
= Endothelial dysfunction -> hypercoagulability & vasoconstriction (=hypertension)
How does the proteinuria and edema occur in gestosis?
- There will be dysfunction and damage of the glomerular endothelium
- Hypertension-induced vasoconstriction of the renal arteries
= Proteinuria and fluid retention
-> causes further hypertension and edema
Complications of gestosis?
Large risks for both fetus and the mother
Mother:
- Every organ can fail
- Death can occur -> often due to ARDS or cerebral hemorrhage
• Hypertension causes placental abruption
• Hypoxia of the fetus can cause abortion or permanent damage
HELLP syndrome (gestosis)?
Hemolysis (H)
Elevated liver enzymes (EL)
Low platelets (LP)
occurs in sever cases of gestosis
Diagnosis of gestosis?
Detected during routine prenatal visits
- BP measurement
- Weighing
- Urine tests
Treatment gestosis?
Only treatment - delivery
Gestational trophoblastic disease?
Previously called "Trophoblastic tumors"
Include 3 lesions associated with pregnancy:
- Hydatidiform mole (complete or partial)
- Invasive mole
- Gestational choriocarcinoma
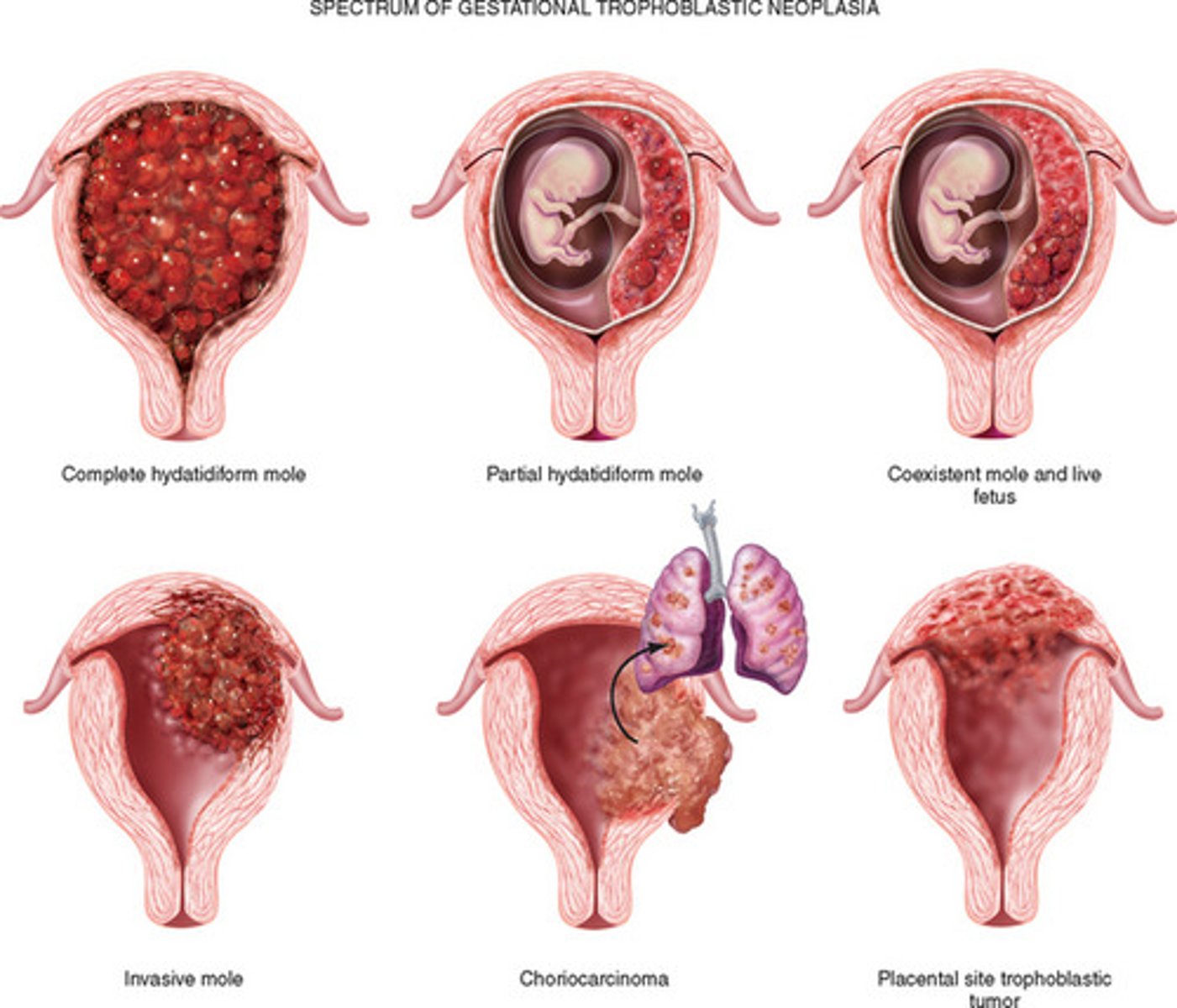
What are the lesions in GTD associated with?
- Abnormal fertilization of the ovum
- Development of tumors and tumor-like lesions (originating from placental cells)
Range from benign to highly malignant
The clinical symptoms, treatment and prognosis is similar - therefore clumped together as a "disease" - however, there are pathological differences
Treatment of moles?
Curettage - Use of a sharp dermal curette to scrape away a skin lesion
Treatment of the choriocarcinoma?
Chemotherapy
Symptoms of GTD?
- Vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic tenderness
Diagnosis of GTD?
Based on:
- Significantly elevated hCG -> due to the proliferation of syncytiotrophoblasts
- Ultrasound & absence of fetal heart sounds
Hydatidiform moles?
Benign gestational trophoblastic diseases
- Occur when an ovum is abnormally fertilized
- In both types: placenta-like tissue develops - in an abnormal way
- Chorionic villi are cystically dilated - looks like grapes
Complete mole - Hydatidiform mole?
Develops when an ovum that contains no genetic material is fertilized by a sperm that duplicates its genetic material -> or rarely if it is fertilized by two sperm at the same time
Most cases result is a 46XX ovum, but 46XY can also occur
Result of a complete mole?
Not compatible with life
- No embryo will develop
Trophoblast and syncytiotrophoblasts do develop -> abnormally
= A placenta-like structure develops, where all chorionic villi are edamatous and dilated
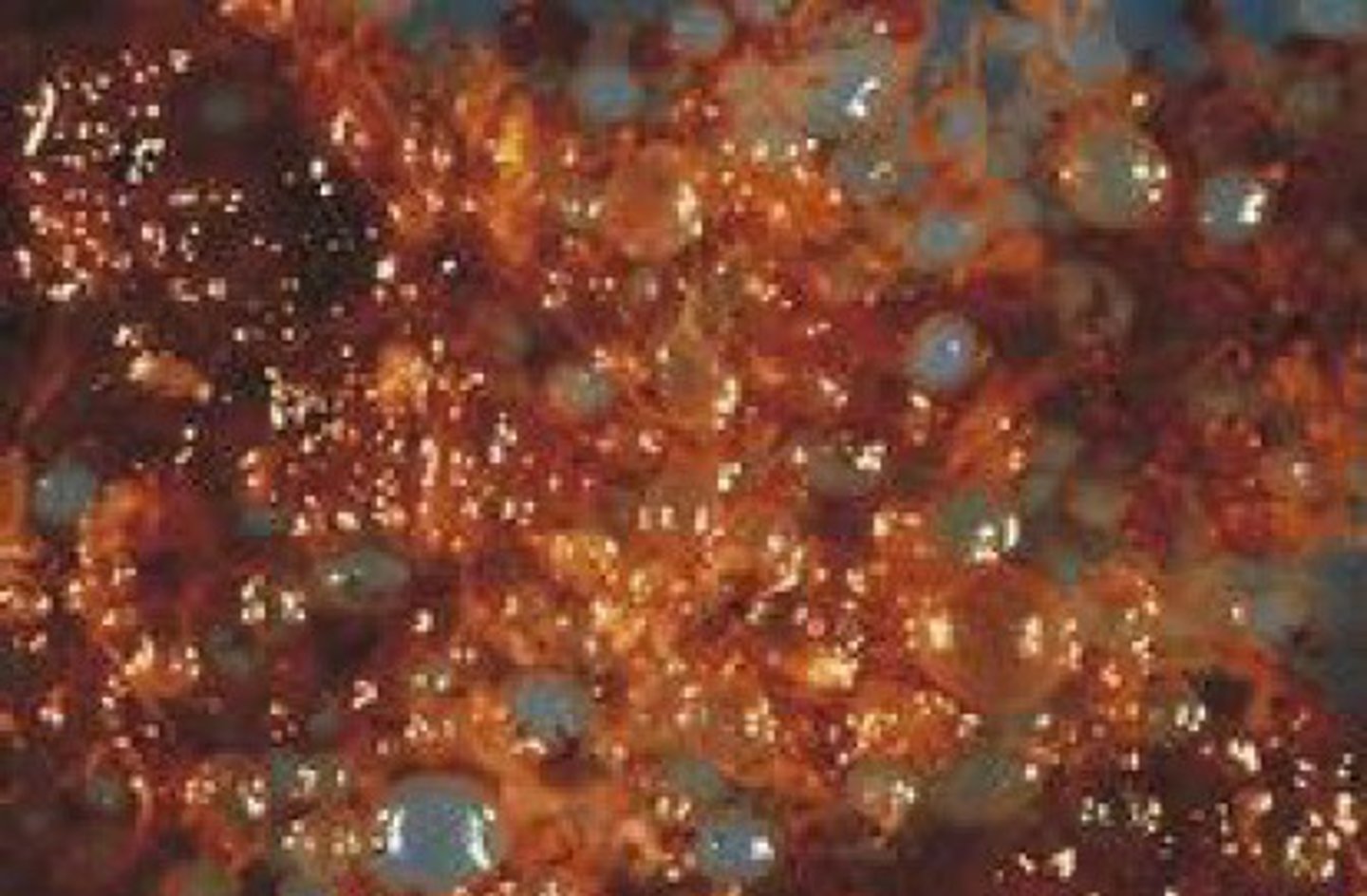
Imcomplete mole - hydatidiform mole?
Develops when a normal ovum is fertilized by a sperm that has its genetic material duplicated or rarely if it is fertilized by two sperm at the same time
= Result is 69XXX, 69XXY or 69XYY ovum
Result of incomplete mole?
Not compatible with life
- Some embryonic tissue will develop (fetal tissue) -> this does not occur in complete mole
- A placenta-like structure develops where some chorionic villi are dilated -> the rest are normal
Invasive moles?
Are complete moles that are locally invasive
- Ca 10% of complete moles become invasive
- Do not metastasize, but rather penetrate deeply into the uterine wall
Removal of invasive mole?
Is difficult to perform with curettage, as it lies deep in the uterine wall
= Chemotherapy may be needed
Gestational choriocarcinoma?
Very aggressive malignant tumor
- Arise from gestational chorionic epithelium
Gestational choriocarcinoma - occurs from?
- 50% of cases -> complete hydatitiform moles
- 25% of cases - after a miscarriage
- 25% of cases - after a normal pregnancy
What is the tumor composed of (Gestational choriocarcinoma)?
Anaplastic cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts
Appear as hemorrhagic, necrotic uterine masses
- Unlike moles, it does NOT form villi
Malignant potential of gestational choriocarcinoma?
- Very aggressive
- Metastasize very early - upon diagnosis most cases have already spread through multiple organs
Necrosis in Gestational choriocarcinoma?
In some cases, necrosis is so extensive that practically nothing of the primary tumor lesion is left
Treatment Gestational choriocarcinoma?
Luckily the cancer is very sensitive to chemotherapy
- Almost 100% of cases are cured -> even w/ metastasis
Why does gestational choriocarcinoma have better prognosis than choriocarcinoma in ovaries/testes?
Is believed due to the presence of paternal antigens on gestational choriocarcinoma
- The maternal immune response on these paternal antigens helps remove the tumor along the chemotherapy